Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class - Xii Sub-Physics - Syllabus Break Up-2022-23 Tigps
Uploaded by
Suman HaldarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class - Xii Sub-Physics - Syllabus Break Up-2022-23 Tigps
Uploaded by
Suman HaldarCopyright:
Available Formats
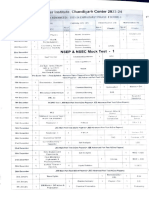
TECHNO INDIA GROUP PUBLIC SCHOOL, BALURGHAT
SYLLABUS BREAK-UP
SESSION-2022-23
CLASS- XII SUBJECT- PHYSICS SUBJECT TEACHER- S.C/A.D
1. BOOK NAME: SCIENCE- NCERT
MONTHS WORKING BOOK CH. CH NAME/ TOPIC
DAYS NO.
1 ELECTRIC FIELDS AND CHARGES
APRIL 20 NCERT
2 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE
3 CURRENT ELECTRICITY
PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT NO.1
3 CURRENT ELECTRICITY
MAY 08 NCERT 4 MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT NO.2
4 MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
JUNE 15 NCERT 5 MAGNETISM AND MATTER
PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT NO.4
JULY 01 NCERT REVISION(1ST PT)
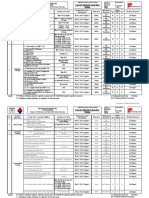
MONTHS WORKING BOOK CH. CH NAME/ TOPIC
DAYS NO.
NCERT 6 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
JULY 22 7 ALTERNATING CURRENTS
NCERT
8 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
9 RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL
INSTRUMENTS
PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT NO.5
9 RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL
INSTRUMENTS
AUGUST 22 NCERT 10 WAVE OPTICS
PRACTICAL ACTIVITY NO.1,2
REVISION (1ST PT+ HALF YEARLY)
SEPTEMBER 02 NCERT
PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT NO.3
MONTHS WORKING BOOK CH. CHNAME/ TOPIC
DAYS NO.
SEPTEMBER 09 NCERT 1 DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND
1 MATTER
PRACTICAL SEC- EXPERIMENT NO.1,5
B
OCTOBER 12 NCERT 1 ATOMS
2
PRACTICAL SEC- EXPERIMENT NO.7,9
B
1 NUCLEI
22 NC 3
NOVEMBER ER
T
NCERT 1 SEMICONDUCTOR
4 -ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES
AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
PRACTICAL SEC- ACTIVITY 1,2
B
REVISION (1ST PT+ HALF YEARLY+ 2ND PT)
DEC 02 NCERT
MONTHS WORKING BOOK CH. CH NAME/ TOPIC
DAYS NO.
REVISION
DEC 15 NCERT (Whole book)
SEC-B ACTIVITY 3
JAN 21 NCERT REVISION
(Whole book)
PRACTICAL/PROJECT
FEB 12 NCERT
NOTE: THERE ARE SOME INTERNAL REDUCTIONS IN THE CHAPTERS. FOR FURTHER CLARIFICATION PLEASE VISIT TO:
https://cbseacademic.nic.in/web_material/CurriculumMain23/SrSec/Physics_SrSec_2022-23.pdf
Chapter Page No . Dropped Topics/
Chapters
Chapter 1: Electric 2–7 1.2 Electric Charge (delete only activity with paper strips
Charges and Fields 47–50 and making
electroscope)
1.3 Conductors and Insulators (delete only concept of
earthing)
1.4 Charging by Induction
Exercises 1.13, 1.25–1.34
Chapter 2: Electrostatic 81 2.15 Energy Stored in a Capacitor (delete only derivation)
Potential and 87–92 Exercises 2.12 to 2.36
Capacitance
Chapter 3: Current 102–103 3.7 Resistivity of Various Materials (delete Tables
Electricity 107–109 3.1 and 3.2 and Carbon resistors, Colour code for
112–113 carbon resistor)
120–124 3.10 Combinations of Resistors – Series and Parallel
127–131 Example 3.5
3.15 Meter Bridge
3.16 Potentiometer
Exercises 3.3, 3.4, 3.10, 3.12, 3.14–3.23
Chapter 4: Moving 135 Table 4.1
Charges and Magnetism 140–142 4.4.1 Velocity Selector
152–153 4.4.2 Cyclotron
162–163 4.8.2 The Toroid
170–172 4.10.3 The Magnetic Dipole Moment of a Revolving Electron
Exercises 4.14–4.28
