Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problems On Average Speed and Average Velocity
Uploaded by
Anjal GuptaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problems On Average Speed and Average Velocity
Uploaded by
Anjal GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
01
NOTE
P H Y S I C S
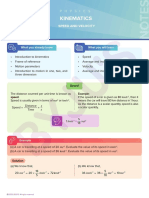
KINEMATICS
PROBLEMS ON AVERAGE SPEED AND
AVERAGE VELOCITY
What you already know What you will learn
• Problems on speed, displacement, and velocity • Examples on average speed and
• Use of integration to find the distance travelled average velocity
Example
If v = 6t + 3 , find the average speed in 2 s.
Solution
t
Total distance
Total distance = ∫ v (t ) dt
0
Average speed =
time
2
= ∫ (6t + 3) dt
0
18
= = 9 ms −1
2 2 2
t2 t
= 6 + 3
2 0 1 0
( )
= 3 22 − 0 + 3 ( 2 − 0)
= 12 + 6 = 18 m
Example
If v(t) = 3t3 + 4t + 2,
(a) Find distance as a function of time ‘t’.
(b) What is the average speed in 3 seconds?
Solution
(a) We know that 3t 4 4t 2
t x (t ) = + + 2t
x (t ) = ∫ v (t ) dt 4 2
0
∫ (3t )
t
x ( t=
) 3
+ 4t + 2 dt
0
t t t
x ( t ) = 3∫ t 3dt + 4∫ tdt + 2∫ dt
0 0 0
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
02
(b) Total distance in 3 s is Total distance
Average speed =
3 × ( 3)
4
4 × ( 3)
2 Total time
x ( 3)
= + + 2×3
4 2 339
4
x ( 3) =
243 + 96 =
4 3
339 339 113
x ( 3) = m = = ms −1
4 4×3 4
Example
If v = (4 – 2t) ms–1, find the average speed and average velocity in 5 s.
Solution
Let,
Initial position of the particle be xi
Final position of the particle be xf
We know that,
t
x f − xi =∫ v (t ) dt
0
t
x f − x=
i ∫ ( 4 − 2t ) dt
0
x f − x i = 4t − t 2 .... (i)
Initial position of the particle is origin, therefore xi = 0
So, final position of the particle at any time t is
From (i)
xf = 4t – t2 .... (ii)
Particle velocity is zero when v(t) = 0
Thus,
v(t) = 4 – 2t = 0
⇒t=2s
Therefore, velocity of particle is zero at t = 2 s.
x = –5 m 0 x=4m
t = 5 s, x = –5 m, v = –6 ms–1 x
Particle moves in a positive x direction between t = 0 s to t = 2 s. At t = 2 s, the particle turns back
and starts moving in a negative x direction between t = 2 s to t = 5 s.
Position of the particle at t = 2 s is
From (ii)
xf = 4t – t2
xf = 4 × 2 – 22
xf = 4 m .... (iii)
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
03
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s to t = 2 s is
= |(Position of particle at t = 2 s) – (Position of particle at t = 0 s)|
= |4 – 0| = 4 m .... (iv)
Position of the particle at t = 5 s is
From (ii)
xf = 4t – t2
xf = 4 × 5 – 52
xf = –5 m .... (v)
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 2 s to t = 5 s is
= |(Position of particle at t = 5 s) – (Position of particle at t = 2 s)|
From (v) and (iii),
= |–5 – 4| = 9 m .... (vi)
Total distance travelled by the particle = (Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s to t = 2 s)
+ (Distance travelled by the particle between t = 2 s to t = 5 s)
From (iv) and (vi),
Total distance travelled by particle = 9 m + 4 m = 13 m
Total distance
Average speed =
Total time
13
= ms −1
5
Total displacement in time t = 0 s to t = 5 s is xf – xi
xf – xi = 4t – t2
Given, t = 5 s
⇒ xf – xi = 4 × 5 – 52
⇒ xf – xi = –5 m
Total displacement
Average veocity =
Total time
−5
=
5
= − 1 ms −1
Example
If v(t) = (3t – 9) ms–1, find the average speed and average velocity in 4 s.
