Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 12 - Biology - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Uploaded by
Astha SaxenaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class 12 - Biology - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Uploaded by
Astha SaxenaCopyright:
Available Formats
NCERT Solutions for Class 12
Biology
Chapter 2- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
1. Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male
and female gametophytes take place.
Ans: In pollen sacs of the anther, male gametophytes (microgametogenesis)
develop up to the 2-celled stage. The nucellus of an ovule is where the
gametophyte develops (megagametogenesis).
2. Differentiate between microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis. Which
type of cell division occurs during these events? Name the structures formed
at the end of these two events?
Ans: Microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis differ in the following ways:
Microsporogenesis Megasporogenesis
The process by which Megasporogenesis is the process
microspore mother cells by which megaspore mother cells
divide and produce pollen are formed and differentiate into
grains is known as megaspores by meiosis.
microsporogenesis.
Located within the pollen sac It is present in the nucellus of the
of the anthers. ovule.
A pollen grain produced by a The megaspores have only one
microspore mother cell functional megaspore.
functions properly.
Results in the formation of Resulting in the formation of
pollen embryo sacs (female
grains (male gametophyte) gametophyte)
Microspore mother cells and The mother cells for megaspores
megaspore mother cells are and microspores enlarge and
every diploid, as they have undergo meiosis in order to
two sets of chromosomes. produce four haplotypical cells
called megaspores and
microspores, respectively.
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 1
3. Arrange the following terms in the correct developmental sequence: Pollen
grain, sporogenous tissue, microspore tetrad, pollen mother cell, male
gametes.
Ans: The sporogenous tissue is composed of a pollen mother cell, a microspore
tetrad, pollen grains, and male gametes.
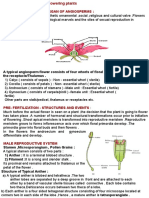
4. With a neat, labeled diagram, describe the parts of a typical angiosperm
ovule.
Ans:
An angiosperm ovary is capable of forming a small structure called an ovule.
Nucellus, a multi-layered cellular tissue, develops as the ovule first appears on
the placenta. Placentas are attached to ovules via a stalk known as a funicle. A
funicle attaches to a placenta at the hilum. The hypodermal cells of the nucellus
enlarge and transform into megaspore mother cells. One haploid cell undergoes
meiosis to form an embryo sac (female gametophyte). The others do not develop.
A pollen tube enters an ovule through a small opening called a micropyle,
surrounded by one or two protective layers. Ovules consist of the nucellus and
integuments of a fully developed embryo.
5. What is meant by monosporic development of female gametophytes?
Ans: The female gametophyte or embryo sac develops only from one of the four
megaspores in many flowering plants. Degeneration occurs in the three remaining
megaspores. The monosporic type of embryo sac formation is referred to as the
monosporic type of embryo development.
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 2
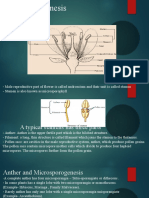
6. A neat diagram explains the 7-celled, 8-nucleate nature of the female
gametophyte.
Ans: Three successive mitotic divisions form it in the megaspore nucleus (or
female gametophyte). The nucleus itself divides into two nuclei which move to
opposite poles to form two nuclei of the embryo sac. The 8-nucleate stage of the
embryo sac is formed after two more sequential mitotic nuclear divisions. A
typical female gametophyte or embryo sac is formed after the 8-nucleate stage.
The antipodal and micropylar end of each of the eight nuclei comprises the six
nuclei grouped. There are two synergids and an egg cell at the center of the egg
apparatus. The polar nuclei are located within the large central cell of the embryo
sac just below the egg apparatus. A typical female gametophyte comprises seven
cells with eight nuclei as both polar nuclei are present within the same cell.
7. What are chasmogamous flowers? Can cross-pollination occur in
cleistogamous flowers? Give reasons for your answer.
Ans: The anther and stigma of chasmogamous flowers are exposed for
pollination. Cleistogamous flowers are incapable of cross-pollination. Therefore,
only self-pollination is caused by these closed flowers. During the dehiscence
process of cleistogamous flowers, anthers dehisce into closed flowers. As a result,
pollen grains are exposed to stigma. Therefore, it is impossible for cross-
pollination to occur, such as Oxalis and Viola.
