Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Analysis No 3 - de Castro, Elyza Jane
Uploaded by
FLORENCE DE CASTROOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Analysis No 3 - de Castro, Elyza Jane
Uploaded by
FLORENCE DE CASTROCopyright:
Available Formats
Batangas State University
COLLEGE OF ACCOUNTANCY, BUSINESS, ECONOMICS
& INTERNATIONAL HOSPITALITY MANAGEMENT
Gov. Pablo Borbon Campus I, Batangas City, Philippines 4200
www.batstate-u.edu.ph. Telefax (043)300-2202 loc226
GRADUATE SCHOOL
ADVANCE STATICTICS (BA 502)
CASE ANALYSIS NO. 3 – ANOVA
Submitted by: De Castro, Elyza Jane M.
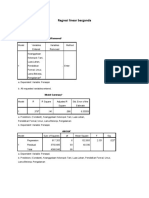
Descriptives
Dependent variable: weight gain
95% Confidence Interval for Mean
N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Lower Bound Upper Bound Minimum Maximum
supplement A 22 12.00 5.099 1.087 9.74 14.26 1 22
supplement B 25 15.44 5.853 1.171 13.02 17.86 7 27
supplement C 22 8.14 3.441 .734 6.61 9.66 4 15
supplement D 27 8.41 2.080 .400 7.58 9.23 2 11
supplement E 30 1.13 .730 .133 .86 1.41 0 2
supplement F 28 6.64 1.096 .207 6.22 7.07 5 9
Total 154 8.29 5.700 .459 7.38 9.19 0 27
Test of Homogeneity of Variances
Dependent variable: weight gain
Levene Statistic df1 df2 Sig.
19.822 5 148 .000
- There are significant differences in weight gain across the food supplements A to F since the
sigma value is 0.000 which is less than .05 (p<.05). In conclusion, the type of food supplements
have a significant effect on the weight gain of fifty-four rats that were examined.
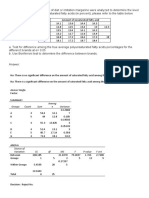
Multiple Comparisons
weight gain
Tukey HSD
(I) food supplement (J) food supplement Mean Difference 95% Confidence Interval
(I-J) Std. Error Sig. Lower Bound Upper Bound
dimension2
supplement A supplement B -3.440* 1.013 .011 -6.36 -.52
supplement C 3.864* 1.045 .004 .85 6.88
dimension3
supplement D 3.593* .995 .006 .72 6.47
supplement E 10.867* .973 .000 8.06 13.68
supplement F 5.357* .987 .000 2.51 8.21
supplement B dimension3
supplement A 3.440* 1.013 .011 .52 6.36
supplement C 7.304* 1.013 .000 4.38 10.23
supplement D 7.033* .962 .000 4.26 9.81
supplement E 14.307* .938 .000 11.60 17.02
supplement F 8.797 *
.954 .000 6.04 11.55
supplement C supplement A -3.864* 1.045 .004 -6.88 -.85
supplement B -7.304 *
1.013 .000 -10.23 -4.38
dimension3
supplement D -.271 .995 1.000 -3.14 2.60
supplement E 7.003 *
.973 .000 4.19 9.81
supplement F 1.494 .987 .657 -1.36 4.34
supplement D supplement A -3.593 *
.995 .006 -6.47 -.72
supplement B -7.033* .962 .000 -9.81 -4.26
dimension3
supplement C .271 .995 1.000 -2.60 3.14
supplement E 7.274* .919 .000 4.62 9.93
supplement F 1.765 .935 .414 -.93 4.46
supplement E supplement A -10.867* .973 .000 -13.68 -8.06
supplement B -14.307 *
.938 .000 -17.02 -11.60
dimension3
supplement C -7.003* .973 .000 -9.81 -4.19
supplement D -7.274 *
.919 .000 -9.93 -4.62
supplement F -5.510* .911 .000 -8.14 -2.88
supplement F supplement A -5.357 *
.987 .000 -8.21 -2.51
supplement B -8.797* .954 .000 -11.55 -6.04
dimension3
supplement C -1.494 .987 .657 -4.34 1.36
supplement D -1.765 .935 .414 -4.46 .93
supplement E 5.510 *
.911 .000 2.88 8.14
weight gain
Tukey HSD a,b
food supplement Subset for alpha = 0.05
N 1 2 3 4
supplement E 30 1.13
supplement F 28 6.64
supplement C 22 8.14
dimensio n1
supplement D 27 8.41
supplement A 22 12.00
supplement B 25 15.44
Sig. 1.000 .461 1.000 1.000
Means for groups in homogeneous subsets are displayed.
a. Uses Harmonic Mean Sample Size = 25.317.
b. The group sizes are unequal. The harmonic mean of the group
sizes is used. Type I error levels are not guaranteed.
