Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stat Mining 34
Uploaded by
Adonis HuaytaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stat Mining 34
Uploaded by
Adonis HuaytaCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamentals 19
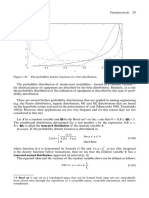
Figure 1.12. An example of the probability mass distribution for a geometric distribution.
Poisson distribution
This distribution was first introduced by Siméon Denis Poisson and published together with
his probability theory (1837).
A practical application of this distribution was made by Władysław Bortkiewicz in 1898
when he was given the task of investigating the number of soldiers in the Prussian army who
were accidentally killed by horse kicks. This investigation led to the Poisson distribution and
according to some researchers to the field of reliability engineering.20
If the random variable X takes values at points k = 0, 1, 2, … with the probability
λk −λ
P( k) = e λ>0 (1.43)
k!
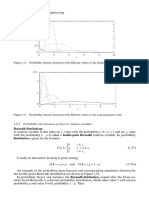
then we say that this random variable has a Poisson distribution (Figure 1.13).
The expected value and the variance are identical and
E(X) = λ σ2(X) = λ (1.44)
If we are interested in the probability distribution of the number of failures of a given type
in a given time interval and the events that occur create a memoryless stream of arrivals, then
the probability distribution of this random variable is given by formula (1.43).
By observing the process of the operation of belt conveyors in mining, we can easily deter-
mine that the mean time between two neighbouring failures is long compared to the mean
time of repair. Thus, it is usually presumed that the operation process from a reliability point
of view is described by the Poisson process of which the probability of the occurrence of k
failures in time t is given by formula (1.43) where the parameter is λt (t – time).
The Poisson distribution can also be applied to systems with a large number of possible
events, each of which is rare and the process of occurring events can usually be described by
the Poisson process. The Poisson distribution is sometimes called a ‘Poissonian’.
1.2.6 Probability distributions of continuous random variables
Uniform distribution
The uniform distribution, sometimes also known as the rectangular distribution, is a distribu-
tion that has a constant probability.
20
Vide: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Poisson_distribution#cite_note-4.
Book.indb 19 12/9/2013 12:22:09 PM
You might also like
- A) Lose Exactly 430 Bags Next Week?Document12 pagesA) Lose Exactly 430 Bags Next Week?Hega TarashiniNo ratings yet
- hmk#7 p-5Document3 pageshmk#7 p-5wliuwNo ratings yet
- Poisson Distribution - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDocument14 pagesPoisson Distribution - An Overview - ScienceDirect Topicspunit_thacker014No ratings yet
- Poisson Distribution & Its Applications: By-Snehil Mishra, Simran, Sandhya Upadhyaya, Shashank Tiwari, Priyanka JarwalDocument30 pagesPoisson Distribution & Its Applications: By-Snehil Mishra, Simran, Sandhya Upadhyaya, Shashank Tiwari, Priyanka JarwalHarsh100% (1)
- MCQ Measures of Dispersion With Correct AnswersDocument9 pagesMCQ Measures of Dispersion With Correct AnswersJyoti Prasad Sahu88% (8)
- Probability and Statistical Inference 9ed (2015) AnswerDocument12 pagesProbability and Statistical Inference 9ed (2015) AnswermarcusNo ratings yet
- Poisson DistributionDocument11 pagesPoisson DistributionSaroj KumarNo ratings yet
- Complete Consistency For Recursive Probability Density Estimator of Widely Orthant Dependent SamplesDocument12 pagesComplete Consistency For Recursive Probability Density Estimator of Widely Orthant Dependent SamplesHouria BessaNo ratings yet
- Poisson Distribution - WikipediaDocument57 pagesPoisson Distribution - WikipediaQurban khaton HussainyarNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument14 pagesChapter INurdin HadihawrunNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Distributions 1Document2 pagesTheoretical Distributions 1bnanduriNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 33Document1 pageStat Mining 33Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Manuscript: Complete Consistency For Recursive Probability Density Estimator of Widely Orthant Dependent SamplesDocument12 pagesManuscript: Complete Consistency For Recursive Probability Density Estimator of Widely Orthant Dependent SamplesHouria BessaNo ratings yet