Chapter 5: Magnetism 176–179 5.2.2 Bar Magnet as an Equivalent Solenoid (delete only
and 180 mathematical treatment)
Matter 185–189 5.2.3 The Dipole in a Uniform Magnetic Field (delete only
191 mathematical treatment)
194–196 Example 5.4
200–203 5.4 Earth’s Magnetism
5.41. Magnetic Declination and Dip
Table 5.2
5.6.2 Para magnetism (delete only Curie’s Law)
5.6.3 Ferromagnetism (delete only Curie’s temperature; and
Hysteresis)
5.7 Permanent Magnets and Electromagnets
Exercises 5.1, 5.2, 5.9–5.11, 5.13–5.25
Chapter 6: 215–219 6.7 Energy Consideration: A Quantitative Study
Electromagnetic 230–232 6.8 Eddy Currents
Induction Exercises 6.6, 6.10–6.17
Chapter 7: Alternating 240 Figure 7.7 Magnetisation and Demagnetisation of an
Current 243 Inductor
246–247 Figure 7.10 Charging and Discharging of a
249–251 Capacitor
255–259 7.6.2 Analytical Solution (of series LCR circuit)
266–268 7.6.3 Resonance (delete only Sharpness of Resonance)
7.8 LC Oscillations
Exercises 7.6, 7.8, 7.10, 7.12–7.26
Chapter 8: 273–274 Example 8.1
Electromagnetic 276–278 8.3.2 Nature of Electromagnetic Waves (delete only about
Waves 279–280 ether and page 277)
287 Example 8.4 and 8.5
Exercises 8.11–8.15
Chapter 9: Ray Optics 318 9.3 Refraction (delete only advanced sunrise and delayed
and Optical Instruments 321–322 sunset)
332–335 9.4.1(i) Mirage
346 9.4.1(ii) Diamond
9.7 Some Natural Phenomena due to Sunlight
9.7.1 The Rainbow
9.7.2 Scattering of Light
Exercise 9.18
Chapter 10: Wave 358–359 10.3.4 Doppler Effect
Optics 359 Example 10.1
363–367 10.5 Interference of Light Waves and Young’s Experiment
368–371 (retain the final
372–376
379–381 expressions for dark and bright fringes but delete the
383–385 derivation; delete expression for fringe width)
10.6 Diffraction (retain only qualitative treatment)
10.6.3 Resolving Power of Optical Instruments
10.6.4 Validity of Ray Optics
10.7.1 Polarisation by Scattering
10.7.2 Polarisation by Reflection
Exercises 10.7–10.21
Chapter 11: Dual Nature 388 Table 11.1
of 397 Example 11.3
Radiation and Matter 400–404 11.8 Wave Nature of Matter (delete only derivation for de
407–413 Broglie wavelength of accelerated electron; and
Heisenberg’s uncertainty
principle)
11.9 Davisson and Germer Experiment
Appendix 11.1 The History of Wave-Particle Flip-Flop
Exercises 11.5, 11.7, 11.12 to 11.14, 11.16, 11.17, 1.19–
11.37
Chapter 12: Atoms 421–422 12.3.1 Spectral Series
424–426 12.4 Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom (retain only the
429 expression for radius of nth possible orbit but delete its
430 derivation)
436–437 12.5 The Line Spectra of the Hydrogen Atom (retain only
qualitative treatment)
Example 12.6
Exercises 12.3, 12.11–12.17
Chapter 13: Nuclei 446–451 13.6.1 Law of Radioactive Decay
452–455 13.6.2 Alpha Decay
462–466 13.6.3 Beta Decay
13.6.4 Gamma Decay
13.7.2 Nuclear Reactor
Exercises 13.1, 13.2, 13.6–13.10, 13.12–13.14, 13.18,
13.22–13.31
Chapter 14: 485–495 14.8 Special Purpose p-n
Semiconductor 497–499 junction Diodes
Electronics: 14.9 Digital Electronics and
Material Devices and Logic Gates
Simple Exercises 14.7–14.15
Circuits
You might also like
- Science 9 Unitd - Unit PlanDocument11 pagesScience 9 Unitd - Unit Planapi-216124570No ratings yet
- MDCAT 9jan Batch-1Document5 pagesMDCAT 9jan Batch-1pearlpearl936No ratings yet
- 2MVA LT BushingDocument1 page2MVA LT Bushingindrajit mondalNo ratings yet