You might also like
- Research Application in Business: AssignmentDocument5 pagesResearch Application in Business: AssignmentrohanNo ratings yet
- Variables EnteredDocument2 pagesVariables EnteredAnas MahfudNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 Analisis Data 1551130202Document7 pagesTugas 1 Analisis Data 1551130202AllRockhiNo ratings yet
- Lampiran III Hasil Penelitian: Descriptive StatisticsDocument2 pagesLampiran III Hasil Penelitian: Descriptive StatisticsYuda SaputraNo ratings yet
- Tabel 1. Descriptive StatisticsDocument11 pagesTabel 1. Descriptive StatisticsVhytaKwOnyureeNo ratings yet
- Univariate Analysis of Variance: WarningsDocument3 pagesUnivariate Analysis of Variance: WarningsSandipan DawnNo ratings yet
- Tugas 5 KomputerDocument5 pagesTugas 5 KomputerbagusadigunawanNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistical Methods, Spss Lab Assignment - 2: AnswerDocument7 pagesApplied Statistical Methods, Spss Lab Assignment - 2: AnswerShiva SasidharNo ratings yet
- Lampiran Spss WordDocument14 pagesLampiran Spss WordZaldy MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Oneway: Oneway DV by Cell /statistics Descriptives Homogeneity /missing Analysis /posthoc Bonferroni GH Alpha (0.05)Document6 pagesOneway: Oneway DV by Cell /statistics Descriptives Homogeneity /missing Analysis /posthoc Bonferroni GH Alpha (0.05)selvi annisaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 5 - Hydrostatic Pressure On Plane Surfaces G2Document19 pagesLab Report 5 - Hydrostatic Pressure On Plane Surfaces G2Raziq HaiqalNo ratings yet
- Test of Homogeneity of VariancesDocument2 pagesTest of Homogeneity of VariancesAulia Husna CahyaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Rabi Maize 2016-17Document4 pagesRabi Maize 2016-17Indivar PrasadNo ratings yet
- QT Report RegressionDocument2 pagesQT Report RegressionABHISEK BEHERANo ratings yet
- Binary LogistikDocument6 pagesBinary LogistikFRANNY FRANGKY WAGANIANo ratings yet
- Appendix: DescriptivesDocument3 pagesAppendix: DescriptivesKHAIRUNISANo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Management Kozhikode Post Graduate Programme PGP 25 - Section D' Cost and Management AccountingDocument5 pagesIndian Institute of Management Kozhikode Post Graduate Programme PGP 25 - Section D' Cost and Management AccountingSwati PorwalNo ratings yet
- 1.06 Acid Neutralization Data FA16 Student Version - FinalDocument10 pages1.06 Acid Neutralization Data FA16 Student Version - Finaljessie sprinklesNo ratings yet
- Lampiran 2Document7 pagesLampiran 2Nanda Juragan Sandal JepitNo ratings yet
- Jasindo Security: Perincian Biaya Jasa Pengamanan Untuk Wilayah JakartaDocument1 pageJasindo Security: Perincian Biaya Jasa Pengamanan Untuk Wilayah JakartamargonoNo ratings yet
- Apendiks A: Data Dan Jadual StatistikDocument5 pagesApendiks A: Data Dan Jadual StatistikMohd Farhan MakhlisNo ratings yet
- BEKASIDocument2 pagesBEKASINazira As MirzaNo ratings yet
- Vclass M9 - Perencanaan EksperimenDocument5 pagesVclass M9 - Perencanaan EksperimenYoga RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 2003 Thailand Elementary Mathematics International Contest Answer KeyDocument1 page2003 Thailand Elementary Mathematics International Contest Answer KeyJohnvic AdiqueNo ratings yet
- 2003 TEMIC Answer PDFDocument1 page2003 TEMIC Answer PDFAurelia RegitaNo ratings yet
- Between-Subjects Factors: Dimension2Document4 pagesBetween-Subjects Factors: Dimension2MomonlitaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Anova ZakiahDocument3 pagesTugas Anova ZakiahRhotascimNo ratings yet
- Staff Promotion of Performance: Note F (1,66) 3.98 STDDocument2 pagesStaff Promotion of Performance: Note F (1,66) 3.98 STDumalkhayr A/rahmaanNo ratings yet
- Regresi Linear BergandaDocument2 pagesRegresi Linear BergandaFatwa MuftiNo ratings yet
- Table 3Document2 pagesTable 3April John B. CabaniogNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 6 Solution: MS MS y T y T N NDocument6 pagesAssignment # 6 Solution: MS MS y T y T N Nsulaiman_GNo ratings yet
- Full Factorial (Minitab 1)Document3 pagesFull Factorial (Minitab 1)Muhammad Fauzan Ansari Bin AzizNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument4 pagesData Analysisisteaq44250No ratings yet