8. Mention two strategies evolved to prevent self-pollination in flowers
Ans: An individual race's vigor and vitality are diminished by continuous self-
pollination. In order to prevent self-pollination and to promote cross-pollination,
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 3
flowering plants have developed many devices. Cross-pollination is most
frequently ensured by dichogamy and self-sterility.
Dichogamy: Different maturation times for the anthers and stigmas prevent self-
pollination.
Self-sterility (or self-incompatibility): pollen grains from some flowers do not
germinate on their stigma due to the presence of self-sterility genes. Examples
include tobacco and potatoes.
9. What is self-incompatibility? Why does self-pollination not lead to seed
formation in self-incompatible species?
Ans: On its stigma, a flower that does not produce pollen grains is incompatible
or self-sterile. This condition is called self-incompatibility or self-sterility. It is
called pollination when pollen grains are transferred from the stigma to the
anthers. As a result of this transference, seeds are formed. The process of self-
pollination occurs when pollen grains are shed from the anther in the same flower
to the stigma in the same flower. Some flowers, however, do not produce seeds
when self-pollination occurs because they contain the same sterile gene on the
pistil and pollen grain. Since pollen grains cannot germinate, male gametes
cannot fertilize egg cells. This prevents the ovule from developing into a seed.
10. What is a bagging technique? How is it useful in a plant breeding
programme?
Ans: A bag of polythene butter paper, when applied to emasculated flowers
(which are in the bud stage), prevents pollen contamination of its stigmas.
Emasculated flowers can be removed from their buds and stuffed into a bag of
butter paper before anthesis. A pre-sterilized brush is used for dusting the stigmas
of mature emasculated flowers with pollen grains of desired male plants. Flowers
are then re-bagged until the fruits are formed. Artificial hybridization uses this
technique primarily. Plant breeders use this technique to prevent unwanted pollen
grains from contaminating the stigma of flowers.
11. What is triple fusion? Where and how does it take place? Name the nuclei
involved in triple fusion.
Ans: Vegetative fertilization is the formation of a triploid primary endosperm
nucleus (PEN) by fusing the second male gamete with the two polar nuclei
present in the central cell of the central cell. The embryo sac is where this process
occurs. The micropylar end of the pollen tube enters the embryo sac after reaching
the ovary. Once the pollen tube has penetrated, its tip ruptures, releasing two male
gametes. To form the diploid zygote, the one male gamete fuses with the egg.
Trichotomy is the method of creating a triploid endosperm by combining the two
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 4
male gametes and the two polar nuclei, and this method is called syngamy. It is a
process of double fertilization in which both events of fertilization coincide.
12. Why do you think the zygote is dormant for some time in a fertilized
ovule?
Ans: Zygotes become embryos after resting for a while. Until some amount of
endosperm forms, most zygotes remain dormant. Developing embryos need this
nutrition to grow and develop properly.
13. Differentiate between:
(a) hypocotyl and epicotyl;
Ans:
Epicotyl Hypocotyl
This is the part of the embryonal The area between the
axis between plumules and cotylendonary node and radicle
cotyledon nodes. forms part of the embryonal axis.
When epicotyl 2 elongates during Hypocotyls extend so that
hypogeal germination, the soil cotyledons emerge from soil
retains the cotyledons. during epigeal germination.
Epicotyls have plumules at their Hypocotyls have radicles at their
terminal ends. terminal ends.
(b) coleoptile and coleorhiza;
Ans:
Coleoptile Coleorhiza
A foliar structure called the Roots and their caps are enclosed
coleoptile surrounds the epicotyl in a sheath called a coleorhiza.
and a leaf primordium.
It protects the plumule during For the first leaf to appear, there
emergence from soil. is an opening at the end of the
coleoptile. The colorhizae are
solid structures.
Plumules are protected from soil Radicles are not protected when
when they emerge from soil. they pass through the soil.
It grows much beyond the grain After emergence from grain it
stops growing
Coleoptile after emergence from Coleorhiza does not come out of
soil soil.
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 5
Germination occurs when the seed It remains nongreen
becomes green and begins to
photosynthesise.
(c) Integument and testa;
Ans:
Integument Testa
The ovule is covered by this In other words, it is the outer
membrane. covering of a seed.
There are two or three layers, and it It is layered and quite thick.
is thin.
Live cells make up its structure. Cells in it are no longer alive.
There are no sclereids. Sclereids are found in abundance
in cells.
