Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ws Light-1 - Reflection 1
Uploaded by
Dj Power0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 page1. The document is a worksheet on light reflection with 10 multiple-choice and descriptive questions.
2. The questions cover topics like the positioning of light bulbs in reflectors, using mirrors to project real and magnified images, the path of light rays reflecting off different types of mirrors, and using mirror formulas to calculate image characteristics.
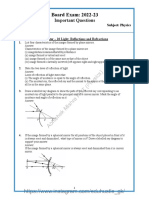
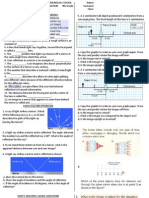
3. Diagrams are included to illustrate image formation using ray diagrams for plane, convex, and concave mirrors placed at different distances from objects.
Original Description:
Original Title
Ws Light-1_Reflection 1 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document is a worksheet on light reflection with 10 multiple-choice and descriptive questions.
2. The questions cover topics like the positioning of light bulbs in reflectors, using mirrors to project real and magnified images, the path of light rays reflecting off different types of mirrors, and using mirror formulas to calculate image characteristics.
3. Diagrams are included to illustrate image formation using ray diagrams for plane, convex, and concave mirrors placed at different distances from objects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pageWs Light-1 - Reflection 1
Uploaded by
Dj Power1. The document is a worksheet on light reflection with 10 multiple-choice and descriptive questions.
2. The questions cover topics like the positioning of light bulbs in reflectors, using mirrors to project real and magnified images, the path of light rays reflecting off different types of mirrors, and using mirror formulas to calculate image characteristics.
3. Diagrams are included to illustrate image formation using ray diagrams for plane, convex, and concave mirrors placed at different distances from objects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Worksheet -Class X, Chapter-10, Light
(1/2: Reflection of Light)
1. In torches, search lights and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed
a) between the pole and the focus of the reflector
b) very near to the focus of the reflector
c) between the focus and centre of curvature of the reflector
d) at the centre of curvature f the reflector.
2. A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of the school laboratory by using a
mirror.
a) Which type of mirror should he use and why?
b) At what distance, in terms of focal length ‘f’ of the mirror , should he place the candle flame to get the
magnified image on the wall?
c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in this case.
d) Can he use this mirror to project a diminished image of the candle flame on the same wall? State ‘how’ if
your answer is ‘yes’ and ‘why not’ if your answer is ‘no’.
3. In this question, two statements are given- one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason
(R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
a) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
c) A is true, but R is false.
d) A is false, but R is true.
Assertion (A):Plane mirror may form real image
Reason (R): Plane mirror forms virtual image if object is real.
4. Explain why a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, gets reflected along
the same path?
5. A 6 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 30 cm. The
distance of the object from the mirror is 45 cm. Use mirror formula to determine the position, nature and
size of the image formed. Also draw labelled ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
6. If the image formed by mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always virtual and
diminished, state the type of the mirror. Draw a ray diagram in support of your answer. Where are such
mirrors are commonly used and why?
7. A 5 cm tall object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the
position, size and nature of the image formed.
8. To construct a ray diagram, we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after
reflection from the mirror. List two such rays and state the path of these rays after reflection in case of
concave mirror. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the images of an object placed between
the pole and focus of a concave mirror.
9. A concave mirror produces three times magnified image on a screen. If the object is placed 20 cm in front of
the mirror , how far is the screen from the object?
10. Suppose you have three concave mirrors, A , B and C of focal lengths 10 cm, 15 cm and 20 cm. For each
concave mirror you perform the experiment of image formation for three values of object distances of 10
cm, 20 cm and 30 cm. By giving reason, answer the following.
(i) For the three object distances identify the mirror/mirrors which will form an image of magnification -1.
(ii) Out of the three mirrors identify the mirror which would be preferred to be used for shaving purpose/
makeup.
(iii) For the mirror B draw ray diagram for image formation for object distances 10 cm and 20 cm.
