Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Traffic Rotaries
Uploaded by
sredhar sOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Traffic Rotaries
Uploaded by
sredhar sCopyright:
Available Formats
Traffic Rotaries
Introduction
Special form of at-grade intersections
laid out for the movement of traffic in
one direction around a central traffic
island
All major conflicts namely the
collision between through and right-
turn movements are converted into
milder conflicts namely merging and
diverging
The vehicles entering the rotary are
gently forced to move in a clockwise
direction in orderly fashion
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 2 / 23
Traffic Movements
Rotary intersection
• Advantages
– Traffic flow is regulated to only one direction of
movement
– Eliminating severe conflicts between crossing
movements
– All the vehicles entering the rotary are gently
forced to reduce the speed and continue to
move at slower speed
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 4 / 23
Rotary intersection
• Advantages
– None of the vehicles need to be stopped, unlike
in a signalized intersection
– Accidents and their severity are much less in
rotaries
– Rotaries are self governing
– Suited for moderate traffic, especially with
irregular geometry or intersections
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 5 / 23
Rotary intersection
• Limitations
– All the vehicles are forced to slow down and negotiate the
intersection
– Cumulative delay will be much higher than channelized
intersection
– Even when there is relatively low traffic, the vehicles are forced
to reduce their speed
– Rotaries require large area of relatively flat land making them
costly at urban areas
– Not suitable when there is high pedestrian movement
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 6 / 23
Guidelines for selection of rotaries
• Suitable
– Traffic entering from all the four approaches are
relatively equal
– More than four approaches
– If there is no separate lanes available for right-turn
traffic
– If the intersection geometry is complex
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 7 / 23
Guidelines for selection of rotaries
– Upper limiting volume 3000 vehicles per hour
– Lower limiting volume 500 vehicles per hour
– Beneficial when the proportion of the right-turn traffic is very
high; typically if it is more than 30%
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 8 / 23
Traffic operations in a rotary
• Diverging
– Traffic operation when the vehicles moving in one direction is
separated into different streams according to their destinations
• Merging
– Merging is the opposite of diverging
– Referred to as the process of joining the traffic coming from
different approaches and going to a common destination into a
single stream
• Weaving
– Combined movement of both merging and diverging
movements in the same direction
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 9 / 23
Design elements
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 10 / 23
Design elements
• Design speed
• Radius at entry
• Exit width
• Radius of central
island
• Weaving length and
width
• Entry and exit
widths
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 11 / 23
Design elements
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 12 / 23
Design elements
• Design speed
– 30 and 40 kmph for urban and rural areas
respectively
• Entry, exit and central island radius
– Entry radius of about 20 and 25 meters is ideal for an
urban and rural design respectively
– Exit radius higher than entry radius and radius of the
rotary island so that vehicles will discharge from
rotary at a higher rate
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 13 / 23
Design elements
• Entry, exit and central island radius
– A general practice is to keep the exit radius as 1.5 to
2 times the entry radius
– If pedestrian movement is higher at the exit approach,
then the exit radius could be set as same as that of
the entry radius
– The radius of the central island which is about 1.3
times that of the entry curve is adequate for all
practical purposes
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 14 / 23
Rotary Design Elements
Weaving Length
• It determines the ease with which the traffic can
merge and diverge.
• It is decided on the basis of factors such as width of
weaving section, average width of entry, total traffic
and speed.
Width of Carriageway at Entry and Exit
Design elements
Weaving width
e1 is width of the carriageway at the entry
e2 is carriageway width at exit
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 17 / 23
Capacity of a rotary
• TRL’s empirical formula
average entry and exit width
Capacity
proportion of weaving traffic
weaving width
length of weaving section
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 18 / 23
Capacity of a rotary
• Weaving operation in a rotary
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 19 / 23
Capacity of a rotary
• Capacity formula is valid only if
– Weaving width at the rotary is in between 6 and 18
meters.
