Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acceleration
Uploaded by
Anjal GuptaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acceleration
Uploaded by
Anjal GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
NOTE
P H Y S I C S
KINEMATICS
ACCELERATION
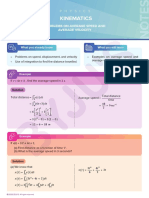
What you already know What you will learn
• Problems on average speed and • Instantaneous speed and velocity
average velocity • Acceleration
Distance to Speed to Velocity
Instantaneous speed
The rate of change of distance with respect to time, when the time interval is infinitesimally small,
is known as instantaneous speed.
Let x be the distance travelled by the particle that varies with time t as,
x = f (t)
Let v be the instantaneous speed
dx
x + dx
0 t t + dt x
Let dx be the distance travelled by the particle in time interval t to t + dt
If dt is a very small time interval, then v can be taken as constant over distance dx.
Therefore,
Distance = Speed × Time
dx = v × dt
Hence,
dx
v (t ) =
dt
Example
The displacement of a particle is given by x = 2t2 + 4t, where x is in meters.
(a) Find the average speed in 2 s. (b) Find the instantaneous speed at 2 s.
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
02
Solution
(a) Distance travelled by the particle in time t is x = (2t2 + 4t) m
Given, t = 2 s
⇒ x = 2 × 22 + 4 × 2
⇒ x = 8 + 8 = 16 m
Therefore, the total distance travelled in 2 s is 16 m.
Total distance
Average speed =
Total time
16 m
⇒ Average speed = = 8 ms -1
2s
dx
(b) Instantaneous speed = v ( t ) =
dt
Given, x = ( 2t + 4t ) m
2
d
⇒ v (t ) =
dt
( 2t 2 + 4t )
⇒ v ( t ) = ( 4t + 4 ) ms -1
At givent t = 2 s, the instantaneous velocity is
v ( 2) = 4 × 2 + 4
v ( 2) = 8 + 4 = 12 ms -1
Example
The displacement of a particle is given by x = (3t2 + 2t + 2) m. Find the following:
(a) Velocity as a function of time t. (b) Average velocity in 4 s.
Solution
dx
(a) v ( t ) = (b) t=0s t=4s
dt
x (m)
Given , x = 3t 2 + 2t + 2 0 2 58
56 m
d x = f (t)
⇒ v ( t ) = (3t 2 + 2t + 2)
dt
Displacement of the particle at 0 s is
⇒ v ( t ) = ( 6t + 2) ms -1
x (0) = 3 × (0) + 2 × 0 + 2
3
x (0) = 2m ........ ( i )
Displacement of the particle at 4 s is
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
03
x ( 4 ) = 3 × 42 + 2 × 4 + 2
x ( 4 ) = 58 m
Displacement of the particle between t = 0 s and t = 4 s
= (Displacement of the particle at 4 s) - (Displacement of the particle at 0 s)
= x ( 4 ) - x (0)
From ( i ) and ( ii ) ,
= 58 m - 2 m = 56 m
Therefore, displacement of the particle in 4 s is 56 m
Total displacement
Average velocity =
Total time
56
= = 14 ms -1
4
Example
The displacement of a particle is given by x = (t2 - 6t + 3) m. Find the following:
(a) Velocity as a function of time t. (b) Average speed in 5 s.
Solution
(a) Velocity of the particle is
dx
v (t ) =
dt
Given, x = t 2 - 6t + 3
d
v ( t ) = ( t 2 - 6t + 3)
dt
v ( t ) = ( 2t - 6 ) ms -1
(b) Displacement of the particle at t = 0 s is of the particle will be zero.
x (0) = (0) - 6 × 0 + 3
2
Now,
x (0) = 3 m ...... ( i ) v(t) = (2t - 6) ms-1
Thus,
Displacement of the particle at t = 5 s is
v (t ) = 0
x (5) = 52 - 6 × 5 + 3
⇒ 2t - 6 = 0
x (5) = -2 m ......(ii)
⇒t = 3 s
Since x (5) is negative, this means that the
particle must have turned between t = 0 s and Therefore, the velocity of the particle is zero
t = 5 s. At the time of turning back, the velocity at t = 3 s.
