Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wala To
Wala To
Uploaded by
Lady Midnight0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesThis document describes the major endocrine glands and their hormones and functions. It outlines the anterior and posterior pituitary glands, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal gland, pancreas, testes, ovaries, thymus gland, and pineal gland. For each gland the hormones produced are listed along with their target tissues and functions in stimulating growth, metabolism, reproduction, and other processes.
Original Description:
Original Title
wala-to
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes the major endocrine glands and their hormones and functions. It outlines the anterior and posterior pituitary glands, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal gland, pancreas, testes, ovaries, thymus gland, and pineal gland. For each gland the hormones produced are listed along with their target tissues and functions in stimulating growth, metabolism, reproduction, and other processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesWala To
Wala To
Uploaded by
Lady MidnightThis document describes the major endocrine glands and their hormones and functions. It outlines the anterior and posterior pituitary glands, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal gland, pancreas, testes, ovaries, thymus gland, and pineal gland. For each gland the hormones produced are listed along with their target tissues and functions in stimulating growth, metabolism, reproduction, and other processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
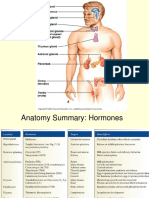
ANTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND
HORMONE TARGET TISSUES FUNCTIONS
Growth Hormone (GH) Most Stimulates growth of bones, muscles and organs
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Thyroid Gland Regulates thyroid gland secretions
(TSH)
GONADOTROPINS
● For Females: ● For Females: promotes ovulation and
Ovaries progesterone production
Luteinizing Hormones (LH)
● For males: Testes ● For Males: Sperm production and
Testosterone
● For Females: ● For Females: follicle maturation and
Follicles in Ovaries estrogen secretion
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone
(FSH) ● For males:
Seminiferous ● For Males: Sperm production
Tubules (Testes)
Prolactin (PRL) ● Mammary Glands Milk Production
● Ovaries
POSTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Kidneys Conserve Water
Oxytocin Uterus Increases uterine contractions during labor
THYROID GLAND
Thyroid Hormones Most Regulates metabolic rates and needed for
growth
Calcitonin Bones Secreted when blood Ca2+ levels are high
PARATHYROID GLAND
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) ● Bones Regulates blood Ca2+ levels
● Kidneys
ADRENAL GLAND
Adrenal Medulla: ● Heart
● Blood vessels Released as part of fight or flight response
Epinephrine and ● Liver
Norepinephrine ● Fat cells
Adrenal Cortex: ● Na+ and H2O retention
● K+ secretion
Aldosterone Kidneys ● Involved with blood pressure and volume
*Type: Mineralocorticoids
● Increases breakdown of fat and protein
Cortisol Most for energy uses
● Reduces inflammatory and immune
*Type: Glucocorticoids responses
● For Females: Sex drive
Androgens Most
● For Males: Secondary sexual
characteristics
PANCREAS
● Liver ● Regulates blood glucose levels
Insulin ● Skeletal Muscle ● After a meal glucose levels are high and
● Adipose Tissue insulin is secreted
*secreted by: Beta cells of the ● Extra glucose is stored in form of
Islets of Langerhans glycogen
● Regulates blood glucose levels
Glucagon ● Between meals glucose levels drop and
Liver glucagon is secreted
*secreted by: Alpha cells of the ● Glucagon allows glycogen to be broken
Islets of Langerhans down into glucose (glycogenolysis)
TESTES
● Aids in sperm and reproductive organ
development and function
● Responsible for adult male secondary
Testosterone Most sex characteristics
● Promotes growth and maturation of male
reproductive system
● Required for cell production
OVARIES
● Stimulates the development of secondary
female characteristics
