Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heat Transfer Assignment Problems on Heat Exchangers
Uploaded by
Belly John Carbonell0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageThis document contains three heat exchanger problems involving calculations of overall heat transfer coefficients, heat transfer rates, outlet temperatures, and fouling factors. Problem 1 involves calculating the overall heat transfer coefficient for a steel tube with and without fins. Problem 2 involves calculating the overall heat transfer coefficient and plotting thermal resistance for a shell and tube heat exchanger with fouling. Problem 3 uses the LMTD method to calculate heat transfer and other values for a double pipe counter-flow heat exchanger, and also considers scale formation over time. Problem 4 uses the NTU-effectiveness method to calculate outlet temperatures for counter-flow and parallel-flow heat exchangers.
Original Description:
Original Title
MEPME 132 - Assignment 3 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains three heat exchanger problems involving calculations of overall heat transfer coefficients, heat transfer rates, outlet temperatures, and fouling factors. Problem 1 involves calculating the overall heat transfer coefficient for a steel tube with and without fins. Problem 2 involves calculating the overall heat transfer coefficient and plotting thermal resistance for a shell and tube heat exchanger with fouling. Problem 3 uses the LMTD method to calculate heat transfer and other values for a double pipe counter-flow heat exchanger, and also considers scale formation over time. Problem 4 uses the NTU-effectiveness method to calculate outlet temperatures for counter-flow and parallel-flow heat exchangers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageHeat Transfer Assignment Problems on Heat Exchangers
Uploaded by
Belly John CarbonellThis document contains three heat exchanger problems involving calculations of overall heat transfer coefficients, heat transfer rates, outlet temperatures, and fouling factors. Problem 1 involves calculating the overall heat transfer coefficient for a steel tube with and without fins. Problem 2 involves calculating the overall heat transfer coefficient and plotting thermal resistance for a shell and tube heat exchanger with fouling. Problem 3 uses the LMTD method to calculate heat transfer and other values for a double pipe counter-flow heat exchanger, and also considers scale formation over time. Problem 4 uses the NTU-effectiveness method to calculate outlet temperatures for counter-flow and parallel-flow heat exchangers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
MEPME 132 – Heat and Mass Transfer
Assignment No. 3 – Heat Exchangers
(Optional Tools: Use Mathcad, EES or MS Excel)
Problem No. 1 (Overall heat transfer coefficient)
A steel tube (k = 50 W/m-K) of ID = 20 mm, OD =26 mm is used to transfer heat from hot gases
flowing over the tube (ho = 200 W/m2-K) to cold water flowing through the tube (h i = 8000
W/m2-K). (a) What is the cold side overall heat transfer coefficient U i? (b) To enhance the heat
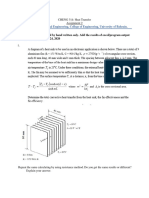
transfer, 16 straight fins of rectangular profile are installed longitudinally along the outer surface
of the tube. The fins equally spaced around the tube, fin thickness being 2 mm and length of 15
mm. Assuming the fin efficiency of 77.92%, what is the corresponding overall heat transfer
coefficient Ui?
Problem No. 2 (Overall heat transfer coefficient and fouling factor)
A shell and tube counter-flow heat exchanger uses copper tubes (k = 380 W/m-C), 20 mm ID
and 23 mm OD. Inside and outside film coefficients are 5000 and 1500 W/m 2-C, respectively.
Fouling factors on the inside and outside may be taken as 0.0004 and 0.001 m 2C/W, respectively.
Calculate the overall heat transfer coefficient based on: (a) outside surface, (b) inside surface,
and (c) Plot the variation of total thermal resistance, Rtotal as k varies from 10 to 400 W/m-C.
Problem No. 3 (LMTD Method)
Water at a rate of 4080 kg/hr is heated from 35 C to 75 C by an oil of C p = 1.9 kJ/kg-K. The heat
exchanger is of counter-flow, double pipe design. The oil enters at 110 C and leaves at 75 C.
Determine the (a) mass flow rate of oil, (b) area of heat exchanger necessary to handle this load,
if overall heat transfer coefficient is 320 W/m2-K.
If after 3 years there is a scale formation on the water side, an the outlet temperature is 60 C for
the same inlet temperatures and flow rates, calculate the (c) heat transferred, (d) outlet
temperature of oil, (e) overall heat transfer coefficient, and (f) water side fouling factor.