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
04
t=3s t=5s t=0s
x (m)
-6 -2 0 3 x = f (t)
As shown in the figure, the particle moved in a negative x - direction between t = 0 s and t = 3 s.
After t = 3 s, the particle turned back and started moving in the positive direction.
Displacement of the particle at t = 3 s is
x (3) = 32 - 6 × 3 + 3
x ( 3) = - 6 m ........ ( iii )
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s and t = 3 s is
= |(Displacement of the particle at t = 3 s) - (Displacement of particle at t = 0 s)|
From (i) and (iii)
= x ( 3) - x ( 0 )
=-6 -3
= 9m ........(iv)
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 3 s and t = 5 s is
= |(Displacement of the particle at t = 5 s) - (Displacement of particle at t = 3 s)|
From (ii) and (iii)
= x ( 5) - x ( 3)
= -2 - ( -6 )
= 4m .......(v)
Total distance travelled by the particle is
= (Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s and t = 3 s) + (Distance travelled by the
particle between t = 3 s and t = 5 s)
From (iv) and (v),
= 9m + 4m = 13m .....(vi)
Total distance
Average speed =
Total time
From ( vi) ,
13
Average speed = ms -1
5
BOARDS
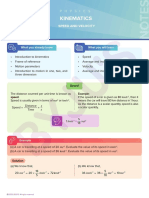
Acceleration
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect to time.
SI unit : ms-2
Average acceleration Instantaneous acceleration
The rate of change of velocity averaged The rate of change of velocity with respect to time
over a defined time interval when the time interval is infinitesimally small.
v f - v i ∆v ∆v dv
a= = a = lim =
∆t →0 ∆t
t f - t i ∆t dt
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
05
Acceleration of the particle is
dv
a (t ) =
dt
1. On differentiating velocity v(t), with v ( t ) = (to
Givenrespect 2
+ t ) we
2ttime, ms -1get acceleration.
d ( 2t 2 + t )
2. On integrating acceleration a(t),a (with
t ) =respect to time, we get velocity.
dt
d d
a (t ) = 2 (t2 ) + (t )
dt dt
Example a ( t ) = ( 4t + 1 ) ms -2
....(i)
At given t = 2 s
Velocity of particle in rectilinear motion is given
Fromas v = (2t( i2)+, t) ms-1. Find the following:
equation
(a) Acceleration at 2 s. (b) Average acceleration in 2 s.
a ( 2) = 4 × 2 + 1
a ( 2) = 9 ms-2
Solution Therefore, acceleration of the particle at t = 2 s is 9 ms-2
∆v v f - v i
(a) Acceleration of the particle is (b) Average acceleration = =
∆t tf - ti
dv
a (t ) = v ( t ) = ( 2t 2 + t ) ms -1
dt
Given v ( t ) = ( 2t 2 + t ) ms -1 v f = v ( 2) = 2 × 22 + 2 = 10 ms -1
d ( 2t 2 + t ) v i = v ( 0) = 2 × 02 + 0 = 0 ms -1
a (t ) = t f = 2 s, t i = 0 s
dt
d 2 d 10 - 0
a (t ) = 2
dt
( t ) + (t )
dt
Average acceleration =
2-0
= 5 ms -2
a ( t ) = ( 4t + 1 ) ms -2
....(i)
At given t = 2 s
From equation ( i ) ,
a ( 2) = 4 × 2 + 1
a ( 2) = 9 ms-2
Therefore, acceleration of the particle at t = 2 s is 9 ms-2
∆v v f - v i
Average acceleration = =
∆t tf - ti
v ( t ) = ( 2t 2 + t ) ms -1
v f = v ( 2) = 2 Displacement [x(t)]
× 22 + 2 = 10 ms -1 Displacement [x(t)]
d x (t)
v i = v ( 0 ) = 2 × 02 + 0 = 0 ms -1
dt ∫ v (t) dt
t f = 2 s, t i = 0 s
Velocity [v(t)] Velocity [v(t)]
10 - 0
Average acceleration = d v (t)= 5 ms -2
2-0
dt ∫ a (t) dt
Acceleration [a(t)] Acceleration [a(t)]
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
You might also like
- 3 Manacsa&Tan 2012 Strong Republic SidetrackedDocument41 pages3 Manacsa&Tan 2012 Strong Republic SidetrackedGil Osila JaradalNo ratings yet
- MINTZBERGDocument32 pagesMINTZBERGgeezee10004464100% (2)
- MKTG 2126 - Assignment 3Document2 pagesMKTG 2126 - Assignment 3omar mcintoshNo ratings yet
- Problems On Average Speed and Average VelocityDocument13 pagesProblems On Average Speed and Average VelocityAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- IntegraDocument1 pageIntegrapradeep707rediffmailNo ratings yet
