0% found this document useful (0 votes)
213 views3 pagesIntro to Reproduction Basics
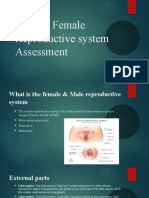
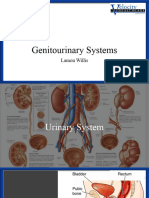
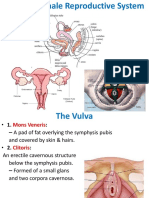
Reproduction can occur asexually or sexually. Asexual reproduction involves a single parent and faster population growth but less variation, while sexual reproduction involves two parents and more variation but slower growth. In asexual reproduction of plants, new individuals are produced through binary fission, budding, spore formation, fragmentation, or regeneration. In sexual reproduction, pollen is transferred from anther to stigma through pollination leading to fertilization and seed production. In humans, the male reproductive system includes the penis and testes which produce sperm, while the female system includes the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, where fertilization can occur.
Uploaded by
yo yeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
213 views3 pagesIntro to Reproduction Basics
Reproduction can occur asexually or sexually. Asexual reproduction involves a single parent and faster population growth but less variation, while sexual reproduction involves two parents and more variation but slower growth. In asexual reproduction of plants, new individuals are produced through binary fission, budding, spore formation, fragmentation, or regeneration. In sexual reproduction, pollen is transferred from anther to stigma through pollination leading to fertilization and seed production. In humans, the male reproductive system includes the penis and testes which produce sperm, while the female system includes the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, where fertilization can occur.
Uploaded by
yo yeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd