Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Consumer Learning and Memory
Uploaded by
Arabelle Bulanon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesOriginal Title
CONSUMER LEARNING AND MEMORY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesConsumer Learning and Memory
Uploaded by
Arabelle BulanonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
CONSUMER LEARNING AND MEMORY RETRIEVAL FROM LTM
WHAT IS LEARNING? Accessibility is defined as the likelihood and ease
It is defined as a change in the content or with which information can be recalled from
organization of a person’s long-term memory. LTM.
It is relatively permanent change in behavior Explicit Memory – the conscious recollection of
caused by experience. an exposure event.
The learner does not need to have experience Implicit Memory – the unconscious retrieval or
directly; we learn when we observe events that previously encountered stimuli. A sense of
affect others. familiarity, feeling of a set of belief about an item.
Learning is an on-going process.
BEHAVIORAL THEORIES
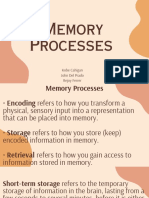
WHAT IS MEMORY?
It is defined as the total accumulation of prior It is based on behavior conditioning.
learning experiences. They are often referred as stimuli-response(S-R)
Memory is a vital part of information processing theories.
and essentially result from learning. Two types of behavioral theories: operant and
classical conditioning.
COMPONENTS OF MEMORY
CLASSICAL CONDITIONING
Short-Term Memory (STM) or working memory
– is the portion of total memory that is currently Unconditioned stimulus (US) – something that
activated or in use. generates a natural response.
The stage where information is processed and Unconditioned response (UR) – the natural
either forgotten or transferred to the long-term response that is generated when a stimulus is
store. perceived.
The temporary warehouse for information of Conditioned stimulus (CS) – the stimulus that a
incoming stimuli. person has learned to respond to.
STM is short lived. Conditioned response (CR) – occurs as a result
Maintenance rehearsal is the continual of a conditioned stimulus.
repetition of a piece of information in order to
hold it in current memory. REPETITION
STM has limited capacity.
It is an important aspect of classical conditioning.
Chunking means organizing individual items
The more times we see or hear a message, the
into groups of related items that can be
more likely we are to take notice of the
processed as a single unit.
information presented.
Constant repetition keeps the brand awareness
Long-Term Memory – is the unlimited permanent
level high and keeps the brands on top of mind.
storage.
It can store numerous types of information.
OPERANT CONDITIONING
Semantic Memory – is the basic knowledge and
Developed by an American psychologist, BF
feeling an individual has about a concept. Skinner.
It involves reinforcement of behavior and is
Episodic Memory – is the memory of sequence of based on the idea that consequences influence
events in which a person participated.
behavior.
Consumers must first engage in a particular
TYPES OF MEMORY ORGANIZATION behavior, followed by a specific consequence,
before learning can occur.
1. Semantic memory – involves association of words Positive reinforcement occurs in the form of
and their meanings. It includes things that are rewards for a particular behavior (positive
common knowledge, such as the names of colors, behavior = positive consequences).
the sounds of letters, the capitals of countries and Negative reinforcement occurs if you do not
other basic facts acquired over a lifetime. engage in a particular behavior or product
(positive behavior = removal of negative
consequences).
Punishment occurs when there is a consequence
of behavior that decreases the likelihood of that
behavior happening in the future (negative
behavior = negative consequences).
COGNITIVE THEORIES
Cognitive theories revolve around the idea that
humans learn through thinking, reasoning and
problem solving rather than a direct experience or
reinforcement.
Three major cognitive theories are: rote learning,
modelling and reasoning.
Rote Learning refers to learning from
memorizing repeated messages.
Vicarious Learning or Modelling involves
consumers learning through observing and
imitating the behavior of others; consumers see
the results or rewards gained by others who use
the product.
Analytical Reasoning is the most complex form
of cognitive learning because an individual need
to innovatively combine the existing information
and new information together and form a new
association and concept.
BRAND IMAGE AND PRODUCT POSITIONING
Brand Image refers to the schematic memory of a
brand. What people think of and feel when they
hear or see a brand name.
