Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UG Most Important
Uploaded by
Sandy MandernaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
UG Most Important
Uploaded by
Sandy MandernaCopyright:
Available Formats
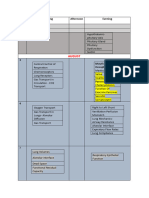
Physiology Most Important Questions 1
Questions RE Related Question RE Related Question RE Related Question RE
General physiology
secondary active transport 2 active transport
cold acclimatization 2 body response to low
tem.
RMP ionic basis of RMP
heat acclimatization
osmosis
passive transport
negative feedback mechanism
Muscle and Nerve
Chronaxie and Rheobase streangth duration
curve
Excitation Contraction Coupling 4 Molecular Basis of 2 sarcotubular
muscle contraction system
Myasthenia gravis 3 Neuro Muscular 2
System
Action potential of Nerve fIber 4 receptor vs action
potential
structure of sarcomere 2
Skeltal muscle and smooth red vs white muscle
muscle fiber
Saltatory conduction
GIT
Exocrine part of pancrease 3
Defecation reflex 2 mass movement 2 gastro- colic reflex
Function of bile 3 bile salts composition functions of gall
bladder
intestinal movements 3 peristalsis 2 segmental law of gut
movement
pharyngeal stage of swallowing deglutination deglutition apnea
function of saliva 2
phases of gastric juice secretion regulation povlov pouch 2
mech of formation of HCl in 2 H secretion peptic ulcer
stomach
Local Harmone of GIT Gastrin secretin somatostatin
function of stomach
Dr Rajnish Kanojia, GMC, Pali
Physiology Most Important Questions 2
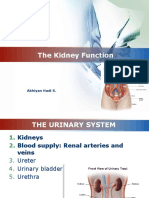
Renal System
Regulation of glomerular GFR ; factor affecting GFR Dynamics in
filteration Filteration;
filteration fraction
Counter Currednt Mechanism 4 multiplier 2 juxtamedullary
nephrons
Clearance, use in RFT 2 creatinin clearance 2 inulin clearance; characterstics of
substances
measuring GFR
JG apprtus 3 macula densa feedback
mechanism
micturition reflex 4
role of ADH in water excretion concentration of urine
pecularities of renal circulation
acidification of urine 2
endocrin function of kidney 2
Tm of glucose
cystometrogram micturition waves
CVS
ECG wave significance 8 leads Augmented Leads Eithenvon triangle
Pace Maker potential 4 SA Nodal Action Action potential of 2
Potential cardiac muscle
Renin Angiotensin System 3 long term regulation of 2 short term 3 Factor affecting
BP, Role of aldosteron regulation of BP, and determinant
barroreceptor of BP
reflex , Buffer
nerves
Atrio ventricular delay 3 conducting system of 2 PR interval
heart Significance and
when Prolonged
pressue n vol change in cardiac cardiac cycle 2 LV , LA pressure
cycle in left ventric change
coronary circulation 3
heart sound Silent gap Korotokoff sound
Cushing reflex 2
cvs change in exercise 2
reynolds number 2
compensatory mechanism in circulatory shock
hemorrhagic shock
CO & method to measure 2 fick's principle
Dr Rajnish Kanojia, GMC, Pali
Physiology Most Important Questions 3
windkessel effect windkessel vessels
factor affecting HR
Respiratory
Function of surfactant 4 Clinical impotance 2 surface tension Hyaline
membrane
Disease
Oxygen dissociation curve 5 significance Bohr's effect on
Oxygen transport
neural regulation of respirtion 4 role of cetral
chemoreceptors
Compliance of lung Diagram 4
co2 transport 4
Timed Vital capacity and use 3 FEV1 in normal and 2
obstructive patients
Pulmonary Circulation 2
Change in intrapulmonary and 2 mech of respiration
intrapleural pressure during
ventilation
hypoxia types
lung volume , capacity spirogram
physiological dead space dead space
caisson's disease
Acclimatization to low pO2 Acclimatization
periodic breathing Chynestokes breathing