- Deniz Korbaltafizik ProjeDocument5 pagesDeniz Korbaltafizik ProjeTaha GümüşNo ratings yet
- Motion in One DimensionDocument7 pagesMotion in One DimensionDiego Escobar MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Arc Length and Surface Area Using Parametric EquationsDocument27 pagesCalculating Arc Length and Surface Area Using Parametric EquationsAli ElbasryNo ratings yet
- PHYS Problem Set 1Document10 pagesPHYS Problem Set 1khaizanjohnNo ratings yet
- Dynamics GLA-2a Sept2017Document27 pagesDynamics GLA-2a Sept2017Izzone PhysireNo ratings yet
- Dynamics GLA 2aDocument9 pagesDynamics GLA 2aFarid AimanNo ratings yet
- MahmutprojeDocument6 pagesMahmutprojeTaha GümüşNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University Student Activity SheetDocument3 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University Student Activity SheetShynne Kylla SarigumbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 PDFDocument13 pagesChapter2 PDFnur antashaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - KinematicsDocument15 pagesWeek 1 - Kinematicsデーナ(ヤギ)No ratings yet
- Mechanics I (APPM1028A and APPM1029A)Document5 pagesMechanics I (APPM1028A and APPM1029A)Thembisile ThusiNo ratings yet
- Exercises - Week 3: Escuela: Ing. Ambiental/Informática Curso: Análisis MatemáticoDocument4 pagesExercises - Week 3: Escuela: Ing. Ambiental/Informática Curso: Análisis MatemáticoMaker 1900No ratings yet
- MIT8 01F16 Chapter4.3Document6 pagesMIT8 01F16 Chapter4.3Channabasava YadramiNo ratings yet
- Full File at Https://testbanku - eu/Solution-Manual-for-Engineering-Mechanics-Dynamics-1st-Edition-by-Soutas-LittleDocument88 pagesFull File at Https://testbanku - eu/Solution-Manual-for-Engineering-Mechanics-Dynamics-1st-Edition-by-Soutas-LittleJersonFabianMaldonadoMorenoNo ratings yet
- Calculus I - Solutions #4Document10 pagesCalculus I - Solutions #4anhducgmc2005No ratings yet
- Kinematics of Rectilinear MotionDocument20 pagesKinematics of Rectilinear Motionnithink100No ratings yet
- Parmatric Equations CHP Assessment C4Document5 pagesParmatric Equations CHP Assessment C4Arthur LongwardNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Take Home Quiz 3Document5 pagesAnswer Key For Take Home Quiz 3Nexty GamingNo ratings yet
- M2.2 KinematicsDocument26 pagesM2.2 KinematicsThomas GuoNo ratings yet
- Cet c599 Mec Apl Ft1 Movrect 1d Exe2Document1 pageCet c599 Mec Apl Ft1 Movrect 1d Exe2Francisco CostaNo ratings yet
- Moving Along a Curve with Specified Speed Using ReparameterizationDocument13 pagesMoving Along a Curve with Specified Speed Using Reparameterizationzhaodong.liangNo ratings yet
- 4P Cartesian CoordinatesDocument14 pages4P Cartesian CoordinatesMark Kenneth BaldoqueNo ratings yet
- Equations of MotionDocument6 pagesEquations of MotionAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Kinematics Applications - Problem SetsDocument5 pagesCalculus - Kinematics Applications - Problem SetswelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Applications of DerivativesDocument53 pagesApplications of Derivativeshiman123No ratings yet
- Wa0035.Document14 pagesWa0035.manu patankarNo ratings yet
- IGNOU Old Question PaperDocument8 pagesIGNOU Old Question PaperMohd PkNo ratings yet
- GW 101217 Sol PDFDocument6 pagesGW 101217 Sol PDFChristineNo ratings yet
- 3 22 PoissonDocument13 pages3 22 PoissonShaukat ShaheeNo ratings yet
- Oscillations Worksheet SolutionsDocument4 pagesOscillations Worksheet SolutionsTinboyNo ratings yet
