0% found this document useful (0 votes)
456 views4 pagesExperiment 3
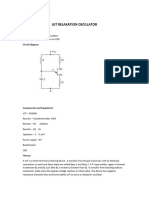
The document describes designing and simulating an astable multivibrator circuit using a 555 timer IC for different duty cycles. It explains the theory of astable multivibrators and provides the component list. Formulas are given to calculate resistor and capacitor values for 50%, 75%, and 40% duty cycles at 1 kHz frequency. The circuit is designed, simulated, and waveforms are observed and measured to verify the duty cycles.
Uploaded by
ARUN KUMAR PCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
456 views4 pagesExperiment 3
The document describes designing and simulating an astable multivibrator circuit using a 555 timer IC for different duty cycles. It explains the theory of astable multivibrators and provides the component list. Formulas are given to calculate resistor and capacitor values for 50%, 75%, and 40% duty cycles at 1 kHz frequency. The circuit is designed, simulated, and waveforms are observed and measured to verify the duty cycles.
Uploaded by
ARUN KUMAR PCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd