Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Nine Types of Intelligence
Uploaded by
Anuradha ItwaruOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Nine Types of Intelligence
Uploaded by
Anuradha ItwaruCopyright:
Available Formats
The Nine Types of Intelligence
By =oward Gardner
1. Naturalist intelligence (“Nature Smart”)
Designates the human ability to discriminate among living things (plants, animals) as well as
sensitivity to other features of the natural world (clouds, rock configurations). This ability was
clearly of value in our evolutionary past as hunters, gatherers, and farmers; it continues to be
central in such roles as botanist or chef. It is also speculated that much of our consumer society
exploits =he naturalist intelligences, which can be mobilized in the discrimination among cars,
sneakers, kinds of makeup, and the like.
2. Musical intelligence (“Musical Smart”)
Musical intelligence is the capacity to discern pitch, rhythm, timbre, and tone. This intelligence
enables us =o recognize, create, reproduce, and reflect on music, as demonstrated by composers,
conductors, musicians, vocalist, and sensitive listeners. Interestingly, there is often =n affective
connection between music and the emotions; and mathematical and musical intelligences may
share common thinking processes. Young adults with this kind of =intelligence are usually
singing or drumming to themselves. They are usually quite aware =f sounds others may miss.
3. logical-Mathematical Intelligence (Number/Reasoning Smart)
Logical-mathematical intelligence is the ability =o calculate, quantify, consider propositions and
hypotheses, and carry out =complete mathematical operations. It enables us to perceive
relationships and connections and to =se abstract, symbolic thought; sequential reasoning skills;
and inductive and deductive thinking patterns. Logical intelligence is usually well developed in
mathematicians, =scientists, and detectives. =/SPAN>Young adults with lots of logical
intelligence are interested in patterns, categories, and relationships. They =re drawn to
arithmetic problems, strategy games and experiments.
4. Existential Intelligence
Sensitivity and capacity to tackle deep questions about human existence, such as the meaning of
life, why do we die, and how did we get here.
5. Interpersonal Intelligence (People Smart”)
Interpersonal intelligence is the ability to understand and interact effectively with others. It
involves effective verbal and nonverbal communication, the ability to note distinctions among
others, sensitivity to the moods and temperaments of others, and the ability to entertain multiple
perspectives. =Teachers, social workers, actors, and politicians all exhibit interpersonal
intelligence. Young adults with this kind of intelligence are leaders among =heir peers, are good
at communicating, and seem to understand others’ feelings and motives.
6. =bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence (“Body Smart”)
Bodily kinesthetic =intelligence is the capacity to manipulate objects and use a variety of
=physical skills. This intelligence also involves a sense of timing and the perfection of skills
through mind–body union. Athletes, dancers, =burgeons, and craftspeople exhibit well-
developed bodily kinesthetic intelligence.
7. Linguistic intelligence (Word Smart)
Linguistic intelligence is the ability to think in words and to use language to express and
=appreciate complex meanings. =/SPAN>Linguistic intelligence allows us to understand the
order and meaning of words and =o apply meta-linguistic skills to reflect on our use of language.
Linguistic intelligence is the most widely shared human competence and is evident in poets,
novelists, =journalists, and effective public speakers. Young adults with this kind of intelligence
enjoy writing, =eading, telling stories or doing crossword puzzles.
8. Intra-personal Intelligence (Self Smart”)
Intra-personal =intelligence is the capacity to understand oneself and one’s thoughts and
feelings, =and to use such knowledge in planning and directioning one’s life. Intra-personal
intelligence involves not only an appreciation of the self, but also of the human condition. It is
evident =n psychologist, spiritual leaders, and philosophers. These young adults may be =hy.
They are very aware of their =own feelings and are self-motivated.
9. Spatial intelligence (“Picture Smart”)
Spatial intelligence is the ability to think in three dimensions. Core capacities include mental
imagery, spatial reasoning, image manipulation, graphic and artistic skills, and an active
imagination. Sailors, pilots, sculptors, painters, and architects all exhibit spatial intelligence.
Young adults with this kind of intelligence may be fascinated with mazes or jigsaw puzzles, or
spend =ree time drawing or daydreaming.
From: Overview of the Multiple Intelligences =heory. Association for Supervision =nd Curriculum Development and Thomas Armstrong.com
You might also like
- Melody Dee: We Are All Great in Our Own Way (Somos Todos Grandiosos En Nuestra Propia Forma)From EverandMelody Dee: We Are All Great in Our Own Way (Somos Todos Grandiosos En Nuestra Propia Forma)No ratings yet
- The Nine Types of IntelligenceDocument2 pagesThe Nine Types of IntelligenceShawn MarkNo ratings yet
- 9 Types of IntelligenceDocument3 pages9 Types of Intelligencesaikumar selaNo ratings yet
- Multiple IntelligenceDocument14 pagesMultiple IntelligenceBeverly Joy BragaisNo ratings yet
- 9 Types of IntelligenceDocument6 pages9 Types of IntelligenceAnonymous DpycJHANo ratings yet
- 9 Types of Intelligence - InfographicDocument3 pages9 Types of Intelligence - Infographicjane arlyn onalNo ratings yet
- The 9 Types of IntelligenceDocument2 pagesThe 9 Types of IntelligenceGre ChieNo ratings yet
- Essay PsikologiDocument4 pagesEssay PsikologiFique FhieqaNo ratings yet
- Language - P1 3triDocument2 pagesLanguage - P1 3triMarcella MagaldiNo ratings yet
- Multiple Intelligence Theory PDFDocument2 pagesMultiple Intelligence Theory PDFChiranjibi Behera ChiruNo ratings yet
- Multiple Intelligence TheoryDocument2 pagesMultiple Intelligence TheoryChiranjibi Behera ChiruNo ratings yet
- Intelligence Howard GardnerDocument12 pagesIntelligence Howard GardnerMarouane EzzaimNo ratings yet
- Linguistic IntelligenceDocument2 pagesLinguistic Intelligenceapi-213030167No ratings yet
- Intellectual Aspect of PersonalityDocument19 pagesIntellectual Aspect of PersonalityKates Morfe Caperina0% (2)
- Multiple Intelligence Power PointDocument14 pagesMultiple Intelligence Power PointJahzel JacaNo ratings yet
- THEORY OF MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCESpptDocument30 pagesTHEORY OF MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCESpptZenda Marie Facinal SabinayNo ratings yet
- Howard Gardner's Multiple Intelligences IntelligenceDocument8 pagesHoward Gardner's Multiple Intelligences IntelligenceAryan DimryNo ratings yet
- Read and Translate The Text About The: Theory of Multiple IntelligenceDocument1 pageRead and Translate The Text About The: Theory of Multiple IntelligenceArtics649No ratings yet
- Definition and Characteristic of IntelligentDocument18 pagesDefinition and Characteristic of Intelligentroel pugataNo ratings yet
- Armstrong Multiple Intelligences Ch1Document4 pagesArmstrong Multiple Intelligences Ch1Jose AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Howard Gardner's Theory of Multiple IntelligencesDocument4 pagesHoward Gardner's Theory of Multiple IntelligencesGina ContilloNo ratings yet
- Multiple Intelligences - Ged101Document6 pagesMultiple Intelligences - Ged101Seth Jarl G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- 8Document2 pages8Jazel Heart EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Multiple intelligences theory explainedDocument6 pagesMultiple intelligences theory explainedYuranys Paola Martinez DiazNo ratings yet
- Intelligence & Multiple IntelligencesDocument4 pagesIntelligence & Multiple IntelligencescrixcrossNo ratings yet
- The Nine Different Types of IntelligenceDocument3 pagesThe Nine Different Types of IntelligenceMarouane EzzaimNo ratings yet
- Child and Ado Pre-Final ActivityDocument3 pagesChild and Ado Pre-Final ActivityShane Marie VenancioNo ratings yet
- Intelligence: Premala.GDocument10 pagesIntelligence: Premala.GPrasadNo ratings yet
- The Idea of Multiple IntelligencesDocument2 pagesThe Idea of Multiple IntelligencesSiti AisyahNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking IntelligenceDocument5 pagesCritical Thinking IntelligencelourdNo ratings yet
- IntelligenceDocument11 pagesIntelligenceUTTARA NAIRNo ratings yet
- MI Theory and ELT ApproachesDocument7 pagesMI Theory and ELT ApproachesCaesar Franz RuizNo ratings yet
- Multiple Intelligences HandoutDocument2 pagesMultiple Intelligences HandoutJermaine BatallerNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCE g6Document6 pagesMULTIPLE INTELLIGENCE g6ZainNo ratings yet
- Sabadal 1Document5 pagesSabadal 1Fatima MacaalayNo ratings yet
- Multiple Intelligence TestDocument4 pagesMultiple Intelligence TestThe BellosNo ratings yet
- IntelligenceDocument20 pagesIntelligenceKaren MaddelaNo ratings yet
- Human Potential: DefinitionDocument15 pagesHuman Potential: DefinitionMaria MandezNo ratings yet
- Group 2: Intelligence Unite EightDocument19 pagesGroup 2: Intelligence Unite EightDaahir SahalNo ratings yet
- Howard Gardner by Cuyugan, Ma. Lourdes Word FileDocument6 pagesHoward Gardner by Cuyugan, Ma. Lourdes Word FilemalouNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Howard Gardner-SDocument12 pagesWeek 3 Howard Gardner-SNur HassanNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12th: CH 1 Variations in Psychological AttributesDocument7 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12th: CH 1 Variations in Psychological Attributessuhani DagarNo ratings yet
- Gardner's Multiple Intelligences PDFDocument12 pagesGardner's Multiple Intelligences PDFBeatriz García MayordomoNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument5 pagesClassificationMaria Tena TapayanNo ratings yet
- Multiple Intelligenc E: (Gardner's)Document21 pagesMultiple Intelligenc E: (Gardner's)Nisolada, Johselle Mariane E.No ratings yet
- 12 Psychology 17.7.2020Document3 pages12 Psychology 17.7.2020BerryNo ratings yet
- Modern Theories of Intelligence: Multiple Intelligence TheoryDocument3 pagesModern Theories of Intelligence: Multiple Intelligence TheoryBerryNo ratings yet
- Multiple Inteligence Theory of Gardner: +2 Psychology Notes Modern Theories of InelligenceDocument3 pagesMultiple Inteligence Theory of Gardner: +2 Psychology Notes Modern Theories of InelligenceBerryNo ratings yet
- Multiple Inteligence Theory of Gardner: +2 Psychology Notes Modern Theories of InelligenceDocument3 pagesMultiple Inteligence Theory of Gardner: +2 Psychology Notes Modern Theories of InelligenceBerryNo ratings yet
- PDAE Lesson 5Document16 pagesPDAE Lesson 5France MendozaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Chapter 1 - The LearnerDocument15 pagesUnit 1 - Chapter 1 - The LearnerGerald RamiloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-AnswersDocument11 pagesChapter 1-Answersdeepika singhNo ratings yet
- 8 Intelligences Description SheetDocument2 pages8 Intelligences Description SheetSilence checkmateNo ratings yet
- 8 Multiple Intelligence: People With Linguistic Intelligence Love and AreDocument2 pages8 Multiple Intelligence: People With Linguistic Intelligence Love and AreEN JennylouNo ratings yet
- 8 Multiple Intelligence of HOWARD GARDNERDocument3 pages8 Multiple Intelligence of HOWARD GARDNERAlona BaylonNo ratings yet
- Howard Gardner's Theory of Multiple IntelligencesDocument12 pagesHoward Gardner's Theory of Multiple Intelligencescentonian websiteNo ratings yet
- Theory of Multiple Intelligences and WhyDocument7 pagesTheory of Multiple Intelligences and WhyEveNo ratings yet
- Multiple Intelligences Classroom PDFDocument6 pagesMultiple Intelligences Classroom PDFClaudia Albuccó AriztíaNo ratings yet
- Fostering Students Academic Performance in Physic PDFDocument16 pagesFostering Students Academic Performance in Physic PDFAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- AP EFN 4302 Week 3 Research Proposal Pilot StudyDocument38 pagesAP EFN 4302 Week 3 Research Proposal Pilot StudyAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- AP EFN 4302 Week 1 Plagiarism APA Style 7th Edition WorkshopDocument63 pagesAP EFN 4302 Week 1 Plagiarism APA Style 7th Edition WorkshopAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Kirchhoffs LawsDocument4 pagesLab 4 - Kirchhoffs LawsAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- AP EFN 4302 Week 2 Research Its ElementsDocument45 pagesAP EFN 4302 Week 2 Research Its ElementsAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Importance of Pedagogical Content Knowledge in Science EducationDocument3 pagesImportance of Pedagogical Content Knowledge in Science EducationAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Analysing Your Sources (Format)Document1 pageAnalysing Your Sources (Format)Anuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Balanced DietDocument1 pageBalanced DietAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - Test TwoDocument3 pagesGrade 10 - Test TwoAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Phy1204 Atoms PresentationDocument6 pagesPhy1204 Atoms PresentationAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 End of Term AssessmentDocument5 pagesGrade 9 End of Term AssessmentAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Importance of Electrical Measurements & CircuitsDocument2 pagesImportance of Electrical Measurements & CircuitsAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Real GasDocument8 pagesReal GasAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Education Secondary Engagement Programme Grade 10 PhysicsDocument4 pagesMinistry of Education Secondary Engagement Programme Grade 10 PhysicsAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- 2012 Advanced Instructional Systems, Inc. and North Carolina State UniversityDocument5 pages2012 Advanced Instructional Systems, Inc. and North Carolina State UniversityAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