- DTS-0007 Neutral Grounding Resistor RADocument6 pagesDTS-0007 Neutral Grounding Resistor RANicodemus Ervino MandalaNo ratings yet
- SplitPDFFile 2Document1 pageSplitPDFFile 2Abhinav ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Well Logging Part-1Document120 pagesWell Logging Part-1مصطفى عصام شيت حمديNo ratings yet
- A105972 PDFDocument42 pagesA105972 PDFKelvin XuNo ratings yet
- IAEA Coordinated Research Project On Development of Harmonized QA/QC Procedures For Maintenance and Repair of Nuclear InstrumentsDocument17 pagesIAEA Coordinated Research Project On Development of Harmonized QA/QC Procedures For Maintenance and Repair of Nuclear InstrumentsMissoft waresNo ratings yet
- Neutron Radiative Capture: Neutron Physics and Nuclear Data in Science and TechnologyFrom EverandNeutron Radiative Capture: Neutron Physics and Nuclear Data in Science and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Demolish Prosedur R0Document10 pagesElectrical Demolish Prosedur R0Hudoyo ChannelNo ratings yet
- I I Applied Physics Lab Manual PDFDocument34 pagesI I Applied Physics Lab Manual PDFY.P.SinghNo ratings yet
- MDCAT Super Batch Repeater Session - 23 Batch-1 28th AprilDocument6 pagesMDCAT Super Batch Repeater Session - 23 Batch-1 28th AprilZoha FatimaNo ratings yet
- Asnt CatalogDocument51 pagesAsnt CatalogMohamed100% (1)
- 4051 F597 PRC320 Modification InstructionsDocument103 pages4051 F597 PRC320 Modification InstructionsColin ChristieNo ratings yet
- NS1 Work Plan Procedure For Circulating Water Piping Installation Rev.2 Part 1 of 5Document46 pagesNS1 Work Plan Procedure For Circulating Water Piping Installation Rev.2 Part 1 of 5namdq-10% (1)
- 10-EA-E-41025 Earthing & Lighting System Design Calculation ReportDocument9 pages10-EA-E-41025 Earthing & Lighting System Design Calculation ReportArunava DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Nde-Uesl-Eql-Ndt-0001 (Equipment List)Document7 pagesNde-Uesl-Eql-Ndt-0001 (Equipment List)George OgbecheNo ratings yet
- Concrete Trial Mix Laboratory Testing: Document Ref - CORP-SYS-01F01 Rev1Document2 pagesConcrete Trial Mix Laboratory Testing: Document Ref - CORP-SYS-01F01 Rev1Belal hassanNo ratings yet
- 1 Oq UFh SALKda MMYOhfd 7 Go GEv Exmc TV 6 ADocument1 page1 Oq UFh SALKda MMYOhfd 7 Go GEv Exmc TV 6 Ayugraajsingh9No ratings yet
- NS1 Work Plan Procedure For Erection of Circulating Water Pump Rev.0 - Part 1 of 3Document53 pagesNS1 Work Plan Procedure For Erection of Circulating Water Pump Rev.0 - Part 1 of 3namdq-1No ratings yet
- Session Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesSession Plan TemplateJoshua AbrizaNo ratings yet
- 2 Mva Bushing Neutral EarthingDocument1 page2 Mva Bushing Neutral Earthingindrajit mondalNo ratings yet
- NTPC DPTDocument495 pagesNTPC DPTKuppan Srinivasan100% (1)
- TWI Hitan: Training Certification SchemeDocument192 pagesTWI Hitan: Training Certification Schemesaliyarumesh2292100% (1)
- TEST SERIES (1) Topper BatchDocument1 pageTEST SERIES (1) Topper Batchwasat59979No ratings yet
- Eddy Current Testing ProcedureDocument10 pagesEddy Current Testing ProcedureLalit MohanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle ProcedureDocument8 pagesMagnetic Particle ProcedureAbdi Wirawan AnggaweNo ratings yet
- NEET Mission Performace AnalyserDocument6 pagesNEET Mission Performace AnalyserNeel MirchandaniNo ratings yet
