Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ABC (Peripherally Acting)
Uploaded by
Sibel ErtuğrulOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ABC (Peripherally Acting)
Uploaded by
Sibel ErtuğrulCopyright:
Available Formats
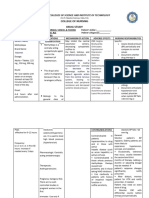
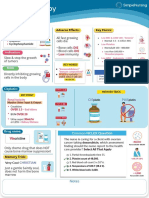
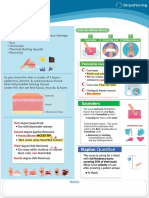
Antihypertensives: Adrenergic blocking drugs
/ Alpha & Beta Central and Peripherally Acting
How it works? “Action” Nursing management
Peripherally acting: Inhibits norepinephrine in the • Monitor intake and output ratios and daily weight
PNS ( treats BPH, HTN) • Assess for edema daily, especially at beginning of
therapy.
Centrally acting: Decreases CNS activity (HTN) • Monitor BP and pulse prior to starting, frequently
during initial dose adjustment and dose increases
and periodically throughout therapy.
• Titrate slowly in patients with cardiac conditions or
those taking other sympatholytic drugs.
Why do we give it? ‘’Reason’’ Report significant changes.
• Transdermal: Instruct patient on proper application
• Certain cardiac arrhythmias of transdermal system. Do not cut or trim unit.
• BAH Transdermal system can remain in place during
• HTN bathing or swimming.
Adverse effects Interactions:
EENT: dry eyes. • Adrenergic: risk of HTN
CV: AV block, bradycardia, hypotension (with • Levodopa: hypotension, decrease levodopa
epidural), palpitations. • Anesthetic agents: increase anesthetic
GI: dry mouth, constipation, nausea, vomiting. • Beta blockers: hypertension
GU: erectile dysfunction. • Lithium: lithium toxicity
Derm: rash, sweating. • Haloperidol: psychotic behavior
F&E: sodium retention, hyperkalemia
Metab: weight gain.
Neuro: paresthesia.
Misc: withdrawal phenomenon
Contraindications
• Central: Hepatic disease ( active ) , MAOI
antidepressant therapy
• Peripheral: ulcerative colitis , peptic ulcer
Generic Trade Central / peripheral Safe dose Route
100 mcg (0.1 mg)
Clonidine Catapres Central PO, TD
BID
250– 500 mg 2– 3
Methyldopa N/A Central PO
times daily
Cardura, Cardura
Doxazosin Periphera 1 mg once daily PO
XL
1 mg 2– 3 times
Prazosin Minipress Periphera PO
daily
You might also like
- Clonidine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageClonidine HydrochloridebluetonksNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugDocument1 pageName of DrugDang Lim SantosNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Catapres (Clonidine)Document2 pagesCatapres (Clonidine)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Folic CHNDocument3 pagesFolic CHNErica EbradaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Management of DepressionDocument66 pagesPharmacological Management of DepressionPriyash JainNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Section: 263Document2 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Section: 263AkiraMamo100% (1)
- 3 Treatment of HypertensionDocument7 pages3 Treatment of HypertensiontiaraNo ratings yet
- Cronic Heart FailureDocument37 pagesCronic Heart FailureHanif RobbanizerNo ratings yet
- Feline Drug Formulary June 2020 FINAL Updated-1Document5 pagesFeline Drug Formulary June 2020 FINAL Updated-1Ernesto GuadarramaNo ratings yet
- Pre Eclampsia Drug StufyDocument3 pagesPre Eclampsia Drug StufyFrances Reina TabaderoNo ratings yet
- CEG Formulary: Cardiac Medications For Dogs: ... Bringing Cardiology Into PracticeDocument6 pagesCEG Formulary: Cardiac Medications For Dogs: ... Bringing Cardiology Into PracticeAngeles MerinoNo ratings yet
- Prevention and Management of Pain, AgitationDocument44 pagesPrevention and Management of Pain, AgitationSiriporn PongpattarapakNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of 30 DrugsDocument56 pagesDrug Study of 30 DrugsDaimin TevesNo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipineVina Jane P Laurel92% (12)
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipineCj LowryNo ratings yet
