Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Republic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Uep - Edu.ph
Uploaded by
Kristel PepitoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Uep - Edu.ph
Uploaded by
Kristel PepitoCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
UNIVERSITY OF EASTERN PHILIPPINES
University Town, Northern Samar
uep.edu.ph uepnsofficial@gmail.com
WILSON NUNGAY EJERCITO
Special Lecturer, UEP-CAC
Credits to Prof. Brenfred Romero
MODULE 8
ELEMENTS OF VISUAL ARTS
OBJECTIVES
▪ Identify the elements of the visual arts
▪ Infuse the connotations of lines and colors in the interpretive type of art
criticism
▪ Master the correct ways of harmonizing colors
The Elements of the Visual Arts
1. Line
2. Color
3. Texture
4. Perspective
5. Space
6. Form
7. Volume
6.1 LINE
It is an important element at the disposal of every artist. It is being used
to represent figures and forms. It has direction. It is moving. It is composed of
points.
Two Kinds of Lines
1. Straight line- one/linear direction; associated with the ideas of
steadiness and force.
2. Curved line- two directions; associated with the ideas of flexibility,
buoyancy and grace, sudden/gradual change of movement or direction
and joyousness.
Kinds of Straight Line:
1. Horizontal Line. It is a line for repose and serenity. It refers to
the ideas of quiescence and calmness. It can be found in a
reclining person, calm bodies of water, landscape, repose and
death. It’s taken from the word HORIZON, the distant meeting of the
earth and the sky.
2. Vertical Line. It connotes to the idea of a dignified figure. It is
poised for action. It is balanced, forceful and dynamic. It can
be found in a standing person, tall tree, statues of saints and
heroes, exaltation of monuments.
3. Diagonal Line. It suggests action and movement. It gives
animation to any composition. It can be found in a running
person.
Credits to Prof. Brenfred Romero
Other Classification of Lines
1. Repetitive Line. A line which repeats/follows one another. Repetition
occurs when two or more lines are drawn within a corner following the
lines of the corner.
2. Contrasting Lines. Are in position to each other form of a contrast.
3. Transition Line. It happens when a curved line cuts across a corner
from an opposition line to another. It modifies the sharpness of vertical
and horizontal lines giving a harmonizing effect.
6.2 COLOR
Delight in color is a universal human characteristic. Color is a property
of light. When color goes out, color goes with it. White light of the sun contains
all the colors of the spectrum: ROYGBIV.
“When a beam of light passes through a prism, the different rays of color
are separated so that we are able to see and identify them.” When a light strikes
a surface, some of the color rays are absorbed while others are reflected. For
example, a blue dress absorbs all the color rays except the blue ray which is
reflected.
Objects that appear to be black absorb practically all the color rays and
reflects none; on the other hand, objects that appear to white reflect all the rays
equally.
3 Dimensions/Attributes/Properties of Color
1. Hue. It gives color its name.
2. Value. It denotes the lightness and darkness of color. It indicates the
degree of luminosity (presence or absence of light)
White- highest value
Medium- halfway
Dark- lowest value
Light- the halfway between white and black
Dark- the point halfway between medium and black
Tints. Are values above the normal.
Shades. Are values below the normal.
3. Intensity. It refers to the brightness or darkness/dullness of color. It
gives color its name. The more black or white is added, the weaker is
the intensity.
Grouping the Colors
1. Primary colors: red, yellow, blue
All other colors are produced by combing any / two of these of
colors.
Credits to Prof. Brenfred Romero
2. Secondary colors: green, violet, orange
Credits to Prof. Brenfred Romero
These colors can be produced by combining two of the primary
colors.
3. Intermediate colors. Yellow-orange, red-orange, red-violet, blue-
violet, blue-green and yellow-green
These can be produced by mixing in equal amount of primary and
secondary colors.
4. Tertiary Colors. Orange-yellow, violet-green, orange-green
These can be produced by combining all equal mixture any two
secondary colors.
▪ Warm Colors (advancing colors). Red, orange and yellow are the warm
hues. These are associated with objects like the sun, fire and other
sources of heat. They are conspicuous, cheerful and stimulating,
vivacious, joyous and exciting.