You might also like
- Light TestDocument8 pagesLight TestAmisha BhandariNo ratings yet
- Assignment Based On Reflection of LightDocument3 pagesAssignment Based On Reflection of Lightnamansaraswat2007No ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction Part 1Document6 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction Part 1Saji JayarajNo ratings yet
- LightReflection & Refractions Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 ScienceDocument9 pagesLightReflection & Refractions Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 ScienceZhugzhuang ZuryNo ratings yet
- St. Teresa School: Holiday Homework Class-X Subject-Physics Chapter-10 (Light)Document4 pagesSt. Teresa School: Holiday Homework Class-X Subject-Physics Chapter-10 (Light)Raghav ghaiNo ratings yet
- LightDocument6 pagesLightVivek saklaniNo ratings yet
- 9TH - Icse - Physics - Worksheet - Reflection of Light 2Document5 pages9TH - Icse - Physics - Worksheet - Reflection of Light 2manojboa100% (3)
- Physics Worksheet - LightDocument3 pagesPhysics Worksheet - Lightcartooncompany73No ratings yet
- Reflection of Light - WorksheetDocument5 pagesReflection of Light - WorksheetDøomNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection 1Document22 pagesLight Reflection 1psnarayanan99No ratings yet
- Light QuestionsDocument9 pagesLight QuestionsTxv RushNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light Set 1Document2 pagesReflection of Light Set 1XxxxxxNo ratings yet
- 10th Pyp1Document2 pages10th Pyp1Rajib KumarNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDocument48 pagesIlovepdf Merged PDFSomik JainNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework Physics Class 10thDocument1 pageHoliday Homework Physics Class 10thKalindi UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- LIGHT-PAST PAPER QnsDocument6 pagesLIGHT-PAST PAPER QnsARSHAD JAMIL100% (1)
- 5+mark+questions +CBSE+X +light +25 12 2019 PDFDocument45 pages5+mark+questions +CBSE+X +light +25 12 2019 PDFPiyushNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet Light: Reflection and Refraction Name of The Student: Grade - XDocument4 pagesPhysics Worksheet Light: Reflection and Refraction Name of The Student: Grade - XSyed Ahmed AdeelNo ratings yet
- Extra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Document5 pagesExtra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Zoha AzizNo ratings yet
- Assignment LightDocument1 pageAssignment Lightshubhutams2No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Light RevDocument24 pagesGrade 10 Light RevDanny BlessyNo ratings yet
- G10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Document10 pagesG10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Urmila GNo ratings yet
- G-10 Physics Important Questions FinalDocument29 pagesG-10 Physics Important Questions FinalRohan SenapathiNo ratings yet
- 10 THDocument3 pages10 THRohitNo ratings yet
- Open Book Test - OpticsDocument9 pagesOpen Book Test - OpticsGagandeep WadhawanNo ratings yet
- 1 - Light Reflection and Refraction (Prashant Kirad)Document11 pages1 - Light Reflection and Refraction (Prashant Kirad)Kshitiz sharmaNo ratings yet
- HOTS On Reflection of LightDocument2 pagesHOTS On Reflection of Lightswadhin100% (4)
- Final Exam Questions #4 - LensDocument4 pagesFinal Exam Questions #4 - Lensanonslu2012No ratings yet
- Test Phy and ChemDocument3 pagesTest Phy and Chemarya starkNo ratings yet
- TS Physics DCEB QuestionsDocument16 pagesTS Physics DCEB QuestionsKrishna KishoreSarvaNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light Worksheet 1Document2 pagesReflection of Light Worksheet 1harpalrana01.hrNo ratings yet
- Light QBDocument3 pagesLight QBAngad SinghNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument7 pagesLight - Reflection & RefractionManya Juneja100% (1)
- Light Worksheet Padhleakshay PDFDocument18 pagesLight Worksheet Padhleakshay PDFanandatulNo ratings yet
- Reflection Light 3Document31 pagesReflection Light 3api-296824694No ratings yet
- 10 LightDocument50 pages10 LightNaveen Kumar100% (1)
- Class 10 - Light Reflection & Refraction-Revision WorksheetDocument4 pagesClass 10 - Light Reflection & Refraction-Revision WorksheetFrederic Francois ChopinNo ratings yet
- One Mark Questions: ISD/X/WKST/SS/2019-20Document3 pagesOne Mark Questions: ISD/X/WKST/SS/2019-20Febronia GraceNo ratings yet
- Worksheet CBSE Class 10 LightDocument6 pagesWorksheet CBSE Class 10 Lightroythomasc50% (4)
- Physics Revision Worksheet Grade X ChlightDocument3 pagesPhysics Revision Worksheet Grade X ChlightKhushi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 10th Light Numerical Question Test Paper-3Document1 page10th Light Numerical Question Test Paper-3Priya TalrejaNo ratings yet
- s5 Physics Holiday Homework WorksheetDocument1 pages5 Physics Holiday Homework WorksheetA.P.SNo ratings yet
- QB 10Document12 pagesQB 10Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Document (29) KhikhikhikhiDocument3 pagesDocument (29) KhikhikhikhiUTKARSH ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Reqelford International Schoo: Light - Worksheet 1Document2 pagesReqelford International Schoo: Light - Worksheet 1shivaNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument3 pagesReflectionRishu yadavNo ratings yet