- MS Drug Study 1Document6 pagesMS Drug Study 1Elijah MarfilNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Mother TDocument14 pagesDrug Study Mother TEuzelle Jeena ArandaNo ratings yet
- (Per System Preferably) : AntihypertensiveDocument4 pages(Per System Preferably) : AntihypertensiveGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- EnalaprilDocument4 pagesEnalaprilGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Med LopressorDocument2 pagesMed LopressorDeanna Lang ThibodauxNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY PsycheDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Psychejulesubayubay5428100% (1)
- Drug Study Edited FinalDocument10 pagesDrug Study Edited FinalPureza Maye SalapangNo ratings yet
- Conscious Sedation: Hayel Gharaibeh, MD. Anesthesia ConsultantDocument84 pagesConscious Sedation: Hayel Gharaibeh, MD. Anesthesia ConsultantKhaled GharaibehNo ratings yet
- Cva Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCva Drug Studykristine86badgirlNo ratings yet
- LabetalolDocument3 pagesLabetalolTri Purma Sari50% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyAnne Marie BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- Atenolol TenorminDocument3 pagesAtenolol TenorminLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- PhenerganDocument2 pagesPhenerganKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Conscious sedation techniques and risksDocument84 pagesConscious sedation techniques and risksKhaled GharaibehNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-PtsdDocument4 pagesDrug Study-PtsdWILMARIE SAPANTANo ratings yet
- Drug LopressorDocument1 pageDrug LopressorSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Managing Hepatic PatientsDocument9 pagesManaging Hepatic PatientsJake Yvan Dizon0% (1)
- Pharma 2Document7 pagesPharma 2FATIMA LAVADIANo ratings yet
- Hydralazine.1 3Document1 pageHydralazine.1 3SNo ratings yet
- 5-Drugs Used in Parkinsonism Summary and QuestionsDocument7 pages5-Drugs Used in Parkinsonism Summary and QuestionsmugtabaNo ratings yet
- IV Plan of Care and Drug Study Methyldopa, Cefuroxime, Dexamethasone, HydralazineDocument9 pagesIV Plan of Care and Drug Study Methyldopa, Cefuroxime, Dexamethasone, HydralazineJHoy JhoyThotNo ratings yet
- Nursing implications for drug administrationDocument9 pagesNursing implications for drug administrationKathrina TumbagaNo ratings yet
- DRUGS in E-CARTDocument8 pagesDRUGS in E-CARTRagual Mica100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyXio PauNo ratings yet
- ANTIPSYCHOTICSDocument25 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICSCheetahboi Shopee100% (4)
- Anti Hypertensive DrugsDocument40 pagesAnti Hypertensive DrugsjawadNo ratings yet
- MethyldopaDocument4 pagesMethyldopaMichael TokongNo ratings yet
- FlecainideDocument3 pagesFlecainideAlexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive DrugsDocument113 pagesAnti Hypertensive DrugsRobert DowneyNo ratings yet
- Agent For Treating Heart FailureDocument26 pagesAgent For Treating Heart FailureClarisse SuanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ClozapineDocument2 pagesDrug Study ClozapineRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- RISPERIDONE Iloilo Doctor's College Nursing Responsibilities for RisperidoneDocument9 pagesRISPERIDONE Iloilo Doctor's College Nursing Responsibilities for RisperidoneColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipineAnonymous QqyLDoW1No ratings yet
- Generic Name:: ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesGeneric Name:: ElectrolytesEleazar Desillarico GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Name WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesDrug Name WPS OfficeCAMILLE GAIL HADJIRANINo ratings yet
- 6.Z8sNyP 6 GHafez HT and Antihypertensive DrugsDocument81 pages6.Z8sNyP 6 GHafez HT and Antihypertensive Drugsyasmin.rahmany03No ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument13 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitieskev mondaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyJohn LesterNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLester Paul SivilaNo ratings yet