▪ Cool Colors (receding colors). Where blue predominates. They suggest
distance, calm, sober, restful, inconspicuous
▪ Denotation. The meaning of a word is taken from books, dictionaries,
etc. It refers to the universal definition of a word.
▪ Connotation. The meaning is varied and is subject to the person’s
personal encounter, tastes, ideologies and preferences. Hence, a single
picture worth a thousand words.
The Language/Connotations of Colors
Color is a form of non-verbal communication. It is not a static energy and
its meaning can change from one day to the next with any individual - it all
depends on what energy they are expressing at that point in time.
The meaning of colors can vary depending on culture and
circumstances. Each color has many aspects to it but one can easily learn the
language of color by understanding a few simple concepts.
Blue is the color of trust, peace, and responsibility. It can suggest loyalty
and integrity as well as conservatism and frigidity. This color is one of trust,
honesty and loyalty. It is sincere, reserved and quiet, and doesn't like to make
a fuss or draw attention. It hates confrontation, and likes to do things in its own
way. From a color psychology perspective, blue is reliable and responsible. This
color exhibits an inner security and confidence.
Green is the color of balance, harmony, and growth. It can mean both
self-reliance as a positive and possessiveness as a negative, among many
other meanings. This is the color of balance and harmony. From a color
psychology perspective, it is the great balancer of the heart and the emotions,
Credits to Prof. Brenfred Romero
creating equilibrium between the head and the heart. From a meaning of colors
perspective, green is also the color of growth, the color of spring, of renewal
and rebirth. It renews and restores depleted energy. It is the sanctuary away
from the stresses of modern living, restoring us back to a sense of well−being.
This is why there is so much of this relaxing color on the earth, and why we
need to keep it that way.
Orange is the color of adventure and social communication and
optimism. From a negative color meaning it is also a sign of pessimism and
superficiality. The color orange radiates warmth and happiness, combining the
physical energy and stimulation of red with the cheerfulness of yellow. It relates
to 'gut reaction' or our gut instincts, as opposed to the physical reaction of red
or the mental reaction of yellow. Orange offers emotional strength in difficult
times. It helps us to bounce back from disappointments and despair, assisting
in recovery from grief. The color psychology of orange is optimistic and uplifting
as it rejuvenates one’s spirit. On the whole, orange is sociable, optimistic,
enthusiastic, cheerful, self-confident, independent, flamboyant, extroverted and
uninhibited, adventurous, the risk-taker, creative flair, warm-hearted, agreeable
and informal.
Red is the color of energy, passion, action, ambition and determination.
It is also the color of anger and sexual passion. This color is a warm and positive
color associated with our most physical needs and our will to survive. It exudes
a strong and powerful masculine energy. Red is energizing. It excites the
emotions and motivates us to take action. It signifies a pioneering spirit and
leadership qualities, promoting ambition and determination. It is also strong-
willed and can give confidence to those who are shy or lacking in will power.
On the other hand, red would also means aggressive and domineering, over-
bearing, tiring, angry and quick-tempered, ruthless, fearful and intolerant,
rebellious and obstinate, resentful, violent and brutal.
Yellow is the color of the mind and the intellect. It is optimistic and
cheerful. However it can also suggest impatience, criticism and cowardice. This
color relates to acquired knowledge. It is the color which resonates with the left
or logic side of the brain stimulating our mental faculties and creating mental
agility and perception. Being the lightest hue of the spectrum, the color
psychology of yellow is uplifting and illuminating, offering hope, happiness,
cheerfulness and fun.
Psychology of Roses
The presence of flowers triggers happy emotions, heightens feelings of
life satisfaction and affects social behaviour in a positive manner far beyond
what is normally believed.”
Rose is considered to be the world’s universal flora of love. Each color
and number of rose means something
▪ One rose for simplicity
▪ Two roses for ready to settle down
▪ Three roses for I love you
Credits to Prof. Brenfred Romero
▪ Red rose for I love you
▪ Pink rose for friendship and thank you
▪ Yellow rose for jovial relationship
▪ Coral/orange rose for desire
▪ Whiter rose for secret affection
▪ Green rose for eternal love
▪ White and red roses to apologize
Color Harmony is the correct combination and arrangement of colors so that
they will appear pleasing to the eyes.