- Sos 28 July Step Regular Session by Saeed Mdcat TeamDocument5 pagesSos 28 July Step Regular Session by Saeed Mdcat TeamTalha Rafique ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Science Classes Week 26 Schedule PostDocument2 pagesScience Classes Week 26 Schedule PostFFFNo ratings yet
- M.tech. Nano - TechnologyDocument25 pagesM.tech. Nano - Technologyaniket londheNo ratings yet
- NDTDocument83 pagesNDTcanveraza3122No ratings yet
- 1.6 Kva Transformer Testing ReportDocument5 pages1.6 Kva Transformer Testing ReportVikrant DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Table Jee Main - 1Document1 pageTable Jee Main - 1azamchishty796No ratings yet
- QP. CodeDocument2 pagesQP. Codeboomadev6321No ratings yet
- Technical Submission Form: Sandia ReportDocument56 pagesTechnical Submission Form: Sandia ReportCJ SnipesNo ratings yet
- NanotechHandbook EDITDocument142 pagesNanotechHandbook EDITArturo EspinoNo ratings yet
- Pm#3 e E2 000 Cs 005 - Capasitor Bank Sizing - Rev 2Document7 pagesPm#3 e E2 000 Cs 005 - Capasitor Bank Sizing - Rev 2Mikha R FanandaNo ratings yet
- NS1 Work Plan Procedure For CW Piping Installation Rev.4Document47 pagesNS1 Work Plan Procedure For CW Piping Installation Rev.4namdq-1No ratings yet
- MDCAT Regular Session 5th June Batch-2Document5 pagesMDCAT Regular Session 5th June Batch-2Muhammad Asim KhanNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Initial Course For Apprentice Technician (Signal) Gr-IiiDocument6 pages7.0 Initial Course For Apprentice Technician (Signal) Gr-IiiAryamn SainiNo ratings yet
- Test Certificate: Reference No.Document3 pagesTest Certificate: Reference No.Maninder ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle Test: Part-ADocument16 pagesMagnetic Particle Test: Part-Adeepak kantipudiNo ratings yet
- Sadara Inspection and Test Plan: Low Voltage (Up To 1Kv) Power and Control Cable SPITP-P-0B031-02 ElectricalDocument3 pagesSadara Inspection and Test Plan: Low Voltage (Up To 1Kv) Power and Control Cable SPITP-P-0B031-02 ElectricalJawaid GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Doeacc Centre, Aurangabad: Activity Short Term CoursesDocument4 pagesDoeacc Centre, Aurangabad: Activity Short Term CoursessafarneoNo ratings yet
- 85 EA E 78035 - 00 Control RoomDocument31 pages85 EA E 78035 - 00 Control RoomAdetunji TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Test PackDocument38 pagesTest PackAbdülHak ÖZkara100% (1)
- 15MW材料表 1031Document2 pages15MW材料表 1031sontnieNo ratings yet
- 08-Plan - Earthing Systems - ExercisesDocument7 pages08-Plan - Earthing Systems - ExercisesYousefNo ratings yet
- Hashtag 45 Physical ScienceDocument5 pagesHashtag 45 Physical ScienceDizzy DeeNo ratings yet
- KH-259-18-19 Qap-Lt-XlpeDocument3 pagesKH-259-18-19 Qap-Lt-XlpeveerendraNo ratings yet
- Revised Result of B.Tech - 8th Semester IT 1140353Document1 pageRevised Result of B.Tech - 8th Semester IT 1140353Pushpendra SinghNo ratings yet
- To - Do List For 22th April 2019 To 27th April 2019Document12 pagesTo - Do List For 22th April 2019 To 27th April 2019MonikaNo ratings yet
- Neet Updated Portions - BookletDocument5 pagesNeet Updated Portions - Bookletrubishaasokan015No ratings yet
- 2.pile Design BibekDocument12 pages2.pile Design Bibeknirez14No ratings yet
- Nuclear Fuel Elements: Design, Fabrication and PerformanceFrom EverandNuclear Fuel Elements: Design, Fabrication and PerformanceNo ratings yet