Product Positioning is a decision by a marketer to
try to achieve a defined brand image relative to
competition within a market segment.
Product Repositioning refers to a deliberate
decision to significantly alter the way the market
views a product.
You might also like
- Chapter 9&10 Prepraration of Consumer BehaviorDocument90 pagesChapter 9&10 Prepraration of Consumer BehaviorTrang Tran ThuNo ratings yet
- Memory-Learning #4Document13 pagesMemory-Learning #4usama iqbalNo ratings yet
- General Psychology ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Psychology ReviewerSherry Lyn Fernandez Lamsen-OrjaloNo ratings yet
- Comparing cognitive and behavioral views of learningDocument50 pagesComparing cognitive and behavioral views of learningKyla BulusNo ratings yet
- Cognitivism ApproachDocument30 pagesCognitivism Approachaltheaalvaran69No ratings yet
- Information ProcessingDocument3 pagesInformation ProcessinggalanlariebabesNo ratings yet
- Perdev - Midterm - 032544Document4 pagesPerdev - Midterm - 032544John Joshua M. ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4-7Document19 pagesLesson 4-7Mayraniel RuizolNo ratings yet
- Psych 101 Cornell Notes Mod 7Document6 pagesPsych 101 Cornell Notes Mod 7christianallenmlagosNo ratings yet
- Understanding Self 4Document5 pagesUnderstanding Self 4Jetro Pi-on PepeNo ratings yet
- Learning and MemoryDocument7 pagesLearning and MemoryJacob RosasNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8.psych ReviewerDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 8.psych ReviewerEdralyn EgaelNo ratings yet
- UTS ReviewerDocument4 pagesUTS ReviewerCyra Mae ColangoyNo ratings yet
- 6Document5 pages6guinilingjojieNo ratings yet
- Part IiDocument58 pagesPart Iiradheshamspate20No ratings yet
- Memory Processes ExplainedDocument25 pagesMemory Processes ExplainedSeth Abes FernandezNo ratings yet
- Memoryandforgetting 160331105704 1Document61 pagesMemoryandforgetting 160331105704 1Farasat Ayoub Baloch100% (1)
- Health Educ NotesDocument9 pagesHealth Educ NotesGrace UyNo ratings yet
- Encoding and Transfer of Information: Lucian ComandaDocument4 pagesEncoding and Transfer of Information: Lucian ComandaKelly SisonNo ratings yet
- Information Processing Psychology Write UpDocument4 pagesInformation Processing Psychology Write UpJess VillacortaNo ratings yet
- Consumer LearningDocument21 pagesConsumer LearningAnkita KharyaNo ratings yet
- It Will Be Forcing Someone To Work in A Poor Working Condition With No ProtectionsDocument14 pagesIt Will Be Forcing Someone To Work in A Poor Working Condition With No Protections陳芷萍No ratings yet
- Information Processing Theory CompressedDocument31 pagesInformation Processing Theory CompressedFerdinand LiquiganNo ratings yet
- Information processing theory and rememberingDocument6 pagesInformation processing theory and rememberingRezqa GusrizalNo ratings yet
- Memory and Learning PartDocument17 pagesMemory and Learning PartMuhammad KamranNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior PP Chapter 4Document36 pagesConsumer Behavior PP Chapter 4tuongvyvyNo ratings yet
- Education Department: Facilitating Learner-Centered TeachingDocument4 pagesEducation Department: Facilitating Learner-Centered TeachingChristopher Ian BuruangaNo ratings yet
- Learning Ok - Done (English)Document8 pagesLearning Ok - Done (English)Aileen TaniaNo ratings yet
- Information ProcessingDocument4 pagesInformation ProcessingJeanelle Marie Ramos50% (2)
- UTS Lesson 1 BETTER STUDENTDocument45 pagesUTS Lesson 1 BETTER STUDENTAguirre, John CastorNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior: Chapter 4, SolomonDocument20 pagesConsumer Behavior: Chapter 4, SolomonNigar GaziyevaNo ratings yet