1) Related Color Harmony
a. Monochromatic Harmony. It employs one color with its tints and
shades. It is made up of several tones in one hue.
b. Adjacent /Analogous Harmony. It is the use of colors which possess
one common color in all their mixture. These colors are found near
each other in the color chart
2) Contrasted Color Harmony. Is a group of color harmonies which is
controlled because the colors are selected and arranged in such a way
that the colors involved are found opposite each other in the color chart.
6.3 TEXTURE. It is the element that deals more directly with the sense of touch,
thru hands. It identifies the characteristic of surfaces which can be rough or
smooth, fine or coarse, shiny or dull, plain or irregular.
6.4 PERSPECTIVE. It deals with the effect of distance upon the appearance of
objects, by means of which the eye judges spatial relationships.
Credits to Prof. Brenfred Romero
2 Kinds of Perspective
1. Linear Perspective. It is the representation of an appearance of distance
by means of converging lines and diminishing sizes.
Foreshortening. A facet of linear perspective which is applied chiefly to
the human figure. It is the representation of objects or parts of the body
as smaller from the point of view of the observer.
2. Aerial Perspective (top-view or bird’s eye view). It is the representation
of relative distances of objects by gradations of tone and color. Objects
become painter in the distance due to the effect of the atmosphere.
Credits to Prof. Brenfred Romero
6.5 SPACE. It refers to interior and exterior spaces.
6.6 FORM. It applies to the over-all design of an artwork. It describes the
structure or shape of an object. “Form follows function.”
6.7 VOLUME. It refers to the amount of space occupied in three dimensions. It
refers to the solidity and thickness. It is said that there should be equal
solidity/thickness in an architecture so as to acquire unified interpretation from
a recipient.
Credits to Prof. Brenfred Romero
LEARNING TASKS
Tertiary colors Cool colors Curved line Navy blue Hue
Line Intensity Warm colors Secondary colors Intermediate colors
Value Color Maroon Contrasting line Color harmony
Sky blue Primary colors Texture Perspective Form
Contrasted color Related color Foreshortening Volume Pink
harmony harmony
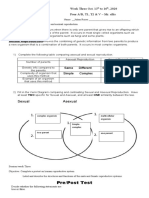
Part I. Remember Me? Identify what is being referred to in each statement. Use
the pool above as your reference. Write your answers on the space before each
number.
1 Gives color its name
2 Combining two secondary colors of equal
amount.
3 The advancing colors
4 Solidity and thickness.
5 Lightness and darkness
6 Red, yellow, blue
7 It happens when a curved line cuts across a
corner from an opposition line to another.
8 Combining one primary color and one
secondary color of equal amount.
9 Property of light.
10 The shade of red.
11 Linear perspective for human figure.
12 Deals with sense touch (smoothness or
roughness).
13 Effect of distance upon the appearance of
objects of which the eye judges spatial
relationships.
14 Correct combination and arrangement of
colors.
15 The receding colors.
16 It follows function.
17 Brightness and darkness.
18 Combination of colors which are in opposite
positions in the color wheel.
19 Composed of a series of points
20 The tint of blue
Credits to Prof. Brenfred Romero
Part II.CAN YOU MATCH ME WITH? Match the concepts with their denotations.
Write only the letter on the blank before the number.
