Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geography Sample 30 Mark Question and Answer
Uploaded by
Catherine Julia O'ConnellOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geography Sample 30 Mark Question and Answer
Uploaded by
Catherine Julia O'ConnellCopyright:
Available Formats
Describe and explain destructive plate boundaries (30M)
A plate is a broken part of the earths crust. Plates move due to convection currents.
Magma heated in lower mantle, rises towards lithosphere, cools and becomes semi-
molten, moves sideways and sinks. This process is continuously repeated. Sideways
movement causes friction. This friction results in the movement of plates. This friction
causes the plates to move apart, collide or move past each other. This is where plate
boundaries are created constructive – where plates separate, destructive – where
plates collide and neutral where plates move past each other. In this answer I will
discuss destructive plate boundaries.
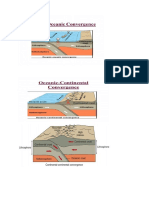
Destructive plate boundaries occur in 3 situations firstly where an oceanic and
continental plate collide e.g. Nazca and south American plates. When a continental and
an oceanic plate collide, the heavier oceanic plate sinks into the mantle. This is called
subduction. During subduction the magma moves up towards the continental crust
above to form explosive volcanic mountains e.g. the Andes. Deep sea trenches form at
the boundary of the colliding plates e.g. Peru Chile trench. Deep sea earthquakes are
associated with these trenches due to the lighter continental plate being pushed
upwards fold mountains are formed e.g. the alps.
Secondly, destructive plate boundaries occur where 2 continental plates collide e.g. the
Indo-Australian Plate is colliding with the Eurasian Plate. When two continental plates
collide, neither plate is subducted. This is because continental plates are too light to be
forced downward. The movement is mainly upwards. This process is called uplift. Both
plates are destroyed at the collision has caused the rock to buckle upwards forming
fold mountains e.g. the Himalayas
Earthquakes are common along continental-continental plate boundaries as friction
between the plates causes the crust to vibrate
Thirdly destructive plate boundaries occur where two oceanic plates collide.
When two oceanic plates collide, the heavier plate subducts underneath the lighter
plate. The plate sinks into the mantle and melts. Magma from the melting plate rises
upwards through the overlying plate. Eventually, the magma reaches the surface,
forming volcanoes. As material from the volcanoes build up, volcanic arc islands are
formed, e.g. the Mariana Islands in the Pacific Ocean
The friction caused between a subducting and an overlying plate leads to strong
earthquakes occurring along the boundary.
You might also like
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of The EarthDocument3 pagesInternal Structure of The Earthmikaya wrightNo ratings yet
- Types of Plate Boundaries Exercise 2Document5 pagesTypes of Plate Boundaries Exercise 2Isabella persadNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic Grade 7Document12 pagesPlate Tectonic Grade 7HassanAbbas MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Tectonics PlatesDocument12 pagesTectonics PlatesChidhuro OwenNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Theory Explained in 10 ModulesDocument4 pagesPlate Tectonics Theory Explained in 10 ModulesArgie Mabag100% (2)
- Notes On Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesNotes On Plate BoundariesDaniel HarrisNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The EarthDocument4 pagesThe Structure of The EarthKishanNo ratings yet
- G10 Science Notes - Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesG10 Science Notes - Plate TectonicsCairo DiazNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and VolcanoesDocument21 pagesEarthquakes and VolcanoesArnold VasheNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Science: Name: Leila Rose Junio Section: 10 Fleming Teacher: Mrs TabiraoDocument7 pagesPortfolio in Science: Name: Leila Rose Junio Section: 10 Fleming Teacher: Mrs TabiraoChristian FloresNo ratings yet
- Tracing The Pacific Ring of FireDocument7 pagesTracing The Pacific Ring of FireSatsuki MomoiNo ratings yet
- Processes That Occur Along Plate BoundariesDocument20 pagesProcesses That Occur Along Plate BoundariesBiancaKookieeNo ratings yet
