Professional Documents
Culture Documents
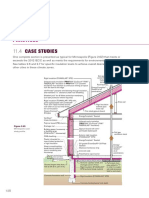
Roofing and Protection Building Tech Notes
Uploaded by
corazon phil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views5 pagesComprehensive review notes for ALE Exam, January 2023
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentComprehensive review notes for ALE Exam, January 2023
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views5 pagesRoofing and Protection Building Tech Notes
Uploaded by
corazon philComprehensive review notes for ALE Exam, January 2023
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Module 6: Radiant barrier
Roofing and Protection Surface color
Lighter – less absorption of heat
BUILDING ENVELOPE Darker – more absorption
Separate the interior from the exterior
Exterior environment
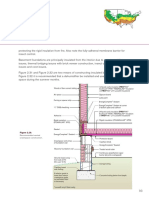
INSULATING MATERIALS:
Heat and cold (thermal), air and water
vapor, liquid water, noise, dust and insects Rigid insulation – flat roof
Impacts the design the most: Flexible insulation – stud walls and attic spaces
Air, vapor, and water Loose-fill insulation – useful when there’s a
container
Interrelated because the flow of air/vapor
through the envelope impact the building Foamed-in-place
thermally, all vapor and water Reflective
Building design and Thermal Comfort
Transfer of Heat: MOISTURE PROTECTION
Conduction, convection, radiation Aluminum foil
During the process of heat transfer Polyethylene sheet/vapor retarder
through a building envelope, all Asphalt
three modes usually come into play Sample:
EPS Beads (not water resistant)
EPS Bun
EPS Board (like Styrofoam board)
Insulating Concrete Forms
XPS Boards
ISO Boards – waterproof
LIMITS OF PLASTIC BOARDS
Sensitive to daylight
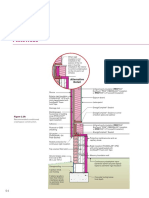
R-VALUE OF A BUILDING COMPONENT
Can be destroyed when used below ground in
R is the thermal resistance heaving termite soils
Measure of the ability of a component to Examples
resist the flow of heat through it
Polyurethane
Raw R Value = 1”
Polyisocyanurate
Rate of heat conduction
Polystyrene
P x Thickness = R
Example:
Formed Concrete
Fiberglass – 3.5 x 3.0 = 11
Cellular concrete
XPS 5.0 x .5” = 2.5 = 3
Low Density:
BASIC ROOF SHAPES
Air
Flat Roof
Polystyrene
Shed/Single Pitch Roof
Density dictates how good a material is
Cable Roof
Hip roof
SURFACE EMISSIVITY: Gamble Roof
The importance of foil: Mansard Roof
Lined foil emits less radiation Pavilion
Unlined foil emits more radiation Butterfly
Reflective insulation
Insulation won’t work without air space
ROOF CONSIDERATIONS DECKING
Load concentrations Cold Deck
Dead load Membrane, deck, insulation
Live Load Warm Deck
Wind Loads Membrane, insulation, deck
Type of roofing Inverted (Protected membrane roof)
Membrane Insulation, membrane, deck
Sheet – any sloped roof
Shingle – piece by piece installation TYPES OF ROOFING
Drainage Membrane – for low-slope (flat) roof
Gutter Sheet – any slope
Drains Shingle – for steep roof
Downspouts
Protection Against:
STRUCTURE TYPES
Water
Joists and sheathing
Moisture
Beams and decking
Air
Flat trusses
Heat
Concrete slabs
Flashing
Measurement
Seal connection of water
Membrane – resist water
Ridge, Hips,Valleys
Eaves, Rakes, Parapets
Openings WATERPROOFING
Interior Effects Sides
Exterior effects Positive Side - waterproofing placed on
outside wall
Negative Side – waterproofing is placed
FLAT ROOF
after wall inside
Minimum slope – ¼” to 12” ( or 2%)
Blind Side – waterproofing placed in
How to create slope between wall/wall opening
Slope the structure Integral
Taper the topping Brand: Sahara (waterproofing material)
Draining Flat Roofs Cementitious
Interior drains Thoroseal
Scuppers Plexyboard
Overflow Drains Flexible
Uses of Flat roofs Aquashield
Covering the building Capillary/Crystalline
Outdoor space Tenex
Structure Types Also called integral waterproofing
Joists and sheathing Goes into pores and seals
Beams and decking Fluid-Applied
Flat trusses Elastomeric analok
Concrete slabs Coating application
Requirement Bentonite
Continuous membrane Can pass as cementitious
Slopes When exposed to water, it smells
Low Slope – less than 3:12
Steep Roof – more than or equal to 3:12
ROOF MEMBRANES
Waterproofing layer Metal Pans
3-5 floors – built up roof membranes (BUR) Slate
2-3 floors – modified bitumen roof membrane Nipa/Anahan/Cogon – thatch roofing
1-2 floors - single ply roof membrane
Other Notes:
BUILT-UP ROOF MEMBRANE Ceiling Joist – is to counter the force of the
roof
Asphalt – given waterproofing
Structural and Non-structural
Felt Roll – reinforcing material
Ridge Board – a structural member
Bitumen
Ridge Beam – non-structural member
Eave and Rake – structural member
Fiberglass Felt – untreated
Dormer – opening in the roof
Asphalt saturated felt
Valley- also known as rally rafter
Ballast – built-u roof surfacing
Hip – also known as hip rafter
PMR System
Castellated Beam
Installing Insulation – rigid insulating
Soffit – outside ceiling or underside of roof
materials
Purlin – for sheet roofing
Cellulose fiber board
Rafter – shingle roofing
Perlitic Board
Cellular glass board
Roof Square – 108 square feet is referred to as
Mineral Fiber board
factory square and 100 square feet is a roof
square
MODIFIED BITUMEN ROOF MEMBRANE
Styrene Butadiene Styrene (SBS) – Cold
Weight of Aggregate surfacing – 400 lb per
Weather
roof square of 4 lb/ft2
Attactic Polypropylene (APP) – Hot Weather
SINGLE PLY ROOF MEMBRANE
EPDM – Thermosetting
PVC – Thermoplastic
TPO – Thermoplastic
Polyolefin
Advantages
EPDM Membrane
PVC Membrane – fire-
resistant
TPO – flexible, affordable
SHINGLE ROOFING
Asphalt Shingle
Wood Shingle / Wood Shakes
Installed piece by piece
Roof tiles
You might also like
- The Modern Bricklayer - A Practical Work on Bricklaying in all its Branches - Volume III: With Special Selections on Tiling and Slating, Specifications Estimating, EtcFrom EverandThe Modern Bricklayer - A Practical Work on Bricklaying in all its Branches - Volume III: With Special Selections on Tiling and Slating, Specifications Estimating, EtcRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Residential Guide 部分134Document1 pageResidential Guide 部分134xinghaijunNo ratings yet
- Thermal and Moisture ProtectionDocument64 pagesThermal and Moisture ProtectionPat BautistaNo ratings yet
- Building Services Building Tech NotesDocument5 pagesBuilding Services Building Tech Notescorazon philNo ratings yet
- Types of Roofs and Roof Structures ExplainedDocument59 pagesTypes of Roofs and Roof Structures ExplainedSai Ashrith MoturiNo ratings yet
- Residential Guide 部分119Document1 pageResidential Guide 部分119xinghaijunNo ratings yet
- Recommended Vented Crawlspace Construction.: Rigid Insulation (FOAMULAR XPS)Document1 pageRecommended Vented Crawlspace Construction.: Rigid Insulation (FOAMULAR XPS)xinghaijunNo ratings yet
- Thermal Insulation: Akanksha Bhakare Sy. B.VocDocument14 pagesThermal Insulation: Akanksha Bhakare Sy. B.VocAkanksha BhakareNo ratings yet
- XPS and Foam BoardDocument6 pagesXPS and Foam BoarddantranzNo ratings yet
- Structural Insulated Panels ExplainedDocument17 pagesStructural Insulated Panels Explainedhtet waiNo ratings yet
- Flat Roof - WikipediaDocument6 pagesFlat Roof - WikipediaIeeeChannaNo ratings yet
- Casa de Madeira Technical-GuideDocument16 pagesCasa de Madeira Technical-GuideJoaquim ArezNo ratings yet
- Nivee Roof Covering PDFDocument12 pagesNivee Roof Covering PDFKalyan RamavathNo ratings yet
- BUILDING TECHNOLOGY Reviewer 01Document17 pagesBUILDING TECHNOLOGY Reviewer 01Camille L. FaustoNo ratings yet
- 09 Ventilated FaçadesDocument29 pages09 Ventilated Façadespedrin32No ratings yet
- BSMT Water Prfing Old VandanaDocument25 pagesBSMT Water Prfing Old Vandanaguruvandana1924No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Roof - 2023Document35 pagesLecture 5 - Roof - 2023Chan LokNo ratings yet
- Residential Guide 部分120Document1 pageResidential Guide 部分120xinghaijunNo ratings yet
- PASSIVE DESIGN - CL - PresentationDocument12 pagesPASSIVE DESIGN - CL - Presentationcyssa2202No ratings yet
- Injection Molding Design GuidelinesDocument4 pagesInjection Molding Design GuidelinesAaselNo ratings yet
- iNJECTION mOLDING5-5Document5 pagesiNJECTION mOLDING5-5AaselNo ratings yet
- RoofDocument55 pagesRoofRosele LabarreteNo ratings yet
- Residential Guide 部分100Document1 pageResidential Guide 部分100xinghaijunNo ratings yet
- BUILDING-TECHNOLOGY-REVIEWER-B5Document8 pagesBUILDING-TECHNOLOGY-REVIEWER-B5DANIEL NOBISNo ratings yet
- THERMALDocument75 pagesTHERMALJuvilasri VigneshNo ratings yet
- INT - Water Proofing SolutionsDocument7 pagesINT - Water Proofing SolutionsMrinal RoyNo ratings yet
- Basement Waterproofing - Lecture 1Document41 pagesBasement Waterproofing - Lecture 1Taanaya100% (1)
- Perlite Concrete IndiaDocument8 pagesPerlite Concrete IndianandanaNo ratings yet
- Insulation Glossary: by The National Mechanical Insulation Committee (NMIC)Document20 pagesInsulation Glossary: by The National Mechanical Insulation Committee (NMIC)acetopposNo ratings yet
- Exterior FinishesDocument4 pagesExterior FinishesCatherineTiongNo ratings yet
- EIFS Wall Construction Provides High R-Value and Moisture ProtectionDocument2 pagesEIFS Wall Construction Provides High R-Value and Moisture Protectionkohatian27796105No ratings yet
- Waterproofing and Damp Proofing - Rep-Ar161b58Document21 pagesWaterproofing and Damp Proofing - Rep-Ar161b58Anna KateurinaNo ratings yet
- Waterproofing Compound GuideDocument47 pagesWaterproofing Compound GuideJaiNo ratings yet
- WaterproofingDocument18 pagesWaterproofinglarnzNo ratings yet
- 02.XII.2020 Dear Class-2: WelcomeDocument46 pages02.XII.2020 Dear Class-2: WelcomeRiddhi ShrivastwaNo ratings yet
- PCO-10techpaper Overview BushingsDocument7 pagesPCO-10techpaper Overview BushingssomeontorrenteNo ratings yet
- Doors & Windows - Abhinav Gaind, MIXX WindowsDocument5 pagesDoors & Windows - Abhinav Gaind, MIXX WindowsRafikul RahemanNo ratings yet
- Residential Guide 部分132Document1 pageResidential Guide 部分132xinghaijunNo ratings yet
- Final Ravatherm XPSX Insulating Inverted Flat RoofsDocument12 pagesFinal Ravatherm XPSX Insulating Inverted Flat RoofsAlin StancuNo ratings yet
- Neral Studies 2Document6 pagesNeral Studies 2mariyaNo ratings yet
- 2020insulation (1)Document33 pages2020insulation (1)felipe.moliveira18No ratings yet
- Insulation TypesDocument16 pagesInsulation TypesBrankoNo ratings yet
- Water Proofing Damp Proofing AND Thermal InsulationDocument19 pagesWater Proofing Damp Proofing AND Thermal InsulationgauriNo ratings yet
- Wood and Wood CompositesDocument23 pagesWood and Wood CompositesAisha SadiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4.2Document5 pagesAssignment 4.2JRayNo ratings yet
- Brushbond TI Flexicoat Insulating CoatingDocument2 pagesBrushbond TI Flexicoat Insulating Coatinganeesh kapaNo ratings yet
- Brosur PentensDocument2 pagesBrosur PentensKaldon DarwisNo ratings yet
- Selecting The Right Insulation Material PDFDocument6 pagesSelecting The Right Insulation Material PDFShahab Z AhmedNo ratings yet
- PROTECT FOUNDATIONS FROM WATER, HEAT AND GASDocument4 pagesPROTECT FOUNDATIONS FROM WATER, HEAT AND GAScorazon philNo ratings yet
- 14radiantbarriers 1Document2 pages14radiantbarriers 1Eugene FrancoNo ratings yet
- Brushbond TI Flexicoat BFLDocument2 pagesBrushbond TI Flexicoat BFLpeashNo ratings yet
- Brushbond TI Flexicoat insulating coatingDocument2 pagesBrushbond TI Flexicoat insulating coatingSameehu TVNo ratings yet
- Neopor Roof Insulation EN PDFDocument16 pagesNeopor Roof Insulation EN PDFJohn Martinos100% (1)
- SHAH MARKETING Trust is built with consistencyDocument4 pagesSHAH MARKETING Trust is built with consistencyNitin ShahNo ratings yet
- Thermal Insulation: Sneha Kesarwani A2180320008Document5 pagesThermal Insulation: Sneha Kesarwani A2180320008Eshita DiwanNo ratings yet
- Systems For Enclosing BuildingsDocument11 pagesSystems For Enclosing BuildingsAidyl Kate BernalNo ratings yet
- Miniature MaterialsDocument2 pagesMiniature MaterialsClark Venson BorricoNo ratings yet
- How To Design A Flat Roof PDFDocument3 pagesHow To Design A Flat Roof PDFMaria Rose Giltendez - BartianaNo ratings yet
- Elastoseal EPDM Roofing SystemsDocument8 pagesElastoseal EPDM Roofing SystemsStephenNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 12Document1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 12corazon philNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 9Document1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 9corazon philNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 8Document1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 8corazon philNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 7Document1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 7corazon philNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 4Document1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 4corazon philNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 10Document1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 10corazon philNo ratings yet
- UTILITIES Pugeda Quiz 21 Three Types of LightingDocument1 pageUTILITIES Pugeda Quiz 21 Three Types of Lightingcorazon philNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 17 Wacu and Split TypeDocument1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 17 Wacu and Split Typecorazon philNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 6Document1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 6corazon philNo ratings yet
- UTILITIES Pugeda Quiz 15 ElevatorDocument1 pageUTILITIES Pugeda Quiz 15 Elevatorcorazon philNo ratings yet
- UTILITIES Pugeda Quiz 22 Types of LightsDocument1 pageUTILITIES Pugeda Quiz 22 Types of Lightscorazon philNo ratings yet
- BT JOE Quiz 3 MetalDocument2 pagesBT JOE Quiz 3 MetalJess AndanNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 11Document1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 11corazon philNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 2Document1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 2corazon philNo ratings yet
- Pugeda Utilities PreboardDocument12 pagesPugeda Utilities Preboardcorazon philNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 5Document1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 5corazon philNo ratings yet
- UTILITIES Pugeda Quiz 19 Sound WaveDocument1 pageUTILITIES Pugeda Quiz 19 Sound Wavecorazon philNo ratings yet
- BT JOE Quiz 4 MasonryDocument1 pageBT JOE Quiz 4 Masonrycorazon phil100% (1)
- Joe BLDG Tech PreboardDocument13 pagesJoe BLDG Tech Preboardcorazon philNo ratings yet
- UTILITIES Quiz 1Document2 pagesUTILITIES Quiz 1Amiel TayagNo ratings yet
- STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS AND THEIR FUNCTIONSDocument8 pagesSTRUCTURAL ELEMENTS AND THEIR FUNCTIONSrogggNo ratings yet
- BT Joe Quiz 2Document1 pageBT Joe Quiz 2corazon philNo ratings yet
- BT JOE Quiz 5 WoodDocument2 pagesBT JOE Quiz 5 Woodcorazon philNo ratings yet
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 3Document1 pageUtilities Pugeda Quiz 3corazon philNo ratings yet
- BT JOE Quiz 1a FormworksDocument2 pagesBT JOE Quiz 1a Formworkscorazon philNo ratings yet
- BT Joe Quiz 1Document1 pageBT Joe Quiz 1corazon philNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture from Pre-Historic to Classical PeriodsDocument19 pagesHistory of Architecture from Pre-Historic to Classical Periodscorazon philNo ratings yet
- Masonry Building Tech NotesDocument13 pagesMasonry Building Tech Notescorazon phil100% (1)
- BT JOE Quiz 6 RoofDocument1 pageBT JOE Quiz 6 Roofcorazon philNo ratings yet
- Refresher Juson BLDG TechDocument29 pagesRefresher Juson BLDG TechTimothy Ryan Wang100% (2)
- MiscDocument23 pagesMisccp2489No ratings yet
- CPG Prevention, Diagnosis & Management of IE PDFDocument182 pagesCPG Prevention, Diagnosis & Management of IE PDFsigitNo ratings yet
- Karl-Fischer TitrationDocument19 pagesKarl-Fischer TitrationSomnath BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- MDD FormatDocument6 pagesMDD FormatEngineeri TadiyosNo ratings yet
- Centrifuge PDFDocument11 pagesCentrifuge PDFسراء حيدر كاظمNo ratings yet
- 2016 Practical Theory Questions SolutionDocument36 pages2016 Practical Theory Questions Solutionsheeess gaadaNo ratings yet
- Programme EnergyDocument9 pagesProgramme EnergyAbdulazizNo ratings yet
- Flood Risk AssessmentDocument167 pagesFlood Risk AssessmentElenne Mendoza Mortel EvoraNo ratings yet
- General and Local AnesthesiaDocument1 pageGeneral and Local Anesthesiaahmedhelper300No ratings yet
- RPT Mathematics Year 5Document24 pagesRPT Mathematics Year 5Anonymous wirViz1tyoNo ratings yet
- 4880 AnsiDocument0 pages4880 AnsiabualamalNo ratings yet
- Bai TapDocument6 pagesBai TapChi VominhNo ratings yet
- Early Daoist Dietary Practices: Examining Ways To Health and Longevity. by Shawn ArthurDocument6 pagesEarly Daoist Dietary Practices: Examining Ways To Health and Longevity. by Shawn ArthurlsdkNo ratings yet
- Disaccharides and PolysaccharidesDocument17 pagesDisaccharides and PolysaccharidesAarthi shreeNo ratings yet
- ECN 202 Final AssignmentDocument10 pagesECN 202 Final AssignmentFarhan Eshraq JeshanNo ratings yet
- KF2.5-200 - With-M-C - GB - 03-15 KRACHT Bomba PDFDocument8 pagesKF2.5-200 - With-M-C - GB - 03-15 KRACHT Bomba PDFJairo Andrés FA100% (1)
- 5 Set Model Question Mathematics (116) MGMT XI UGHSSDocument13 pages5 Set Model Question Mathematics (116) MGMT XI UGHSSSachin ChakradharNo ratings yet
- Audit of Intangible AssetDocument3 pagesAudit of Intangible Assetd.pagkatoytoyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Health History SummaryDocument1 pageNursing Health History SummaryHarvey T. Dato-onNo ratings yet
- Media ExercisesDocument24 pagesMedia ExercisesMary SyvakNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of Soids5!1!13Document20 pagesBand Theory of Soids5!1!13Ravi Kumar BanalaNo ratings yet
- Latin Fathers On Spirit PDFDocument20 pagesLatin Fathers On Spirit PDFZakka LabibNo ratings yet
- Guided Reading Activity: The Reach of ImperialismDocument2 pagesGuided Reading Activity: The Reach of ImperialismevertNo ratings yet
- Angle Beam Transducer Dual ElementDocument5 pagesAngle Beam Transducer Dual ElementWilliam Cubillos PulidoNo ratings yet
- The Law of DemandDocument13 pagesThe Law of DemandAngelique MancillaNo ratings yet
- Banking Services: Geographical QuestionsDocument5 pagesBanking Services: Geographical QuestionsSudhanshu SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Mechanik Lammert ContentDocument3 pagesMechanik Lammert Contentapi-129423309No ratings yet
- Research Methodology: by Asaye Gebrewold (PHD Candidate)Document17 pagesResearch Methodology: by Asaye Gebrewold (PHD Candidate)natnael haileNo ratings yet
- 05-Program Design and AnalysisDocument78 pages05-Program Design and AnalysisTarq AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Learning and Teaching in The Clinical EnvironmentDocument4 pagesLearning and Teaching in The Clinical EnvironmentDaniel Alejandro Lozano MorenoNo ratings yet
- How to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionFrom EverandHow to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsFrom EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (242)
- Building Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 2From EverandBuilding Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Field Guide for Construction Management: Management by Walking AroundFrom EverandField Guide for Construction Management: Management by Walking AroundRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Art of Welding: Featuring Ryan Friedlinghaus of West Coast CustomsFrom EverandThe Art of Welding: Featuring Ryan Friedlinghaus of West Coast CustomsNo ratings yet
- Building Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 1From EverandBuilding Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 1Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Welding for Beginners in Fabrication: The Essentials of the Welding CraftFrom EverandWelding for Beginners in Fabrication: The Essentials of the Welding CraftRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Complete Guide to Building Your Own Home and Saving Thousands on Your New HouseFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Building Your Own Home and Saving Thousands on Your New HouseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- 1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideFrom Everand1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedFrom EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- An Architect's Guide to Construction: Tales from the Trenches Book 1From EverandAn Architect's Guide to Construction: Tales from the Trenches Book 1No ratings yet
- Markup & Profit: A Contractor's Guide, RevisitedFrom EverandMarkup & Profit: A Contractor's Guide, RevisitedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (11)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsFrom EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Industrial Waste Treatment HandbookFrom EverandIndustrial Waste Treatment HandbookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Estimator's General Construction Manhour ManualFrom EverandEstimator's General Construction Manhour ManualRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- How to Build a Tiny Portable House: With Plans and InstructionsFrom EverandHow to Build a Tiny Portable House: With Plans and InstructionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Civil Engineer's Handbook of Professional PracticeFrom EverandCivil Engineer's Handbook of Professional PracticeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationFrom EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
- The Everything Woodworking Book: A Beginner's Guide To Creating Great Projects From Start To FinishFrom EverandThe Everything Woodworking Book: A Beginner's Guide To Creating Great Projects From Start To FinishRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)