- ChemotherapyDocument1 pageChemotherapySibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- HypothermiaDocument1 pageHypothermiaSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Drugs 1 UpdatedDocument1 pageNCLEX Drugs 1 UpdatedSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument1 pageEpithelial TissuesSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- EthambutolDocument1 pageEthambutolSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- ContraceptionDocument1 pageContraceptionSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Antiemetics (Anti-Nausea & Vomiting)Document1 pageAntiemetics (Anti-Nausea & Vomiting)Sibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Care for Minor BurnsDocument1 pageCare for Minor BurnsSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Heparin vs. Warfarin: FAST vs. LONG EffectsDocument1 pageHeparin vs. Warfarin: FAST vs. LONG EffectsSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Atropine - Symptomatic BradycardiaDocument1 pageAtropine - Symptomatic BradycardiaSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Acid Neutralizers - v2Document1 pageAcid Neutralizers - v2Sibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media Pediatrics Visual & Audio Pathophysiology Causes Signs Symptoms Nursing CareDocument1 pageOtitis Media Pediatrics Visual & Audio Pathophysiology Causes Signs Symptoms Nursing CareSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- 9 ECG Strips On The NCLEXDocument1 page9 ECG Strips On The NCLEXSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Allopurinol & ColchicineDocument1 pageAllopurinol & ColchicineSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- ABG Practice Questions - 2Document1 pageABG Practice Questions - 2Sibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- PNS Drugs: A/B Blocking Drugs and Their Nursing ManagementDocument1 pagePNS Drugs: A/B Blocking Drugs and Their Nursing ManagementSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Oliveira Shayna 1000 English Collocations in 10 Minutes A Da PDFDocument128 pagesOliveira Shayna 1000 English Collocations in 10 Minutes A Da PDFvikas dubeyNo ratings yet
- ADHD - AmphetaminesDocument1 pageADHD - AmphetaminesSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- 4 Rules For AntidepressantsDocument1 page4 Rules For AntidepressantsSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- 3 Step ABG Interpretation - 2Document1 page3 Step ABG Interpretation - 2Sibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- 6 Test Tips of AntibioticsDocument1 page6 Test Tips of AntibioticsSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- 650 English Phrases For Everyday Speaking - Facebook Com LinguaLIB PDFDocument50 pages650 English Phrases For Everyday Speaking - Facebook Com LinguaLIB PDFMahmoud Abd El HadiNo ratings yet
- MKNC Notes PDFDocument60 pagesMKNC Notes PDFVanessa AntonetteNo ratings yet
- 500 Real English PhrasesDocument38 pages500 Real English PhrasesIon Sava100% (2)
- 300 Basic English SentencesDocument19 pages300 Basic English SentencesFaizullahMagsi100% (1)
- NCLEX Cram Sheet: Essential Nursing Exam Facts in <40 CharactersDocument12 pagesNCLEX Cram Sheet: Essential Nursing Exam Facts in <40 CharactersSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- 5 Step EKG InterpretationDocument1 page5 Step EKG InterpretationSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- 300 Basic English SentencesDocument19 pages300 Basic English SentencesFaizullahMagsi100% (1)
- NCLEX Cram Sheet: Essential Nursing Exam Facts in <40 CharactersDocument12 pagesNCLEX Cram Sheet: Essential Nursing Exam Facts in <40 CharactersSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Ipcr Accomplishment June To Dec 2020Document3 pagesIpcr Accomplishment June To Dec 2020edwardraymond holl0% (1)