Problem No. 3 (NTU-Effectiveness Method)
Consider a heat exchanger (HX) for cooling oil at 180 C, with water entering at 25 C. Mass flow
rates of oil and water are 2.5 and 1.2 kg/s, respectively. Area of HX is 16 m 2. Calculate the outlet
temperatures of both fluids for (a) counter-flow HX, and (b) for parallel flow HX. Specific heat
data for oil and water are: 1900 J/kg-C and 4184 J/kg-C, respectively. Overall U = 285 W/m2-C.
You might also like
- Assignment 5 PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment 5 PDFRima ChinnasamyNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger CalculationsDocument3 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchanger Calculationsmimie azideeNo ratings yet
- HMT 113401 Anna UnivDocument5 pagesHMT 113401 Anna Univsathiya_ramNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer (MEE - 306) RCS (Makeup) (EngineeringDuniya - Com)Document3 pagesHeat Transfer (MEE - 306) RCS (Makeup) (EngineeringDuniya - Com)Sanjay ShreeshaNo ratings yet
- Examen+1+calor+th 16Document4 pagesExamen+1+calor+th 16Denisse M. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- CHENG314 Ass2 S1 20 21Document3 pagesCHENG314 Ass2 S1 20 21Imi_dash9No ratings yet
- 8S 2105 Mepc22 1Document2 pages8S 2105 Mepc22 1Challa YachendraNo ratings yet
- Icam (Lille) - Heat Exchanger Course Icam 2 - Autumn 2003 Heat Exchanger Examples - Sheet 2Document3 pagesIcam (Lille) - Heat Exchanger Course Icam 2 - Autumn 2003 Heat Exchanger Examples - Sheet 2FahmiRamdanNo ratings yet
- Use of Heat and Mass Transfer Data Books, Steam Tables Are PermittedDocument4 pagesUse of Heat and Mass Transfer Data Books, Steam Tables Are Permitted3rajaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - Year 4 - 20MECH28H - Heat Transfer (Final 2021)Document4 pagesFinal Exam - Year 4 - 20MECH28H - Heat Transfer (Final 2021)youssefNo ratings yet
- Me52102 - HMT Sheet - I Conduction Jul-Dec'23Document3 pagesMe52102 - HMT Sheet - I Conduction Jul-Dec'23HarshNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Anna University Question BankDocument6 pagesHeat Transfer: Anna University Question BankaeroacademicNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Design Problems and CalculationsDocument2 pagesHeat Exchanger Design Problems and CalculationsDenisse M. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Ay1011sem1 Me3122eDocument3 pagesAy1011sem1 Me3122eCammy MiunoNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Tutorial Conduction ConvectionDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer Tutorial Conduction Convectionpushkal0% (2)
- Chn-201 Tutorial 2 - Autumn 16-17-1Document2 pagesChn-201 Tutorial 2 - Autumn 16-17-1Prashant RajNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument2 pagesQuestionsPYRUS MALUSNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems Heat TransferDocument12 pagesSolved Problems Heat TransferFaisal SadaatNo ratings yet
- Cycle Test 1 Set1Document6 pagesCycle Test 1 Set1logeshboy007No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Yik Vui KongNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Tutorial 2Document2 pagesHeat Transfer Tutorial 2vicopipNo ratings yet
- Model Exam.2.2Document3 pagesModel Exam.2.2Srinivasan PichandiNo ratings yet
- L-3ff-2/ME Date: 18/04/2022Document40 pagesL-3ff-2/ME Date: 18/04/2022MD. BAKTIAR ALAM KABIRNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem Set 1 - Three Heat Transfer TechniquesDocument4 pagesPractice Problem Set 1 - Three Heat Transfer TechniquesDan Mc0% (1)
- Tut 4 Heat ExchangersDocument2 pagesTut 4 Heat ExchangersGomolemo BaarxxNo ratings yet
- T.E. (Mechanical) (Semester - I) Examination, 2011 Heat Transfer (2008 Pattern) (New)Document4 pagesT.E. (Mechanical) (Semester - I) Examination, 2011 Heat Transfer (2008 Pattern) (New)saurabhNo ratings yet
- Bbbdnitm, Lko Mechanical Department Subject-Heat and Mass Transfer UNIT-5 Assignment-5 Section-A Short Questions: (2 Marks)Document2 pagesBbbdnitm, Lko Mechanical Department Subject-Heat and Mass Transfer UNIT-5 Assignment-5 Section-A Short Questions: (2 Marks)Hoài ThươngNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Heat TransferDocument8 pagesFluid Mechanics and Heat Transfervenkat_nsnNo ratings yet