– Ratio of weaving width to weaving length of the
roundabout is in between 0.12 and 0.4
– Proportion of weaving traffic to non-weaving traffic in
the rotary is in the range of 0.4 and 1
– Weaving length available at the intersection is in
between 18 and 90 m
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 20 / 23
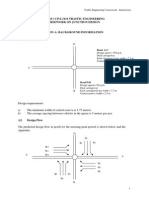
Example
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 22 / 23
Example- Solution
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 23 / 23
Example- Solution
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 24 / 23
Example- Solution
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 25 / 23
Example- Solution
12/8/2022 Traffic Rotaries 26 / 23
You might also like
- 08/23/2022 Road Intersection 1Document50 pages08/23/2022 Road Intersection 1black webNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Cross Section ElementsDocument41 pagesLecture 5 - Cross Section ElementsMalik UmarNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument133 pagesChapter ThreeMamuye Busier YesufNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument133 pagesChapter ThreeMamuye Busier YesufNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document132 pagesChapter 3Anteneh GeremewNo ratings yet
- RotaryDocument23 pagesRotaryprashantyadav98100% (1)
- Traffic and TransportDocument62 pagesTraffic and TransportJeffy GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Roundabout FigueroaDocument32 pagesRoundabout FigueroaSima Viorel100% (1)
- Roundabout Figueroa PDFDocument32 pagesRoundabout Figueroa PDFjdaoukNo ratings yet
- STPDF1 - Highway Geometric DesignDocument31 pagesSTPDF1 - Highway Geometric DesignLuis FonbuenaNo ratings yet
- Batch 10A Mini ProjectDocument24 pagesBatch 10A Mini ProjectRaghu Vamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- CTEV201-Module 5 Junctions 2023Document24 pagesCTEV201-Module 5 Junctions 2023Singo austinNo ratings yet
- ADI Module 2Document16 pagesADI Module 2vs.shernazNo ratings yet
- Geometric Design Facilities of HighwayDocument80 pagesGeometric Design Facilities of Highwayc/qaadir100% (1)
- Elements of Road X-Section PDFDocument20 pagesElements of Road X-Section PDFMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 1Document142 pagesModule 2 1Pankaj N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Transportation Engineering II (Lec - 4)Document16 pagesTransportation Engineering II (Lec - 4)ali hasanNo ratings yet
- Traffic Design and Visual AidsDocument40 pagesTraffic Design and Visual AidsPrakash SamshiNo ratings yet
- Transportation - II: by Engr. Muhammad Waseem Lecturer Department of Civil Engineering UET, JalozaiDocument38 pagesTransportation - II: by Engr. Muhammad Waseem Lecturer Department of Civil Engineering UET, JalozaiShahid AliNo ratings yet
- 2-Ce103-1 Highway Development and PlanningDocument32 pages2-Ce103-1 Highway Development and PlanningUnesca TeeNo ratings yet
- CE 312 Designing The HighwayDocument94 pagesCE 312 Designing The HighwayAgbon TangogNo ratings yet
- Mini Roundabout PDFDocument36 pagesMini Roundabout PDFGopi C Shrestha100% (1)
- Intro Transportation PDFDocument7 pagesIntro Transportation PDFberkely19No ratings yet
- Highway Geometric Alignment and Design LectureDocument98 pagesHighway Geometric Alignment and Design LectureMatthew MazivanhangaNo ratings yet
- Rotary IntersectionDocument24 pagesRotary IntersectionPark Leo0% (1)
- Traffic Signal DesignDocument37 pagesTraffic Signal Designsredhar sNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document68 pagesUnit 5Gundrathi Narendra GoudNo ratings yet
- Consistency and Design SpeedDocument36 pagesConsistency and Design SpeedJocydane PachecoNo ratings yet
- RROW and Geometric DesignDocument51 pagesRROW and Geometric DesignJaymark Soriano100% (1)