- Science Plate BoundariesDocument3 pagesScience Plate BoundariesAshley VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - 2nd Quarter EarthquakeDocument1 pageActivity 1 - 2nd Quarter Earthquakejay pascualNo ratings yet
- Review Lessons: Essential Questions: 1.what Are The Three Types of 2.when Do They Occur?Document43 pagesReview Lessons: Essential Questions: 1.what Are The Three Types of 2.when Do They Occur?maris100% (1)
- Milfa FilesDocument2 pagesMilfa Filesjolfa fradejasNo ratings yet
- Shear Stress: FaultDocument2 pagesShear Stress: Faultbae joohyunNo ratings yet
- Graben Is A Valley With A Distinct Escarpment On Each Side Caused by The Displacement of A Block of LandDocument3 pagesGraben Is A Valley With A Distinct Escarpment On Each Side Caused by The Displacement of A Block of LandEhr WinNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics NotesDocument41 pagesPlate Tectonics NotesWilfred MuiaNo ratings yet
- Divergent Plate Boundaries Are Locations Where Plates Are Moving Away From OneDocument4 pagesDivergent Plate Boundaries Are Locations Where Plates Are Moving Away From OneJann Roed FloresNo ratings yet
- Convergent Boundaries: Divergent BoundaryDocument3 pagesConvergent Boundaries: Divergent BoundaryTrishia PinedaNo ratings yet
- Plate BoundariesDocument5 pagesPlate BoundariesMaria Sophia ManuelNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument14 pagesPlate TectonicsCarl AducaNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesPlate TectonicsAmelia KaisersinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesLesson 2 Plate Tectonicsrobyngaylebautista2No ratings yet
- Subject:: ModèleDocument10 pagesSubject:: ModèleAnouar ChraibiNo ratings yet
- Note For Earth and Life Science3Document5 pagesNote For Earth and Life Science3Apple Mae AlegriaNo ratings yet
- Earth's interior and plate tectonicsDocument2 pagesEarth's interior and plate tectonicsRohin Amit WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Earth Movements and Resultant LandformsDocument25 pagesEarth Movements and Resultant LandformsEmille Grace NistalNo ratings yet
- Seafloor Spreading HandoutsDocument1 pageSeafloor Spreading Handoutsbae joohyunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Plate BoundariesNgaatendwe kodogoNo ratings yet
- g10 - Science-Sl 4 Plate Boundaries Ay 2021-2022Document4 pagesg10 - Science-Sl 4 Plate Boundaries Ay 2021-2022Mark Niño JavierNo ratings yet
- Science PeriodicalDocument10 pagesScience PeriodicalduranfredrichinocianNo ratings yet
- Hand OutsDocument6 pagesHand OutsMJ DejosNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document9 pagesScience 10Myca IlustrisimoNo ratings yet
- How Plates MoveDocument5 pagesHow Plates Movelucasjorgelindo6335No ratings yet
- Plate BoundariesDocument4 pagesPlate BoundariesRoland Rawlins IgaborNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Plates NotesDocument3 pagesTectonic Plates NotesAngelica CamilonNo ratings yet
- Sci ReviewerDocument7 pagesSci ReviewerBxbble BerriNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries Are The Zones Where The EarthDocument2 pagesPlate Boundaries Are The Zones Where The Earthrachel adavanNo ratings yet
- Diastrophism Content PaperDocument24 pagesDiastrophism Content PaperKayraine Mae Edillor CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 8 ScienceDocument16 pagesReviewer 8 ScienceJhanna Gil BuctolanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of Plate BoundariesIsla VermilionNo ratings yet
- SCEC Explains Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesSCEC Explains Plate TectonicsHendro Novianto100% (3)
- What Is PLATE Tectonics?Document51 pagesWhat Is PLATE Tectonics?Jane Idk100% (1)
- EARTH SCIENCE ReviewerDocument11 pagesEARTH SCIENCE ReviewerLeira EroaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document1 pageLesson 1Fullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- شرح تيكتونكس - ٠٥١٨٣٨Document27 pagesشرح تيكتونكس - ٠٥١٨٣٨Mohammed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessDocument23 pagesEndogenic Processleomar ignacioNo ratings yet
- Paleomagnetism: Curie PointDocument47 pagesPaleomagnetism: Curie PointTyler MroskoNo ratings yet
- Convergent Boundary Divergent Boundary: Plate BoundariDocument3 pagesConvergent Boundary Divergent Boundary: Plate Boundarimarianneb.dulfoNo ratings yet
- Igcse Plate Tectonics 2015Document39 pagesIgcse Plate Tectonics 2015api-261914272100% (3)