Solution
Let,
Initial position of the particle be xi
Final position of the particle be xf
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
04
We know that,
t
∫ v (t ) dt
x f − xi =
0
t
x f − x=
i ∫ (3t − 9) dt
0
3t 2
x f − x i= − 9t .... (i)
2
Initial position of the particle is the origin, therefore xi = 0
So, final position of the particle at any time t is
From (i)
3t 2
xf
= − 9t .... (ii)
2
Velocity of the particle is zero when v(t) = 0
Thus,
v(t) = (3t – 9) = 0
⇒t=3s
Therefore, at t = 3 s velocity of the particle is zero.
x = –13.5 m 0
x = –12 m
x
t = 4 s, x = –12 m, v = 3 ms–1
Particle moves in negative x direction between t = 0 s to t = 3 s. At t = 3 s, the particle turns back
and starts moving in positive x direction.
Position of the particle at t = 3 s is
From (ii),
3t 2
xf
= − 9t
2
3 × 32
xf
= −9 ×3
2
−27
xf = = − 13.5 m .... (iii)
2
Therefore,
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s to t = 3 s is
= |(Position of particle at t = 3 s) – (Position of particle at t = 0 s)|
From (iii),
= |–13.5 – 0|
= 13.5 m .... (iv)
Position of the particle at t = 4 s is
From (ii),
3t 2
xf
= − 9t
2
3 × 42
xf = − 9 × 4 =− 12 m .... (v)
2
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
05
Therefore,
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 3 s to t = 4 s is
= |(Position of particle at t = 4 s) – (Position of particle at t = 3 s)|
From (v) and (iii),
= |– 12 – (–13.5)|
= 1.5 m .... (vi)
Total distance travelled by the particle = (Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s to t = 3 s)
+ (Distance travelled by the particle between t = 3 s to t = 4 s)
From (vi) and (iv),
Total distance travelled by particle = 13.5 + 1.5 = 15 m
Total distance
Average Speed =
Total time
15
= ms −1
4
Total displacement in time t = 0 s to t = 4 s is xf – xi
3t 2
x f − x i= − 9t
2
Given t = 4 s
3 × 42
⇒ x f −=
xi −9×4
2
⇒ x f − xi =24 − 36 =− 12 m
Total displacement
Average Veocity =
Total time
−12
=
4
= − 3 ms −1
Example
If v = (t – 2) ms–1, find the average speed and average velocity in 3 s.
Solution
Let,
Initial position of the particle be xi
Final position of the particle be xf
We know that,
t
x f − xi =∫ v (t ) dt
0
t
x f − x=i ∫ (t − 2) dt
0
t2
x f − xi = − 2t .... (i)
2
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
06
Initial position of the particle is the origin, therefore xi = 0
So, final position of the particle at any time t is
From (i)
t2
x=
f − 2t .... (ii)
2
Velocity of the particle is zero when v(t) = 0
Thus,
v(t) = (t – 2) = 0
⇒t=2s
Therefore, at t = 2 s velocity of the particle is zero.
x = –2 m 0
x = –1.5 m
x
t = 3 s, x = –1.5 m, v = 1 ms–1
Particle moves in negative x direction between t = 0 s to t = 2 s. At t = 2 s, the particle turns back
and starts moving in positive x direction.