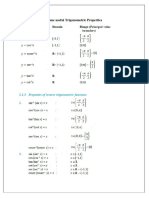
- Some Useful Trigonometric PropertiesDocument3 pagesSome Useful Trigonometric PropertiesAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Cycleof ViolencestagesDocument3 pagesCycleof ViolencestagesAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- 11 Methods For Improving Your MemoryDocument5 pages11 Methods For Improving Your MemorySon PalNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Memory ImprovementDocument2 pagesTop 10 Memory ImprovementAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- The Ear Parts and FunctionsDocument2 pagesThe Ear Parts and FunctionsAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Constructivism As A Paradigm For Teaching and LearningDocument13 pagesConstructivism As A Paradigm For Teaching and LearningAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Process Skills N MemoryDocument2 pagesProcess Skills N MemoryAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Trends IN SCIENCEDocument12 pagesTrends IN SCIENCEAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Cognition N MetacognitionDocument7 pagesCognition N MetacognitionAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Facts Concepts and GeneralisationsDocument2 pagesFacts Concepts and GeneralisationsAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- EDC2101 Teacher Leadership in The ClassroomDocument7 pagesEDC2101 Teacher Leadership in The ClassroomAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- MetacognitionDocument2 pagesMetacognitionAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- Counselling TechniquesDocument91 pagesCounselling TechniquesPranay PandeyNo ratings yet
- The Counselor As A ConsultantDocument30 pagesThe Counselor As A ConsultantAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- A319/A320/A321 Technical Training Manual Mechanics / Electrics & Avionics Course 33 LightsDocument224 pagesA319/A320/A321 Technical Training Manual Mechanics / Electrics & Avionics Course 33 LightsAhmedHamdyElsaidy100% (3)
- BS 01726-2-2002Document18 pagesBS 01726-2-2002Joana Casta100% (1)
- 2.e-Learning Chapter 910Document23 pages2.e-Learning Chapter 910ethandanfordNo ratings yet
- "Network Security": Alagappa UniversityDocument1 page"Network Security": Alagappa UniversityPRADEEPRAJANo ratings yet
- Year 7 Bugs Lesson 2Document1 pageYear 7 Bugs Lesson 2api-293503824No ratings yet
- Automation & Artificial Intelligence: Robots and Their ApplicationsDocument93 pagesAutomation & Artificial Intelligence: Robots and Their ApplicationsManal AndhereNo ratings yet
- Floor CraneDocument6 pagesFloor CranejillianixNo ratings yet
- Latest Information Technology Trends 2023Document5 pagesLatest Information Technology Trends 2023Salveigh C. TacleonNo ratings yet
- Media KitDocument22 pagesMedia KitEmilyNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour of Titan WatchesDocument57 pagesConsumer Behaviour of Titan Watchesmanu100% (1)
- Brake CMMDocument262 pagesBrake CMMvishalsachanameNo ratings yet
- JSMSC - TDv3 6 20Document251 pagesJSMSC - TDv3 6 20Jason20170% (1)
- Sample Id: Sample Id: 6284347 Icmr Specimen Referral Form Icmr Specimen Referral Form For For Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2) Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2)Document2 pagesSample Id: Sample Id: 6284347 Icmr Specimen Referral Form Icmr Specimen Referral Form For For Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2) Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2)Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL REPORTSDocument34 pagesFINANCIAL REPORTSToni111123No ratings yet
- NView NNM (V5) Operation Guide PDFDocument436 pagesNView NNM (V5) Operation Guide PDFAgoez100% (1)
- 2020-Effect of Biopolymers On Permeability of Sand-Bentonite MixturesDocument10 pages2020-Effect of Biopolymers On Permeability of Sand-Bentonite MixturesSaswati DattaNo ratings yet
- Business English 2, (ML, PI, U6, C3)Document2 pagesBusiness English 2, (ML, PI, U6, C3)Ben RhysNo ratings yet
- SAP HCM - Default Wage Types - Info Type 0008Document6 pagesSAP HCM - Default Wage Types - Info Type 0008cjherrera2No ratings yet
- Kak MhamadDocument1 pageKak MhamadAyub Anwar M-SalihNo ratings yet
- ANNEXURE IV Dec 2022 enDocument17 pagesANNEXURE IV Dec 2022 enadvocacyindyaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Improvement Strategies in TQMDocument28 pagesContinuous Improvement Strategies in TQMSimantoPreeomNo ratings yet