A. Lines
1. straight line A. Action and movement
2. curved line B. Quiescence and calmness
3. horizontal line C. Balanced and forceful
4. vertical line D. Buoyancy and grace
5. diagonal line E. Steadiness and force
F. Repose and movement
B. Colors
1. red A. Joy and jealousy
2. yellow B. Young and virgin
3. blue C. Death and end
4. green D. Love and war
5. black E. Earth and passion
F. Noble and peace
C. Roses
1. one rose A. Desire
2. white and red roses B. Thank you
3. two roses C. I love you
4. pink rose D. Simplicity
5. coral/orange rose E. Secret affection
F. Apologizing
Credits to Prof. Brenfred Romero
You might also like
- Arts New LessonDocument18 pagesArts New LessonkatemonroidNo ratings yet
- Interior Report-2Document44 pagesInterior Report-2p9m6q9dfwrNo ratings yet
- Least Common Multiple PDFDocument5 pagesLeast Common Multiple PDFJhona NinalgaNo ratings yet
- ELEMENTS OF THE VISUAL ARTS EXPLAINEDDocument2 pagesELEMENTS OF THE VISUAL ARTS EXPLAINEDAlexa S. CanillasNo ratings yet
- Lec 4: Color - Part 01 (CE-214)Document30 pagesLec 4: Color - Part 01 (CE-214)Tariq HasanNo ratings yet
- Hum 01 UNIT 5 Lessons 12 and 3Document17 pagesHum 01 UNIT 5 Lessons 12 and 3Bj Apostol QuejaNo ratings yet
- 77mnoik874bdaugaDocument33 pages77mnoik874bdaugakabambaleonard4No ratings yet
- Color PsychologyDocument20 pagesColor PsychologyHaider AliNo ratings yet
- Color Theory Hand-OutsDocument5 pagesColor Theory Hand-OutsMJ TimoganNo ratings yet
- Art and Design NotesDocument33 pagesArt and Design NotesKirigo KiambiNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Chapter 6Document16 pagesModule 3 - Chapter 6Mary Joyce SolitaNo ratings yet
- Humanities - MidtermDocument164 pagesHumanities - MidtermLorence Jude Angelo AlmazanNo ratings yet
- Elements of Art: Crisostomo Pantaleon Pascual Raguindin SalacDocument41 pagesElements of Art: Crisostomo Pantaleon Pascual Raguindin SalacSarang SNo ratings yet
- Colors Evoke Emotions & MemoriesDocument2 pagesColors Evoke Emotions & MemoriesJan Jenver IluminNo ratings yet
- The Elements of ArtDocument10 pagesThe Elements of ArtCleizel Mei FlorendoNo ratings yet
- PaintingDocument13 pagesPaintingHams on the Go100% (1)
- Color Analysis InsightsDocument20 pagesColor Analysis InsightsJonathan Ivan OroNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT Final Write UpDocument31 pagesEXPERIMENT Final Write UpdevanshiNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Meaning of COLOURDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The Meaning of COLOURRosmainah OsmanNo ratings yet
- Elements of DesignDocument34 pagesElements of DesignKattie Bosi AngoluanNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Meaning of ColorDocument3 pagesUnderstanding The Meaning of ColorAdelaide Andre LozadaNo ratings yet
- DOCUMENT ResearchDocument3 pagesDOCUMENT ResearchaizirtNo ratings yet
- Colors: Color Basics Meaning of ColorsDocument45 pagesColors: Color Basics Meaning of ColorsKim Frances HerreraNo ratings yet
- What Can Colours Mean?colour Symbology CollationDocument8 pagesWhat Can Colours Mean?colour Symbology Collation44robert123No ratings yet
- The Meaning and Properties of ColorDocument36 pagesThe Meaning and Properties of ColorPaulo Bollosa100% (1)
- Colours IntroductionDocument121 pagesColours IntroductionDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Lesson 7 & 8 on VALUE and COLORDocument5 pagesModule 8 - Lesson 7 & 8 on VALUE and COLORJoshua Urbana DaganNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument211 pagesArt AppreciationClaudine NaturalNo ratings yet
- Elements of Interior Design-Part 5 ColorDocument80 pagesElements of Interior Design-Part 5 ColorZaidNo ratings yet
- The Psychology of ColorsDocument6 pagesThe Psychology of Colorsapi-253187572No ratings yet
- GEC5 Chapter3 Elements Visual ArtsDocument56 pagesGEC5 Chapter3 Elements Visual ArtsCharlene Eusebio Calunsag LlapitanNo ratings yet
- Explore the Elements of ArtDocument21 pagesExplore the Elements of ArtAmy CerdaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Elements of ArtDocument11 pagesLesson 2 Elements of ArtJay-Jay BordeosNo ratings yet
- the emotions of color,meaning,symbolism&psychologyDocument22 pagesthe emotions of color,meaning,symbolism&psychologyBisrateab FekaduNo ratings yet