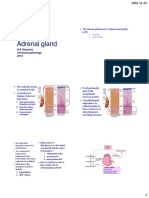
Endocrinology
Cushing Syndrom 3 cushing vs addison
Synthesis of thyroid harmone 4 Role of iodin regulation of
thyroid secretion
Pituitary and thyroid dwarf 3
Conn's Syndrome 2
non metabolic function of function of
glucocorticoids glucocorticoids
Hyperparathyroidism effect of parathroid action of
harmone parathyroid
harmone
regulation of aldosteron aldosteron escape
GTT Curve DM vs insipidus vasopresin 2
Tetany
Hypothalamo hypophyseal tract
and portal system
Second messenger
Dr Rajnish Kanojia, GMC, Pali
Physiology Most Important Questions 4
Blood
erythroblastosis fetalis 5 Rh incompatibility hemolytic disease neonatal jaundice
of new born
Stages of erythropoisis 6 Control of
erythropoisis
Function of plasma proteins 4
Intrinsic pathway of Blood 4 fibrinolytic system extrinsic pathway 2 Hemostasis,
coagulation extrinsic and
intrinsic
mechanism
Anticoagulants 2 Dicoumoral
iron deficiency anemia 2 Aetiological thalassemia herediatory
classification of spherocytosis
anaemia
Cynosis 2
cell mediate immunity 2
blood coagulation test thrmbocytopenia
Incompitable Blood Transfusion
jaundice types
Reproductive
Spermatogenesis 4 spermiogenesis
Contraceptive methods Oral Contraceptive 3 safe period female
contraceptive
methods
Harmonal Changes during MC 4 LH surge ovulation
Milk Ejection Reflex 4 Lactation Oxytocin 2
feto placental unit 3
hCG 2 pregnancy test
control of testicular activity hypothalamic pituitory hypothalamo
testicle axis pituitary gonadal
axis
action of estrogen
Functions of testosteron 2 sertoli cells
turners syndrome
function of placenta
CNS
EPSP and IPSP 4 Pre and post synaptic
inhibition
Reffered Pain 3 gate control theory 2
analgesic system of body 2 analgesic pathway
fast vs slow pain 2 pathway pain producing superficial vs
substasnces deep pain
Dr Rajnish Kanojia, GMC, Pali
Physiology Most Important Questions 5
properties of syapse 3 synapes chemical vs 2
electrical synaps
UMN and LMN 2 UMN lesion vs LMN 2
lesion
REM Sleep 2 REM Sleep vs Non REM 2
sleep
Neural connection of cerebellum Function of cerebellum 2 structure of spino cerebellar
cerebellum connection
caudate circuit of basal ganglia function of basal 2 BG connections Parkinson's 2
ganglia disease, L DOPA in
Parkinsonism
Brown squard syndome hemisection of spinal
cord
Muscle spindle and neural function of muscle 2
connection spindle
vegetative function of function of temp regulation
hypothalamus hypothalamus role of
hypothalamus
pathway of pyramidal tract pyramidal vs 2 cortico spinal
extrapyramiddle pathway
stretch vs withdraw reflex supraspinal control of superficial vs deep babinski sign
stretch reflex reflex
type of receptors adaptation of receptor
CSF fuction, composition
thalamic phantom limb
Monosynaptic and polysynaptic
reflexes
Special Sense
Visual pathway 7 light reflex pathway lesion
Organ of corti 3 travelling waves
colour blindness 2
auditory pathway 2
otolith organ 2
Motor aphasia
dark adaptation
Rods and cones photoreceptor night blindness Phototopic and
mechanism Scotopic vision
Dr Rajnish Kanojia, GMC, Pali
You might also like
- Nuclear Receptors in Drug MetabolismFrom EverandNuclear Receptors in Drug MetabolismWen XieNo ratings yet
- MLT All Questions CompiledDocument4 pagesMLT All Questions Compiledfellow80966No ratings yet
- Physio UNI ImpDocument8 pagesPhysio UNI Impiphonekifotos2No ratings yet
- Course of Syllabus For Physiology: Total Time Required For Physiology: Minimum Two SemestersDocument13 pagesCourse of Syllabus For Physiology: Total Time Required For Physiology: Minimum Two Semestersapi-3728690No ratings yet
- Work ProgDocument9 pagesWork Progyamanuel25No ratings yet
