Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BOHR'S MODEL AND EARLY QUANTUM MODELS OF THE ATOM
Uploaded by
Akash SinghOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BOHR'S MODEL AND EARLY QUANTUM MODELS OF THE ATOM
Uploaded by
Akash SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
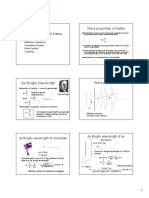
Sub atomic particles Hydrogen spectrum BOHR'S MODEL OF AN ATOM TOWARDS QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL
Electron . Electron in H atom can move around the nucleus in a circular
charge of an e-
–1.6022 × 10–19 c
path of fixed radius DUAL NATURE OF MATTER HEISENBERG'S
J.J. THOMSON Mass of an e– . Each orbit has a definite energy and is known as energy • Every microscopic particle in the motion UNCERTAINITY PRINCIPLE
–9.1 × 10 31 kg level or stationary level. has dual nature (wave and particle
• Discovered electron(s–) nature) and produce matter waves.
It is impossible to measure
Proton . When an electron jumps from a lower energy level to to simultaneously the exact momentum
• Proposed plum pudding Model charge of a proton (p+) higher one, energy is absorbed and vice versa. and exact position of a microscopic
+1.6 × 10-19 c 27 • wavelength of matter waves moving particle.
(De=Broglie's wavelength)
Mass of a p+ . Angular momentum of electron h
ELECTRON 1.6 × 10 kg h h ∆X . ∆P ≥
= mevr = n
h
n = 1, 2, 3 λ= = 7π
POSITIVE SPACE
Neutron 2π mv p
Discovered by James n2 ° Z2
Radius (r) = 0.529 × A Energy (E) = -13.6 × ev
Chadwick. Charge Z n2
on Neutron is 0.
Z
QUANTUM MECHANICS
Mass of a Neutron is Velocity (v) = 2.18 × 10 ×
6
m/sec
n
ERNEST 1.6 × 10 27kg
. Fundamental equation was developed by Schrodinger know as
RUTHERFORD Schrodinger wave equation.
SERIES
• Discovered proton (P ) +
LIMITATION d2ψ d 2ψ d2 ψ 8π2m
• a-partical experiment + + + (E - U)ψ = 0
Lyman n1 = 1 n2 = 2, 3... dx2 dy2 dz2 h2
• Proposed Rutherford's
n1 = 2 n2 = 3, 4... . Applicable to only one e- system eg: H, He+
model of an atom (1911) Balmer . The electrons in an atom have quantized values of energy.
• Atom consist of two parts n2 = 4, 5...
Paschen n1 = 3 . It could not explain Zeeman effect and stark effect. . By evaluating ψ2 at different points around the nucleus in aN
nucleus and extra nucleus
part Bracket n1 = 4 n2 = 5, 6... atom, we can predict the probability of finding the electron.
NUCLEUS Pfund n1 = 5 n2 = 6, 7...
+
STRUCTURE QUANTUM NUMBER
ORBIT
. Wavelength of radiation emitted when an
e- jumps from n2 to n1. 1. Principle quantum No. (n) = 1, 2, 3, 4... shell = K, L, M, N
1 = R Z2 1 - 1
λ H n12 n22
OF ATOM 2. Azimuthal Quantum No. (l) = for given value of n, l can have
ELECTRO-MAGNETIC WAVE THEORY RH = Rydberg’s constant
values from 0 to n - 1)
= 109677 cm-1 3. Magnetic quantum no. (m) = for subshells with 'l' value,
. Wavelength: Distance between successive crest and trough
m can have values from -l to +l and Total value of m= 2l + 1
. Frequency: Number of waves passed through ENERGY LEVEL 4. Spin quantum number = s = + 1 , - 1
a point in 1 sec. c PLANK'S THEORY 2
λ= 2
υ
Light travells in the form of small energy packets
known as "Photons".
NODES
x E = hυ
Where h = Plank’s Constant RULES FOR Space or region, wher finding the
probability of e- is zero
h = 6.623 × 10–34 Js ARRANGING ELECTRONS
TYPES:- • Radial node = (n - l -1)
λ
Electric field PHOTOELECTRIC • Angular node = l
(a) Aufbau principle: Electrons • Total node = n - 1
BLACK BODY EFFECT
occupy lowest energy level
A Ejection of
RADIATION Beam of electron
First and then move to the next
Magnetic field energy level.