- Answer To AE 108 Handout No.7Document2 pagesAnswer To AE 108 Handout No.7AndreaaAAaa TagleNo ratings yet
- 404 PRJDocument4 pages404 PRJOmar SheibanyNo ratings yet
- Bảng phụ lục: Coefficients (a)Document5 pagesBảng phụ lục: Coefficients (a)nguyentuansang02No ratings yet
- Exp-Des ActDocument4 pagesExp-Des Actjoselle macaspacNo ratings yet
- Approved Budget For The ContractDocument25 pagesApproved Budget For The ContractBryle James Nanglegan100% (1)
- Exp 7 Results and DiscussionsDocument13 pagesExp 7 Results and DiscussionsChali HaineNo ratings yet
- CTC Structure: 7% Component A Component B Component C Component D Component E Component FDocument1 pageCTC Structure: 7% Component A Component B Component C Component D Component E Component FRajarshi DaharwalNo ratings yet
- StandardizedRegression Vartanian ExamplesDocument2 pagesStandardizedRegression Vartanian ExamplesNazia SyedNo ratings yet
- Regressi Linear BergandaDocument3 pagesRegressi Linear BergandaFajar LadungNo ratings yet
- SITXFIN003 - Case Study Part 3Document7 pagesSITXFIN003 - Case Study Part 3detailed trickzNo ratings yet
- First Model:: Table1a.Case Processing SummaryDocument8 pagesFirst Model:: Table1a.Case Processing Summarybisma ZamanNo ratings yet
- Spss TeguhDocument1 pageSpss TeguhsaidilNo ratings yet
- Problem#1Document3 pagesProblem#1jas lacsonNo ratings yet
- (B) Determine The Average Annual Earnings of Workers For Each Level of Education. Please Also Plot The Results in A Bar GraphDocument3 pages(B) Determine The Average Annual Earnings of Workers For Each Level of Education. Please Also Plot The Results in A Bar GraphMohammadNo ratings yet
- Result of Squash Seed PolvoronDocument3 pagesResult of Squash Seed PolvoronRonuel Patrick Beaco SalaZarNo ratings yet
- Topic Wise Bundle PDF Course Quantitative Aptitude-Approximation Set-1 (Eng)Document11 pagesTopic Wise Bundle PDF Course Quantitative Aptitude-Approximation Set-1 (Eng)Nikhil SharmaNo ratings yet
- CMA - Hallstead - Section D - Group19Document8 pagesCMA - Hallstead - Section D - Group19Swati PorwalNo ratings yet
- Model Variables Entered Variables Removed Method 1Document3 pagesModel Variables Entered Variables Removed Method 1ToellNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity C2: Maharlika Yolk: Part 2: Difference Averages Totals AveragesDocument4 pagesLearning Activity C2: Maharlika Yolk: Part 2: Difference Averages Totals AveragesMary R. R. PanesNo ratings yet
- Simpson RuleDocument6 pagesSimpson RuleAnwar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Univariate Analysis of Variance: Between-Subjects FactorsDocument3 pagesUnivariate Analysis of Variance: Between-Subjects FactorsVindyJulianTryKurniawanNo ratings yet
- SOL. MAN. - CHAPTER 8 - NOTES (Part 2)Document7 pagesSOL. MAN. - CHAPTER 8 - NOTES (Part 2)Fhrauline Manaois RamosNo ratings yet
- Ailla Marie Basbas - Multiple Regression-ADocument2 pagesAilla Marie Basbas - Multiple Regression-A202110452No ratings yet
- Chapter 45 - Teacher's ManualDocument5 pagesChapter 45 - Teacher's ManualHohohoNo ratings yet
- Univariate Analysis of Variance: WarningsDocument7 pagesUnivariate Analysis of Variance: WarningsSandipan DawnNo ratings yet
- Vol. Cut & Fill - BicDocument1 pageVol. Cut & Fill - BicDevikaAgusstienNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document12 pagesChapter 11FLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Budget Analyst Interview QuestionsDocument6 pagesBudget Analyst Interview QuestionsFLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Accounting QuestionsDocument12 pagesAccounting QuestionsFLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Part 1Document26 pagesCapital Budgeting Part 1FLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Chapter13 FinmanDocument22 pagesChapter13 FinmanFLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Questionnaire - Proposal (Finman)Document5 pagesQuestionnaire - Proposal (Finman)FLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Written Report - Chapter 3Document3 pagesComprehensive Written Report - Chapter 3FLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- CASE ANALYSIS No 1 in StatisticsDocument4 pagesCASE ANALYSIS No 1 in StatisticsFLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Strategic Management - Theory Mastering Strategy - Art and ScienceDocument6 pagesStrategic Management - Theory