The ovule produces it at the The ovule outer integument is the
chalazal end. source of the ovule structure.
Integument is prefertilized. Structures that develop
postfertilization are called testa
(d) Perisperm and pericarp.
Ans:
Perisperm Pericarp
It serves as the nucleus of the seed. From the ovary wall develops a
covering for the fruit.
Seeds contain it. It is a component of fruit.
Usually, it is dry. There is no moisture or flesh in it.
Many times, seeds do not function Protection and nutrition are also
properly. provided by this covering.
Seeds without perisperm are rare. Every fruit contains this.
14. Why is an apple called a false fruit? Which part(s) of the flower forms
the fruit?
Ans: True fruit is an ovary that has ripened botanically. Often called false fruits,
these are fruits in which the thalamus, floral parts, and ovary are present—apples,
strawberries, cashews, etc. Mainly the fleshy thalamus of apples can be eaten—
the ovaries from a parthenocarpic fruit after or without fertilization.
15. What is meant by emasculation? When and why does a plant breeder
employ this technique?
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 6
Ans: The stem of a flower bud is systematically excised to remove the anthers
and stamens before they die. In order to minimize self-pollination, this is done.
Hybridization by artificial means includes emasculation. This method is used by
plant breeders to prevent the pollination of adjacent flowers and pollinate stigmas
with pollens of the desired variety.
16. If one can induce parthenocarpy through the application of growth
substances, which fruits would you select to induce parthenocarpy and why?
Ans: The fruit of the parthenocarpy is seedless. The ovary does not fertilize them
before they develop. A few seedless fruits are of great economic importance, such
as banana, grape, orange, pineapple, guava, watermelon, and lemon. In fruits with
edible seeds or seeds (e.g., pomegranates), parthenocarpy is not selected.
17. Explain the role of tapetum in the formation of pollen-grain walls.
Ans: Microsporangia are surrounded by a thin layer called the tapetum.
Multinucleated and polyploidy tapetal cells make up the tissue. Pollen grains
develop as a result of them. Ubisch bodies are found in these cells and contribute
to the ornamentation of the microspores and pollen grains. Sporopollenin is a
substance produced by the Ubisch bodies of the tapetal cells. This substance is
present on the exine layer of pollen grains. A spiny appearance is attributed to the
exine of pollen grains due to the presence of this compound.
18. What is apomixis and what is its importance?
Ans: The asexual reproduction process of apomixis results in seeds without
fertilization, such as in certain species of Asteraceae and Grasses. The hybrid seed
industry relies on this method. Increasing productivity is the leading reason for
cultivating hybrids. However, the main problem is the need to grow hybrid seeds
annually since seeds from hybrid plants do not preserve hybrid characteristics for
long periods because of the segregation of characters. By introducing apomixis
into hybrid seeds, this can be avoided. As a result, scientists are seeking genes
associated with apomixis.
Class XII Biology www.vedantu.com 7
You might also like
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- Biology 2 PucDocument23 pagesBiology 2 PucTULASI BAINo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plnts-12thDocument14 pagesChapter 2 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plnts-12thMadhav GourNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - TEXTUAL EXERCISE - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 2 - TEXTUAL EXERCISE - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSyed Mohdammad AliNo ratings yet
- G 5 R HCUyfm 1 N23 O6 o 4 QduDocument10 pagesG 5 R HCUyfm 1 N23 O6 o 4 Qdudhairyasuthar2749No ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument35 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsKumar Munendra PrfNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsRaveena GhodeswarNo ratings yet
- Seed Formation and DevelopmentDocument12 pagesSeed Formation and DevelopmentSabir Ahamed90% (20)
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 2: Back of Chapter QuestionsDocument9 pagesCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 2: Back of Chapter QuestionsSatvik MishraNo ratings yet
- CH - 2 - Ncert SolutionsDocument5 pagesCH - 2 - Ncert SolutionsJanani VijayarajNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Lower and Higher PlantsDocument89 pagesReproduction in Lower and Higher Plantsmohdyasir6643No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Revision NotesDocument68 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Revision NotespranjaylakshitaNo ratings yet