- Elements of Design: Lines, Colors, Shapes & MoreDocument37 pagesElements of Design: Lines, Colors, Shapes & MoreSharlyn GalonoNo ratings yet
- The essential elements of art and their roles in compositionDocument35 pagesThe essential elements of art and their roles in compositionEli Ayase75% (4)
- Brown and Beige Minimalist Vintage Scrapbook Self-Introduction PresentationDocument28 pagesBrown and Beige Minimalist Vintage Scrapbook Self-Introduction PresentationDaryl Shelby SurbanNo ratings yet
- Painting Techniques & Styles ExplainedDocument19 pagesPainting Techniques & Styles ExplainedFjane camotaNo ratings yet
- Meaning of ColorsDocument4 pagesMeaning of ColorsDavex GwapoNo ratings yet
- Reiki Handout Aura Color Meanings and SignificanceDocument1 pageReiki Handout Aura Color Meanings and Significanceeleni papageorgiouNo ratings yet
- Red. A Primary Color, This Color Is The "Hottest" One Out of The Warm Colors Group, andDocument6 pagesRed. A Primary Color, This Color Is The "Hottest" One Out of The Warm Colors Group, andMelissa LyonsNo ratings yet
- NLPSC Art Appreciation Chapter on Visual ElementsDocument8 pagesNLPSC Art Appreciation Chapter on Visual ElementsJessica May ChavezNo ratings yet
- The Color WheelDocument8 pagesThe Color WheelAhnNo ratings yet
- Arts ElementsDocument6 pagesArts ElementsNathalie GetinoNo ratings yet
- COLORDocument10 pagesCOLORmojica.arquiliz0001No ratings yet
- Visual Element of Arts, LIne and ColorDocument2 pagesVisual Element of Arts, LIne and ColorWilsonNo ratings yet
- Color Psychology, Color Meaning, and Subliminal Messages in ArtDocument9 pagesColor Psychology, Color Meaning, and Subliminal Messages in ArtM Thali VR100% (1)
- Printhandler AshxDocument54 pagesPrinthandler AshxrenatonealNo ratings yet
- Color Theory On FashionDocument37 pagesColor Theory On FashionMuhammad Hassan. Muhammad Hassan.No ratings yet
- UnitII - Language of ArtDocument60 pagesUnitII - Language of ArtRona mae MinaNo ratings yet
- GE 106 Art Appreciation WK 3Document18 pagesGE 106 Art Appreciation WK 3daryl.pradoNo ratings yet
- Element of Visual ArtsDocument28 pagesElement of Visual ArtsJustine LausNo ratings yet
- Alexandra T. Manzano Bsn-Iii Ncm105: Personality Based On ColorDocument5 pagesAlexandra T. Manzano Bsn-Iii Ncm105: Personality Based On ColorAlejandro Lucena TrinidadNo ratings yet
- BlueDocument5 pagesBluevampirediares21100% (1)
- Color Theory, Schemes and Psychology ExplainedDocument24 pagesColor Theory, Schemes and Psychology ExplainedFrancis DavidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Elements of The Visual Arts C. Diagonal LinesDocument5 pagesChapter 4: Elements of The Visual Arts C. Diagonal LinesYo MamaNo ratings yet
- Elements of ArtDocument73 pagesElements of ArtJanlawrence JaderNo ratings yet
- Colour Theory ExplainedDocument15 pagesColour Theory ExplainedAnshika GoelNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Uep - Edu.phDocument6 pagesRepublic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Uep - Edu.phKristel PepitoNo ratings yet
- Processes of BirthDocument51 pagesProcesses of BirthKristel PepitoNo ratings yet
- AP Module 3Document11 pagesAP Module 3Kristel PepitoNo ratings yet
- PE TransesDocument4 pagesPE TransesKristel PepitoNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document3 pagesActivity 3Kristel PepitoNo ratings yet
- 16 Balance TestDocument15 pages16 Balance Testelga saniNo ratings yet
- HSB Julian Reyes 4ab 1Document3 pagesHSB Julian Reyes 4ab 1Kéññy RèqüēñåNo ratings yet
- Ex 2013 1 (Recurrent)Document30 pagesEx 2013 1 (Recurrent)alh basharNo ratings yet
- Ceiling Fans Sensa Series: F Yuragi Function (Natural Breeze)Document1 pageCeiling Fans Sensa Series: F Yuragi Function (Natural Breeze)TYNo ratings yet
- Material ManagementDocument106 pagesMaterial ManagementRomi AfriansyahNo ratings yet
- Line Pack Presentation - Dec 2018Document7 pagesLine Pack Presentation - Dec 2018Goran JakupovićNo ratings yet
- Friends of Hursley School: Late Summer NewsletterDocument6 pagesFriends of Hursley School: Late Summer Newsletterapi-25947758No ratings yet