Estrogen Most ● Matures female reproductive organs
● Helps prepare uterus to receive a
fertilized egg
*produced by: Graafian ● Helps maintain pregnancy
Follicles or Placenta ● Prepares the breast to produce milk
● Acts with estrogen to bring about the
Progesterone Most menstrual cycle
● Helps in the implantation of an embryo in
*produced by: Corpus Luteum the uterus
THYMUS GLAND
Thymosin Immune system tissues Promotes immune system development and
function
PINEAL GLAND
Melatonin Hypothalamus ● Plays a role in onset of puberty
● Controls circadian rhythms - sleep wake
cycle
You might also like
- Patho Immune System PathologyDocument7 pagesPatho Immune System PathologyCoy Nuñez100% (1)
- USMLE Platinum Notes Step 1, Second EditionDocument574 pagesUSMLE Platinum Notes Step 1, Second EditionDumitru Harsenie97% (34)
- Organs of The Immune SystemDocument19 pagesOrgans of The Immune SystemprabuNo ratings yet
- Teach Yourself Head and NeckDocument33 pagesTeach Yourself Head and NeckSambili Tonny100% (7)
- Visual Diagnosis in Chinese MedicineDocument3 pagesVisual Diagnosis in Chinese Medicineapi-275305557No ratings yet
- Hypovolemic ShockDocument2 pagesHypovolemic Shockatilano_patrickNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Disease of Newborn Class NotesDocument37 pagesHemolytic Disease of Newborn Class NotesElvisNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Breast, Milk Production, and Milk-EjectionDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Breast, Milk Production, and Milk-EjectionDeepak Ghimire100% (2)
- Hormones: Test Yourself 15.1 (Page 287)Document3 pagesHormones: Test Yourself 15.1 (Page 287)leeNo ratings yet
- Science 9: Quarter 3: Role of HormonesDocument2 pagesScience 9: Quarter 3: Role of Hormonescrizlie enotNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument32 pagesEndocrine Systemlee bon hukNo ratings yet
- Estrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesDocument57 pagesEstrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesBramwell K. MiteiNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Dental Trauma PDFDocument175 pagesHandbook of Dental Trauma PDFSuman KumarNo ratings yet
- InTech-Yamamoto New Scalp Acupuncture Ynsa Development Principles Safety Effectiveness and Clinical ApplicationsDocument17 pagesInTech-Yamamoto New Scalp Acupuncture Ynsa Development Principles Safety Effectiveness and Clinical Applicationsdasamoro100% (3)
- Immunohematology and Blood Banking Techniques PDFDocument172 pagesImmunohematology and Blood Banking Techniques PDFandersonalbino100% (4)
- Lecture 3 Aesthetics Study of Art and BeautyDocument186 pagesLecture 3 Aesthetics Study of Art and BeautyLady MidnightNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 7Document301 pagesLecture 2 7Lady MidnightNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 SCIENCE-REVIEWER-3rd-QuarterDocument3 pagesGRADE 10 SCIENCE-REVIEWER-3rd-QuarterKaitlin MamarilNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 - Animal Form and FunctionDocument5 pagesBio 11 - Animal Form and FunctionNikkaa XOXNo ratings yet
- Hormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelDocument38 pagesHormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- Group-5-FeedbackMechanismAndEndocrineSystrmDocument3 pagesGroup-5-FeedbackMechanismAndEndocrineSystrmCarousel Mae TayrosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9: Endocrine System: Prepared by Arianne V. JulianDocument34 pagesLesson 9: Endocrine System: Prepared by Arianne V. JulianGisselleNo ratings yet
- Padlan, Syra May M. - Endocrine System Assignment PDFDocument3 pagesPadlan, Syra May M. - Endocrine System Assignment PDFSyra May PadlanNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland: Anterior: Gland Hormone Target Tissues ResponseDocument2 pagesPituitary Gland: Anterior: Gland Hormone Target Tissues ResponseHiraya ManawariNo ratings yet
- Bio 133 Chap 11Document12 pagesBio 133 Chap 11Sam AbasNo ratings yet
- Mind Map On Endocrinology of Human For BSC StudentsDocument3 pagesMind Map On Endocrinology of Human For BSC Students2023ebcs499No ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Parathyroid GlandDocument29 pagesThe Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Parathyroid GlandRaed Abu HamadNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer LT1 - Q4Document2 pagesScience Reviewer LT1 - Q4Cara IsabelNo ratings yet
