Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity 1 - 2nd Quarter Earthquake
Uploaded by
jay pascualOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity 1 - 2nd Quarter Earthquake
Uploaded by
jay pascualCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity 1- 2nd Quarter Section: 8- Forgiveness
EARTHQUAKE
MEMBERS:
Dangel Lei Dolor
Cristopher Isles
Myrthle Clarize R. Pascual
ANSWERS TO THE QUESTIONS
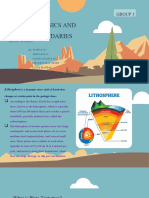
1. Water forms some features of Earth's surface such as rivers, oceans, beaches and lakes. Other surface features, such as
mountains, earthquakes and volcanoes, are formed when large pieces of the Earth’s outer layer move slowly by plate tectonics.
2. A divergent boundary occurs when two tectonic plates move away from each other. Along these boundaries,
earthquakes are common and magma (molten rock) rises from the Earth’s mantle to the surface, solidifying to create
new oceanic crust. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge and Pacific Ring of Fire are two examples of divergent plate boundaries.
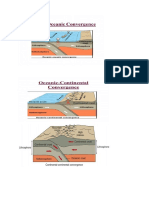
When two plates come together, it is known as a convergent boundary. The impact of the colliding plates can cause
the edges of one or both plates to buckle up into a mountain ranges or one of the plates may bend down into a deep
seafloor trench. A chain of volcanoes often forms parallel to convergent plate boundaries and powerful earthquakes
are common along these boundaries. At convergent plate boundaries, oceanic crust is often forced down into the
mantle where it begins to melt. Magma rises into and through the other plate, solidifying into granite, the rock that
makes up the continents. Thus, at convergent boundaries, continental crust is created and oceanic crust is destroyed.
Two plates sliding past each other forms a transform plate boundary. One of the most famous transform plate
boundaries occurs at the San Andreas fault zone, which extends underwater. Natural or human-made structures that
cross a transform boundary are offset—split into pieces and carried in opposite directions. Rocks that line the
boundary are pulverized as the plates grind along, creating a linear fault valley or undersea canyon. Earthquakes are
common along these faults. In contrast to convergent and divergent boundaries, crust is cracked and broken at
transform margins, but is not created or destroyed
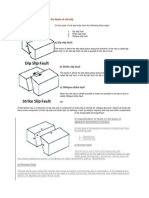
3. Sudden motions along faults cause rocks to break and move suddenly, releasing the stored up stress energy to
create an earthquake. A slip is the distance rocks move along a fault and can be up or down the fault plane.
4. .three different types of faults: Normal, Reverse, and Transcurrent (Strike-Slip). Normal faults form when the
hanging wall drops down. ... Reverse faults form when the hanging wall moves up. The forces creating reverse faults
are compressional, pushing the sides together.
You might also like
- g10 - Science-Sl 4 Plate Boundaries Ay 2021-2022Document4 pagesg10 - Science-Sl 4 Plate Boundaries Ay 2021-2022Mark Niño JavierNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries: Earth's Surface Is Dramatically Reshaping Itself in An Endless, Slow-Motion Movement Called PlateDocument3 pagesPlate Boundaries: Earth's Surface Is Dramatically Reshaping Itself in An Endless, Slow-Motion Movement Called Platedaisy sorianoNo ratings yet
- Milfa FilesDocument2 pagesMilfa Filesjolfa fradejasNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Group 3Document17 pagesEarth Science Group 3reignchan640No ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Theory Explained in 10 ModulesDocument4 pagesPlate Tectonics Theory Explained in 10 ModulesArgie Mabag100% (2)
- Plate Boundaries and EffectsDocument3 pagesPlate Boundaries and EffectsjnlljoyNo ratings yet
- M1-Topic 2. Plate Tectonics and Faults-1Document11 pagesM1-Topic 2. Plate Tectonics and Faults-1Mark Andykenn Liaga MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Review Lessons: Essential Questions: 1.what Are The Three Types of 2.when Do They Occur?Document43 pagesReview Lessons: Essential Questions: 1.what Are The Three Types of 2.when Do They Occur?maris100% (1)
- Tectonic Plates NotesDocument3 pagesTectonic Plates NotesAngelica CamilonNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes: by Emman ValleDocument17 pagesEarthquakes: by Emman ValleRaul Carl CapinpuyanNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument14 pagesPlate TectonicsCarl AducaNo ratings yet
- Science Plate BoundariesDocument3 pagesScience Plate BoundariesAshley VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesPlate TectonicsAmelia KaisersinghNo ratings yet
- Tracing The Pacific Ring of FireDocument7 pagesTracing The Pacific Ring of FireSatsuki MomoiNo ratings yet
