Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M11GM Ia 1
Uploaded by
Windel Q. BojosOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
M11GM Ia 1
Uploaded by
Windel Q. BojosCopyright:
Available Formats
City of Bogo Science and Arts Academy
St. Joseph Village, Cogon, Bogo City, Cebu
Instructional Plan
DLP No: 1 Learning Area: General Mathematics Grade Level: XI Quarter: 1 Duration: 60 mins
Represents real – life situations using functions, including
Learning Competency Code: M11GM-Ia-1
piece – wise functions.
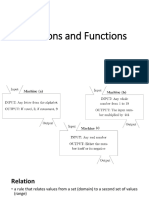
A function relates an input to an output.
Key It is like a machine that has an input and an output. The domain is the input while the range is
Concepts/Understanding the output. The domain is an independent value while the range depends upon the value of the
to be Developed domain. The machine is the function.
Piecewise functions are functions in pieces.
Objectives At the end of the lesson, 75% of the students will be able to:
Knowledge Define function, piece – wise function, domain and range;
Skills Site real-life situations where function is applied; solve equations involving functions;
Attitude Display proper hygiene; and
Values Maka - tao
Content Piece – wise function
Learning Resources LM’s, TG’s, chalk and board
Procedures
Introductory Activity What is function? One to one relationship
(15 mins) - Many to one relationship
Can you site an example of a thing or a situation where you considered a function?
- GF and BF relationship
- Toothbrush
- Napkin
What is piece-wise function?
- Functions that are in pieces (actually they don’t really know)
Example:
- Electric Fan
- Blender
Motivation.
Magic Box
Which of these machines, if you know the input, you can determine a single or unique
output easily?
- a, c, d and f
Is machine e a function?
- No, because the output is two; positive and negative.
In each group, site at least one real-life situation the same with the magic box where an input gives
an output out from a certain rule. (ex. Automatic Tubig Machine - ATM)
In your example, what is the product?
(water)
How did you come up with the output?
(by inserting one – peso (1) coin, the output will come out)
Analysis ( 5 mins)
Was there an instance where the output cannot be determined?
(yes, if not one - peso coin is inserted, like 25 centavo coin)
Are there instances in your life where functions can be applied? How?
(yes, by studying hard i got good grades)
What is the output of the following?
1. Printer (hard copy)
Abstraction (5 mins) 2. Bank ATM (money)
Does the output affect the input?
(no, only the input affects the output)
Application (15 mins) What do you think is the output in the following input following these rules?
1. 3x+8 ; choose five values of x and determine the output
2. 4x-2 ; choose five values of x and determine the output
Assessment 1. Define function, domain, range and piece – wise function in your own words.
(15 mins) 2. Give me the output:
2.1. f(x) = 3x – 8 ; x = 2
2.2. f(x) = 2x – 4 ; x = 2
2.3. f(x) = 6 – 7x ; x = -1
2.4. f(x) = x2 – 4 ; x = -2
Agreement Give me the output
1. f(x)=
Remarks
Reflection
Prepared by:
ALGEN A. OLING
Bibliography
pp. 2 – 21, General Mathematics, Orlando A. Oronce
pp. 1 - 10 , General Mathematics (TG), Deped
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hy0N-90gCu0
https://www.khanacademy.org/math/algebra-home/alg-functions/alg-piecewise-functions/v/piecewise-
function-example
https://www.khanacademy.org/math/algebra-home/alg-functions/alg-piecewise-functions/e/evaluating-
piecewise-functions
Appendices
Magic Box
Function machines Activity, pp. 3 – 4, General Mathematics (TG)
Application
1. If x = 1,2,3,4,5
Then the output are, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23
2. If x = 1,2,3,4,5
Then the output are, 2, 6, 10, 14, 18
Assessment
2. Function – a relation where each element in the domain (input) is related to only one value in the range
(output) by some rule.