Position of the particle at t = 2 s is
From (ii),
t2
x=f − 2t
2
22
x f= − 2×2
2
xf =2−4= −2 m .... (iii)
Therefore,
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s to t = 2 s is
= |(Position of particle at t = 2 s) – (Position of particle at t = 0 s)|
From (iii),
= |–2 – 0|
= 2 m .... (iv)
Position of the particle at t = 3 s is
From (ii),
t2
x=f − 2t
2
32
x f = − 2 × 3 =− 1.5 m .... (v)
2
Therefore,
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 2 s to t = 3 s is
= |(Position of particle at t = 3 s) – (Position of particle at t = 2 s)|
From (iii) and (v),
= |– 1.5 – (–2)|
= 0.5 m .... (vi)
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
07
Total distance travelled by the particle = (Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s to t = 2 s)
+ (Distance travelled by the particle between t = 2 s to t = 3 s)
From (iv) and (vi),
Total distance travelled by particle = 2 + 0.5 = 2.5 m
Total distance
Average speed =
Total time
2.5
= ms −1
3
Total displacement in time t = 0 s to t = 3 s is xf – xi
From (i),
t2
x f − xi = − 2t
2
Given t = 3 s
32
⇒ x f − xi = − 2×3
2
9
⇒ x f − x i = − 6 =− 1.5 m
2
Total displacement
Average veocity =
Total time
−1.5
=
3
= − 0.5 ms −1
Example
If v(t) = (6 – 2t) ms–1, find the average speed and average velocity in 10 s.
Solution
Let,
Initial position of the particle be xi
Final position of the particle be xf
We know that,
t
∫ v (t ) dt
x f − xi =
0
t
x f − x i= ∫ (6 − 2t ) dt
0
x f − xi = 6t − t 2 .... (i)
Initial position of the particle is origin, therefore xi = 0
So, final position of the particle at any time t is
From (i)
xf = 6t – t2 .... (ii)
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
08
Particle velocity is zero when v(t) = 0
Thus,
v(t) = (6 – 2t) = 0
⇒ (6 – 2t) = 0
⇒t=3s
Therefore, at t = 3 s velocity of particle is zero.
x = –40 m 0 x=9m
x
t = 5 s, x = –40 m, v = –14 ms–1
Particle moves in a positive x direction between t = 0 s to t = 3 s. At t = 3 s, the particle turns back
and starts moving in the opposite direction.
Position of the particle at t = 3 s is
From (ii)
xf = 6t – t2
xf = 6 × 3 – 32
xf = 18 – 9 = 9 m .... (iii)
Therefore,
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s to t = 3 s is
= |(Position of particle at t = 3 s) – (Position of particle at t = 0 s)|
= |9 – 0|
= 9 m .... (iv)
Position of the particle at t = 10 s is
From (ii)
xf = 6t – t2
xf = 6 × 10 – 102
xf = –40 m .... (v)
Therefore,
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 3 s to t = 10 s is
= |(Position of particle at t = 10 s) – (Position of particle at t = 3 s)|
From (v) and (iii),
= |– 40 – 9)| = 49 m .... (vi)
Total distance travelled by the particle = (Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s to t = 3 s)
+ (Distance travelled by the particle between t = 3 s to t = 10 s)
From (vi) and (iv),
Total distance travelled by particle = 49 m + 9 m = 58 m
Total distance
Average speed =
Total time
58
= ms −1
10
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
09
Total displacement in time t = 0 s to t = 10 s is xf – xi
xf – xi = 6t – t2
Given, t = 10 s
⇒ xf – xi = 6 × 10 – 102
⇒ xf – xi = –40 m
Total displacement
Average veocity =
Total time
−40
=
10
= − 4 ms −1
Example
If v = t2 – 2t, find the average speed and average velocity in 4 s.
Solution
Let,
Initial position of the particle be xi
Final position of the particle be xf
We know that,
t
∫ v (t ) dt
x f − xi =
0
∫ (t )
t
x f − x=i 2
− 2t dt
0
t3 .... (i)
x f − xi = − t2
3
Initial position of the particle is the origin, therefore xi = 0
So, final position of the particle at any time t is
From (i)
t3
x=f − t2 .... (ii)
3
Velocity of the particle is zero when v(t) = 0
Thus,
v(t) = t2 – 2t = 0
⇒ t (t – 2) = 2 s
⇒ t = 0 s and t = 2 s
Therefore, at t = 0 s and t = 2 s velocity of the particle is zero.