- Graben Is A Valley With A Distinct Escarpment On Each Side Caused by The Displacement of A Block of LandDocument3 pagesGraben Is A Valley With A Distinct Escarpment On Each Side Caused by The Displacement of A Block of LandEhr WinNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries ActivityDocument5 pagesPlate Boundaries ActivityMaestro de GrapicoNo ratings yet
- Research in Earth and Life ScienceDocument2 pagesResearch in Earth and Life ScienceJohn DaleNo ratings yet
- Voc 3 8th 2020-03-23 at 10.47.04 AMDocument8 pagesVoc 3 8th 2020-03-23 at 10.47.04 AMJasir June DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Q1Document80 pagesReviewer Q1Keanna marie GanaNo ratings yet
- Convergent Boundaries: Divergent BoundaryDocument3 pagesConvergent Boundaries: Divergent BoundaryTrishia PinedaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Plate BoundariesNgaatendwe kodogoNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of Plate Boundaries: Divergent, Convergent, TransformDocument2 pages3 Types of Plate Boundaries: Divergent, Convergent, TransformZenly AlleraNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of Plate BoundariesIsla VermilionNo ratings yet
- Geography Handout 4Document14 pagesGeography Handout 4LoviNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries Are The Zones Where The EarthDocument2 pagesPlate Boundaries Are The Zones Where The Earthrachel adavanNo ratings yet
- Effects of Divergent Boundaries ExplainedDocument9 pagesEffects of Divergent Boundaries Explainedalaiza cabilladaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesNotes On Plate BoundariesDaniel HarrisNo ratings yet
- Types of Plate Boundaries: 1. Convergent Boundaries - Where Two Plates Are CollidingDocument2 pagesTypes of Plate Boundaries: 1. Convergent Boundaries - Where Two Plates Are CollidingstephNo ratings yet
- Study Guide AnswersDocument4 pagesStudy Guide AnswersYeashika GovilaNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and VolcanoesDocument21 pagesEarthquakes and VolcanoesArnold VasheNo ratings yet
- Types of Plate Boundaries Exercise 2Document5 pagesTypes of Plate Boundaries Exercise 2Isabella persadNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of The EarthDocument3 pagesInternal Structure of The Earthmikaya wrightNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Science: Name: Leila Rose Junio Section: 10 Fleming Teacher: Mrs TabiraoDocument7 pagesPortfolio in Science: Name: Leila Rose Junio Section: 10 Fleming Teacher: Mrs TabiraoChristian FloresNo ratings yet
- Earthquake LessonDocument46 pagesEarthquake LessonAvis pittNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Landforms: by Johnathan RiemersDocument8 pagesTectonic Landforms: by Johnathan Riemerstiel7235No ratings yet
- How Plates MoveDocument5 pagesHow Plates Movelucasjorgelindo6335No ratings yet
- G10 Science Notes - Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesG10 Science Notes - Plate TectonicsCairo DiazNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument41 pagesEarthquakeASNINo ratings yet
- Divergent Plate Boundaries Are Locations Where Plates Are Moving Away From OneDocument4 pagesDivergent Plate Boundaries Are Locations Where Plates Are Moving Away From OneJann Roed FloresNo ratings yet
- Tectonics PlatesDocument12 pagesTectonics PlatesChidhuro OwenNo ratings yet
- Sci ReviewerDocument7 pagesSci ReviewerBxbble BerriNo ratings yet
- Subject:: ModèleDocument10 pagesSubject:: ModèleAnouar ChraibiNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument5 pagesPlate Tectonic TheoryDenise Anne SolidadNo ratings yet
- Geography Sample 30 Mark Question and AnswerDocument1 pageGeography Sample 30 Mark Question and AnswerCatherine Julia O'ConnellNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic Grade 7Document12 pagesPlate Tectonic Grade 7HassanAbbas MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Notes in Science (Semi-Final)Document5 pagesNotes in Science (Semi-Final)Rachel Hanh AbaloNo ratings yet
- Article On What Forms in Divergent Boundaries and TransformDocument2 pagesArticle On What Forms in Divergent Boundaries and TransformGUILLER BELENNo ratings yet
- EndogenicDocument38 pagesEndogenicAngelica SeñaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Plate BoundariesDocument24 pagesLesson 2 - Plate BoundariesArnel Jeffrey OñateNo ratings yet
- q1 m6Document16 pagesq1 m6mtchqnlNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics PPDocument30 pagesPlate Tectonics PPdazwerk123No ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Web Quest StudentDocument8 pagesPlate Tectonics Web Quest Studentapi-33569025579% (24)
- Notes Leaving Certificate Physical GeographyDocument39 pagesNotes Leaving Certificate Physical GeographySurbhi Singhal 0313No ratings yet
- The Different Processes That Occur Along The Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesThe Different Processes That Occur Along The Plate Boundariesrachel adavanNo ratings yet