- Traffic ManagementDocument43 pagesTraffic ManagementJeffy GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Geometric Design of HighwayDocument111 pagesGeometric Design of Highwayhana myka gatonNo ratings yet
- Designing HighwayDocument153 pagesDesigning HighwayGraezelNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Traffic EngineeringDocument65 pagesCH 1 Traffic Engineeringblack webNo ratings yet
- Highway Geometric DesignDocument34 pagesHighway Geometric DesignHilary DonaldsonNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 - Lecture1 CIV241Document51 pagesUNIT 1 - Lecture1 CIV241Soumya MishraNo ratings yet
- Geometric Cross Section - Highways: GeneralDocument16 pagesGeometric Cross Section - Highways: GeneralAngel Alyza SisonNo ratings yet
- Dibyendu Sengupta Geometric Design For Highways v1 PDFDocument50 pagesDibyendu Sengupta Geometric Design For Highways v1 PDFbharadwaj keerthi100% (1)
- Transportation Slide PDFDocument147 pagesTransportation Slide PDFMd ZimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document30 pagesLecture 9Mohamed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Sight Distance: TR 320 Highway Geometric DesignDocument27 pagesLecture 4: Sight Distance: TR 320 Highway Geometric DesignIsmail A IsmailNo ratings yet
- Geometric Design of Highways (2 Units)Document31 pagesGeometric Design of Highways (2 Units)Gerald MagingaNo ratings yet
- Highway Geometric DesignDocument89 pagesHighway Geometric Designphani sankarNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1Document15 pagesModule 3.1James LabarintoNo ratings yet
- Cross Sectional Elements: 12.2.1 FrictionDocument9 pagesCross Sectional Elements: 12.2.1 FrictionravishnkNo ratings yet
- Geometric Design 1Document59 pagesGeometric Design 1Maria Divina Romero TabuaNo ratings yet
- NaviDocument36 pagesNaviSubbaReddyNo ratings yet
- Traffic IslandDocument9 pagesTraffic Islandanthropolozist entertainNo ratings yet
- CH-3 Geometric Design of HighwaysDocument146 pagesCH-3 Geometric Design of HighwaysRmesh jhaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Supply Chain ManagementDocument106 pagesModule 7 - Supply Chain ManagementPooja Shah100% (1)
- Ometric Design of Highways-1Document72 pagesOmetric Design of Highways-1Rajas AthalyeNo ratings yet
- Design of RoundaboutDocument28 pagesDesign of RoundaboutKarthika SNo ratings yet
- Highway Enterance ExamDocument31 pagesHighway Enterance ExamKebede ShawergaNo ratings yet
- 4565chapter 4 (1), Hoghway Geometric DesignDocument66 pages4565chapter 4 (1), Hoghway Geometric DesignKarim AljawhariNo ratings yet
- Hill RoadsDocument28 pagesHill RoadskoushikNo ratings yet
- HIGHWAYS, Geometric Design and Components of HighwaysDocument75 pagesHIGHWAYS, Geometric Design and Components of Highwaysabubakar100% (1)
- 2.2 Design Criteria of HighwaysDocument26 pages2.2 Design Criteria of HighwaysMikealla David100% (1)
- At Grade IntersectionDocument12 pagesAt Grade IntersectionRainnie Casandra100% (1)
- Casestudy of Roundabout at KandivaliDocument9 pagesCasestudy of Roundabout at KandivaliKishore PrajapatNo ratings yet
- CE 453 Highway Design Iowa State University Highway Design Criteria OverviewDocument22 pagesCE 453 Highway Design Iowa State University Highway Design Criteria OverviewHaile G/MariamNo ratings yet
- Motor Truck Logging Methods Engineering Experiment Station Series, Bulletin No. 12From EverandMotor Truck Logging Methods Engineering Experiment Station Series, Bulletin No. 12No ratings yet
- Preprocessing PDFDocument41 pagesPreprocessing PDFsredhar sNo ratings yet
- Intro To Big Data PDFDocument42 pagesIntro To Big Data PDFsredhar sNo ratings yet
- Data Science PDFDocument11 pagesData Science PDFsredhar sNo ratings yet
- FDamsDocument76 pagesFDamssredhar sNo ratings yet
- Data Preprocessing in PythonDocument12 pagesData Preprocessing in Pythonsredhar sNo ratings yet
- Traffic Safety and EnvironmentDocument49 pagesTraffic Safety and Environmentsredhar sNo ratings yet