- Physeo Microbiology 2019Document358 pagesPhyseo Microbiology 2019Harald Vogt100% (1)
- Lourdes College Nursing Program Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLourdes College Nursing Program Drug Studypinksapphire929100% (2)
- A Modified Acid-Fast Staining Method For Rapid Detection ofDocument5 pagesA Modified Acid-Fast Staining Method For Rapid Detection ofWan HafizNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Dental Caries in The Young PermanentDocument39 pagesTreatment of Dental Caries in The Young PermanentShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- CA 2 - CHN Review 50 Items PretestDocument10 pagesCA 2 - CHN Review 50 Items PretestAlibasher Macalnas100% (1)
- PATH 1 ALL Lectures Final1Document2,054 pagesPATH 1 ALL Lectures Final1Andleeb ImranNo ratings yet
- Gall Bladder DiseaseDocument11 pagesGall Bladder Diseasedarellejaide100% (1)
- Ruetten 2008Document9 pagesRuetten 2008Creator DocNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fish Health ManagementDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Fish Health ManagementnlribeiroNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms and Their Respective Place in The Living WorldDocument22 pagesMicroorganisms and Their Respective Place in The Living WorldAyesha MasoodNo ratings yet
- Toxicological and Pharmacokinetic Properties of Sucralose 6 Acetate and Its Parent Sucralose in Vitro Screening AssaysDocument36 pagesToxicological and Pharmacokinetic Properties of Sucralose 6 Acetate and Its Parent Sucralose in Vitro Screening AssayswipiriNo ratings yet
- Informed Consent For Lasik SurgeryDocument2 pagesInformed Consent For Lasik SurgeryMoerieda RinquestNo ratings yet
- Alberta Stroke Program Early CT ScoreDocument15 pagesAlberta Stroke Program Early CT ScoreRainickBrenhizarNavarroNo ratings yet
- Immuno ArraysDocument36 pagesImmuno Arraysvishuraja50% (2)
- Postmortem Toxicology - Farmasi ForensikDocument20 pagesPostmortem Toxicology - Farmasi Forensikedrina elfia rosaNo ratings yet
- Folliculitis Decalvans Update July 2019 - Lay Reviewed July 2019Document4 pagesFolliculitis Decalvans Update July 2019 - Lay Reviewed July 2019sjeyarajah21No ratings yet
- Anemia: Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument8 pagesAnemia: Rheumatoid ArthritistyasNo ratings yet
- Post Stroke WritingDocument9 pagesPost Stroke WritingAdi ParamarthaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Deploying Student NursesDocument2 pagesGuidelines For Deploying Student NursesDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- The gross structure of the human respiratory systemDocument14 pagesThe gross structure of the human respiratory systemSaraNo ratings yet
- 600 First أسئلة القصيمDocument165 pages600 First أسئلة القصيمFatema AlaaliNo ratings yet
- Juvenile RaDocument27 pagesJuvenile RaEdwardNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Iodide Chemical Properties Uses EffectsDocument3 pagesHydrogen Iodide Chemical Properties Uses EffectsJohn KellyNo ratings yet
- The 13 Remedies of DR John Henry Clarke: SULPHUR (Brimstone Flowers of Sulphur.)Document20 pagesThe 13 Remedies of DR John Henry Clarke: SULPHUR (Brimstone Flowers of Sulphur.)Anonymous eKt1FCDNo ratings yet
- Bloodborne Pathogens PPT v-03!01!17Document44 pagesBloodborne Pathogens PPT v-03!01!17kunalphalswal0005No ratings yet
- The Voice of PLC 1101Document6 pagesThe Voice of PLC 1101The Plymouth Laryngectomy ClubNo ratings yet
- Workplace Hazards Ang Their Ill EffectdDocument110 pagesWorkplace Hazards Ang Their Ill EffectdJanissaries NivercaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of ICD-10 and DSM-IV Criteria For Postconcussion SyndromedisorderDocument19 pagesComparison of ICD-10 and DSM-IV Criteria For Postconcussion Syndromedisorderneoraymix blackNo ratings yet
- Hiv and Aids in Children3Document25 pagesHiv and Aids in Children3Kazau FwalangaNo ratings yet