- Animal Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesAnimal Endocrine SystemAaron ZNo ratings yet
- Animal HormonesDocument2 pagesAnimal HormonesSameer Singh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- No Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandDocument3 pagesNo Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandKush KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY-LEC-Endocrine-System-1Document7 pagesANAPHY-LEC-Endocrine-System-1christinemaeloslos10No ratings yet
- 7sistem EndokrinDocument72 pages7sistem EndokrinAlfianaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesEndocrine SystemAdelfa LibanonNo ratings yet
- Review in Science 3rd QuarterDocument8 pagesReview in Science 3rd QuarterAyeisha ReyesNo ratings yet
- Endo EndoDocument45 pagesEndo EndomaoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System & MenstruationDocument3 pagesEndocrine System & MenstruationRochelle Leigh PaclebNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument2 pagesThyroid GlandacNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Hormones and AgingDocument10 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones and AgingTushar ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Hormones and AgingDocument10 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones and AgingTushar ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyDocument28 pagesEndocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyHumaira BadatNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesAnaphy Endocrine SystemFraiza BirowaNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology PhysiologyDocument13 pagesEndocrinology PhysiologyTanveer aminNo ratings yet
- Important Interview TipsDocument2 pagesImportant Interview TipsyasirtanoliNo ratings yet
- Animal HormonesDocument16 pagesAnimal HormonesMaria Theresa HerreroNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Lect 4Document78 pagesEndocrine Lect 4Wajiha IffatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Part 1 and 2Document51 pagesEndocrine System Part 1 and 2Wajiha IffatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PresentationDocument231 pagesEndocrine System PresentationKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine Systemnickbelle05No ratings yet
- 2 Types of Glands: Gland Hormone FunctionDocument6 pages2 Types of Glands: Gland Hormone FunctionHessah Balmores DupitasNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 Case Analysis 2Document9 pagesNCM 116 Case Analysis 2Dominic DegraciaNo ratings yet
- RT211 Module 12: Endocrine GlandsDocument9 pagesRT211 Module 12: Endocrine GlandskhaizamaerNo ratings yet
- 10 Biology 1 - 16 - 07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDocument32 pages10 Biology 1 - 16 - 07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsErivieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 UNIT IIDocument10 pagesChapter 2 UNIT IIAyen LatosaNo ratings yet
- Glands & Harmone (Top MCQ)Document29 pagesGlands & Harmone (Top MCQ)mat kumarNo ratings yet
- Activity Science - TableDocument4 pagesActivity Science - TableMiranda MirandaNo ratings yet
- 10 Female Sex HormonesDocument14 pages10 Female Sex HormonesRana AbdullahNo ratings yet
- (Pha) Le 5Document19 pages(Pha) Le 5Gabby TanNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Ncma217 (2b) Lec Reproductive and Sexual HealthDocument10 pagesWeek 2 Ncma217 (2b) Lec Reproductive and Sexual HealthABEGAIL BALLORANNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument2 pagesHormonesaddiekboringNo ratings yet
- Hormone GroupDocument35 pagesHormone GroupNeph VargasNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands WorksheetDocument3 pagesEndocrine Glands Worksheeteyra rosliNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands: Grade 10 ScienceDocument15 pagesEndocrine Glands: Grade 10 ScienceJohn Rick PerezNo ratings yet
