Professional Documents
Culture Documents
THIAZOLE
Uploaded by
ALISYA SOPHIA MOHAMMAD ABU SHAHID CHRISCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
THIAZOLE
Uploaded by
ALISYA SOPHIA MOHAMMAD ABU SHAHID CHRISCopyright:
Available Formats
AROMATICITY (30seconds)
Thiazole is a 5 membered ring which consists of 3 Carbon, 1 nitrogen and 1 sulphur. All
of this are sp2 hybridized. Since it is sp2 hybridization, it makes thiazole as a planar
thiazole ring structure. Each ring atom has unhybridized p orbital that is perpendicular to
the plane of the sigma bond. The total number of non- bonding electrons are 6 which is 3
comes from the carbon, 1 from nitrogen and 2 from sulfur. The resonance of 6 electrons
shows thiazole follows the Huckels rule which is 4n+2 where n equals to 1. So, we can
conclude thiazole is an aromatic compound.
Reactivity(30s)
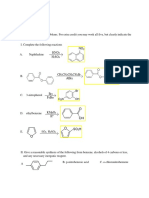
In thiazole, it undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction at C2. It attacks at c2 bcs of
the electron deficient nature. In order to make the nucleophilic substitution occur, a
strong nucleophile or activation of the ring are needed. This reaction is more preferred at
c2 because position 2 is freely undergo substitution while c4 will not give any
substitution product and c5 does not give product as easily as at c2. So this is why
nucleophilic substitution reaction for thiazole attacks at c2.
30s
One of the drugs that contains thiazole is sulphathiazole. It is a short acting sulfonamide
antibiotic and used in combination of sulfabenzamide and sulfacetamide to treat vaginal
infections. It is effective against gram positive and gram negative pathogenic
microorganism.Although no longer used in humans, it is used in cattle.
The second drug is famotidine. It is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist that decreases the
stomach acid production. It is used to prevent ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
Another drug is thiamine or also known as vitamin B1. It is to prevent vitamin B1 deficiency. The
key features are
1m
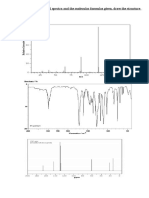
For the proton nmr spectrum of thiazole, there are 3 types of protons where first proton is at C
bond to S and N, second types of proton at C bond to nitrogen and third type of proton is at
carbon attach to sulphur. This means there are 3 different signals of NMR spectrum that leads to
3 peaks. From the graph, this line shows A, the middle line is B and this line is C. In A, it is far
away from 0. It is downfield with highest ppm compared to the other 2 signals. This is bcs the
position of proton is near to the electronegative atom which is S and N. This causes the nucleus
proton to be deshielded. For the middle line, it is downfield too but has lower ppm compared to
A because the proton is attach only to nitrogen. It has also decreased shielding. For the most
right line which is shown as C, it has the lowest frequency compared to the other 2 signals
because it is attach to sulphur which is less electronegative than nitrogen. There is only one
proton gives the peak in line A,B and C which is 1H. For splitting, A is singlet as it does not have
any neighboring atom ,meanwhile for B and C it is doublet as they have one neighboring atom.
Next is about the mass spectrometry. The molecular ion peak is 85. In the first elimination, CHN
is eliminated. It is M-27. For the second elimination, CHCHN will be eliminated and causes it to
be M-40. Molecular peak or also known as base peak have 100%abundance.
You might also like
- Applications of NMR Spectroscopy in Inorganic ChemistryDocument11 pagesApplications of NMR Spectroscopy in Inorganic ChemistryDhanaswamy Ilangeswaran92% (12)
- Spectroscopy ManualDocument21 pagesSpectroscopy Manualanthor100% (2)
- Analysis of Results in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) SpectrosDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Results in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) SpectrostypodleeNo ratings yet
- Unknown 3 SmaugDocument8 pagesUnknown 3 Smaugapi-248990050No ratings yet
- (Organo) Part BDocument9 pages(Organo) Part BAmirul Amin Bin ShukriNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Exercises, Chapter 19: Okuyama & Maskill: Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesSolutions To Exercises, Chapter 19: Okuyama & Maskill: Organic ChemistryM Irfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Substi-Wps OfficeDocument54 pagesAromatic Substi-Wps OfficeTariq ZiaNo ratings yet
- 0 - Mesomeric effec-WPS OfficeDocument11 pages0 - Mesomeric effec-WPS OfficeNida AdreesNo ratings yet
- Armo FinalDocument6 pagesArmo Finalapi-319676256No ratings yet