Mastering Strategy - Art and ScienceFLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Written Report in Strategic ManagementDocument7 pagesComprehensive Written Report in Strategic ManagementFLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- CASE ANALYSIS 4 in StatisticsDocument5 pagesCASE ANALYSIS 4 in StatisticsFLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Case Analysis No. 5-RegressionDocument5 pagesCase Analysis No. 5-RegressionFLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Case Analysis No. 2-T-TestDocument2 pagesCase Analysis No. 2-T-TestFLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Case Analysis No. 5-RegressionDocument5 pagesCase Analysis No. 5-RegressionFLORENCE DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Effect of Liquidity Risk On Performance of Deposit Money Banks in NigeriaDocument6 pagesEffect of Liquidity Risk On Performance of Deposit Money Banks in NigeriaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- 02.certificate of Compliance FM UkDocument10 pages02.certificate of Compliance FM Ukmyatthura870No ratings yet
- Algebra1 Review PuzzleDocument3 pagesAlgebra1 Review PuzzleNicholas Yates100% (1)
- Week 8: Spread-Spectrum Modulation - Direct Sequence Spread SpectrumDocument79 pagesWeek 8: Spread-Spectrum Modulation - Direct Sequence Spread SpectrumAmir MustakimNo ratings yet
- Haberman Data Logistic Regression AnalysisDocument5 pagesHaberman Data Logistic Regression AnalysisEvelynNo ratings yet
- IPE SakibBhaiMagicChothaDocument55 pagesIPE SakibBhaiMagicChothaTousif SadmanNo ratings yet
- PTN Guide Compilation by EmeraldchowDocument24 pagesPTN Guide Compilation by EmeraldchowMirzaNo ratings yet
- AIMMS Modeling Guide - Linear Programming TricksDocument16 pagesAIMMS Modeling Guide - Linear Programming TricksgjorhugullNo ratings yet
- Lubricants - McMaster-CarrDocument8 pagesLubricants - McMaster-CarrjeanyoperNo ratings yet
- Beamforming For 4.9G/5G Networks: Exploiting Massive MIMO and Active Antenna TechnologiesDocument12 pagesBeamforming For 4.9G/5G Networks: Exploiting Massive MIMO and Active Antenna TechnologiesAymen Ben zinebNo ratings yet
- Dimensions and Methodology of Business Studies Dec 2018Document2 pagesDimensions and Methodology of Business Studies Dec 2018Nallavenaaya Unni100% (1)
- Hemo TecaDocument17 pagesHemo TecaMafer PilcoNo ratings yet
- How The Audiences Feel Closer and Connected To Their Culture With StorytellingDocument7 pagesHow The Audiences Feel Closer and Connected To Their Culture With Storytellingmarcelo quezadaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document90 pagesUnit 1Atul Jaysing PatilNo ratings yet
- Evolis User ManualDocument28 pagesEvolis User ManualIonmadalin1000No ratings yet
- 1802SupplementaryNotes FullDocument235 pages1802SupplementaryNotes FullCourtney WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Burnay, Bushman & Laroi - 2019Document10 pagesBurnay, Bushman & Laroi - 2019TinyjurshNo ratings yet
- Wish Upon A STAR: Presented By: Daulo, Eunice R. III - Block 3Document17 pagesWish Upon A STAR: Presented By: Daulo, Eunice R. III - Block 3nhyce18No ratings yet
- Xgenus X-Ray PDFDocument61 pagesXgenus X-Ray PDFAli NuriNo ratings yet
- 1506a E88tag3 PDFDocument5 pages1506a E88tag3 PDFmohammad javad golNo ratings yet
- Submission Letter To LBUDocument46 pagesSubmission Letter To LBUramesh bajracharyaNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarm SymbolsDocument6 pagesFire Alarm Symbolscarlos vasquezNo ratings yet
- Pradeep Kshetrapal - Genius Physics (Class 12) - For IIT-JEE and CBSE 2 - Libgen - LiDocument338 pagesPradeep Kshetrapal - Genius Physics (Class 12) - For IIT-JEE and CBSE 2 - Libgen - Lisujan subediNo ratings yet
- Advanced Office Add-In DevelopmentDocument40 pagesAdvanced Office Add-In DevelopmentReadoneNo ratings yet
- Original Research PapersDocument13 pagesOriginal Research Papersrikaseo rikaNo ratings yet
- Law of DemandDocument16 pagesLaw of DemandARUN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Sem06 Gca InsoDocument2 pagesSem06 Gca InsoBogdan PistolNo ratings yet
- Ad 9915Document47 pagesAd 9915Jime nitaNo ratings yet
- 93c3 Document 3Document14 pages93c3 Document 3NONON NICOLASNo ratings yet
- Motorola Talkabout T82 PDFDocument184 pagesMotorola Talkabout T82 PDFAlex TamayoNo ratings yet