- All Simulation LecturesDocument41 pagesAll Simulation LecturesMohanad SulimanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Uncertainty NotesDocument15 pagesEngineering Uncertainty NotesKaren Chong YapNo ratings yet
- Poisson Distribution and ApplicationDocument3 pagesPoisson Distribution and Applicationibraheem alsarrajNo ratings yet
- 11 - Queing Theory Part 1Document31 pages11 - Queing Theory Part 1sairamNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Association of America Is Collaborating With JSTOR To Digitize, Preserve and Extend Access To The American Mathematical MonthlyDocument23 pagesMathematical Association of America Is Collaborating With JSTOR To Digitize, Preserve and Extend Access To The American Mathematical MonthlyhayeswNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2: Assignment 2 - Group 2 - DR Balqis RehanDocument21 pagesAssignment 2: Assignment 2 - Group 2 - DR Balqis RehanMOHAMAMED BOSSNo ratings yet
- 3.5.16 Probability Distribution PDFDocument23 pages3.5.16 Probability Distribution PDFGAURAV PARIHARNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Random Variables Lecture - 5: Some Standard Discrete Probability Distributions Discrete Random VariablesDocument6 pagesModule 3: Random Variables Lecture - 5: Some Standard Discrete Probability Distributions Discrete Random VariablesabimanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To General Relativity - G. T.hooftDocument68 pagesIntroduction To General Relativity - G. T.hooftmostafa-tallat70No ratings yet
- Unit 3: Photo-Elasticity: Nature of Light, Wave Theory of LightDocument32 pagesUnit 3: Photo-Elasticity: Nature of Light, Wave Theory of Lightrakesh khadeNo ratings yet
- 02 Distributions Revisions-1Document7 pages02 Distributions Revisions-1Mohanad SulimanNo ratings yet
- Relativistic Stochastic Processes and Related QuestionsDocument24 pagesRelativistic Stochastic Processes and Related QuestionsShweta SridharNo ratings yet
- Chaos Lecture NotesDocument16 pagesChaos Lecture Notessl1uckyNo ratings yet
- Brownian Motion and Wiener IntegralDocument5 pagesBrownian Motion and Wiener IntegralGP75No ratings yet
- QT-Random Variable and Probability Distribution-1Document4 pagesQT-Random Variable and Probability Distribution-1nikhithakleninNo ratings yet
- Distribution of The Time To Explosion For One-Dimensional DiffusionsDocument35 pagesDistribution of The Time To Explosion For One-Dimensional DiffusionsCesar RosalesNo ratings yet
- Probability TheoryDocument6 pagesProbability TheoryYoussef EmadNo ratings yet
- 03 - Probability Distributions and EstimationDocument66 pages03 - Probability Distributions and EstimationayariseifallahNo ratings yet
- Stein's Method For Poisson-Exponential DistributionsDocument21 pagesStein's Method For Poisson-Exponential Distributionsmingminggo002No ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide To Fragility, Vulnerability and Risk-PorterDocument50 pagesA Beginner's Guide To Fragility, Vulnerability and Risk-PorterSUDHARMA RAJA REDDY SANAPUREDDYNo ratings yet
- Use of Poisson Distribution in Highway Traffic: Daniel L. GerloughDocument78 pagesUse of Poisson Distribution in Highway Traffic: Daniel L. GerloughJasoncampbellNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument39 pagesChapter OneOmotayo AbayomiNo ratings yet
- Math Term PaperDocument18 pagesMath Term PaperYashu DhingraNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document22 pagesPaper 2Marcos FlorezNo ratings yet
- Bsa Unit 4Document6 pagesBsa Unit 4Predator Helios 300No ratings yet
- Queing Theory 2023-24Document40 pagesQueing Theory 2023-24Sakiya PNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document16 pagesModule 5japsbatmanNo ratings yet
- Clarification Poisson Process and Poisson Distribution: 17th July' 2013Document3 pagesClarification Poisson Process and Poisson Distribution: 17th July' 2013Pradipta Patra100% (1)
- Probability Densities 1Document38 pagesProbability Densities 1Armand DaputraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 HHJJDocument6 pagesLecture 11 HHJJHarshita ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Bivariate Probability Distributions - Part I: Insan TUNALI EC 531 - Econometrics IDocument50 pagesBivariate Probability Distributions - Part I: Insan TUNALI EC 531 - Econometrics ITayhan OzenNo ratings yet