4 16
x=– m x= m
3 0 3
x
16
t = 4 s, x = m, v = 8 ms–1
3
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
10
Particle moves in negative x direction between t = 0 s to t = 2 s. At t = 2 s, the particle turns back
and starts moving in positive x direction.
Position of the particle at t = 2 s is
From (ii),
23
xf
= − 22
3
8 4
xf = − 4 = − m .... (iii)
3 3
Therefore,
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s to t = 2 s is
= |(Position of particle at t = 2 s) – (Position of particle at t = 0 s)|
From (iii),
4
=− −0
3
4
= m .... (iv)
3
Position of the particle at t = 4 s is
From (ii),
t3
x=f − t2
3
43
xf
= − 42
3
16
xf = m .... (v)
3
Therefore,
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 2 s to t = 4 s is
= |(Position of particle at t = 4 s) – (Position of particle at t = 2 s)|
From (v) and (iii),
16 4
= − −
3 3
20
= m .... (vi)
3
Total distance travelled by the particle = (Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s to t = 2 s)
+ (Distance travelled by the particle between t = 2 s to t = 4 s)
From (iv) and (vi),
4 20
Total distance travelled by particle = + = 8m
3 3
Total distance
Average speed =
Total time
8
= = 2 ms −1
4
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
11
Total displacement in time t = 0 s to t = 4 s is xf – xi
From (i),
t3
x f − xi = − t2
3
Given t = 4 s
43
⇒ x f − xi = − 42
3
16
⇒ x f − xi = m
3
Total displacement
Average veocity =
Total time
16
=
3× 4
4
= ms −1
3
Example
If v(t) = t2 – 5t + 6, find the average speed and average velocity in 5 s.
BOARDS NEET
Solution
Let,
Initial position of the particle be xi
Final position of the particle be xf
We know that,
t
∫ v (t ) dt
x f − xi =
0
∫ (t )
t
x f − x=i 2
− 5t + 6 dt
0
t 3 5t 2
x f − xi = − + 6t .... (i)
3 2
Initial position of the particle is origin, therefore xi = 0
So, final position of the particle at any time t is
From (i)
t 3 5t 2
xf = − + 6t .... (ii)
3 2
Velocity of the particle is zero when v(t) = 0
Thus,
t2 – 5t + 6 = 0
⇒ (t – 2) (t – 3) = 0
⇒ t = 2 s and t = 3 s
Therefore, at t = 2 s and t = 3 s velocity of the particle is zero.
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
12
14
x= m
3
0
x
9 55
x=0m m x= x= m
2 6
55
t = 5 s, x = m, v = 6 ms–1
6
Particle moves in a forward positive x direction between t = 0 s and t = 2 s. At t = 2 s, the particle
turns back and moves in the negative x direction. At t = 3 s, the particle again turns back and moves
in a forward positive x direction.