- One to one relationship
- Many to one relationship
3. Domain – the set of all possible values that the variable x can take.
4. Range – the set of all possible values that the variable x can take.
5. Piece – wise function – function that are in pieces
6. f(x) = 3x – 8 8. f(x) = 6 – 7x
f(2) = 3(2) – 8 f(-1) = 6 – 7(-1)
f(2) = 6 – 8 f(-1) = 6 +7
f(2) = -2 f(-1) = 13
7. f(x) = 2x – 4 9. f(x) = x2 – 4
f(2) = 2(2) – 4 f(-2) = (-2)2 – 4
f(2) = 4 – 4 f(-2) = 4 – 4
f(2) = 0 f(-2) = 0
You might also like
- Chapter 3 (Lessons 1-4)Document95 pagesChapter 3 (Lessons 1-4)Retchelle Palmero SangcoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Functions and Piecewise FunctionsDocument48 pagesLesson 1 Functions and Piecewise FunctionsGeraldine ElisanNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- SHSGenMath EvaluatingFunctionsDocument7 pagesSHSGenMath EvaluatingFunctionsMonesse Angela Montemayor100% (1)
- Basic Calculus Grade 11 Quarter 4Document4 pagesBasic Calculus Grade 11 Quarter 4Kazandra Cassidy Garcia100% (1)
- Quarter 1 Module 1 FunctionsDocument20 pagesQuarter 1 Module 1 FunctionsDYLANNo ratings yet
- SHS Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesSHS Lesson PlanNiño Lemuel Lazatin Concina100% (1)
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Educ21 - The School As A Cultural InstitutionDocument48 pagesEduc21 - The School As A Cultural InstitutionCel BayNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsAira Jane Irarum78% (18)
- Grade 11 1st Quarter STEM Pre Calculus Module 2 Designing With Circles PC11AG Ia 234Document16 pagesGrade 11 1st Quarter STEM Pre Calculus Module 2 Designing With Circles PC11AG Ia 234Jil IanNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Quantitative ResearchDocument25 pagesPractical Research 2 Quantitative Researchphilip galizaNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics Quarter 1: Week 4Document40 pagesGeneral Mathematics Quarter 1: Week 4Mavros AngelusNo ratings yet
- A Lesson Plan in General MathematicsDocument2 pagesA Lesson Plan in General Mathematicsgrace jane ButacNo ratings yet
- Composite Functions: General Mathematics (Cor 005)Document15 pagesComposite Functions: General Mathematics (Cor 005)Rinoa Caye Villa-abrilleNo ratings yet
- Population and SampleDocument35 pagesPopulation and SampleMargie FernandoNo ratings yet
- Week 1. Day 2 (Lesson 2)Document6 pagesWeek 1. Day 2 (Lesson 2)Gladzangel LoricabvNo ratings yet
- GenMath11 - Q1 - Mod3 - One To One and Inverse Function - v3Document24 pagesGenMath11 - Q1 - Mod3 - One To One and Inverse Function - v3Manelyn Taga100% (2)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsJay CachoNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Gen. Math Modules W1-3Document19 pagesGrade 11 Gen. Math Modules W1-3Encluna Lindon JayNo ratings yet
- M11GM Ia 1Document2 pagesM11GM Ia 1Neil LumongsodNo ratings yet
- Functionspart 1 UnitportfolioDocument5 pagesFunctionspart 1 Unitportfolioapi-346342108No ratings yet
- General-Mathematics Q1 Module-1Document19 pagesGeneral-Mathematics Q1 Module-1Malen GallegosNo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument36 pagesRelations and FunctionsRailley Zcyrelle Ace LacsonNo ratings yet
- L-2 - Functions and ITFDocument91 pagesL-2 - Functions and ITF41Kevin Thomas XI-BNo ratings yet
- Composite FunctionsDocument12 pagesComposite FunctionsLizbethHazelRiveraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Function: Tr. Kclyn TagayunDocument17 pagesLesson 1. Function: Tr. Kclyn TagayunKclynNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Unit Learning Objective 1Document15 pagesPolynomial Unit Learning Objective 1api-296658056No ratings yet
- GENMATH 11 - Q1 - W1 - Mod1Document30 pagesGENMATH 11 - Q1 - W1 - Mod1JEFFREY GALANZANo ratings yet
- Function-Operations 2Document33 pagesFunction-Operations 2api-276566085No ratings yet
- GenMath-11 Quarter1 Module1Document25 pagesGenMath-11 Quarter1 Module1Bruce GonzalvoNo ratings yet
- DLP GenMathDocument7 pagesDLP GenMathHyu Ed GallardoNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONDocument22 pagesFUNCTIONROSEMARIE CORTAVISTANo ratings yet
- Gen Math11 - Q1 - Mod12 - Inverse of One To One Functions - 08082020Document16 pagesGen Math11 - Q1 - Mod12 - Inverse of One To One Functions - 08082020Leo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- GenMath11 - Q1 - Mod3 - One To One and Inverse Function - v3Document24 pagesGenMath11 - Q1 - Mod3 - One To One and Inverse Function - v3Manelyn Taga0% (1)