- Complex cognitive processes explainedDocument9 pagesComplex cognitive processes explainedAhmad ShahNo ratings yet
- Theories of Learning and Learning MetaphorsDocument4 pagesTheories of Learning and Learning MetaphorsTrisha Mei Nagal50% (2)
- Psychological Foundation of CurriculumDocument34 pagesPsychological Foundation of CurriculumAlgen Jewel BalbinNo ratings yet
- Theories of Motor LearningDocument58 pagesTheories of Motor LearningIndira Naidu Boddapati60% (5)
- Information Processing TheoryDocument6 pagesInformation Processing TheoryHsu Sandi AungNo ratings yet
- Let Principles of Teaching-NotesDocument13 pagesLet Principles of Teaching-NotesTiffany Moore100% (1)
- Learning and Memomy in Biological PerspectiveDocument13 pagesLearning and Memomy in Biological PerspectiveTim AroscoNo ratings yet
- 11.learning and MemoryDocument19 pages11.learning and Memorykholoud220No ratings yet
- Information Processing TheoryDocument43 pagesInformation Processing TheoryALISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Information Processing TheoryDocument21 pagesInformation Processing TheoryJhon Dave Nemenzo Bayon-on100% (2)
- Memory and ForgettingDocument20 pagesMemory and ForgettingHammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- MEMORY - Key processes and modelsDocument9 pagesMEMORY - Key processes and modelsjxstynzNo ratings yet
- EDPSY - L2 - Cognitive Views of LearningDocument3 pagesEDPSY - L2 - Cognitive Views of LearningJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- AQA Psychology MRN GlossaryDocument12 pagesAQA Psychology MRN GlossaryKaren FernandesNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed 5 - Ralph Jeano Murillo - Iii Bped BDocument35 pagesProf. Ed 5 - Ralph Jeano Murillo - Iii Bped BRalph jeano murilloNo ratings yet
- Ate ShyraDocument14 pagesAte ShyraSHYRA MAE DOBLONNo ratings yet
- MolinaDocument34 pagesMolinaMelody Latayada HiocoNo ratings yet
- Reflexes, and All Emotion and Thoughts Are A: Information Processing-Explain The Ways TheDocument5 pagesReflexes, and All Emotion and Thoughts Are A: Information Processing-Explain The Ways TheEgil SantosNo ratings yet
- Types, Stages and Processes of MemoryDocument25 pagesTypes, Stages and Processes of MemoryAyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Memory and Forgetting: Learning OutcomesDocument34 pagesChapter Four Memory and Forgetting: Learning OutcomesNigussie Berhanu100% (1)
- Psychology ReviewDocument7 pagesPsychology ReviewGiangNo ratings yet
- Module 10 Information ProcessingDocument6 pagesModule 10 Information ProcessingRacky BalboaNo ratings yet
- Learning ProcessDocument10 pagesLearning ProcessRicardo ChungNo ratings yet
- Module 10Document16 pagesModule 10Starlight Melody FloresNo ratings yet
- Consumer Perception and Learning: By:-Ghanshyam Mishra Juhi Sethi Kanika Bhasin. Manisha Chaudhary Vinod BhatiDocument47 pagesConsumer Perception and Learning: By:-Ghanshyam Mishra Juhi Sethi Kanika Bhasin. Manisha Chaudhary Vinod BhatiManisha ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document4 pagesModule 4Hanz PeñamanteNo ratings yet
- Chapter+8 Memory+and+thinkingDocument3 pagesChapter+8 Memory+and+thinkingBUENA VISTANo ratings yet
- Group Influences On Consumer BehaviorDocument2 pagesGroup Influences On Consumer BehaviorArabelle BulanonNo ratings yet
- Family and HouseholdDocument2 pagesFamily and HouseholdArabelle BulanonNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviorDocument3 pagesConsumer BehaviorArabelle BulanonNo ratings yet
- Interactions of Science and Technology and Nation BuildingDocument2 pagesInteractions of Science and Technology and Nation BuildingArabelle BulanonNo ratings yet