Position of the particle at t = 2 s is
From (ii),
( 2) 5 ( 2)
3 2
xf = − + 6 ( 2)
3 2
8 20
xf = − + 12
3 2
14
xf = m .... (iii)
3
Position of the particle at t = 3 s is
From (ii),
( 3) 5 ( 3)
3 2
xf = − + 6 ( 3)
3 2
27 45
xf = − + 18
3 2
9
xf = m .... (iv)
2
Position of the particle at t = 5 s is
From (ii),
( 5) 5 ( 5)
3 2
xf = − + 6 ( 5)
3 2
125 125
xf = − + 30
3 2
55
xf = m .... (v)
6
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s to t = 2 s is
= |(Position of particle at t = 2 s) – (Position of particle at t = 0 s)|
From (iii),
14
= −0
3
14 .... (vi)
= m
3
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
13
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 2 s to t = 3 s is
= |(Position of particle at t = 3 s) – (Position of particle at t = 2 s)|
From (iii) and (iv),
9 14
= −
2 3
1
= m .... (vii)
6
Distance travelled by the particle between t = 3 s to t = 5 s is
= |(Position of particle at t = 5 s) – (Position of particle at t = 3 s)|
From (v) and (iv),
55 9
= −
6 2
14
= m .... (vii)
3
Total distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s and t = 5 s is = (Distance travelled by the
particle between t = 0 s to t = 2 s) + (Distance travelled by the particle between t = 2 s to t = 3 s) +
(Distance travelled by the particle between t = 3 s to t = 5 s)
14 1 14
= + +
3 6 3
57
= m .... (viii)
6
Total displacement in time t = 0 s to t = 5 s is xf – xi
From (ii),
t 3 5t 2
⇒ x f − xi = − + 6t
3 2
( 5) 5 ( 5)
3 2
⇒ x f − x=i − + 6 ( 5)
3 2
125 125 55
⇒ x f − x=i − + 30= m .... (ix)
3 2 6
Total distance travelled
Average speed =
Total time
From ( viii ) ,
57
6 57
= =
Average speed ms −1
5 30
Total displacement
Average velocity =
Total time
From ( ix ) ,
55
6 11
= =
Average speed ms −1
5 6
© 2020, BYJU'S. All rights reserved
You might also like
- M2.2 KinematicsDocument26 pagesM2.2 KinematicsThomas GuoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AccelerationDocument5 pagesAccelerationAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Parmatric Equations CHP Assessment C4Document5 pagesParmatric Equations CHP Assessment C4Arthur LongwardNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions: Terry Lee Advanced MathematicsDocument3 pagesPractice Questions: Terry Lee Advanced MathematicsEren SevinceNo ratings yet
- MATH 100 Final Solutions 2022Document24 pagesMATH 100 Final Solutions 20223389andyNo ratings yet
- Cet c599 Mec Apl Ft1 Movrect 1d Exe2Document1 pageCet c599 Mec Apl Ft1 Movrect 1d Exe2Francisco CostaNo ratings yet
- SR Elite, Aiims S60, Neet MPL, LTC - Ic Grand Test - 2 Key & Sol - 20-04-19Document5 pagesSR Elite, Aiims S60, Neet MPL, LTC - Ic Grand Test - 2 Key & Sol - 20-04-19Ayan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Deniz Korbaltafizik ProjeDocument5 pagesDeniz Korbaltafizik ProjeTaha GümüşNo ratings yet
- Unit-4, Vector Differential CalculusDocument31 pagesUnit-4, Vector Differential CalculusSujatha VivekNo ratings yet
- Final Lab 4Document2 pagesFinal Lab 4Justin DrawbertNo ratings yet
- Differential and Integral Calculus 2 - Homework 2 SolutionDocument5 pagesDifferential and Integral Calculus 2 - Homework 2 SolutionDominikNo ratings yet
- Integrales Por Cambio de Variable: SolucionesDocument5 pagesIntegrales Por Cambio de Variable: SolucionesNazaret Donoso PinedaNo ratings yet
- 2011 蔡淳仁 FinalDocument3 pages2011 蔡淳仁 Final陳浚維No ratings yet
- Deq11 Final SolDocument3 pagesDeq11 Final Sol陳浚維No ratings yet
- Integral ComplicadaDocument1 pageIntegral ComplicadafxaviersgNo ratings yet