- ME151117 Heat Transfer Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesME151117 Heat Transfer Exam QuestionsG.Chaitanya KiranNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesInstructions:: Gujarat Technological UniversityKislay ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- CHE 210 Midterm Exam SolutionsDocument11 pagesCHE 210 Midterm Exam SolutionsJaspreet SandhuNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Tutorial Sheet 5Document4 pagesHeat Exchanger Tutorial Sheet 5Charlotte BNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Tutorial Sheet 5Document4 pagesHeat Exchanger Tutorial Sheet 5Charlotte BNo ratings yet
- KCT 2010-2011 HTDocument4 pagesKCT 2010-2011 HTask4krishnanNo ratings yet
- rr320306 Heat TransferDocument8 pagesrr320306 Heat TransferSrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- 10 Numerical 10Document1 page10 Numerical 10Aakash AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - HMTDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank - HMTSUNDARAMAHALINGAM ANo ratings yet
- RA 9A23501 Heat Transfer in BioprocessesDocument2 pagesRA 9A23501 Heat Transfer in BioprocessessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Document AnalysisDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer Document Analysisbhaskar5377No ratings yet
- MAE 101C (Spring 2020) - Midterm Exam #2: Problem 1 (20 Points)Document1 pageMAE 101C (Spring 2020) - Midterm Exam #2: Problem 1 (20 Points)Dinger RectileNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Assignment QuestionsDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer Assignment QuestionsMurali KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ihte Que BankDocument2 pagesIhte Que BankNikunj PatelNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Second Law 2016Document7 pagesAssignment 2 Second Law 2016Mohit SInhaNo ratings yet
- Ass 7Document4 pagesAss 7Puneet MeenaNo ratings yet
- Me8693 Heat and Mass Transfer - QBDocument5 pagesMe8693 Heat and Mass Transfer - QBmeckup123No ratings yet
- Heat transfer and heat exchangers problemsDocument2 pagesHeat transfer and heat exchangers problemsArul KumarNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer (MCC 15102) Assignmnet - 1: A F B C D EDocument4 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer (MCC 15102) Assignmnet - 1: A F B C D ERotten AppleNo ratings yet
- Heatex 02 AwDocument3 pagesHeatex 02 AwyvethendoNo ratings yet
- Final HMT AssignmentsDocument7 pagesFinal HMT Assignments544 vishwavijay PatilNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument2 pagesHeat TransferAmal JoyNo ratings yet
- Prob Sheet Heat ExchangerDocument2 pagesProb Sheet Heat ExchangerAnonymous mXicTi8hB0% (1)
- Sheet (3.1) Heat Exchangers Analysis Using LMTD MethodDocument2 pagesSheet (3.1) Heat Exchangers Analysis Using LMTD MethodAya Bekhet 1253No ratings yet
- End-Semester Question PaperDocument4 pagesEnd-Semester Question PaperRabey The physicistNo ratings yet
- C and RDocument7 pagesC and Rinba oli50% (2)
- Assignment 2 2021 FinalDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 2021 FinalRichard GrahamNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 NumericalDocument11 pagesUnit-1 NumericalDr. M. Mohan Jagadeesh kumarNo ratings yet
- HT AssignDocument2 pagesHT AssignSai Chand Arkham KingNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2PNNo ratings yet
- ChE Laws and Ethics ModuleDocument272 pagesChE Laws and Ethics ModuleBelly John CarbonellNo ratings yet
- ZUEC 2022 Product GuideDocument12 pagesZUEC 2022 Product GuideBelly John CarbonellNo ratings yet
- MEPME 132 - Assignment 2Document2 pagesMEPME 132 - Assignment 2Belly John CarbonellNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency For Electric MotorsDocument27 pagesEnergy Efficiency For Electric MotorsBelly John CarbonellNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument1 pageQuizBelly John CarbonellNo ratings yet