- Philippine Science and Technology HistoryDocument3 pagesPhilippine Science and Technology HistoryArabelle BulanonNo ratings yet
- Intercultural CommunicationDocument17 pagesIntercultural Communicationleana leanaNo ratings yet
- Wise Consumer RightsDocument5 pagesWise Consumer RightsbryanNo ratings yet
- Overview of Business CommunicationDocument189 pagesOverview of Business CommunicationRahul BirabaraNo ratings yet
- Gita in EssenceDocument15 pagesGita in EssenceBhanoji Rao, VadlamaniNo ratings yet
- Awakened IndiaDocument18 pagesAwakened IndiaRaghuram SatishNo ratings yet
- Supporting DetailsDocument30 pagesSupporting DetailsMIRZA HUDA ATHIRAH MOKHTARNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy of The Human Person Day 1Document54 pagesIntroduction To Philosophy of The Human Person Day 1John Caezar Yatar100% (2)
- Nature Versus NurtureDocument6 pagesNature Versus NurtureJoshNo ratings yet
- Research Atl Continuum Pyp 1Document6 pagesResearch Atl Continuum Pyp 1Mrs. J. Joel-IbehNo ratings yet
- RESEARCHANDPUBLICATIONETHSantosh Kumar YadavDocument21 pagesRESEARCHANDPUBLICATIONETHSantosh Kumar YadavVijay Singh Kumar VijayNo ratings yet
- Mediareview Education After Art: A Review of Letting Art Teach: Art Education After Joseph BeuysDocument5 pagesMediareview Education After Art: A Review of Letting Art Teach: Art Education After Joseph BeuyskathrynNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1: Inquiry-Based Learning ExplainedDocument1 pagePractical Research 1: Inquiry-Based Learning ExplainedPT MangilaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Presentors Media and Digital LiteracyDocument28 pagesGroup 1 Presentors Media and Digital LiteracyJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Chap 5: Perception and Individual Decision Making: Chapter ReviewDocument6 pagesChap 5: Perception and Individual Decision Making: Chapter ReviewKim TiênNo ratings yet
- The Power of Options: Always Give Yourself Four Ways To WinDocument9 pagesThe Power of Options: Always Give Yourself Four Ways To WinSamarth KharbandaNo ratings yet
- RWS ReviewerDocument7 pagesRWS ReviewerAirene JabagatNo ratings yet
- Future of PettlepDocument5 pagesFuture of PettlepLoweNo ratings yet
- Uc3-Solveaddress General Workplace ProblemsDocument30 pagesUc3-Solveaddress General Workplace ProblemsErethro CytesNo ratings yet
- Cosmotheandric Vision of Raimond PanikkarDocument42 pagesCosmotheandric Vision of Raimond PanikkarAnto ParekkadanNo ratings yet
- Haddock & Maio 2017Document3 pagesHaddock & Maio 2017Diego ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- 22-Steps For Building ResilienceDocument2 pages22-Steps For Building ResilienceUmer ArshadNo ratings yet
- Directing essentialsDocument15 pagesDirecting essentialsLeela JainNo ratings yet
- MSD PPT - EMOTIONSDocument21 pagesMSD PPT - EMOTIONSBHANUNo ratings yet
- The Significance of Death in The Existence of The Human PerwsonDocument11 pagesThe Significance of Death in The Existence of The Human PerwsonCherry Mae DagaasNo ratings yet
- Elements of CommunicationDocument3 pagesElements of CommunicationNovelyn GanelaNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Research PaperDocument5 pagesHow To Write A Research PaperCha Tangan-Penol100% (1)
- Review of Related Literature (RRL)Document17 pagesReview of Related Literature (RRL)Jay Miraflores50% (2)
- Time Mangement NikinDocument35 pagesTime Mangement NikinShweta MadhuNo ratings yet
- Living Life to the FullestDocument4 pagesLiving Life to the FullestAlyanna SalongaNo ratings yet
- 3 Helth Nursing Informatics Technology - 020222Document5 pages3 Helth Nursing Informatics Technology - 020222Akshata Bansode100% (1)