Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Seafloor Spreading Act
Uploaded by
Del Mundo Kristi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Seafloor spreading act
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesSeafloor Spreading Act
Uploaded by
Del Mundo KristiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
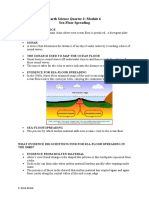
Sea-Floor Spreading
The longest chain of mountains in the world is the system of mid-ocean
ridges. In the mid-1900s, scientists mapped the mid-ocean ridges using sonar. Sonar
is a device that bounces sound waves off underwater objects and then records the
echoes of these sound waves. The mid-ocean ridges curve along the sea floor,
extending into all of Earth’s oceans. Most of the mountains in the mid-ocean ridges lie
hidden under hundreds of meters of water. A steep-sided valley splits the top of some
mid-ocean ridges. The Earth’s ocean floors move like conveyor belts, carrying the
continents along with them, as they move. This movement begins at a mid-ocean
ridge. A ridge forms along a crack in the oceanic crust. At a mid-ocean ridge, molten
material rises from the mantle and erupts. The molten material then spreads out,
pushing older rock to both sides of the ridge. As the molten material cools, it forms a
strip of solid rock in the center of the ridge. Then more molten material splits apart the Questions:
strip of solid rock that formed before, pushing it aside. This process, called sea-floor 1. Name and describe the feature of the ocean floor shown at A.
spreading, continually adds new material to the ocean floor.
2. Describe the process shown occurring at B, and explain what results from this.
Scientists have found strange rocks shaped like pillows in the central valley of mid-
ocean ridges. Such rocks can form only if molten material hardens quickly after 3. What happens to old oceanic crust as new molten material rises from the mantle?
erupting under water. The presence of these rocks supports the theory of sea-floor
spreading. More support came when scientists discovered that the rock that makes 4. The arrows on the figure show the ocean floor spreading from the ridge. What are
up the ocean floor lies in a pattern of magnetized “stripes. The pattern is the same on three kinds of evidence scientists have found to support this idea?
both sides of the ridge. These stripes hold a record of reversals in Earth’s magnetic 1.
field. The final proof of sea-floor spreading came from rock samples obtained by
drilling into the ocean floor. Scientists found that the farther from a ridge the rocks 2.
were taken, the older they were. The ocean floor does not just keep spreading.
Instead, it sinks beneath deep underwater canyons called deep-ocean trenches. 3.
Where there are trenches, subduction takes place. Subduction is the process by
which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle. 5. What process is shown occurring at C, and why does it occur?
At deep-ocean trenches, subduction allows part of the ocean floor to sink back into
the mantle, over tens of millions of years. 6. A device that scientists use to map the ocean floor is _________________.
The processes of subduction and sea-floor spreading can change the size and shape 7. The feature on the ocean floor at C is called a(n) _________________.
of the oceans. Because of these processes, the ocean floor is renewed about every
200 million years. The Pacific Ocean is shrinking. Its many trenches are swallowing
8. The process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor is called
more ocean crust than the mid-ocean ridge is producing. The Atlantic Ocean is
______________.
expanding. In most places, the oceanic crust of the Atlantic Ocean is attached to
continental crust. As the Atlantic’s floor spreads, the continents along its edges
9. The process by which the ocean floor sinks into the mantle is called
also move.