- Part A Statistics Class 1Document3 pagesPart A Statistics Class 1WILMOIS MASTERNo ratings yet
- Distribution: Dr. H. Gladius Jennifer Associate Professor SPH, SrmistDocument23 pagesDistribution: Dr. H. Gladius Jennifer Associate Professor SPH, SrmistCharan KNo ratings yet
- 02 Distributions Revisions-1Document11 pages02 Distributions Revisions-1mohanned salahNo ratings yet
- 1967-Frankel, Acrivos-On The Viscosity of A Concentrated Suspension of Solid SpheresDocument7 pages1967-Frankel, Acrivos-On The Viscosity of A Concentrated Suspension of Solid SpheresjvchiqueNo ratings yet
- Penrose 1967Document23 pagesPenrose 1967Jack Ignacio Nahmías100% (1)
- Part 1Document107 pagesPart 1Amine HadjiNo ratings yet
- Lecture One 2016-OriginalDocument40 pagesLecture One 2016-OriginalCut Wan Mulia RahmiNo ratings yet
- Convergence of Random Variables - WikipediaDocument17 pagesConvergence of Random Variables - Wikipediasandeep aNo ratings yet
- Conditional Expectation and Least Squares PredictionDocument12 pagesConditional Expectation and Least Squares PredictionAndreaNo ratings yet
- 1986 - Random Walk Models of MovementDocument6 pages1986 - Random Walk Models of MovementmarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document30 pagesChapter 2Michiel Van VoorenNo ratings yet
- Transport Properties: Diffusion, Fick's Laws, Random Walks: 13th February 2011Document6 pagesTransport Properties: Diffusion, Fick's Laws, Random Walks: 13th February 2011amirNo ratings yet
- Lectures On Approximation by Polynomials: J.G. BurkillDocument75 pagesLectures On Approximation by Polynomials: J.G. BurkillLovinf FlorinNo ratings yet
- Submitted To The Annals of ProbabilityDocument60 pagesSubmitted To The Annals of ProbabilityGaston GBNo ratings yet
- Gao 2019Document6 pagesGao 2019snehamoy.pramanikNo ratings yet
- On of Maximum And: The Principle Entropy The Earthquake Frequency - Magnitude RelationDocument9 pagesOn of Maximum And: The Principle Entropy The Earthquake Frequency - Magnitude RelationJoaquín AguileraNo ratings yet
- ANG2ed 3 RDocument135 pagesANG2ed 3 Rbenieo96No ratings yet
- Introduction To Stochastic Processes: 3.1 Brownian MotionDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Stochastic Processes: 3.1 Brownian MotionAndxp51No ratings yet
- Cosmology in (2 + 1) -Dimensions, Cyclic Models, and Deformations of M2,1. (AM-121), Volume 121From EverandCosmology in (2 + 1) -Dimensions, Cyclic Models, and Deformations of M2,1. (AM-121), Volume 121No ratings yet
- Stat Mining 54Document1 pageStat Mining 54Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 50Document1 pageStat Mining 50Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat-Mining 280Document1 pageStat-Mining 280Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 55Document1 pageStat Mining 55Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 56Document1 pageStat Mining 56Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat-Mining 282Document1 pageStat-Mining 282Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 57Document1 pageStat Mining 57Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 46Document1 pageStat Mining 46Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 51Document1 pageStat Mining 51Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 45Document1 pageStat Mining 45Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 47Document1 pageStat Mining 47Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 52Document1 pageStat Mining 52Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 49Document1 pageStat Mining 49Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 53Document1 pageStat Mining 53Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 39Document1 pageStat Mining 39Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 43Document1 pageStat Mining 43Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 42Document1 pageStat Mining 42Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 41Document1 pageStat Mining 41Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 29Document1 pageStat Mining 29Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 48Document1 pageStat Mining 48Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 30Document1 pageStat Mining 30Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 44Document1 