- High Sensitivity Counting Techniques: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationFrom EverandHigh Sensitivity Counting Techniques: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis of Organic Compounds by Combined Application of Spectroscopic MethodsFrom EverandStructural Analysis of Organic Compounds by Combined Application of Spectroscopic MethodsNo ratings yet
- APL GuntherDocument4 pagesAPL GuntherLiviu BadeaNo ratings yet
- S5 Physics Electricity ContinuedDocument39 pagesS5 Physics Electricity ContinuedNANGOYE DEONo ratings yet
- Philippine Electronics Code - Volume 1Document28 pagesPhilippine Electronics Code - Volume 1Eunice GeronaNo ratings yet
- Eee20. Wireless C Based Power Theft Identifier.Document3 pagesEee20. Wireless C Based Power Theft Identifier.Cris AngelesNo ratings yet
- Det1013 - Electrical Technology: Introduction To Electric CircuitDocument118 pagesDet1013 - Electrical Technology: Introduction To Electric Circuitcaj7687No ratings yet
- ELTR100 Sec1 InstructorDocument175 pagesELTR100 Sec1 InstructorVinod VijayanNo ratings yet
- Full Download Welding Principles and Applications 7th Edition Jeffus Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Welding Principles and Applications 7th Edition Jeffus Test Bankja420wwright100% (22)
- 0 - Tugas Bahasa Inggris - Rut Uli Arta Siregar - TK6ADocument15 pages0 - Tugas Bahasa Inggris - Rut Uli Arta Siregar - TK6AAkun VivoNo ratings yet
- High Voltage EngineeringDocument22 pagesHigh Voltage EngineeringVishnu Ajith0% (1)
- GCSE Physcis WorksheetsDocument11 pagesGCSE Physcis WorksheetsMuhammad Talha SubhaniNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Protection FundamentalsDocument52 pagesOvercurrent Protection Fundamentalsger80100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - PLC Hardware ComponentsDocument88 pagesChapter 2 - PLC Hardware Componentsbob71% (7)
- Solenoid Valves BasicsDocument47 pagesSolenoid Valves BasicsGary8100% (6)
- Seminar On Moving Coil Type Linear Compressor: Juned R. KaziDocument12 pagesSeminar On Moving Coil Type Linear Compressor: Juned R. KaziJuned Aashiqe RasoolNo ratings yet
- Science (Physics, Biology) : PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument15 pagesScience (Physics, Biology) : PAPER 1 Multiple Choicemstudy123456No ratings yet
- Marine Electrical SystemDocument26 pagesMarine Electrical SystemAbdallah Mansour100% (1)
- STD 12 Physics 2 Board Question Paper Maharashtra BoardDocument6 pagesSTD 12 Physics 2 Board Question Paper Maharashtra BoardTashvi Kulkarni100% (1)
- 22-23 Electricity and Magnet Study Guide CompletedDocument5 pages22-23 Electricity and Magnet Study Guide Completedapi-234287636No ratings yet
- 220kv GSSDocument46 pages220kv GSSAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- (FESTO) Electropneumatics - Basic LevelDocument270 pages(FESTO) Electropneumatics - Basic Levelprf197588% (8)
- Physics 12: JUNE 2000Document42 pagesPhysics 12: JUNE 2000Gkid GkidNo ratings yet
- Presn. On Gen. SWRDDocument60 pagesPresn. On Gen. SWRDbijoy100% (1)
- Electric and Electronic Hand ToolsDocument9 pagesElectric and Electronic Hand ToolsJustin Codie C. DauzNo ratings yet
- 13779Document43 pages13779jacobbrittoNo ratings yet
- Commissioning Manual - Final PDFDocument161 pagesCommissioning Manual - Final PDFRakesh Kannan100% (1)
- Neutral GroundingDocument9 pagesNeutral Groundingmspd2003No ratings yet
- ANPR ReportDocument52 pagesANPR ReportPuneet Kumar Singh0% (1)
- Calculation SheetDocument14 pagesCalculation SheetmohitNo ratings yet
- Lec 6Document27 pagesLec 6MalcolmNo ratings yet