- Example: Problem 3.10.46 Related Rates: 110.109 Calculus I (Phys Sci & Eng) Professor Richard BrownDocument2 pagesExample: Problem 3.10.46 Related Rates: 110.109 Calculus I (Phys Sci & Eng) Professor Richard BrownAmmiel BuisingNo ratings yet
- (MATH1014) (2014) (S) Midterm-Wftamaa 88121Document4 pages(MATH1014) (2014) (S) Midterm-Wftamaa 88121amo.liiyingNo ratings yet
- Alvaro.. Integral Definidad DadaDocument3 pagesAlvaro.. Integral Definidad Dadaprofe.williamprietoNo ratings yet
- Mechanics I (APPM1028A and APPM1029A)Document12 pagesMechanics I (APPM1028A and APPM1029A)Nirvana BeannieNo ratings yet
- Trigo SubstitutionDocument4 pagesTrigo SubstitutionAdobo ToyoNo ratings yet
- Indefinite Integration - Complete Theory, Part-2 EDocument58 pagesIndefinite Integration - Complete Theory, Part-2 E2006orindamshawNo ratings yet
- f18 Practice Midterm1 SolutionsDocument21 pagesf18 Practice Midterm1 SolutionsAlgerian AissaouiNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answer: Additional MathematicsDocument20 pagesSuggested Answer: Additional Mathematicsapi-19650882No ratings yet
- IB 14tanget Normal (66 70)Document3 pagesIB 14tanget Normal (66 70)eamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- X Integrals 7Document1 pageX Integrals 7MasudRanaNo ratings yet
- Calculus I - Solutions #4Document10 pagesCalculus I - Solutions #4anhducgmc2005No ratings yet
- Week 5 - Signal Representations Using Fourier Series Activities Part 2Document7 pagesWeek 5 - Signal Representations Using Fourier Series Activities Part 2siarwafaNo ratings yet
- 2013 JC2 H2 Math Post MYE Revision Paper Solns For Students PDFDocument9 pages2013 JC2 H2 Math Post MYE Revision Paper Solns For Students PDFDouglas TanNo ratings yet
- Arc Length and Surface Area in Parametric Equations: MATH 211, Calculus IIDocument27 pagesArc Length and Surface Area in Parametric Equations: MATH 211, Calculus IIAli ElbasryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 ELEC351Document23 pagesLecture 03 ELEC351Qasim YahyaNo ratings yet
- IntegraDocument1 pageIntegrapradeep707rediffmailNo ratings yet
- Teacher 20081012 1758Document4 pagesTeacher 20081012 1758Lulu LiuNo ratings yet
- Soln 2Document4 pagesSoln 2SayantanNo ratings yet
- 08 Mate Matic As Financier AsDocument4 pages08 Mate Matic As Financier AsMariaJose Muñoz UlloaNo ratings yet
- Exam-Style Paper 3B - Pure 3: X LN (4 2t)Document3 pagesExam-Style Paper 3B - Pure 3: X LN (4 2t)Thomas NgangaNo ratings yet
- Punto PenduloDocument2 pagesPunto PenduloRuben David González PerezNo ratings yet
- Solutions: G S C CDocument11 pagesSolutions: G S C Capi-3781640No ratings yet
- A First Course in Differential Equations Solutions Odd Exercises PDFDocument62 pagesA First Course in Differential Equations Solutions Odd Exercises PDFFernandoNo ratings yet
- Dynamics GLA 2aDocument9 pagesDynamics GLA 2aFarid AimanNo ratings yet
- Moving Along Curve Specified SpeedDocument13 pagesMoving Along Curve Specified Speedzhaodong.liangNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Dropper (JEE)Document16 pagesTest 1 Dropper (JEE)Kundan KumarNo ratings yet
- SLG Math5 5.1.2 The Tangent Line and Derivative of A Function Part 2Document4 pagesSLG Math5 5.1.2 The Tangent Line and Derivative of A Function Part 2jvvuvuuv lopezNo ratings yet
- Problem Solutions Chapter 1.: NA AtomsDocument15 pagesProblem Solutions Chapter 1.: NA AtomsmtekbicakNo ratings yet
- Solucion Del Libro Ed2 PDFDocument945 pagesSolucion Del Libro Ed2 PDFOscar Steven AvilaNo ratings yet
- Definite IntegrationDocument8 pagesDefinite IntegrationKarthik BingiNo ratings yet
- FLUID Dynamics Assignment 1Document51 pagesFLUID Dynamics Assignment 1Aberamasundari SelvaNo ratings yet