Direction of
A perfect obsorber or
light
(b) Pauli Exclusion principle: No two s-SHAPE OF
z
propogation emitter of light. e- can have same set of all 4 ORBITALS
i.e Absorber or emits all W0 = Hυ0 quantuM numbers. y
type of frequency/
Hυ = W0 + K.E. (c) Hund's rule: If two or more
radiation orbitals of equal energy
E = hυ0 + K.E.
available, then electron will
ELECTRO-MAGNETIC occupy them singly before filled
x
SPECTRUM in pairs. Z
. Electromagnetic spectrum is a collection
ATOMIC SPECTRA p- ORBITALS 1s orbital
CHARACTERISITICS space electromagnetic waves arranged (DUMBELL SHAPE)
OF WAVE according to frequency and wavelength. EMISSION
ABSORPTION
d-ORBITALS ( Double Dumbell shape )
(a) Wavelength (λ) . Wavelength of visible light is from 400nm SPECTRA y y y
y z
to 750nm.
Spectrum of the SPECTRA z
y y
(b) wave no. (υ−) Spectrum of electromagnetic radiation
(c) Frequency (υ)
Increasing Frequency (v)
Radio Infra- visible radiation emitted emitted or absorbed by an It is like x x x
(d) Time Period (T)
Micro UV- x- Gamma Cosmic
waves waves red light rays rays rays
x x
rays
by a substance electron during transition photographic x x
(e) Velocity (c)
that has absorbed from one energy level to negative of an z z z
(f) Amplitude (A)
Increasing wavelength(λ) energy emission spectra 2px 3dy zpz 3dxy 3dyz 3dz2
another 3dxz 3dx2 - y
2
anand_mani16 DR. Anand Mani https://www.anandmani.com/ https://discord.io/anandmani t.me/anandmani001
You might also like
- BOHR'S MODEL AND EARLY QUANTUM MODELS OF THE ATOMDocument103 pagesBOHR'S MODEL AND EARLY QUANTUM MODELS OF THE ATOMVINOD KUMAR MEENA PGT CHEMISTRY, KVSNo ratings yet
- Proton Physics: Structure and Properties of the ProtonDocument13 pagesProton Physics: Structure and Properties of the ProtonKhalid AhmedNo ratings yet
- AS Physics Data and Formulae: For Use in Exams From The June 2016 Series OnwardsDocument4 pagesAS Physics Data and Formulae: For Use in Exams From The June 2016 Series OnwardsJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Aqa 7408 SDB PDFDocument8 pagesAqa 7408 SDB PDFAbdullah ZakaNo ratings yet
- CH 02 - Atomic Structure Bonding - OkDocument31 pagesCH 02 - Atomic Structure Bonding - OkAlex ReedNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure ChemDocument20 pagesAtomic Structure ChemsearchhistorycollectionNo ratings yet
- P11 Dual Nature Radiation - MatterDocument1 pageP11 Dual Nature Radiation - Matterpujansonani677No ratings yet
- Wave Nature of MatterDocument17 pagesWave Nature of MatterHARSH GARGNo ratings yet
- H2 2021 Prelim Phy P1Document18 pagesH2 2021 Prelim Phy P1Khaled GamalNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature Radiation - MatterDocument1 pageDual Nature Radiation - Mattersarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Material Nano Minggu - 5Document22 pagesMaterial Nano Minggu - 5Michael Robert Tua NababanNo ratings yet
- Physics XII Concept Maps PDFDocument15 pagesPhysics XII Concept Maps PDFcbsegirlsaipmt100% (1)
- Wave Properties of MatterDocument4 pagesWave Properties of MatterMalik MaazNo ratings yet
- 26 Modern Physics Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument7 pages26 Modern Physics Formula Sheets QuizrrDhairya SharmaNo ratings yet
- 26 Modern Physics Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument5 pages26 Modern Physics Formula Sheets QuizrrSwapnil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry (1) : From Classical To Quantum MechanicsDocument17 pagesPhysical Chemistry (1) : From Classical To Quantum MechanicsNAMENo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2SyahshaiNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics, Advanced Course Scattering Theory: - Understanding of MatterDocument50 pagesQuantum Mechanics, Advanced Course Scattering Theory: - Understanding of Matter7747252No ratings yet
- Class 11 CH 2 Structure of AtomDocument5 pagesClass 11 CH 2 Structure of AtomSulaiman Khan0% (1)
- PH 310 SlidesDocument44 pagesPH 310 SlidesBushra IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Im 1482154379 PDFDocument23 pagesIm 1482154379 PDFramlakhanNo ratings yet