- The Different Processes That Occur Along The Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesThe Different Processes That Occur Along The Plate Boundariesrachel adavanNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesPlate TectonicsZara AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Four LayersDocument12 pagesThe Four LayersNanette A. Marañon-SansanoNo ratings yet
- Research in Earth and Life ScienceDocument2 pagesResearch in Earth and Life ScienceJohn DaleNo ratings yet
- Plate BoundariesDocument17 pagesPlate BoundariesKyle Krizzia Esplana IINo ratings yet
- Reviewer Ni MadukusoDocument2 pagesReviewer Ni MadukusoAndrei Maddox PilotNo ratings yet
- Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia's 2017 Voluntary National Reviews on SDGsDocument52 pagesFederal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia's 2017 Voluntary National Reviews on SDGsAshagre MekuriaNo ratings yet
- Manual Instlacion y Servicio Logix Magnum IT and CV ValvesDocument69 pagesManual Instlacion y Servicio Logix Magnum IT and CV ValvesmortifileNo ratings yet
- Gym Membership AgreementDocument3 pagesGym Membership Agreementzde thai100% (1)
- Assess Effectiveness of Video Assisted Teaching Programme On Learning Disabilities of School Children Among Primary School Teachers in Selected Schools of PalvonchaDocument5 pagesAssess Effectiveness of Video Assisted Teaching Programme On Learning Disabilities of School Children Among Primary School Teachers in Selected Schools of PalvonchaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- SvagreementDocument28 pagesSvagreementRowena RayosNo ratings yet
- Chap4 Q Consumer Behavior and Marketing StrategiesDocument14 pagesChap4 Q Consumer Behavior and Marketing StrategiesAdib WasiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - HTT547Document33 pagesChapter 3 - HTT547Faadhil MahruzNo ratings yet
- Drugs MnemonicsDocument6 pagesDrugs MnemonicsDarrylJavier100% (1)
- If You Have Guts Then Dare To Be DIFFERENTDocument20 pagesIf You Have Guts Then Dare To Be DIFFERENTChirag Saiya (PHILOSOPHER) - SPIRITUAL Speaker and Writer100% (1)
- The Declaration of Alma-Ata at 40Document19 pagesThe Declaration of Alma-Ata at 40Nicole MedinaNo ratings yet
- Public Provident Fund Card Ijariie17073Document5 pagesPublic Provident Fund Card Ijariie17073JISHAN ALAMNo ratings yet
- EOA 2023 VISIOMER Portfolio Brochure en Digital RZ InteraktivDocument13 pagesEOA 2023 VISIOMER Portfolio Brochure en Digital RZ Interaktivichsan hakimNo ratings yet
- Adime Malnutrition and OncolgyDocument6 pagesAdime Malnutrition and Oncolgyapi-300587226100% (1)
- Dengue Fever in The PhilippinesDocument27 pagesDengue Fever in The PhilippinesDale Marie RenomeronNo ratings yet
- The Death Penalty-Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesThe Death Penalty-Literature Reviewapi-582834189No ratings yet
- GRADE 5 Answer Sheet q1 Module 9&10Document6 pagesGRADE 5 Answer Sheet q1 Module 9&10Jina Mellino OrbitaNo ratings yet
- Divine Intervention Episode 5 Cardio A Physiology1Document18 pagesDivine Intervention Episode 5 Cardio A Physiology1Swisskelly1No ratings yet
- WRAP EMS Guide Mar2015Document64 pagesWRAP EMS Guide Mar2015mike24872267No ratings yet
- Cranes & Hoists ProgramDocument28 pagesCranes & Hoists ProgramImtiyaz AkhtarNo ratings yet
- CyberstalkingDocument22 pagesCyberstalkingManasa M DharNo ratings yet
- Clearing Clutter With Eft PDFDocument23 pagesClearing Clutter With Eft PDFIftikhar Hassun100% (2)
- Materials Needed For Breast Care:: Repeat This Step Until The Breast Is CleanDocument4 pagesMaterials Needed For Breast Care:: Repeat This Step Until The Breast Is CleanGulayan, Renz Bryelle T.No ratings yet
- Ureteral Trauma Profile in Soetomo Hospital January 2006 - December 2011Document9 pagesUreteral Trauma Profile in Soetomo Hospital January 2006 - December 2011Nurhafidin RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- The Impact of ProstitutionDocument6 pagesThe Impact of ProstitutionLea TanNo ratings yet
- AcetophenoneDocument3 pagesAcetophenonepriteshpatNo ratings yet
- Root of Women’s Oppression According to Psychoanalytic FeminismDocument8 pagesRoot of Women’s Oppression According to Psychoanalytic FeminismPrincess Janine SyNo ratings yet
- Oil Keeper Job at PacrimDocument2 pagesOil Keeper Job at Pacrimwinda chairunissaNo ratings yet
- Ia On Solubility EquilibriumDocument8 pagesIa On Solubility Equilibriumapi-235913605100% (1)
- 2 Second Grade English Diagnostic Test (Autoguardado)Document5 pages2 Second Grade English Diagnostic Test (Autoguardado)MELISSA KARENTH MONTES PINTONo ratings yet
- DAVAO DOCTORS COLLEGE NURSING DRUG STUDYDocument3 pagesDAVAO DOCTORS COLLEGE NURSING DRUG STUDYJerremy LuqueNo ratings yet