_________________.
10. A chain of underwater mountains along which sea-floor spreading occurs is a
_____________________________
You might also like
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- On the Origin of Continents and Oceans: Book 2: The Earths Rock RecordFrom EverandOn the Origin of Continents and Oceans: Book 2: The Earths Rock RecordNo ratings yet
- Sea Floor Spreading ReadingDocument5 pagesSea Floor Spreading Readingapi-262318021No ratings yet
- Sea Floor Spreading Worksheet With KEY 1k69y7wDocument4 pagesSea Floor Spreading Worksheet With KEY 1k69y7wSally PocamasNo ratings yet
- Sea Floor Spreading WorksheetDocument2 pagesSea Floor Spreading WorksheetjNo ratings yet
- Lars Vanheuverzwyn - #6 - SEA-FLOOR SPREADING WORKSHEETDocument9 pagesLars Vanheuverzwyn - #6 - SEA-FLOOR SPREADING WORKSHEETLars vanheuverzwynNo ratings yet
- Sa Floor Spreading WorksheetDocument6 pagesSa Floor Spreading Worksheettroyb2267No ratings yet
- The Seafloor SpreadingDocument7 pagesThe Seafloor SpreadingJessa SumayangNo ratings yet
- Sea Floor Spreading 4.4Document13 pagesSea Floor Spreading 4.4Joyce CabidogNo ratings yet
- Sea-Floor Spreading - GR 6Document3 pagesSea-Floor Spreading - GR 6Jung Ahn HongNo ratings yet
- Earth Science For STEM: Quarter 2 - Module 6: Seafloor SpreadingDocument7 pagesEarth Science For STEM: Quarter 2 - Module 6: Seafloor SpreadingCheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Quarter 2 Module 6Document3 pagesEarth Science Quarter 2 Module 6Rhianne Grace CastroNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Ocean Basin and Seafloor SpreadingDocument33 pagesStructure of The Ocean Basin and Seafloor SpreadingchealandNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Seafloor SpreadingDocument10 pagesThe Theory of Seafloor SpreadingAnonymous vbSkmwNo ratings yet
- Continental DriftDocument7 pagesContinental DriftSantanu ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Spreadin G: Presented By: Ivy AsuncionDocument21 pagesSpreadin G: Presented By: Ivy AsuncionMhiss RigorNo ratings yet
- Studying Seafloor SpreadingDocument2 pagesStudying Seafloor SpreadingKyle Mejica GastarNo ratings yet
- Sea Floor SpreadingDocument29 pagesSea Floor Spreadingthatkidmarco22No ratings yet
- Continental Drift and Seafloor SpreadingDocument44 pagesContinental Drift and Seafloor SpreadingjNo ratings yet
- Seafloor SpreadingDocument5 pagesSeafloor SpreadingEman VidalloNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Seafloor SpreadingDocument28 pagesModule 5 Seafloor SpreadingOwene Miles AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument43 pagesPlate Tectonicspaulopasker80No ratings yet
- Oceanography: Submitted ToDocument7 pagesOceanography: Submitted TosameenNo ratings yet
- Sea-Floor Spreading: Presentation By: Jay Paul M. Mascareñas Ma. Angle Gwyne Lingon John Loyd ManuelDocument18 pagesSea-Floor Spreading: Presentation By: Jay Paul M. Mascareñas Ma. Angle Gwyne Lingon John Loyd ManuelKimsabu DoldamNo ratings yet
- Sea-Floor Spreading Power PointDocument22 pagesSea-Floor Spreading Power PointKyla RyNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Quarter 2 Module 7Document6 pagesEarth Science Quarter 2 Module 7Rhianne Grace CastroNo ratings yet
- Earthsci Module-10Document17 pagesEarthsci Module-10Alyssa AngelaNo ratings yet
- The Seafloor SpreadingDocument18 pagesThe Seafloor Spreadingdbenben38No ratings yet
- Seafloor SpreadingDocument33 pagesSeafloor SpreadingSoulnimexNo ratings yet
- SMS 1201 A K M Mohiuddin FinalDocument16 pagesSMS 1201 A K M Mohiuddin FinalA.K.M. MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- ELECT1-week 9 CHAPTER 5 ENDOGENIC PROCESSESDocument12 pagesELECT1-week 9 CHAPTER 5 ENDOGENIC PROCESSESRenNo ratings yet
- Sea-Floor SpreadingDocument24 pagesSea-Floor SpreadingStacy Pancho LumanogNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q1 Week 7 The Earths Mechanism - Causes of Plate Movement 2Document30 pagesScience 10 Q1 Week 7 The Earths Mechanism - Causes of Plate Movement 2xan yxNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 1 Reviewer G10Document12 pagesScience Quarter 1 Reviewer G10jahri ruzeraNo ratings yet