- (Gs Material Science) : Structure of Atom and Interatomic BondingDocument23 pages(Gs Material Science) : Structure of Atom and Interatomic BondingramlakhanNo ratings yet
- 01 - Atoms and Periodic TableDocument21 pages01 - Atoms and Periodic Table04 Nguyễn Việt Bảo 12A3No ratings yet
- Electrostatic PDFDocument18 pagesElectrostatic PDFTanayaNo ratings yet
- 2 QuantumMechanicsDocument28 pages2 QuantumMechanicsdothaibinhca2004No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Chemistry Sk015 SESSION 2020 / 2021Document36 pagesAtomic Structure: Chemistry Sk015 SESSION 2020 / 2021Daniel LimNo ratings yet
- NCERT PUNCH Chemistry Class 11 Complete Book Flattened SignedDocument304 pagesNCERT PUNCH Chemistry Class 11 Complete Book Flattened Signedsd0806787No ratings yet
- Prerequisite Atomic Structure and Quantum ConceptsDocument20 pagesPrerequisite Atomic Structure and Quantum ConceptsmahyarbNo ratings yet
- Intro To QM & Electronic StructureDocument18 pagesIntro To QM & Electronic Structure周子暄No ratings yet
- Lecture 4.11Document34 pagesLecture 4.11ethio universeNo ratings yet
- 3C24BasicIdeas BW TVDocument27 pages3C24BasicIdeas BW TVRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Ap 5Document4 pagesAp 5MARTÍN SOLANO MARTÍNEZNo ratings yet
- 10 Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationDocument7 pages10 Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationnagarajanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: Cbse Neet JEE Mains AdvancedDocument34 pagesMechanics: Cbse Neet JEE Mains AdvancedLoyd CometaNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument34 pagesPhysics FormulasLoyd CometaNo ratings yet
- JC2 Physics H2 2018 RafflesDocument88 pagesJC2 Physics H2 2018 RafflesVarshLokNo ratings yet
- 무기화학 1 ch2Document5 pages무기화학 1 ch2최마리아No ratings yet
- Overview of Solid State PhysicsDocument1 pageOverview of Solid State PhysicsHenkVriesNo ratings yet
- ch1 - Review of QEDocument21 pagesch1 - Review of QEfuyoungNo ratings yet
- 2019 JC2 H2 Physics Anderson Serangoon Junior CollegeDocument90 pages2019 JC2 H2 Physics Anderson Serangoon Junior Collegeeternal vorceNo ratings yet
- Table of Physical ConstantsDocument1 pageTable of Physical ConstantsGarry Yan DiazNo ratings yet
- Compre - Last Edited - 5pmDocument21 pagesCompre - Last Edited - 5pmPKBNo ratings yet
- 6-Quantum-Particle (Students Copy)Document12 pages6-Quantum-Particle (Students Copy)Kunal kumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Mechanics: Cbse Neet JEE Mains AdvancedDocument11 pages1 Mechanics: Cbse Neet JEE Mains AdvancedMohammad AnasNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Cheat Sheet Ver 1Document18 pagesSemiconductor Cheat Sheet Ver 1testerJesterNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument18 pagesPhysics FormulasShubhamNo ratings yet
- PriorelectroDocument12 pagesPriorelectroArasIlgazNo ratings yet
- Atomic Phyiscs Part 2Document70 pagesAtomic Phyiscs Part 2Findx proNo ratings yet
- Data and Formula BookletDocument5 pagesData and Formula Booklet王涛No ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument1 pageElectricity and MagnetismJulia KarakiNo ratings yet
- HWS Computational PDFDocument34 pagesHWS Computational PDFBheim LlonaNo ratings yet
- Russi 2016Document7 pagesRussi 2016yulliarperezNo ratings yet
- Ch. 44: Quarks, Leptons and The Big Bang The Fundamental ParticlesDocument4 pagesCh. 44: Quarks, Leptons and The Big Bang The Fundamental ParticlesvaibhavdkNo ratings yet
- 5-Bohr's Atomic ModelDocument10 pages5-Bohr's Atomic ModelKush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Iitk PDFDocument154 pagesIitk PDFPankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 Short Note-EMDocument9 pagesUnit 01 Short Note-EMShashiNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structure Analysis TechniquesDocument156 pagesCrystal Structure Analysis TechniquesVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Old and New Problems in Elementary ParticlesFrom EverandOld and New Problems in Elementary ParticlesG PuppiNo ratings yet