pageStat Mining 44Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 37Document1 pageStat Mining 37Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 35Document1 pageStat Mining 35Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 38Document1 pageStat Mining 38Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 32Document1 pageStat Mining 32Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 40Document1 pageStat Mining 40Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 33Document1 pageStat Mining 33Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 36Document1 pageStat Mining 36Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Stat Mining 31Document1 pageStat Mining 31Adonis HuaytaNo ratings yet
- Asymmetric Power Distribution: Theory and Applications To Risk MeasurementDocument31 pagesAsymmetric Power Distribution: Theory and Applications To Risk Measurementgado semaNo ratings yet
- Geomitric DistributionDocument18 pagesGeomitric DistributionTaanzNo ratings yet
- Probability DistributionsDocument59 pagesProbability DistributionsAkibZ ARTNo ratings yet
- Segunda Asignación de Estadística Aplicada A La Ingeniería Química 2016 IDocument5 pagesSegunda Asignación de Estadística Aplicada A La Ingeniería Química 2016 IKevin RojasNo ratings yet
- Probability Concepts and Applications: To AccompanyDocument98 pagesProbability Concepts and Applications: To AccompanyChincel G. ANINo ratings yet
- Statistics For Business and Economics: Discrete Random Variables and Probability DistributionsDocument59 pagesStatistics For Business and Economics: Discrete Random Variables and Probability Distributionsfour threepioNo ratings yet
- Multivariate Risks - Part II: Enkelejd HashorvaDocument50 pagesMultivariate Risks - Part II: Enkelejd Hashorvadavid AbotsitseNo ratings yet
- Probability and StatisticsDocument2 pagesProbability and StatisticsRishav Malla ThakuriNo ratings yet
- Law 1 Stat q3 Week 1 2Document12 pagesLaw 1 Stat q3 Week 1 2Eunice BautistaNo ratings yet
- What Is Kurtosis - Definition, Examples & FormulaDocument10 pagesWhat Is Kurtosis - Definition, Examples & Formula[CO - 174] Shubham MouryaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1 36-705 Brief Review of Basic ProbabilityDocument7 pagesLecture Notes 1 36-705 Brief Review of Basic ProbabilityPranav SinghNo ratings yet
- 1-Handout One-An Overview of Descriptive Statistics-Chapter 1&2Document22 pages1-Handout One-An Overview of Descriptive Statistics-Chapter 1&2Ahmed rafiqNo ratings yet
- EEN - 321 Digital Communications: Dr. Omer Mohsin Mubarak Assistant ProfessorDocument32 pagesEEN - 321 Digital Communications: Dr. Omer Mohsin Mubarak Assistant ProfessorMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Discrete Variable and Probability DistributionsDocument26 pagesDiscrete Variable and Probability DistributionsJeff RiveraNo ratings yet
- MTH 210A Lec 1-8 2020 PDFDocument120 pagesMTH 210A Lec 1-8 2020 PDFmnzNo ratings yet
- Poisson Distribution 2Document14 pagesPoisson Distribution 2KashafNo ratings yet
- Probability of R Successes in N TrialsDocument33 pagesProbability of R Successes in N Trialsdevavrat.singhNo ratings yet
- Lesson No.5. Continuous Random VariableDocument3 pagesLesson No.5. Continuous Random VariableNguyễn Việt Hoàng BI11-095No ratings yet
- PQT Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesPQT Lesson PlanK.SUBRAMANINo ratings yet
- Stat 110, Lecture 7 Continuous Probability Distributions: Bheavlin@stat - Stanford.eduDocument35 pagesStat 110, Lecture 7 Continuous Probability Distributions: Bheavlin@stat - Stanford.edujamesyuNo ratings yet
- F Tables PDFDocument5 pagesF Tables PDFSIMRAN GIDWANI 2238961No ratings yet
- AnFrek HujanDocument76 pagesAnFrek HujanFahmiNo ratings yet
- Math3160s13-Hw11 Sols PDFDocument3 pagesMath3160s13-Hw11 Sols PDFPei JingNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Standard Normal DistributionDocument2 pagesCumulative Standard Normal DistributionSALINGA MARK ANDREWNo ratings yet
- Sample! Sample!: Property of STI Weeks 7 - 9 SH1923Document26 pagesSample! Sample!: Property of STI Weeks 7 - 9 SH1923Brix AguasonNo ratings yet
- The Binomial, Poisson, and Normal Distributions: Modified After Powerpoint by Carlos J. Rosas-AndersonDocument39 pagesThe Binomial, Poisson, and Normal Distributions: Modified After Powerpoint by Carlos J. Rosas-AndersonIT manNo ratings yet