0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views6 pagesLesson 3 - Displacement-Time Graph
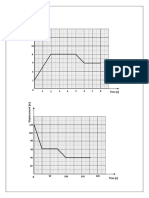
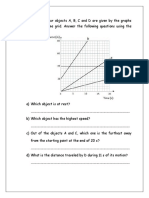
- A displacement-time graph shows how an object's position changes over time relative to a fixed point, with displacement on the y-axis and time on the x-axis.
- For an object at rest, the graph is a horizontal line, as its displacement does not change over time.
- For an object in motion, the slope of the line represents the object's speed, with a steeper slope indicating a higher speed. The direction of the slope shows the object's direction of motion relative to the fixed point.
Uploaded by
binuk wCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views6 pagesLesson 3 - Displacement-Time Graph
- A displacement-time graph shows how an object's position changes over time relative to a fixed point, with displacement on the y-axis and time on the x-axis.
- For an object at rest, the graph is a horizontal line, as its displacement does not change over time.
- For an object in motion, the slope of the line represents the object's speed, with a steeper slope indicating a higher speed. The direction of the slope shows the object's direction of motion relative to the fixed point.
Uploaded by
binuk wCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Understanding Displacement-Time Graphs: Explains the basic concept and necessity of displacement-time graphs, including how distance and time relate to an object's position.
- Displacement-Time Graph Construction: Describes how to construct displacement-time graphs using a practical example of a person walking.
- Graph Interpretation and Slope Analysis: Delves into the interpretation of graphs, focusing on speed as represented by slope and its significance.
- Calculating Speed Using Gradient: Provides a method for calculating speed from displacement-time graphs via gradient calculations.
- Graphical Properties Overview: Concludes with a summary of graph types - horizontal, upwards, and downwards, discussing what each indicates about object motion.