- 50Q - NucleiDocument8 pages50Q - NucleiAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of WaterDocument9 pagesChemical Properties of WaterAkhilesh PaswanNo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument6 pagesRelations and FunctionsTalveda Shreya100% (1)
- CapacitorDocument20 pagesCapacitorAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom ChartDocument10 pagesPlant Kingdom ChartAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- Tayug National High School Remediation Exam in Science 8 Quarter 3Document3 pagesTayug National High School Remediation Exam in Science 8 Quarter 3Athena ChoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding Lesson PlanGabriel ClaverieNo ratings yet
- 2023 - H2 - 4 - Electric Field - Tut - SolnDocument14 pages2023 - H2 - 4 - Electric Field - Tut - SolndadaseahNo ratings yet
- Color: A Coloring Book byDocument19 pagesColor: A Coloring Book byMarta Pérez Madrid50% (2)
- BreakdownDocument10 pagesBreakdownAomlnw SgrNo ratings yet
- Indian National Physics Olympiad helps identify talented physics studentsDocument150 pagesIndian National Physics Olympiad helps identify talented physics studentsakhileshNo ratings yet
- Correlations Between Electral Conductivity and Aging Behaviour of 7010 Base AluminiumDocument7 pagesCorrelations Between Electral Conductivity and Aging Behaviour of 7010 Base Aluminiumferhat aydoganNo ratings yet
- Francis Aston and The Mass SpectrographDocument7 pagesFrancis Aston and The Mass SpectrographAhmed Ali SoomroNo ratings yet
- Magnet Therapy and Protocols For Osteoporosis 2004 (Pag 18) by William H. Philpott - Negative Field On Brain and Spine For Pain, TreatmentsDocument25 pagesMagnet Therapy and Protocols For Osteoporosis 2004 (Pag 18) by William H. Philpott - Negative Field On Brain and Spine For Pain, Treatmentsitetejac100% (2)
- The Effect of Gamma Rays.... Analysis....Document37 pagesThe Effect of Gamma Rays.... Analysis....Michael J Moody Jr.100% (1)
- Engineering Chemistry - (Malestrom)Document602 pagesEngineering Chemistry - (Malestrom)Sandeep Kotagiri75% (8)
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Lionel messiNo ratings yet
- Full Package - EPDocument178 pagesFull Package - EPretterateNo ratings yet
- 2018 Book HandbookOfMaterialsCharacteriz PDFDocument612 pages2018 Book HandbookOfMaterialsCharacteriz PDFJohn TorrezNo ratings yet
- Physics Second Year Volume IDocument253 pagesPhysics Second Year Volume ISaalinraj SantharajNo ratings yet
- ULAS Sci8Q3 WK 5 6Document10 pagesULAS Sci8Q3 WK 5 6Joan MarieNo ratings yet
- Conductivity and Resistance MechanismsDocument40 pagesConductivity and Resistance MechanismshkaruvathilNo ratings yet
- 20th Century PhysicsDocument313 pages20th Century PhysicsjeffNo ratings yet
- Dental Radiography Principles and Techniques 5th Edition Iannucci Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesDental Radiography Principles and Techniques 5th Edition Iannucci Solutions ManualJoshuaAllensoie98% (54)
- Band Theory of The Electronic Properties of Solids 2Document2 pagesBand Theory of The Electronic Properties of Solids 2Srinivas SaiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Transition ElementsDocument4 pagesChemistry Transition Elementsyaiwen96No ratings yet
- SEM and TEM Difference PDFDocument13 pagesSEM and TEM Difference PDFJyotirmoy Das100% (1)
- Understanding ElectricityDocument12 pagesUnderstanding ElectricityrezarayaNo ratings yet
- Visualizing Geology 3rd Edition Murck Test BankDocument25 pagesVisualizing Geology 3rd Edition Murck Test BankSamanthaHughesqjiko100% (17)
- Democritus' Atomic ModelDocument7 pagesDemocritus' Atomic Modelkarla callejaNo ratings yet
- PCBMTeo-Effective Interfaces Between Fullerene Derivatives and CH3NH3PbI3Document11 pagesPCBMTeo-Effective Interfaces Between Fullerene Derivatives and CH3NH3PbI3Angel Manuel Gómez CoronelNo ratings yet
- STD 12th Precise Physics 2 Notes Science MH BoardDocument21 pagesSTD 12th Precise Physics 2 Notes Science MH BoardAkhilesh SengarNo ratings yet
- Atom, Molecul and IonDocument62 pagesAtom, Molecul and IonChamilass YayaNo ratings yet
- Build An Atom Phet WorksheetDocument4 pagesBuild An Atom Phet Worksheetapi-542317996No ratings yet