- Mechanics I (APPM1028A and APPM1029A)Document12 pagesMechanics I (APPM1028A and APPM1029A)Nirvana BeannieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2Fahad AliNo ratings yet
- Applied MechanicsDocument92 pagesApplied MechanicsAbhishek JoshiNo ratings yet
- CH 6-Applications of DerivativesDocument53 pagesCH 6-Applications of DerivativesAnshuman Singh100% (1)
- NCERT Books For Class 12 Maths Chapter 6Document53 pagesNCERT Books For Class 12 Maths Chapter 6Ashutosh GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lemh 106Document53 pagesLemh 106Siddharth BangaNo ratings yet
- MATH 100 Final Solutions 2022Document24 pagesMATH 100 Final Solutions 20223389andyNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1: GivenDocument14 pagesProblem Set 1: GivenMahid DandamunNo ratings yet
- IB-13rate Measure 63-65Document2 pagesIB-13rate Measure 63-65eamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- Application of DerivativesDocument40 pagesApplication of DerivativesOm PrakashNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 Motion in SpaceDocument7 pagesMODULE 4 Motion in SpaceMASHITAH MAISARAH ZAILINo ratings yet
- Integrating Along A Curve: Distance Traveled and LengthDocument2 pagesIntegrating Along A Curve: Distance Traveled and LengthDavid HumeNo ratings yet
- Section - B: Multiple Choice Type Questions: 1. Answer (1, 3, 4) 2. Answer (2, 3, 4)Document22 pagesSection - B: Multiple Choice Type Questions: 1. Answer (1, 3, 4) 2. Answer (2, 3, 4)sarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Unit-4, Vector Differential CalculusDocument31 pagesUnit-4, Vector Differential CalculusSujatha VivekNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line - DPP-05 (Of Lec-08) - Arjuna NEET 2024Document3 pagesMotion in A Straight Line - DPP-05 (Of Lec-08) - Arjuna NEET 2024kumar ashvikNo ratings yet
- M3S14/M4S14 (SOLUTIONS) Survival Analysis and Actuarial ApplicationsDocument13 pagesM3S14/M4S14 (SOLUTIONS) Survival Analysis and Actuarial ApplicationsVen koyNo ratings yet
- Application of DerivativesDocument59 pagesApplication of DerivativesTarun KumarNo ratings yet
- My Notes On Faber1983Document25 pagesMy Notes On Faber1983Miguel Angel GiménezNo ratings yet
- Position: + 3.00, Where X Is in Meters and T Is in Seconds. DetermineDocument5 pagesPosition: + 3.00, Where X Is in Meters and T Is in Seconds. Determineanggian anggraeniNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1: PHY2048 Discussion-Fall 09Document2 pagesQuiz 1: PHY2048 Discussion-Fall 09Clement CharlesNo ratings yet
- 03 KinematicsDocument39 pages03 KinematicsOlabode EgbinolaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Particle Motion 40Document20 pagesKinematics Particle Motion 40Omar Khairy Abdul-Hamid RostomNo ratings yet
- Math IA On The Brachistochrone ProblemDocument16 pagesMath IA On The Brachistochrone ProblemGowri Kashyap100% (2)
- Problem 3.10.46 Related RatesDocument2 pagesProblem 3.10.46 Related RatesAmmiel BuisingNo ratings yet
- Kinematics in One Dimension: X V T at V V + at X V T+ atDocument67 pagesKinematics in One Dimension: X V T at V V + at X V T+ atHel JustNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Laws of VectorsDocument5 pagesLaws of VectorsAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- V-T Curve and IntegrationDocument5 pagesV-T Curve and IntegrationAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Speed and VelocityDocument9 pagesSpeed and VelocityAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Vectors..Document7 pagesIntroduction To Vectors..Anjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Numericals On Equations of MotionDocument8 pagesNumericals On Equations of MotionAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Motion Under Gravity.Document8 pagesMotion Under Gravity.Anjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To KinematicsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To KinematicsAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Equations of MotionDocument6 pagesEquations of MotionAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- If Sentences Type 1 First Type Conditionals Grammar Drills - 119169Document2 pagesIf Sentences Type 1 First Type Conditionals Grammar Drills - 119169Ivanciu DanNo ratings yet