- Note CH 1 Sexual Reproduction Flowering Plant 2Document25 pagesNote CH 1 Sexual Reproduction Flowering Plant 2Aditi ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument35 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDiksha TNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in planTSSDocument56 pagesReproduction in planTSSParis JarrettNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument22 pagesChapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSushil RajbharNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes For Class 12Document10 pagesBiology Notes For Class 12Sasi LokeshNo ratings yet
- GSB Textback ch.1. Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants DR - Phemie FernandesDocument8 pagesGSB Textback ch.1. Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants DR - Phemie Fernandespranavjain558No ratings yet
- Class 12 Bio CH 1Document6 pagesClass 12 Bio CH 1AbhishekDwivediNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerDocument30 pagesClass 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerSufiyanNo ratings yet
- 203RZDocument13 pages203RZSohan PkNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ReproductionDocument8 pagesWorksheet ReproductionStefani KavangoNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Biology Chapter 2 and 3Document24 pagesClass Xii Biology Chapter 2 and 3rajyashree.bitNo ratings yet
- GymnospermaeDocument63 pagesGymnospermaeMief MifdaulNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument9 pagesModule 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsMorgan BrownNo ratings yet
- 2.sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument39 pages2.sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsIshvaryaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument9 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantsDikansha JasaiwalNo ratings yet
- BIODocument16 pagesBIOVeankatapathy 613 Xl group BNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chapter 1Document34 pagesClass 12 Chapter 1Aditya MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Male and Female GametophytesDocument10 pagesChapter 2 - Male and Female Gametophyteskangethemoses371No ratings yet
- Notebook CH 2 Q&aDocument6 pagesNotebook CH 2 Q&aumamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- MF009 5A Plant Reproduction James L2Document27 pagesMF009 5A Plant Reproduction James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology NcertSolutions Chapter 2 PDFDocument10 pages12 Biology NcertSolutions Chapter 2 PDFKaran bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plant 2 - 210806 - 214931Document10 pagesChapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plant 2 - 210806 - 214931Ompriya SNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsChandanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Objectives1.1-1.8Document54 pagesPresentation On Objectives1.1-1.8Shadecia DinnallNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsKrittika DasNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument25 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsGagan DesaiNo ratings yet
- XX 3 LOl An 45 G OG7 Eo Dam FDocument9 pagesXX 3 LOl An 45 G OG7 Eo Dam FGauri PopalghatNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument19 pagesSexual ReproductionjojopebblesNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction Alevel Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesSexual Reproduction Alevel Flowering Plantsbarasasamuel922No ratings yet
- Fertilization in PlantsDocument17 pagesFertilization in PlantsManisha KumariNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument13 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plantsshikaanara8686No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document13 pagesChapter 2Anirudh CNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document34 pagesUnit 1Narveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction CHP 7Document19 pagesSexual Reproduction CHP 7Nabaratna BiswalNo ratings yet
- Botany Super Sheet Chapter 10:plant Reproduction: Reference Books:biology 1 Paper by DR - Abul HasanDocument13 pagesBotany Super Sheet Chapter 10:plant Reproduction: Reference Books:biology 1 Paper by DR - Abul HasanFarhan Azmain FahimNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology NcertSolutions Chapter 2Document10 pages12 Biology NcertSolutions Chapter 2Manas Ranjan JenaNo ratings yet
- 117 - Fertilisation and Seed ProductionDocument4 pages117 - Fertilisation and Seed ProductionPeter TingNo ratings yet
- Key Notes - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument17 pagesKey Notes - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsAngelina DaisyNo ratings yet