- Science: Endocrine & Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesScience: Endocrine & Nervous SystemLUISE DANIELLA DELOS REYES DOLOTALLASNo ratings yet
- Physio Endo 4Document21 pagesPhysio Endo 4Hoth HothNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEMDocument3 pagesENDOCRINE SYSTEMmarasigan.michaelalouiseNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands 5PMDocument3 pagesEndocrine Glands 5PMRhod Jayson RicaldeNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology 2016Document52 pagesEndocrinology 2016Aman Singh RaoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Control of Our Bodies HomeostasisDocument22 pagesEndocrine System: Control of Our Bodies HomeostasisMary SutingcoNo ratings yet
- Jaipur National University: Sonia Gupta BPT Ist Year PhysiologyDocument5 pagesJaipur National University: Sonia Gupta BPT Ist Year PhysiologySonia guptaNo ratings yet
- HORMONESDocument2 pagesHORMONESDa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Lecture_8 EndocrineDocument4 pagesLecture_8 EndocrineBafrin ShaqlawaNo ratings yet
- Async Ina2 Medicalsurgicalnsg Midterm Usls Bsn4 Feb2023 v2 With Vids AsynchDocument156 pagesAsync Ina2 Medicalsurgicalnsg Midterm Usls Bsn4 Feb2023 v2 With Vids AsynchMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Puzzle - Sources of CapitalDocument1 pagePuzzle - Sources of CapitalLady MidnightNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System GuideDocument5 pagesFemale Reproductive System GuideLady MidnightNo ratings yet
- EM Feasibility Plan OutlineDocument5 pagesEM Feasibility Plan OutlineLady MidnightNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System E-ManualDocument4 pagesMale Reproductive System E-ManualLady MidnightNo ratings yet
- Logic: Set TheoryDocument16 pagesLogic: Set TheoryLady MidnightNo ratings yet
- Anaphy EmanualDocument12 pagesAnaphy EmanualLady MidnightNo ratings yet
- MODULE4 (9) Art and Anthropology: Cultural Relativism: Prepared by Dr. Allan C. OrateDocument111 pagesMODULE4 (9) Art and Anthropology: Cultural Relativism: Prepared by Dr. Allan C. OrateLady MidnightNo ratings yet
- Neurological Disorders With Sleep Alterations: Cristina Panea, MD, PHD Elias Emergency University Hospital BucharestDocument20 pagesNeurological Disorders With Sleep Alterations: Cristina Panea, MD, PHD Elias Emergency University Hospital BucharestGrig GrigNo ratings yet
- Sensory LabDocument7 pagesSensory LabNicole PramonoNo ratings yet
- An Awareness Session On Blood Donation and Its ImportanceDocument40 pagesAn Awareness Session On Blood Donation and Its Importancekushi krishnaNo ratings yet
- PAT2 BiologyDocument54 pagesPAT2 BiologyPONo ratings yet
- Major Categories Sense Organs: 1. (Movement: Tactation, Proprioception, and Hearing)Document12 pagesMajor Categories Sense Organs: 1. (Movement: Tactation, Proprioception, and Hearing)Carlos Enrique Pijo PerezNo ratings yet
- Breathing LessonsDocument3 pagesBreathing LessonsMichael W.100% (4)
- Pheochromocytoma Clinical CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesPheochromocytoma Clinical CharacteristicsAndrea MéndezNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument2 pagesAnatomymhredNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Heart in DetailDocument101 pagesPhysiology of Heart in Detailakanksha sharmaNo ratings yet
- Hap-1 Question Paper BP101T 2019-20 1st SemesterDocument1 pageHap-1 Question Paper BP101T 2019-20 1st SemesterLavanya Tanguturi yellaNo ratings yet
- 3 Advantage of Free Ex 3Document13 pages3 Advantage of Free Ex 3Farrukh ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Central Cord SyndromeDocument3 pagesCentral Cord SyndromehanzukikNo ratings yet
- Body Fluid 1Document55 pagesBody Fluid 1Anonymous z3afjyy1aNo ratings yet
- 12th Biology Lab ManualDocument4 pages12th Biology Lab ManualVasudha GudiNo ratings yet
- MHC Class II DeficiencyDocument2 pagesMHC Class II DeficiencyBre GlynnNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesThe Endocrine SystemRODGIELYN MAE GEJONNo ratings yet
- 01 Archaeous - LessonDocument6 pages01 Archaeous - LessonJonJonTattooartistNo ratings yet
- Digestion Board Game - Tiered Task Sheet-2Document5 pagesDigestion Board Game - Tiered Task Sheet-2api-295423685No ratings yet