- Gamble V Tyson MSJDocument41 pagesGamble V Tyson MSJTHROnlineNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/preparation and of The Company/undertakingDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/preparation and of The Company/undertakingBalasubramanian AnanthNo ratings yet
- Little ThingsDocument3 pagesLittle ThingszwartwerkerijNo ratings yet
- Armv8-A Instruction Set ArchitectureDocument39 pagesArmv8-A Instruction Set ArchitectureraygarnerNo ratings yet
- Engr2227 Apr03Document10 pagesEngr2227 Apr03Mohamed AlqaisiNo ratings yet
- A Rail-To-Rail Constant Gain Buffered Op-Amp For Real Time Video ApplicationsDocument8 pagesA Rail-To-Rail Constant Gain Buffered Op-Amp For Real Time Video Applicationskvpk_vlsiNo ratings yet
- Rose Jean AlvarezDocument15 pagesRose Jean AlvarezMika Ela Pantaleon Doria100% (1)
- Business Judgment Rule and Directors' Duty to Inform in Smith v Van GorkomDocument1 pageBusiness Judgment Rule and Directors' Duty to Inform in Smith v Van GorkomDorothy ParkerNo ratings yet
- St. Francis de Sales Sr. Sec. School, Gangapur CityDocument12 pagesSt. Francis de Sales Sr. Sec. School, Gangapur CityArtificial GammerNo ratings yet
- 7 - NIBL - G.R. No. L-15380 Wan V Kim - DigestDocument1 page7 - NIBL - G.R. No. L-15380 Wan V Kim - DigestOjie SantillanNo ratings yet
- Reporte Corporativo de Louis Dreyfus Company (LDC)Document21 pagesReporte Corporativo de Louis Dreyfus Company (LDC)OjoPúblico Periodismo de InvestigaciónNo ratings yet
- Coffee TestDocument6 pagesCoffee TestAmit Satyen RaviNo ratings yet
- SecASC - M02 - Azure Security Center Setup and ConfigurationDocument53 pagesSecASC - M02 - Azure Security Center Setup and ConfigurationGustavo WehdekingNo ratings yet
- D41P-6 Kepb002901Document387 pagesD41P-6 Kepb002901LuzioNeto100% (1)
- Transformers Obj Questions PDFDocument8 pagesTransformers Obj Questions PDFphaniputta100% (2)
- Year 12 Holiday Homework Term 3Document4 pagesYear 12 Holiday Homework Term 3Lucas GauciNo ratings yet
- Atlas Ci30002Tier-PropanDocument3 pagesAtlas Ci30002Tier-PropanMarkus JeremiaNo ratings yet
- Winter's Bracing Approach RevisitedDocument5 pagesWinter's Bracing Approach RevisitedJitendraNo ratings yet
- Huang V Tesla State of Calif 20190430Document20 pagesHuang V Tesla State of Calif 20190430jonathan_skillings100% (1)
- Mechanism of Heat TransferDocument31 pagesMechanism of Heat Transferedna padreNo ratings yet
- IBM TS2900 Tape Autoloader RBDocument11 pagesIBM TS2900 Tape Autoloader RBLeonNo ratings yet
- Summative Test For Quadratic Equations2Document2 pagesSummative Test For Quadratic Equations2AsmiraMangontra0% (1)
- Contemporary Issue in StrategyDocument13 pagesContemporary Issue in Strategypatrick wafulaNo ratings yet
- 2 Both Texts, and Then Answer Question 1 On The Question Paper. Text A: Esports in The Olympic Games?Document2 pages2 Both Texts, and Then Answer Question 1 On The Question Paper. Text A: Esports in The Olympic Games?...No ratings yet
- Lodha GroupDocument2 pagesLodha Groupmanish_ggiNo ratings yet
- Su1 Assessment U01Document14 pagesSu1 Assessment U01Cristian Seas ArceNo ratings yet