- To Quantitative Analysis: To Accompany by Render, Stair, Hanna and Hale Power Point Slides Created by Jeff HeylDocument94 pagesTo Quantitative Analysis: To Accompany by Render, Stair, Hanna and Hale Power Point Slides Created by Jeff HeylNino NatradzeNo ratings yet
- Teams Training GuideDocument12 pagesTeams Training GuideImran HasanNo ratings yet
- SAC SINGLAS Accreditation Schedule 15 Apr 10Document5 pagesSAC SINGLAS Accreditation Schedule 15 Apr 10clintjtuckerNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Internship ReportDocument69 pagesBajaj Internship ReportCoordinator ABS100% (2)
- Cloud Computing For Industrial Automation Systems - A ComprehensiveDocument4 pagesCloud Computing For Industrial Automation Systems - A ComprehensiveJason FloydNo ratings yet
- Biokimia - DR - Maehan Hardjo M.biomed PHDDocument159 pagesBiokimia - DR - Maehan Hardjo M.biomed PHDHerryNo ratings yet
- Anubis - Analysis ReportDocument17 pagesAnubis - Analysis ReportÁngelGarcíaJiménezNo ratings yet
- Key Differences Between Natural Sciences and Social SciencesDocument6 pagesKey Differences Between Natural Sciences and Social SciencesAshenPerera60% (5)
- P150EDocument4 pagesP150EMauro L. KieferNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveFrom EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNo ratings yet
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Make Money with ChatGPT: Your Guide to Making Passive Income Online with Ease using AI: AI Wealth MasteryFrom EverandMake Money with ChatGPT: Your Guide to Making Passive Income Online with Ease using AI: AI Wealth MasteryNo ratings yet
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldFrom EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessFrom EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessNo ratings yet
- The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldFrom EverandThe Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (107)
- Who's Afraid of AI?: Fear and Promise in the Age of Thinking MachinesFrom EverandWho's Afraid of AI?: Fear and Promise in the Age of Thinking MachinesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- AI and Machine Learning for Coders: A Programmer's Guide to Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandAI and Machine Learning for Coders: A Programmer's Guide to Artificial IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (104)
- Mastering Large Language Models: Advanced techniques, applications, cutting-edge methods, and top LLMs (English Edition)From EverandMastering Large Language Models: Advanced techniques, applications, cutting-edge methods, and top LLMs (English Edition)No ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking HumansFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking HumansRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- Midjourney Mastery - The Ultimate Handbook of PromptsFrom EverandMidjourney Mastery - The Ultimate Handbook of PromptsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 2084: Artificial Intelligence and the Future of HumanityFrom Everand2084: Artificial Intelligence and the Future of HumanityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (81)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.From EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (15)
- AI Money Machine: Unlock the Secrets to Making Money Online with AIFrom EverandAI Money Machine: Unlock the Secrets to Making Money Online with AINo ratings yet
- 100+ Amazing AI Image Prompts: Expertly Crafted Midjourney AI Art Generation ExamplesFrom Everand100+ Amazing AI Image Prompts: Expertly Crafted Midjourney AI Art Generation ExamplesNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence & Generative AI for Beginners: The Complete GuideFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence & Generative AI for Beginners: The Complete GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Make Money Online Using ChatGPT Prompts: Secrets Revealed for Unlocking Hidden Opportunities. Earn Full-Time Income Using ChatGPT with the Untold Potential of Conversational AI.From EverandHow to Make Money Online Using ChatGPT Prompts: Secrets Revealed for Unlocking Hidden Opportunities. Earn Full-Time Income Using ChatGPT with the Untold Potential of Conversational AI.No ratings yet
- The AI Advantage: How to Put the Artificial Intelligence Revolution to WorkFrom EverandThe AI Advantage: How to Put the Artificial Intelligence Revolution to WorkRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- Power and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandPower and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (38)