- 核磁共振部分习题及答案 1Document14 pages核磁共振部分习题及答案 1Tariq Rahim MarwatNo ratings yet
- Carbon 13 SpectrosDocument53 pagesCarbon 13 SpectrossaheedvkNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Orgo II Exam 1 Version A (UD) Answer KeyDocument8 pagesChemistry-Orgo II Exam 1 Version A (UD) Answer KeyNesrine LaradjiNo ratings yet
- C-13 NMRDocument29 pagesC-13 NMREnesEmreTaşNo ratings yet
- Difficult Questions On Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesDifficult Questions On Organic Chemistrytarunbirbanga100% (1)
- McMurry OC8e EV CH15 PDFDocument18 pagesMcMurry OC8e EV CH15 PDFCrizel Ricaro100% (1)
- Heterocyclic Compounds 3 فصل ثاني مرحلة ثانية مادة العضويةDocument59 pagesHeterocyclic Compounds 3 فصل ثاني مرحلة ثانية مادة العضويةMahendra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 22 and Applications of C NMR: Subject ChemistryDocument13 pages22 and Applications of C NMR: Subject ChemistrySaurav PaulNo ratings yet
- PyridineDocument5 pagesPyridineMohini BajajNo ratings yet
- C-13 NMR and DEPTDocument41 pagesC-13 NMR and DEPTV G Viju Kumar100% (1)
- CHEM 2425. Chapter 15. Benzene and Aromaticity - Homework - WDocument10 pagesCHEM 2425. Chapter 15. Benzene and Aromaticity - Homework - WLina RamojNo ratings yet
- 11.7 - Heterocyclic Amines - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument9 pages11.7 - Heterocyclic Amines - Chemistry LibreTextsAnyumiza InnocentNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11. Free Radical ReactionsDocument7 pagesChapter 11. Free Radical ReactionsGilang HerjunaNo ratings yet
- C NMR SpectrosDocument17 pagesC NMR SpectrosAhmad AlShahrourNo ratings yet
- Benzyne MechanismDocument14 pagesBenzyne MechanismsaheedvkNo ratings yet
- The Role of Magnesium in PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesThe Role of Magnesium in PhotosynthesisMateus CogoNo ratings yet
- A16 - Spectrocscopic IdentificationDocument2 pagesA16 - Spectrocscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument25 pagesOrganic ChemistryhimanisinghbasnalNo ratings yet
- AromaticityDocument12 pagesAromaticityV G Viju KumarNo ratings yet
- Challenge Problems 3Document3 pagesChallenge Problems 3Sweg SwegNo ratings yet
- c13ppt 150515121301 Lva1 App6892Document16 pagesc13ppt 150515121301 Lva1 App6892kiran yaseenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2014Document103 pagesChemistry 2014Godfred EkyeNo ratings yet
- Abs and Fluor of TPPH2Document11 pagesAbs and Fluor of TPPH2morikao21No ratings yet
- AromaticDocument38 pagesAromaticDerrick Maatla MoadiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organometallic Chem 01-4Document21 pagesIntroduction To Organometallic Chem 01-4Aparna DuggiralaNo ratings yet
- NMRDocument56 pagesNMRWesam Elsayed MehannaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem. IV. BCH 2210 Cat 1 and Ii INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer ALL Questions in Section A (40 Marks)Document19 pagesOrganic Chem. IV. BCH 2210 Cat 1 and Ii INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer ALL Questions in Section A (40 Marks)Brian MbuguaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3. Reactions of C-Linked and N-Linked Substituents: Short Course On Heterocyclic ChemistryDocument41 pagesLecture 3. Reactions of C-Linked and N-Linked Substituents: Short Course On Heterocyclic ChemistryeraborNo ratings yet
- Inductive EffectDocument4 pagesInductive Effectimranahmadshs2014No ratings yet
- Ans. The Structures of Gly, Asp, Lys, Arg Are Shown BelowDocument11 pagesAns. The Structures of Gly, Asp, Lys, Arg Are Shown BelowDiksha SinghNo ratings yet
- Trends PDFDocument4 pagesTrends PDFjayScoreNo ratings yet
- Pyridine Reactions: University College of Pharmaceutialsciences K.U. CampusDocument16 pagesPyridine Reactions: University College of Pharmaceutialsciences K.U. CampusVã RãNo ratings yet
- TB Chapter15Document9 pagesTB Chapter15Luke SkywalkerNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Study Card (Extracted From P. Yurkanis Bruice) 7Document1 pageOrganic Chemistry Study Card (Extracted From P. Yurkanis Bruice) 7David DualNo ratings yet
- NMRDocument9 pagesNMRShabnam Fatima SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Zam P BLOCK NW 4Document212 pagesZam P BLOCK NW 4mrrsiddiquiNo ratings yet
- What Are IR Radiations?: Basic PrincipleDocument8 pagesWhat Are IR Radiations?: Basic PrincipleHania KhanNo ratings yet
- Formation of BenzeneDocument39 pagesFormation of BenzenehfrizviNo ratings yet
- 2017 H2 Chemistry Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsDocument5 pages2017 H2 Chemistry Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsLee Jun HuiNo ratings yet