- Plate Movements and BoundariessDocument29 pagesPlate Movements and BoundariessZei LandichoNo ratings yet
- Plate BoundariesDocument17 pagesPlate BoundariesKyle Krizzia Esplana IINo ratings yet
- What Is PLATE Tectonics?Document51 pagesWhat Is PLATE Tectonics?Jane Idk100% (1)
- Tectonic Movements: Can They Change An EcosystemDocument19 pagesTectonic Movements: Can They Change An Ecosystemmeljan degamonNo ratings yet
- Three Main Types of Plate BounderiesDocument2 pagesThree Main Types of Plate BounderiesNyrrah PolvorosaNo ratings yet
- Day_3_Attendance_and_ParticipationDocument2 pagesDay_3_Attendance_and_Participationjay pascualNo ratings yet
- Day_4_Attendance_and_ParticipationDocument2 pagesDay_4_Attendance_and_Participationjay pascualNo ratings yet
- senior scout orientation pptDocument58 pagessenior scout orientation pptjay pascualNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan for Grade 7Document7 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan for Grade 7jay pascualNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan for Grade 7Document7 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan for Grade 7jay pascualNo ratings yet
- The Ag-Mn-Pb-Zn Vein, Replacement, and Skarn Deposits ofDocument36 pagesThe Ag-Mn-Pb-Zn Vein, Replacement, and Skarn Deposits ofjuniorandrade2009No ratings yet
- Polyphase Deformation and Strain Migration On The Septentrional-Oriente Fault Zone in The Windward Passage, Northern Caribbean Plate BoundaryDocument25 pagesPolyphase Deformation and Strain Migration On The Septentrional-Oriente Fault Zone in The Windward Passage, Northern Caribbean Plate BoundaryAlana SéguierNo ratings yet
- Rock Deformation: Stress, Strain, Folds and FaultsDocument29 pagesRock Deformation: Stress, Strain, Folds and FaultsjoeyNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Evolution of Tripura-Mizoram Fold Belt 1983Document9 pagesTectonic Evolution of Tripura-Mizoram Fold Belt 1983Sujit DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Caracteristics of Epithermal DepositsDocument14 pagesCaracteristics of Epithermal DepositsJym B. Ch.No ratings yet
- DRRRM Module Lesson 3-6Document24 pagesDRRRM Module Lesson 3-6Naomi BelonioNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Systems of Indonesia PDFDocument28 pagesPetroleum Systems of Indonesia PDFWahyu Probo Ananto HadiNo ratings yet
- 3 Seismologifundamental3Document202 pages3 Seismologifundamental3Hilmi AdibNo ratings yet
- Blouberg Nature Reserve Visitor GuideDocument99 pagesBlouberg Nature Reserve Visitor GuideJeff W MorrisNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument6 pagesEndogenic ProcessesBenjamin AmbiaNo ratings yet
- Nature and Occurence of HK RocksDocument57 pagesNature and Occurence of HK RocksYau Ka Ki JackyNo ratings yet
- 10 1 1 625 3048 PDFDocument20 pages10 1 1 625 3048 PDFShankar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Cable Bolt Optimisation at Mine Bousquet-PaperDocument25 pagesCable Bolt Optimisation at Mine Bousquet-PaperKevin MarroquínNo ratings yet
- Classification of FaultsDocument3 pagesClassification of FaultsAbdul Moeed KalsonNo ratings yet
- Geography 9 CHP 3-1Document12 pagesGeography 9 CHP 3-1xyz 999100% (1)
- Asad Seismic Zones of PakistanDocument5 pagesAsad Seismic Zones of PakistanM Baqir IsmailNo ratings yet
- Geology of Central Park from Rocks to IceDocument25 pagesGeology of Central Park from Rocks to IceShe TimbancayaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional Geolistrik 2Document12 pagesJurnal Internasional Geolistrik 2agusitampan100% (1)
- Structural Geology Seminar - Volumen I - SDocument441 pagesStructural Geology Seminar - Volumen I - SJuan Diego LozanoNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - Earth and Space FinalDocument107 pagesUnit IV - Earth and Space FinalRonel BuhayNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Lesson Plan 2022Document5 pagesEarthquake Lesson Plan 2022Maylyn Grace Dalumpines-Colon EbonaloNo ratings yet
- California Seismic Hazard MapReportDocument65 pagesCalifornia Seismic Hazard MapReportnotavalidemail1952No ratings yet
- Kink MethodDocument7 pagesKink MethodOktoberiman SNo ratings yet
- GEOPHYS130 L12 Focal MechanismsDocument57 pagesGEOPHYS130 L12 Focal MechanismsHafiz SaputraNo ratings yet
- Chamberlain Et Al 2001 4th IAS Extended AbstractDocument3 pagesChamberlain Et Al 2001 4th IAS Extended AbstractRegina EfraimNo ratings yet
- AtlasPoCu CCC 20190805Document33 pagesAtlasPoCu CCC 20190805David GoteraNo ratings yet
- EL M/ Week 5 6Document20 pagesEL M/ Week 5 6Mariels FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 DRRRDocument28 pagesChapter 4 DRRRwendell john medianaNo ratings yet
- World Geography Sumit Sir EnglishDocument63 pagesWorld Geography Sumit Sir EnglishRavindra Rajput100% (1)
- Field Report of KashmirDocument26 pagesField Report of KashmirAbdullah FarooqNo ratings yet