- Q2-Earth Science For STEM-WEEK6Document3 pagesQ2-Earth Science For STEM-WEEK6queancy euleNo ratings yet
- Earth Science SHS 14.3 The Seafloor SpreadingDocument14 pagesEarth Science SHS 14.3 The Seafloor SpreadingCamille AnibNo ratings yet
- Outline Ocean Basin ReportingDocument7 pagesOutline Ocean Basin Reporting「 」No ratings yet
- Earth Continental Drift Plate Tectonics Sea Floor Spreading-0Document59 pagesEarth Continental Drift Plate Tectonics Sea Floor Spreading-0MALOU ELEVERANo ratings yet
- The Structure and Evolution of Ocean BasinsDocument31 pagesThe Structure and Evolution of Ocean BasinsApril Tapayan100% (1)
- Chapter 10Document4 pagesChapter 10seraphinehundredNo ratings yet
- Evolution Ocean BasinDocument36 pagesEvolution Ocean BasinKyle ManilaNo ratings yet
- Plate Movements and Boundaries Science Presentation in Dark Blue Teal StyleDocument48 pagesPlate Movements and Boundaries Science Presentation in Dark Blue Teal StyleAngeline AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 7 Plate TectonicsDocument10 pagesLab Activity 7 Plate TectonicskleinkeaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics ArticleDocument2 pagesPlate Tectonics Articleapi-254428474No ratings yet
- Q2.6 Seafloor SpreadingDocument18 pagesQ2.6 Seafloor SpreadingJhon KyleNo ratings yet
- Earth Continental Drift Plate Tectonics Sea Floor Spreading-0Document59 pagesEarth Continental Drift Plate Tectonics Sea Floor Spreading-0roziel A.mabitasanNo ratings yet
- ErtrwtwtDocument12 pagesErtrwtwtCamlon KhajarNo ratings yet
- Group 4: Villaluz, Suzanne P. Bulatao, Athena Huang, Zoe Johnstone, Nicola Marfal, Emed Moya, Robb Reyes, ZoeDocument21 pagesGroup 4: Villaluz, Suzanne P. Bulatao, Athena Huang, Zoe Johnstone, Nicola Marfal, Emed Moya, Robb Reyes, ZoeChloen Ha SungNo ratings yet
- Science First Quarter TopicsDocument15 pagesScience First Quarter TopicsJoshua DaywanNo ratings yet
- Earth Science q2 Week 3 - Refined - EditedDocument28 pagesEarth Science q2 Week 3 - Refined - EditedNoemi AlmerinoNo ratings yet
- Evidence: The Continental Jigsaw PuzzleDocument6 pagesEvidence: The Continental Jigsaw PuzzleChristopher Shane GonzalesNo ratings yet
- GO - HandnoteDocument3 pagesGO - HandnoteMosfiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 Tectonic Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesActivity 5 Tectonic Plate BoundariesaiahNo ratings yet
- Earthquake: Major Plates Minor PlatesDocument8 pagesEarthquake: Major Plates Minor Platesalyssa babylaiNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesPlate TectonicsJulius Memeg Panayo100% (1)
- Oceanography Lesson 2 Continental Margin AutosavedDocument12 pagesOceanography Lesson 2 Continental Margin AutosavedAnalyn DegamhonNo ratings yet
- 1 Plate TectonicsDocument11 pages1 Plate TectonicsAyman M SNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document76 pagesScience 10Alma MuertaNo ratings yet
- The Earths Mechanism Seafloor Spreading TheoryDocument22 pagesThe Earths Mechanism Seafloor Spreading Theoryjia aganaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - M04 - L03 - Q2 - W3Document4 pagesEarth Science - M04 - L03 - Q2 - W3Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- MWSP-2nd QTRDocument3 pagesMWSP-2nd QTRDel Mundo KristiNo ratings yet
- EARTH'S LAYERS CrosswordEARTH'S LAYERS Crossword - WordMintDocument2 pagesEARTH'S LAYERS CrosswordEARTH'S LAYERS Crossword - WordMintDel Mundo KristiNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift PuzzleDocument2 pagesContinental Drift PuzzleDel Mundo KristiNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document1 pageActivity 1Del Mundo KristiNo ratings yet
- Conti PuzzleDocument1 pageConti PuzzleDel Mundo KristiNo ratings yet
- Q1 Science 4 Module 2Document40 pagesQ1 Science 4 Module 2Del Mundo KristiNo ratings yet
- MELC 5 Instructional Learning PlanDocument1 pageMELC 5 Instructional Learning PlanDel Mundo KristiNo ratings yet
- MELC 4 Instructional Learning PlanDocument1 pageMELC 4 Instructional Learning PlanDel Mundo KristiNo ratings yet
- Review Module 22 Geotechnical 3 Nov 2020Document4 pagesReview Module 22 Geotechnical 3 Nov 2020Ma Ella Mae LogronioNo ratings yet