- Traffic Signal DesignDocument37 pagesTraffic Signal Designsredhar sNo ratings yet
- ChannelizationDocument12 pagesChannelizationsredhar sNo ratings yet
- Signal Co OrdinationDocument9 pagesSignal Co Ordinationsredhar sNo ratings yet
- Salient FeaturesDocument2 pagesSalient FeaturesAkshay ShindeNo ratings yet
- Management Information System "Infrastructure"Document13 pagesManagement Information System "Infrastructure"maba261067% (3)
- Free-Draining Daylighted SubbasesDocument2 pagesFree-Draining Daylighted SubbasesBridger WangNo ratings yet
- LogView 7 - Untitled PDFDocument5 pagesLogView 7 - Untitled PDFMaza Yudha ErlandaNo ratings yet
- Đề Key Vstep Writing - Vstep SvDocument22 pagesĐề Key Vstep Writing - Vstep SvHà Phương PhạmNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Boq - Civil Work of Kilpauk ResidenceDocument12 pagesPreliminary Boq - Civil Work of Kilpauk ResidenceVasanthakumarNo ratings yet
- eBOOK - Election Guide - Nickolaus BauerDocument144 pageseBOOK - Election Guide - Nickolaus BauerToni BotesNo ratings yet
- CBD - 20220816 - PPT - Intro To PPP - DILG NEO - Final (Aug20)Document37 pagesCBD - 20220816 - PPT - Intro To PPP - DILG NEO - Final (Aug20)Dianne GraceNo ratings yet
- PR-09-14 ModulysGP GB Press ReleaseDocument2 pagesPR-09-14 ModulysGP GB Press Releasejbperfecto_csciNo ratings yet
- Volume 3 Part 2 Chapter 2Document71 pagesVolume 3 Part 2 Chapter 2HaZr AfiszNo ratings yet
- 4701-Article Text-13620-1-10-20141206Document33 pages4701-Article Text-13620-1-10-20141206EdiNo ratings yet
- Dams: Parts, PakistanDocument22 pagesDams: Parts, PakistanEnigmatic Yousafzai100% (1)
- Decatur Tree OrdinanceDocument25 pagesDecatur Tree OrdinanceZachary HansenNo ratings yet
- Bored Pile Design in Stiff Clay IDocument21 pagesBored Pile Design in Stiff Clay IVardhanNo ratings yet
- Vision 2040Document136 pagesVision 2040ambryx2001No ratings yet
- Assignment QuestionDocument4 pagesAssignment QuestionTerwabe WapagovskiNo ratings yet
- EthiopiaDocument32 pagesEthiopiaTesfaye Mulu100% (1)
- Schedule - G 1Document6 pagesSchedule - G 1A RajaNo ratings yet
- National Slum PolicyDocument28 pagesNational Slum PolicyPushpendra100% (7)
- Time Table For Gate ArchitectureDocument10 pagesTime Table For Gate ArchitectureMOHAMMAD SIDDIQ SALIMNo ratings yet
- Role Agriculture in Developing CountriesDocument190 pagesRole Agriculture in Developing CountriesSuhas KandeNo ratings yet
- Land Value Capture Finance For Transport Accessibility A Review 2012 Journal of Transport GeographyDocument8 pagesLand Value Capture Finance For Transport Accessibility A Review 2012 Journal of Transport GeographyZen ZeeNo ratings yet
- Rules of Thumb Geotech MonitoringDocument1 pageRules of Thumb Geotech MonitoringMadan Kumar AnnamNo ratings yet
- Did You Know That Underpinning of Foundations Is Notifiable Work Under The Building RegulationsDocument7 pagesDid You Know That Underpinning of Foundations Is Notifiable Work Under The Building RegulationsNur Hidayah100% (1)
- The Mechanics of Soils AND: FoundationsDocument7 pagesThe Mechanics of Soils AND: FoundationsRAJIT KUMAR YADAVNo ratings yet
- Load Forecasting For Modern Distribution SystemsDocument114 pagesLoad Forecasting For Modern Distribution SystemsMikhaelRodriguezNo ratings yet
- The Information Technology (It) Industry in Bangalore: A Case of Urban Competitiveness in India?Document25 pagesThe Information Technology (It) Industry in Bangalore: A Case of Urban Competitiveness in India?Neerupa Rajiv SisodiaNo ratings yet
- Single-Line & Gas Schematic Diagramme: Double BusbarDocument21 pagesSingle-Line & Gas Schematic Diagramme: Double BusbarVictor GuzmanNo ratings yet
- The History of The Philippines EssayDocument9 pagesThe History of The Philippines EssayMario SalinasNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2405896322019449 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S2405896322019449 MainRia Idola SurbaktiNo ratings yet