- Estimation of Fabric Opacity by ScannerDocument7 pagesEstimation of Fabric Opacity by ScannerJatiKrismanadiNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1-Module 2 Modern ArtDocument20 pagesQuarter 1-Module 2 Modern ArtKimberly Trocio Kim100% (1)
- English HL Grade 8 Language Exam Nov 2017 MEMODocument12 pagesEnglish HL Grade 8 Language Exam Nov 2017 MEMOThegn's PicklesNo ratings yet
- PTC Document Status: (Updated 11 November 2015)Document5 pagesPTC Document Status: (Updated 11 November 2015)AndersonGabriel23No ratings yet
- SilverDocument16 pagesSilversharma_shruti0% (1)
- Cefiget-Range-Leaflet-PakistanDocument2 pagesCefiget-Range-Leaflet-PakistanZafran KhanNo ratings yet
- Singaporean Notices To Mariners: Section ContentDocument35 pagesSingaporean Notices To Mariners: Section ContentGaurav SoodNo ratings yet
- Fiber Crops - FlaxDocument33 pagesFiber Crops - Flaxmalath bashNo ratings yet
- TCB E-F 015cukDocument2 pagesTCB E-F 015cukTempcoNo ratings yet
- Interfacial Phenomena in Pharmaceutical FormulationDocument21 pagesInterfacial Phenomena in Pharmaceutical FormulationNickson DrabeNo ratings yet
- Kraby System 2018Document22 pagesKraby System 2018soga010178No ratings yet
- Imsa Catalog Imsa CatDocument16 pagesImsa Catalog Imsa CatDaniel TelloNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Freestanding Cooling Double Door ARC 2140Document5 pagesService Manual: Freestanding Cooling Double Door ARC 2140Sergio ZapataNo ratings yet
- HymssheetDocument4 pagesHymssheettoby_wardmanNo ratings yet
- Juxtaposition and Non Motion Varese BridDocument13 pagesJuxtaposition and Non Motion Varese BridIvan Eiji Yamauchi SimurraNo ratings yet
- Rate Constant Determination 2Document8 pagesRate Constant Determination 2Divya UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 and 2Document67 pagesChapter 1 and 2Tle SupawidNo ratings yet
- Packaging Materials and Handling Technique: Dr. Ranjeet SinghDocument48 pagesPackaging Materials and Handling Technique: Dr. Ranjeet Singharon demagiba100% (1)
- K2N Final Internship ReportDocument55 pagesK2N Final Internship ReportAceZeta0% (1)
- GREEN AIR CONDITIONER Mechanical Presentation TopicsDocument9 pagesGREEN AIR CONDITIONER Mechanical Presentation TopicsCerin91No ratings yet
- Dip HenyDocument60 pagesDip HenyJinn Tanakrit HansuranantNo ratings yet
- Monthly Fire Extinguisher Inspection ChecklistDocument2 pagesMonthly Fire Extinguisher Inspection ChecklistisaacbombayNo ratings yet
- Rites of Acceptance For Altar Servers PDFDocument3 pagesRites of Acceptance For Altar Servers PDFJohn Carl Aparicio100% (1)
- The Complete Guide to Drawing & Illustration: A Practical and Inspirational Course for Artists of All AbilitiesFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Drawing & Illustration: A Practical and Inspirational Course for Artists of All AbilitiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Coloring Book for Adults & Grown Ups : An Easy & Quick Guide to Mastering Coloring for Stress Relieving Relaxation & Health Today!: The Stress Relieving Adult Coloring PagesFrom EverandColoring Book for Adults & Grown Ups : An Easy & Quick Guide to Mastering Coloring for Stress Relieving Relaxation & Health Today!: The Stress Relieving Adult Coloring PagesRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (12)
- Creative Abstract Watercolor: The beginner's guide to expressive and imaginative paintingFrom EverandCreative Abstract Watercolor: The beginner's guide to expressive and imaginative paintingNo ratings yet
- Painting Successful Watercolours from PhotographsFrom EverandPainting Successful Watercolours from PhotographsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Art Models AnaRebecca002: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models AnaRebecca002: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Painting Perspective, Depth & Distance in WatercolourFrom EverandPainting Perspective, Depth & Distance in WatercolourRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Fundamentals of Watercolour Landscapes: Paintings for all seasonsFrom EverandThe Fundamentals of Watercolour Landscapes: Paintings for all seasonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Beginner's Guide To Procreate: Characters: How to create characters on an iPad ®From EverandBeginner's Guide To Procreate: Characters: How to create characters on an iPad ®3dtotal PublishingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Stunning Watercolor Seascapes: Master the Art of Painting Oceans, Rivers, Lakes and MoreFrom EverandStunning Watercolor Seascapes: Master the Art of Painting Oceans, Rivers, Lakes and MoreNo ratings yet