- Case MNGT On Cysto-TURPDocument86 pagesCase MNGT On Cysto-TURPAndelaliz SantiagoNo ratings yet
- New Physio TTDocument8 pagesNew Physio TTangeginger6No ratings yet
- Endocrine ' Endocrine ' Section Iii: Endocrine-Physiology Endocrine-PhysiologyDocument20 pagesEndocrine ' Endocrine ' Section Iii: Endocrine-Physiology Endocrine-PhysiologyLuis Jose VelazquezNo ratings yet
- ID Pengetahuan Remaja Putri Tentang Cara MeDocument3 pagesID Pengetahuan Remaja Putri Tentang Cara MeAyu Wita DewiNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Gastric Electrical and Mechanical Activity by Cholinesterases in MiceDocument17 pagesRegulation of Gastric Electrical and Mechanical Activity by Cholinesterases in MiceRaluca MosoiaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland Physiology (DRDocument77 pagesAdrenal Gland Physiology (DRapi-3769252100% (4)
- CHRONOPHARMACOLOGYDocument5 pagesCHRONOPHARMACOLOGYalfiya mujawarNo ratings yet
- 2010 2physDocument12 pages2010 2physlahiruwan123No ratings yet
- Pain Revised-Book-2014Document167 pagesPain Revised-Book-2014Maria AngelescuNo ratings yet
- The Hypocretins: Setting The Arousal ThresholdDocument11 pagesThe Hypocretins: Setting The Arousal ThresholdQiantuNo ratings yet
- Rhythms of Life: Circadian Disruption and Brain Disorders Across The LifespanDocument17 pagesRhythms of Life: Circadian Disruption and Brain Disorders Across The LifespanSeBass B ToledoNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: - Ridho IslamieDocument27 pagesUrinary System: - Ridho IslamieLaksmi DwiNo ratings yet
- NCM 106: Self Directed Learning Activity Name and Section: John Michael O. Villanueva BSN 2 ADocument4 pagesNCM 106: Self Directed Learning Activity Name and Section: John Michael O. Villanueva BSN 2 AKaye PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- Key Terms Summary Sheet Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesKey Terms Summary Sheet Muscular SystemskidamarinkNo ratings yet
- Chrono Biology SeminarDocument39 pagesChrono Biology SeminarSurabhi VishnoiNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Urinary System (2020)Document55 pagesFundamental of Urinary System (2020)Nadya PutriNo ratings yet
- Neuropharmacology of The ENSDocument34 pagesNeuropharmacology of The ENS120420314No ratings yet
- Angiotensin II Induces Fibronectin Expression in Human Peritoneal Mesothelial Cells Via Erk 12 and p38 MAPKDocument10 pagesAngiotensin II Induces Fibronectin Expression in Human Peritoneal Mesothelial Cells Via Erk 12 and p38 MAPKCarlos Martinez SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic and Adrenergic PharmacologyDocument40 pagesCholinergic and Adrenergic PharmacologyAhmad Adam AhmadNo ratings yet
- Beta Blockers and Other Sympatholytic AgentsDocument43 pagesBeta Blockers and Other Sympatholytic AgentsAriel OlshevskyNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument9 pagesAdrenal GlandUhuebor DavidNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic System: Dr. Mozna TalpurDocument18 pagesAdrenergic System: Dr. Mozna TalpurShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- Zee 2013Document16 pagesZee 2013Ricardo HernandezNo ratings yet
- PERFUSION monitoring-SYSTEMIC-ghalebDocument49 pagesPERFUSION monitoring-SYSTEMIC-ghalebGHALEB A. AlmekhlafiNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Week 7 ReviewerDocument16 pagesNCM 106 Week 7 ReviewerCrecia Bullecer2No ratings yet
- Clinical Case 04-2019 - by SlidesgoDocument59 pagesClinical Case 04-2019 - by SlidesgoAnnumNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Rationale Intervention Rationale EvaluationHerald Jones LamirezNo ratings yet