- Specification of Cyclopean ConcreteDocument5 pagesSpecification of Cyclopean ConcreteSeptian Anggoro100% (11)
- Science-Grade 9 Learner Activity Sheets Quarter 3-Week 1: Types of Volcanoes First Edition, 2021Document12 pagesScience-Grade 9 Learner Activity Sheets Quarter 3-Week 1: Types of Volcanoes First Edition, 2021orculloNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Volume Urbant Heught - Rev Mei-For Mc0Document4,870 pagesMonitoring Volume Urbant Heught - Rev Mei-For Mc0eibeffebieNo ratings yet
- Lesoni Fakame Tuluta A Loi FofongaDocument4 pagesLesoni Fakame Tuluta A Loi FofongaHaitelenisia Hei'ululua KAMANo ratings yet
- Big Science Competition Year 9 2020Document17 pagesBig Science Competition Year 9 2020PepsicleNo ratings yet
- OLD-WSL-MIN-SOP-013 - Making Safe of Underground WorkingsDocument15 pagesOLD-WSL-MIN-SOP-013 - Making Safe of Underground WorkingscoleighscornerNo ratings yet
- DESIGN CRITERIA Structural Design CriterDocument25 pagesDESIGN CRITERIA Structural Design CriterAl Patrick Dela CalzadaNo ratings yet
- MST 01Document118 pagesMST 01Micaela EncinasNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis - History of Architecture - Mayan, Aztec, IncaDocument8 pagesComparative Analysis - History of Architecture - Mayan, Aztec, IncaMillenia domingoNo ratings yet
- SLK WordDocument14 pagesSLK WordIerdna RamosNo ratings yet
- Hydrolithological Investigation For Near-Surface ADocument10 pagesHydrolithological Investigation For Near-Surface AEdilson LourencoNo ratings yet
- IPA18 80 G Manusrcipt Ver1Document13 pagesIPA18 80 G Manusrcipt Ver1billal_m_aslamNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Slope Management and Slope Engineering Practices in MalaysiaDocument16 pagesHow To Improve Slope Management and Slope Engineering Practices in MalaysiaAs RazakNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction and ManagementDocument3 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction and ManagementMedija FamilyNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Skill 3-5 - Anisa BasriantiDocument4 pagesAssignment of Skill 3-5 - Anisa Basriantianisa basriantiNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Assessment Report by Bryan Consultants, Inc.Document2 pagesPreliminary Assessment Report by Bryan Consultants, Inc.wfaachannel8No ratings yet
- Volcanoes: By: Beldianu Andrei-Cosmin Geografie Anul IDocument22 pagesVolcanoes: By: Beldianu Andrei-Cosmin Geografie Anul IAndrewNo ratings yet
- Reading Test (B) AK Gr4 SECOND TERMDocument6 pagesReading Test (B) AK Gr4 SECOND TERMAsmaa MostafaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis:: Novel: Journey To The Centre of The Earth - Literary AnalysisDocument6 pagesSynopsis:: Novel: Journey To The Centre of The Earth - Literary Analysisina_mawarosa86No ratings yet
- Chapter Two DRDocument30 pagesChapter Two DRيا ابا صالح المهديNo ratings yet
- Unu-Gtp-Sc-23-0604a Drilling in Menengai High Temperature Field - Drilling Equipment and Well DesignDocument11 pagesUnu-Gtp-Sc-23-0604a Drilling in Menengai High Temperature Field - Drilling Equipment and Well DesignPrince MubaiwaNo ratings yet
- (Prelim) Mineral ResourcesDocument19 pages(Prelim) Mineral ResourcesMarkNo ratings yet
- 00251300bars95001 Cdfe00 149Document149 pages00251300bars95001 Cdfe00 149Mohammed HijaziNo ratings yet
- Is 6966 1989 (PART 1) Hydraulics Design of Barrages and WeirsDocument12 pagesIs 6966 1989 (PART 1) Hydraulics Design of Barrages and Weirsarvind.singhNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Pretreatment For Tunnel Karst Cave During Excavation: A Case Study of Guangxi, ChinaDocument12 pagesResearch Article: Pretreatment For Tunnel Karst Cave During Excavation: A Case Study of Guangxi, Chinasvs dmrNo ratings yet
- National Geographic Kids RocksDocument34 pagesNational Geographic Kids RocksStuNo ratings yet
- Geometallurgy and Mineral Processing Presentation, 2021Document13 pagesGeometallurgy and Mineral Processing Presentation, 2021Arnold AsieduNo ratings yet
- Lecture Planner - Geography - PDF OnlyDocument2 pagesLecture Planner - Geography - PDF OnlysohamadmaneofficialNo ratings yet
- OrienteeringDocument33 pagesOrienteeringDale Robert B. CaoiliNo ratings yet