- General Mathematics Q1 Module 7 FINALDocument19 pagesGeneral Mathematics Q1 Module 7 FINALRosette Ann GapolNo ratings yet
- As 1 EaasdfDocument18 pagesAs 1 EaasdfKiefer SioNo ratings yet
- A. Definition of A Function: Video Tutorial For Parts A, B, CDocument10 pagesA. Definition of A Function: Video Tutorial For Parts A, B, CmomathtchrNo ratings yet
- LP For Disabilities, Giftedness, TalentedDocument11 pagesLP For Disabilities, Giftedness, TalentedAlma Mae PutongNo ratings yet
- Calculus: Quarter 1-Self-Learning Activity Sheet (S-LAS) - 1b Evaluating FunctionsDocument25 pagesCalculus: Quarter 1-Self-Learning Activity Sheet (S-LAS) - 1b Evaluating FunctionsGerrylie GallardoNo ratings yet
- Share CHAPTER QUIZDocument2 pagesShare CHAPTER QUIZJay Em Kristel MengulloNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 Week 4 Module 9Document12 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 Week 4 Module 9Barez Fernandez ZacNo ratings yet
- Sci Bono Mathematics Module 1 3 Final PDFDocument120 pagesSci Bono Mathematics Module 1 3 Final PDFHector BanquezNo ratings yet
- Math 111 Midterm #2 Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesMath 111 Midterm #2 Practice ProblemsCassie ChenNo ratings yet
- GCSEAndIGCSEFM FunctionsDocument45 pagesGCSEAndIGCSEFM FunctionsSri Devi NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- Intro To FunctionDocument32 pagesIntro To FunctionMark Kirby De Las LlagasNo ratings yet
- Language 0f MathDocument57 pagesLanguage 0f MathChristian Dave Balasa100% (1)
- Department of Education: Mimaropa RegionDocument24 pagesDepartment of Education: Mimaropa RegionEinjhel Gaverielle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document17 pagesUnit 3api-341967669No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Note Packet MPLGDocument34 pagesUnit 5 Note Packet MPLGBenjie Sucnaan ManggobNo ratings yet
- Agoo Kiddie Special School High School Department San Antonio, Agoo, La Union S.Y 2020-2021 General Mathematics 11Document6 pagesAgoo Kiddie Special School High School Department San Antonio, Agoo, La Union S.Y 2020-2021 General Mathematics 11Gerica Esmeña PescasioNo ratings yet
- Revisiting Functions: Lesson DescriptionDocument11 pagesRevisiting Functions: Lesson DescriptionPrincess Joie RamosNo ratings yet
- GM - W1-4 (Activity)Document11 pagesGM - W1-4 (Activity)Jhezza Mae Coraza TeroNo ratings yet
- Week 1 GMDocument41 pagesWeek 1 GMJhanjhan BoniNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument54 pagesFunctionsLORENZO PALUMBONo ratings yet
- Reflective Journal Learning (Week 8: August 7-9, 2017)Document2 pagesReflective Journal Learning (Week 8: August 7-9, 2017)roselle0212No ratings yet
- 12x Lesson2 Ml4edDocument18 pages12x Lesson2 Ml4edPETERNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Function As ModelDocument4 pagesLesson 1 Function As ModelJOHN RANDEL ALCANTARANo ratings yet
- GenMath11 - Q1 - Mod26 - Domain and Range of Logarithmic Functions - 08082020Document16 pagesGenMath11 - Q1 - Mod26 - Domain and Range of Logarithmic Functions - 08082020Leo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 1 Finding Roots (30 Points)Document2 pages1 Finding Roots (30 Points)aniket patelNo ratings yet
- Function OperationsDocument27 pagesFunction OperationsYohannes AndualemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Functions Grade 11general MathDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Functions Grade 11general Mathabarramichelle14No ratings yet
- General Mathematics Q1W01Document11 pagesGeneral Mathematics Q1W01Loren Kingston MelendezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Comparative Anlysis ...Document21 pagesChapter 1 Comparative Anlysis ...Windel Q. BojosNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE Exam IN MEASURES OF CENTRAL LOCATIONDocument3 pagesSAMPLE Exam IN MEASURES OF CENTRAL LOCATIONWindel Q. BojosNo ratings yet
- Exponent ActivityDocument1 pageExponent ActivityWindel Q. BojosNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central LocationDocument1 pageMeasures of Central LocationWindel Q. BojosNo ratings yet
- Deciles & PercentilesDocument9 pagesDeciles & PercentilesWindel Q. BojosNo ratings yet