- Full File at Https://testbanku - eu/Solution-Manual-for-Engineering-Mechanics-Dynamics-1st-Edition-by-Soutas-LittleDocument88 pagesFull File at Https://testbanku - eu/Solution-Manual-for-Engineering-Mechanics-Dynamics-1st-Edition-by-Soutas-LittleJersonFabianMaldonadoMorenoNo ratings yet
- Para CirclesDocument1 pagePara CirclesteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- Vector-Valued FunctionsDocument21 pagesVector-Valued Functionspapu corelNo ratings yet
- MAS102 Wed 8:00pm Quiz 3 ID: Name:: F 0 and × F 0, Then F 0Document2 pagesMAS102 Wed 8:00pm Quiz 3 ID: Name:: F 0 and × F 0, Then F 0AnarRzayevNo ratings yet
- Rectilinear Motion Using Integration Solutions To Selected Problems Calculus 9 Edition Anton, Bivens, DavisDocument14 pagesRectilinear Motion Using Integration Solutions To Selected Problems Calculus 9 Edition Anton, Bivens, DavisalfieNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University: Equation Time Instantaneous VelocityDocument3 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University: Equation Time Instantaneous VelocityShynne Kylla SarigumbaNo ratings yet
- DX DX DX: Solution Class-12Th - Mathematics - Sample Paper - 4 Class 12 - MathematicsDocument8 pagesDX DX DX: Solution Class-12Th - Mathematics - Sample Paper - 4 Class 12 - MathematicsMUSKAN YADAVNo ratings yet
- Amanecida UNI - Trigonometría (Juan Chomba - Cesar Ponce)Document3 pagesAmanecida UNI - Trigonometría (Juan Chomba - Cesar Ponce)josedflorescalachuaNo ratings yet
- DOC-20190613-WA0017 ArdDocument6 pagesDOC-20190613-WA0017 ArdMuthia FeblianaNo ratings yet
- DX t+3 T 3 CDocument4 pagesDX t+3 T 3 CMaría Vela FontisNo ratings yet
- Brilliant'S Progressive Test: All India Engineering Entrance Examination, 2011Document15 pagesBrilliant'S Progressive Test: All India Engineering Entrance Examination, 2011Harshit JainNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Trigonometric Equation - Homework - 01Document3 pagesDPP - 01 - Trigonometric Equation - Homework - 01ANAND JHANo ratings yet
- ECE316H1 - 20201 - 641586556718ECE316 Problem Set Solutions Merged-20Document79 pagesECE316H1 - 20201 - 641586556718ECE316 Problem Set Solutions Merged-20Vama DaveNo ratings yet
- Laws of VectorsDocument5 pagesLaws of VectorsAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- V-T Curve and IntegrationDocument5 pagesV-T Curve and IntegrationAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Vectors..Document7 pagesIntroduction To Vectors..Anjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Speed and VelocityDocument9 pagesSpeed and VelocityAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Numericals On Equations of MotionDocument8 pagesNumericals On Equations of MotionAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Motion Under Gravity.Document8 pagesMotion Under Gravity.Anjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To KinematicsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To KinematicsAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Equations of MotionDocument6 pagesEquations of MotionAnjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- St. Joseph's College of Engineering, Chennai-119 Department of Mechanical Engineering Sub. Name: Dynamics of Machinery Sub - Code: ME2302Document7 pagesSt. Joseph's College of Engineering, Chennai-119 Department of Mechanical Engineering Sub. Name: Dynamics of Machinery Sub - Code: ME2302Rahul ThoratNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements 1 002Document19 pagesMachine Elements 1 002MelindaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Wave Propagation On GroundDocument22 pagesChapter 8 - Wave Propagation On GroundQuang HưngNo ratings yet