- Hypomagnesemia: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesHypomagnesemia: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- (Kuliah 3) Mekanisme Akupunktur Medik Sari18Document65 pages(Kuliah 3) Mekanisme Akupunktur Medik Sari18callNo ratings yet
- Dr. Niranjan Murthy H L Asst. Prof. of Physiology SSMC, TumkurDocument39 pagesDr. Niranjan Murthy H L Asst. Prof. of Physiology SSMC, Tumkurnirilib100% (1)
- Renin Angiotensin System and the HeartFrom EverandRenin Angiotensin System and the HeartWalmor C. De MelloNo ratings yet
- II-Pharmacology of The Autonomic Autonomic Ne Nervous Rvous Sys System TEMDocument88 pagesII-Pharmacology of The Autonomic Autonomic Ne Nervous Rvous Sys System TEMks asNo ratings yet
- Sanson 2006Document8 pagesSanson 2006Caratasu Catalin CezarNo ratings yet
- Overview of PhysiologyDocument35 pagesOverview of Physiologyمعاذ عبد الكريم البازليNo ratings yet
- Tmp1a96 TMPDocument80 pagesTmp1a96 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- CVJ 49 PG 583Document4 pagesCVJ 49 PG 583paula gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Module 1A - Ch.1 (Cells, Tissues and Homeostasis) 2023Document24 pagesModule 1A - Ch.1 (Cells, Tissues and Homeostasis) 2023futurebiologist00pNo ratings yet
- G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRS)Document21 pagesG-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRS)amaliyana mega100% (2)
- Lecture 6 - Adrenergic AgonistsDocument24 pagesLecture 6 - Adrenergic AgonistsHadiya RohitNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agonists Lecture 1 - ClarkDocument49 pagesAdrenergic Agonists Lecture 1 - ClarkHaileris1No ratings yet
- Sympathetic Modulation by Antihypertensive DrugsDocument3 pagesSympathetic Modulation by Antihypertensive Drugsthomas albertNo ratings yet
- ReviewDocument19 pagesReviewfebyan yohanesNo ratings yet
- Autacoid - SerotoninDocument4 pagesAutacoid - SerotoninJohn Ellard M. SaturnoNo ratings yet
- Angiografía Por RMDocument13 pagesAngiografía Por RMJhoan OsorioNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOLOGY MOST IMPORTANT TOPIC (Dr. Arun Sir)Document1 pagePHYSIOLOGY MOST IMPORTANT TOPIC (Dr. Arun Sir)alka.noteshelfNo ratings yet
- Physiology DR - KKDocument259 pagesPhysiology DR - KKHARIHARAN VNo ratings yet
- 2008 51 519-528 Alan H. Gradman, and Rishi Kad: Renin Inhibition in HypertensionDocument12 pages2008 51 519-528 Alan H. Gradman, and Rishi Kad: Renin Inhibition in HypertensionFausto CamachoNo ratings yet
- And Fj-Adrenergic Receptor Subtypes: Properties, Distribution and RegulationDocument15 pagesAnd Fj-Adrenergic Receptor Subtypes: Properties, Distribution and RegulationsupriyoNo ratings yet
- Normal Sleep Physiology SlidesDocument27 pagesNormal Sleep Physiology SlidesAmitShettyNo ratings yet
- Student Name: Date: Patient Identifier: Patient Medical Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis (Use PES/PE Format)Document4 pagesStudent Name: Date: Patient Identifier: Patient Medical Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis (Use PES/PE Format)Darmatius NambaiNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Drugs Acting On ANS - Synchronous Session Ver 2Document7 pagesNCM 106 Drugs Acting On ANS - Synchronous Session Ver 2Crecia Bullecer2No ratings yet
- Buku Miller's Anesthesia BAB 20 Dan 21Document88 pagesBuku Miller's Anesthesia BAB 20 Dan 21Rahma TomuNo ratings yet
- Vpap - Sta St-A - iVAPS - User ManualDocument55 pagesVpap - Sta St-A - iVAPS - User ManualDiabestes-stuffNo ratings yet
- KZ-103-EN149-test-report For SURGICAL MASKDocument12 pagesKZ-103-EN149-test-report For SURGICAL MASKMd. Moniruzzaman Precision GroupNo ratings yet