- Watercolor Botanical Garden: A Modern Approach to Painting Bold Flowers, Plants, and CactiFrom EverandWatercolor Botanical Garden: A Modern Approach to Painting Bold Flowers, Plants, and CactiRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Gelli Arts® Printing Guide: Printing Without a Press on Paper and Fabric Using the Gelli Arts® PlateFrom EverandGelli Arts® Printing Guide: Printing Without a Press on Paper and Fabric Using the Gelli Arts® PlateNo ratings yet
- Discovering Watercolor: An Inspirational Guide with Techniques and 32 Skill-Building Projects and ExercisesFrom EverandDiscovering Watercolor: An Inspirational Guide with Techniques and 32 Skill-Building Projects and ExercisesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Zentangle 2, Expanded Workbook EditionFrom EverandZentangle 2, Expanded Workbook EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Acrylic Painting: Learn How to Paint Easy Techniques with Acrylic Paint (with photos)From EverandAcrylic Painting: Learn How to Paint Easy Techniques with Acrylic Paint (with photos)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Art Models Ginger040: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models Ginger040: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Layers of Meaning: Elements of Visual JournalingFrom EverandLayers of Meaning: Elements of Visual JournalingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Everything Drawing Book: From Basic Shape to People and Animals, Step-by-step Instruction to get you startedFrom EverandThe Everything Drawing Book: From Basic Shape to People and Animals, Step-by-step Instruction to get you startedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Art Models Saju027: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models Saju027: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Art Models SarahAnn031: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models SarahAnn031: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- Art Models Becca425: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models Becca425: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Portrait Painting in Oil: 10 Step by Step Guides from Old Masters: Learn to Paint Portraits via Detailed Oil Painting DemonstrationsFrom EverandPortrait Painting in Oil: 10 Step by Step Guides from Old Masters: Learn to Paint Portraits via Detailed Oil Painting DemonstrationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Expressive Digital Painting in ProcreateFrom EverandExpressive Digital Painting in ProcreateRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Journal with Purpose: Over 1000 motifs, alphabets and icons to personalize your bullet or dot journalFrom EverandJournal with Purpose: Over 1000 motifs, alphabets and icons to personalize your bullet or dot journalRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (39)
- Creative Watercolor: A Step-by-Step Guide for BeginnersFrom EverandCreative Watercolor: A Step-by-Step Guide for BeginnersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- The Art of Tinkering: Meet 150+ Makers Working at the Intersection of Art, Science & TechnologyFrom EverandThe Art of Tinkering: Meet 150+ Makers Working at the Intersection of Art, Science & TechnologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Art Models Adrina032: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceFrom EverandArt Models Adrina032: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Easy and Fun Cartooning Techniques for Drawing Comics and MangaFrom EverandEasy and Fun Cartooning Techniques for Drawing Comics and MangaNo ratings yet
- How To Draw Chibi: Learn Drawing Supercute Chibi Characters for Kids and Beginners - Easy Step-By-Step TutorialsFrom EverandHow To Draw Chibi: Learn Drawing Supercute Chibi Characters for Kids and Beginners - Easy Step-By-Step TutorialsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)