- DPP-4 - JEE Main Adv. Kinematics - Position Velocity and Acceleration Graph 1682966766329Document5 pagesDPP-4 - JEE Main Adv. Kinematics - Position Velocity and Acceleration Graph 1682966766329SAHIL KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- PX267 - Hamilton MechanicsDocument2 pagesPX267 - Hamilton MechanicsRebecca Rumsey100% (1)
- Sri Vidya College of Engineering and Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Question Bank)Document4 pagesSri Vidya College of Engineering and Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Question Bank)Ajinkya RajeNo ratings yet
- HW-2 2Document3 pagesHW-2 2Ozan YakarNo ratings yet
- L15 Work & Kinetic Energy Hirotaka SatoDocument44 pagesL15 Work & Kinetic Energy Hirotaka SatoImperial ReckerNo ratings yet
- Structural Dynamics Hw2 - SolDocument6 pagesStructural Dynamics Hw2 - SolmostafaNo ratings yet
- Fortnightly Test Series: Corporate Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005, Phone: 011-47623456Document35 pagesFortnightly Test Series: Corporate Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005, Phone: 011-47623456StockPlusIndiaNo ratings yet
- Tan 3/2 Tan 2/3 Sin 2/3 Cos 2/3: (CPMT 1993)Document3 pagesTan 3/2 Tan 2/3 Sin 2/3 Cos 2/3: (CPMT 1993)AshwinNo ratings yet
- Goda RandomwavebreakingDocument12 pagesGoda RandomwavebreakingputhenkulamNo ratings yet
- Two DOFDocument78 pagesTwo DOFMazhar Ali100% (1)
- Sarthak PPT - 1Document20 pagesSarthak PPT - 1Dharmendra PatelNo ratings yet
- 781 Notefile 1 1657619758 PDFDocument185 pages781 Notefile 1 1657619758 PDFRaj AwinasheNo ratings yet
- Doppler EffectDocument4 pagesDoppler EffectTheo MolotoNo ratings yet
- DR SH GR 12 Chapter 1 To PrintDocument9 pagesDR SH GR 12 Chapter 1 To PrintEvelyn Kate MCANo ratings yet
- Recap f5 Physics Express NotesDocument26 pagesRecap f5 Physics Express NotesWan MajdahNo ratings yet
- Rotational Dynamics Lesson 2Document2 pagesRotational Dynamics Lesson 2Chung Chee YuenNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics Lab - Viva-QuestionsDocument6 pagesEngineering Physics Lab - Viva-QuestionsBC PurchasNo ratings yet
- Nu Esat Refresher 2Document77 pagesNu Esat Refresher 2PortgasD.AceNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Lab Report FlywheelDocument10 pagesDynamic Lab Report FlywheelNoa Bawie100% (1)
- Consolidated Structural DyanmicsDocument7 pagesConsolidated Structural DyanmicsVijay AravindNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Prandtl Meyer FlowDocument38 pagesLecture 9 - Prandtl Meyer Flowvandamme789No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Motion and Vectors Section Quiz On Vectors With AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Motion and Vectors Section Quiz On Vectors With AnswersLili100% (1)
- Appendix A: Dimensionless Groups: By. Robert B. HeimannDocument2 pagesAppendix A: Dimensionless Groups: By. Robert B. HeimannGusti Ayoe NurjanahNo ratings yet
- 10 - Hydraulic Jump and Its Usefulness in The Design of Irrigation StructuresDocument11 pages10 - Hydraulic Jump and Its Usefulness in The Design of Irrigation StructuresSandeep sahNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Q P Paper IDocument10 pagesProjectile Motion Q P Paper IsagarNo ratings yet
- Unclassie: !R IedDocument167 pagesUnclassie: !R IedIcNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment 4 - Linear Momentum and Impulse: Problem 1 (25 PTS) - What A Kick!Document1 pageHomework Assignment 4 - Linear Momentum and Impulse: Problem 1 (25 PTS) - What A Kick!Sơn Trường NguyễnNo ratings yet