- V. Kulish Human Respiration Anatomy and Physiology - Mathematical Modeling - Numerical Simulation and Applications Advances in Bioengineering 2006Document243 pagesV. Kulish Human Respiration Anatomy and Physiology - Mathematical Modeling - Numerical Simulation and Applications Advances in Bioengineering 2006Sofiah QotrunadaNo ratings yet
- BS en 00140-1999Document22 pagesBS en 00140-1999myenas87No ratings yet
- CMO 09 s2007Document55 pagesCMO 09 s2007XtiaRNo ratings yet
- Respiratory NCLEX Practice Test Part 1: Guillain-Barré SyndromeDocument20 pagesRespiratory NCLEX Practice Test Part 1: Guillain-Barré SyndromeHasan A AsFour100% (2)
- Effect of PEEP On Dead Space in An Experimental Model of ARDSDocument10 pagesEffect of PEEP On Dead Space in An Experimental Model of ARDSFernando SousaNo ratings yet
- High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation: Theory and Practical Applications Jane PillowDocument39 pagesHigh-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation: Theory and Practical Applications Jane PillowJimmy PinoNo ratings yet
- 22 Respiratory SystemDocument99 pages22 Respiratory SystemvanderphysNo ratings yet
- Mech Vent For Fun & BenefitDocument196 pagesMech Vent For Fun & BenefitJade Providence100% (1)
- Plasma: Ifcc Transport Storage BloodDocument6 pagesPlasma: Ifcc Transport Storage BloodFalanta SandaNo ratings yet
- Exchange SurfacesDocument15 pagesExchange SurfacesShushovan Usha BanikNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Dead Space Ventilation Physiology of RespirationDocument55 pagesVentilation Dead Space Ventilation Physiology of RespirationkuhutansittinurhalizaNo ratings yet
- DR - Kannan Nair JR - Consultant Apollo HospitalsDocument62 pagesDR - Kannan Nair JR - Consultant Apollo HospitalsKannan NairNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation Basic ModesDocument37 pagesMechanical Ventilation Basic ModesAmr El TaherNo ratings yet
- Breathing CircuitsDocument20 pagesBreathing CircuitsQworldNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Handbook WordDocument55 pagesVentilation Handbook WordHndr100% (2)
- CAPNOGRAPHYDocument72 pagesCAPNOGRAPHYNikita JainNo ratings yet
- 97893990619016Document14 pages97893990619016Khawla BahryNo ratings yet
- 2023.1 CICM Primary ProgramDocument52 pages2023.1 CICM Primary ProgramHani MikhailNo ratings yet
- Anaesthetic Breathing Systems: Mapleson ClassificationDocument6 pagesAnaesthetic Breathing Systems: Mapleson ClassificationDr Olivia JacobNo ratings yet
- GE Procare B40 Supplies and AccessoriesDocument20 pagesGE Procare B40 Supplies and AccessoriesRoman RufoNo ratings yet
- Essential Respiratory Calculation: Lung Volumes, Dead Space, and Alveolar VentilationDocument6 pagesEssential Respiratory Calculation: Lung Volumes, Dead Space, and Alveolar VentilationHéctor GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Mechanical VentilationDocument63 pagesBasics of Mechanical VentilationDiem KhueNo ratings yet
- 2013 Mock Test Instructions and ScriptDocument13 pages2013 Mock Test Instructions and ScriptsuperhumannzNo ratings yet
- Formulas and Calculations (Study Guide)Document86 pagesFormulas and Calculations (Study Guide)Ravneet singh100% (2)
- 3.5 Physiology Respiratory SystemDocument31 pages3.5 Physiology Respiratory Systemsimbolon.2202561040No ratings yet
- Pulmonary VentilationDocument22 pagesPulmonary VentilationOliviaNo ratings yet
- I.C.T ASSIGNMENT On Human RespirationDocument48 pagesI.C.T ASSIGNMENT On Human RespirationjeetudongreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Respiratory Systems NotesDocument11 pagesChapter 9 Respiratory Systems NotesCaleb DodgeNo ratings yet