- LightDocument4 pagesLightjillgoldNo ratings yet
- Optics TestDocument2 pagesOptics Testiskenderbey100% (1)
- NCERT ExemplarDocument10 pagesNCERT Exemplarrohitpatra708024No ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction Part 2Document7 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction Part 2Saji JayarajNo ratings yet
- Weekly TEst 20th Sep 2021Document4 pagesWeekly TEst 20th Sep 2021Sarvesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Light CLASS 10Document10 pagesLight CLASS 10Ashwini PramodNo ratings yet
- Question Physics1Document9 pagesQuestion Physics1Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction: Questions To PracticeDocument4 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction: Questions To PracticeH E Man ShuNo ratings yet
- g10 ScienceDocument21 pagesg10 ScienceMOHAMMADMUNAWARSAIFNo ratings yet
- Light and Geometric OpticsDocument53 pagesLight and Geometric OpticsLeah May Tamayo ManayonNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument14 pagesLight Reflection and RefractionKalpesh UradeNo ratings yet
- Light ReflectionDocument1 pageLight ReflectionTanmay SanchetiNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Chapter 12 LightDocument12 pagesClass 7 Chapter 12 Lightsiddharthsg37No ratings yet
- Optics and Optical Instruments: An IntroductionFrom EverandOptics and Optical Instruments: An IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- GRAVITATION-Shafee Sir.Document20 pagesGRAVITATION-Shafee Sir.jimmyemandeeNo ratings yet
- MA-05 Heat Balance CalculationDocument5 pagesMA-05 Heat Balance Calculationy ly thienNo ratings yet
- Sugar Plant Specifications 5000 TCD-7500 TCDDocument104 pagesSugar Plant Specifications 5000 TCD-7500 TCDtsrinivasan508375% (4)
- CD-BA1500H: Service ManualDocument52 pagesCD-BA1500H: Service ManualmrudzinskasNo ratings yet
- TVP Case Studies - Industrial Process HeatDocument6 pagesTVP Case Studies - Industrial Process HeatRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- HSE-BMS-011 Crane & Lifting SafetyDocument51 pagesHSE-BMS-011 Crane & Lifting SafetySatya NaiduNo ratings yet
- 2004 VCF Tables - SGS Implementation (A4)Document1 page2004 VCF Tables - SGS Implementation (A4)Adrian RuizNo ratings yet
- Cable CatologueDocument69 pagesCable CatologueJyoti ShekharNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Hydraulic Mechanics Important MCQ PDFDocument11 pagesMechanical Engineering Hydraulic Mechanics Important MCQ PDFGaneshNo ratings yet
- Displacement Sensors: 1. Resistance Based and Optical Incremental Sensors of Position TaskDocument7 pagesDisplacement Sensors: 1. Resistance Based and Optical Incremental Sensors of Position TaskBoobalan ThirugnanasambandamNo ratings yet
- Dielectric AbsorptionDocument4 pagesDielectric AbsorptionbookbumNo ratings yet
- Location and Control SurveyDocument63 pagesLocation and Control SurveyMaxine MukokiNo ratings yet
- Assigning R and SDocument12 pagesAssigning R and SApurba Sarker ApuNo ratings yet
- Chimney SizingDocument7 pagesChimney SizingAli MustafaNo ratings yet
- DYNSIM Best Practices 1 - CompressorDocument21 pagesDYNSIM Best Practices 1 - CompressorEmre TokgözNo ratings yet
- Parasi HydraulicsDocument203 pagesParasi Hydraulicsabhishek5810No ratings yet
- 56 - Isijint 2015 231 PDFDocument13 pages56 - Isijint 2015 231 PDFRaphael Mariano de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installation and Maintenance NC Ii Quarter 2 Module Week 5-6Document42 pagesElectrical Installation and Maintenance NC Ii Quarter 2 Module Week 5-6Cristal Gumalang100% (1)
- Group of AutomorphismsDocument5 pagesGroup of AutomorphismsAnkit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- System1 Plots - Machinery-Diagnostic - Part1Document16 pagesSystem1 Plots - Machinery-Diagnostic - Part1Thyagaraju PalisettyNo ratings yet
- Apollon 1Document42 pagesApollon 1Munteanu Maria-MagdalenaNo ratings yet
- TED and YTED (ATEX) Digital Pressure Switches: Specifications (20°C)Document4 pagesTED and YTED (ATEX) Digital Pressure Switches: Specifications (20°C)Максимум КазакевичNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Interview QuestionsDocument1 pagePressure Vessel Interview Questionsdh6802No ratings yet
- Kutchina e Catalogue Retail Mail2Document25 pagesKutchina e Catalogue Retail Mail2Manjita BudhirajaNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers - ET Level 1Document4 pagesQuestions & Answers - ET Level 1Jawad MunirNo ratings yet
- Design of Modern CNC Machines and Mechatronic ElementsDocument37 pagesDesign of Modern CNC Machines and Mechatronic Elementsnagappa talawarNo ratings yet
- ANZ MEGEN1 Quick Start Guide 139184-200505Document2 pagesANZ MEGEN1 Quick Start Guide 139184-200505林No ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 ARO 3011 Fall 2021 VVDocument54 pagesLECTURE 1 ARO 3011 Fall 2021 VVRukiezillaNo ratings yet
- Vectors and 3D Geometry For Jee Advanced 3Rd Edition G Tewani All ChapterDocument47 pagesVectors and 3D Geometry For Jee Advanced 3Rd Edition G Tewani All Chapterwade.escamilla468100% (4)
- 3va9988-0ba22-SHUNT TRIPDocument4 pages3va9988-0ba22-SHUNT TRIPLeonardo CAMARGO CAMARGONo ratings yet