- QuartilesDocument11 pagesQuartilesWindel Q. BojosNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE Examination in ELEMENTARY STATDocument2 pagesSAMPLE Examination in ELEMENTARY STATWindel Q. BojosNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument2 pagesActivityWindel Q. BojosNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE Examination in Teaching Mathematics in The Primary GradesDocument3 pagesSAMPLE Examination in Teaching Mathematics in The Primary GradesWindel Q. BojosNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Inteaching Mathematics in The Primary GradesDocument2 pagesFinal Examination Inteaching Mathematics in The Primary GradesWindel Q. BojosNo ratings yet
- Number SentencesDocument1 pageNumber SentencesWindel Q. BojosNo ratings yet
- Report - Classifications of Assessment.Document4 pagesReport - Classifications of Assessment.jyNo ratings yet
- 13442-Article Text-68718-1-10-20220630Document11 pages13442-Article Text-68718-1-10-20220630Tasya LaseNo ratings yet
- اقتصاديات التعليم وأثرها في النمو والتنمية الاقتصادية والاجتماعية في دول الخليج العربيDocument18 pagesاقتصاديات التعليم وأثرها في النمو والتنمية الاقتصادية والاجتماعية في دول الخليج العربيLamiae KarroukNo ratings yet
- Addend AnalyticsDocument8 pagesAddend Analyticsadarsh tiwariNo ratings yet
- Sustainability and Economy - A Paradigm For Managing Entrepreneurship Towards Sustainable DevelopmentFDocument21 pagesSustainability and Economy - A Paradigm For Managing Entrepreneurship Towards Sustainable DevelopmentFArmando Tarupí MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Revised Cape TimetableDocument18 pagesRevised Cape TimetabledijojnayNo ratings yet
- Eksrhyky Usg: JK"V H Izks - KSFXDH Lalfkku Bykgkckn Iz KXJKT Bykgkckn &211004 HKKJRDocument2 pagesEksrhyky Usg: JK"V H Izks - KSFXDH Lalfkku Bykgkckn Iz KXJKT Bykgkckn &211004 HKKJRKrishna sahNo ratings yet
- Thomas H. Leahey: RHR SciencesDocument10 pagesThomas H. Leahey: RHR SciencesMáthé AdriennNo ratings yet
- Cultural Psych Module 1 Introduction To Indigenous PsychologyDocument2 pagesCultural Psych Module 1 Introduction To Indigenous PsychologyAlmira BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Practical ResearchDocument38 pagesChapter 5 Practical ResearchJan Carlo PandiNo ratings yet
- Recruitment of Teachers For Junior Secondary Schools For Interns and Permanent and PensionableDocument38 pagesRecruitment of Teachers For Junior Secondary Schools For Interns and Permanent and PensionablePeris KamangaNo ratings yet
- 476-Article Text-1989-1-10-20210227Document7 pages476-Article Text-1989-1-10-20210227ApreliaNo ratings yet
- Shri Madhwa Vadiraja Institute of Technology & Management: Vishwothama Nagar, Bantakal - 574 115, Udupi DistDocument50 pagesShri Madhwa Vadiraja Institute of Technology & Management: Vishwothama Nagar, Bantakal - 574 115, Udupi DistSiju V SomanNo ratings yet
- Spoken Discourse Aquino PDFDocument2 pagesSpoken Discourse Aquino PDFCebujano Chenee R.No ratings yet
- Models OF Disability: Medical Model & Social ModelDocument11 pagesModels OF Disability: Medical Model & Social ModelMARC VINCENT BALILINGNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Remedial Class On Students'Learning - LRDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Remedial Class On Students'Learning - LRruhani.han99No ratings yet
- HOTS QuestionsDocument3 pagesHOTS Questionsjoy macatingraoNo ratings yet
- Nature of GeographyDocument241 pagesNature of GeographyIndrajit PalNo ratings yet
- Guiding New Development in The Historic Core Case of Mumbai Metro at D.N. Road Station PrecinctDocument6 pagesGuiding New Development in The Historic Core Case of Mumbai Metro at D.N. Road Station PrecinctInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Terrence Farrell 5230 Mini Unit PlanDocument4 pagesTerrence Farrell 5230 Mini Unit Planapi-571243562No ratings yet
- SOE Lesson 1 INTRO TO SOCIOLOGY For TMD 20Document27 pagesSOE Lesson 1 INTRO TO SOCIOLOGY For TMD 20given kalukanguNo ratings yet
- Assignment #4Document2 pagesAssignment #4kel dataNo ratings yet
- CompReg 25AUGUST2020Document5,032 pagesCompReg 25AUGUST2020starNo ratings yet
- BIT 2319 Artificial Intelligence: Nyairo EvansonDocument56 pagesBIT 2319 Artificial Intelligence: Nyairo EvansonRuth LeleiNo ratings yet
- Architecture PresentationDocument28 pagesArchitecture PresentationpmcarqxnoogfbprtcfNo ratings yet
- M & E ToolsDocument28 pagesM & E ToolsIbrahim Mohamed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Criminal Justice - 2022-2023Document2 pagesCriminal Justice - 2022-2023Tara HamiltonNo ratings yet