- Plus Two Botany - Public Exam - Express RevisionDocument170 pagesPlus Two Botany - Public Exam - Express RevisionLena AlbertNo ratings yet
- Biology Passing Pacakage KarthikDocument22 pagesBiology Passing Pacakage Karthikvarshithajadhav6No ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter-02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument9 pagesClass 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter-02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsVerma AjjuNo ratings yet
- Plant DevelopmentDocument115 pagesPlant DevelopmentarumalammaNo ratings yet
- Anther&Pollen CultureDocument17 pagesAnther&Pollen CulturenadyaawlNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Notes BiologyDocument12 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Notes BiologyHarshu JiNo ratings yet
- MICROSPOROGENOSISDocument20 pagesMICROSPOROGENOSISMerlyn CuantiosoNo ratings yet
- Unit VI. Plant DevelopmentDocument48 pagesUnit VI. Plant DevelopmentANNE MARGUERITE BARETENo ratings yet
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- SC3 - Reem Rachel AbrahamDocument4 pagesSC3 - Reem Rachel AbrahamGopi JampaniNo ratings yet
- PeafowlDocument10 pagesPeafowlshrimaulicomputerssNo ratings yet
- Biofertilizer SylDocument3 pagesBiofertilizer SylsahibNo ratings yet
- Pendulum Training PDFDocument13 pagesPendulum Training PDFSovietPrimeNo ratings yet
- Superhero Genetics ActivityDocument4 pagesSuperhero Genetics ActivityAnna StittNo ratings yet
- Elementary Science Department Pre - Test in Science ViDocument5 pagesElementary Science Department Pre - Test in Science ViHarold ArradazaNo ratings yet
- J Esthet Restor Dent - 2024 - Esquivel - Timing Implant Provisionalization Decision Making and Systematic WorkflowDocument10 pagesJ Esthet Restor Dent - 2024 - Esquivel - Timing Implant Provisionalization Decision Making and Systematic WorkflowDANTE DELEGUERYNo ratings yet
- Southern and Northern HybridizationDocument6 pagesSouthern and Northern Hybridizationyaqoob008No ratings yet
- Amino Acids in Human Nutrition and Health (PDFDrive)Document579 pagesAmino Acids in Human Nutrition and Health (PDFDrive)Arthur TourinhoNo ratings yet
- Sesamoid Bone: Jump ToDocument8 pagesSesamoid Bone: Jump ToBet Mustafa EltayepNo ratings yet
- 24 - Origin of SpeciesDocument31 pages24 - Origin of SpeciesTazneen Hossain TaniNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12Not meNo ratings yet
- Biotech Reviewer PDFDocument31 pagesBiotech Reviewer PDFGerald LimNo ratings yet
- Basidiomycota: Mushrooms, Bracket Fungi, Puffballs, Rusts and SmutsDocument76 pagesBasidiomycota: Mushrooms, Bracket Fungi, Puffballs, Rusts and SmutsaaronNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 506Document4 pagesAssignment - 506tariq mashalNo ratings yet
- Adult Health Nursing 9Th Edition Kim Cooper Full ChapterDocument67 pagesAdult Health Nursing 9Th Edition Kim Cooper Full Chaptercarmen.england668100% (3)
- Biomechanics, Prosthetic & Orthotics BME 2205: Anatomical MovementDocument33 pagesBiomechanics, Prosthetic & Orthotics BME 2205: Anatomical Movementmorris loguyaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AF in CHFDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of AF in CHFBimaIndraNo ratings yet
- Cardiac L4Document19 pagesCardiac L4Qutaybah JahmanyNo ratings yet
- Breeding Seasons and Lambing SeasonsDocument16 pagesBreeding Seasons and Lambing SeasonsVijaya lakshmiNo ratings yet
- Name: Avizah Bin Hamzah Id/Class: 1816440013 / Icp of Science EducationDocument4 pagesName: Avizah Bin Hamzah Id/Class: 1816440013 / Icp of Science EducationAvizah Bin HamzahNo ratings yet
- What Is Autism?: Characteristics of Children With AutismDocument7 pagesWhat Is Autism?: Characteristics of Children With AutismAnandNarayananNo ratings yet
- 3ADocument2 pages3AmontesonicNo ratings yet
- Final Assesment Agr519 (E-Poster)Document1 pageFinal Assesment Agr519 (E-Poster)Noor Syazwan NasirNo ratings yet
- Skin Response Meter Viva QuestionsDocument7 pagesSkin Response Meter Viva QuestionssaurabhdabasNo ratings yet
- Microbiology, Usmle EndpointDocument208 pagesMicrobiology, Usmle EndpointYazan M Abu-FaraNo ratings yet
- Value Sheet - PreciControl ClinChem Multi 1.05117208922.Lot-410119.Exp-2023-01-31.V288.enDocument13 pagesValue Sheet - PreciControl ClinChem Multi 1.05117208922.Lot-410119.Exp-2023-01-31.V288.enLAB CITO RSUDZANo ratings yet
- Five Element CorrespondancesDocument22 pagesFive Element CorrespondancesDavid Drepak100% (1)
- 00 - Contents Everyday Science MCQsDocument5 pages00 - Contents Everyday Science MCQsmimtiazshahid100% (1)
- EngineeringDocument116 pagesEngineeringPriyank SoodNo ratings yet