- NMR 7.Document36 pagesNMR 7.Imran KhanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Organic ChemistryDocument34 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Organic ChemistryYeison Andrey Sanchez ChicanganaNo ratings yet
- Ws10 AnswersDocument4 pagesWs10 AnswersKassimNo ratings yet
- GOC NotesDocument43 pagesGOC NotesSudhanshu HedaNo ratings yet
- Selective Propynylation of CinnamaldehydeDocument6 pagesSelective Propynylation of CinnamaldehydeBogdan StefanNo ratings yet
- NMR Lec 5Document18 pagesNMR Lec 5Fatima AhmedNo ratings yet
- 3-Bromo-2-Butanol When Treated With HBR Threo DL PairDocument54 pages3-Bromo-2-Butanol When Treated With HBR Threo DL PairSarthak Singh100% (1)
- Inhibitors & UncouplersDocument7 pagesInhibitors & UncouplersValentino Dhiyu AsmoroNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Shift: NMR Course, 4Document15 pagesThe Chemical Shift: NMR Course, 4Anselmo Mtz GagosNo ratings yet
- Report NMRDocument13 pagesReport NMRsarahNo ratings yet
- Concerning Amines: Their Properties, Preparation and ReactionsFrom EverandConcerning Amines: Their Properties, Preparation and ReactionsRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Tetrahedron Reports on Organic Chemistry: Volume 4.31-40From EverandTetrahedron Reports on Organic Chemistry: Volume 4.31-40Derek BartonNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument1 pageDrugsALISYA SOPHIA MOHAMMAD ABU SHAHID CHRISNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document8 pagesTutorial 1ALISYA SOPHIA MOHAMMAD ABU SHAHID CHRISNo ratings yet
- PHC 513 Flipped Class QuestionDocument17 pagesPHC 513 Flipped Class QuestionALISYA SOPHIA MOHAMMAD ABU SHAHID CHRISNo ratings yet
- PHC411 - Practical 3 - Oct 2021 - StudentsDocument14 pagesPHC411 - Practical 3 - Oct 2021 - StudentsALISYA SOPHIA MOHAMMAD ABU SHAHID CHRISNo ratings yet
- Effective Viscosity Prediction of Crude Oil-Water Mixtures With High Water FractionDocument11 pagesEffective Viscosity Prediction of Crude Oil-Water Mixtures With High Water FractionVanessa RiosNo ratings yet
- Name: Sajeel Khan Roll#:M.phil-SSP-03-F19 Class: M.phil SSP (Morning) Subject: Optical Properties of Solid Submitted TODocument8 pagesName: Sajeel Khan Roll#:M.phil-SSP-03-F19 Class: M.phil SSP (Morning) Subject: Optical Properties of Solid Submitted TOAnonymous f7wV1lQKRNo ratings yet
- Tanker Safety GuideDocument24 pagesTanker Safety Guideintan nNo ratings yet
- Buckling AnalysisDocument26 pagesBuckling AnalysisbachNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document29 pagesPresentation 1api-666280932No ratings yet
- Preparation and Evaluation Ofmyoconductive Ecg GelDocument3 pagesPreparation and Evaluation Ofmyoconductive Ecg GelpgeneraliNo ratings yet
- Wellstream Flexibles StudentDocument204 pagesWellstream Flexibles StudentVictor HiromatsuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Mcmurry - 9th Edition)Document60 pagesChapter 2 (Mcmurry - 9th Edition)Paolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- Light 6 QPDocument8 pagesLight 6 QPmwagweNo ratings yet
- Service Rutin Genset September 2020Document10 pagesService Rutin Genset September 2020Wahyu Alfa OmegaNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms in Modern Engineering DesignDocument363 pagesMechanisms in Modern Engineering DesignGholamreza Mahmoodi100% (1)
- Classical Mechanics (NETGATE) PDFDocument30 pagesClassical Mechanics (NETGATE) PDFSaley SaeedNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan ObejktifDocument12 pagesPemeriksaan ObejktifMuhammad FadhilNo ratings yet
- TDS 11 Hydraulic AnimationDocument17 pagesTDS 11 Hydraulic Animationahmed.kareem.khanjerNo ratings yet
- (De Gruyter Textbook) Tadros, Tharwat F. - Polymeric Surfactants Dispersion Stability and Industrial Applications (2017) - Libgen - LiDocument288 pages(De Gruyter Textbook) Tadros, Tharwat F. - Polymeric Surfactants Dispersion Stability and Industrial Applications (2017) - Libgen - LishaziaNo ratings yet
- P 12-16 PRIYANKA Finite Element Analysis of Internally Ply Drop-Off Composite LaminatesDocument5 pagesP 12-16 PRIYANKA Finite Element Analysis of Internally Ply Drop-Off Composite LaminatesEditorijer IjerNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument14 pagesProteinKharyl Roisse CastillanoNo ratings yet
- Klueber Elektrische kontakte-ENDocument12 pagesKlueber Elektrische kontakte-ENppdsoeyahooNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines - at 6302 Question Bank: Unit - 1Document8 pagesMechanics of Machines - at 6302 Question Bank: Unit - 1Daniel DasNo ratings yet
- VDM® Alloy 625 - Nickel Iron Alloy - MatmatchDocument4 pagesVDM® Alloy 625 - Nickel Iron Alloy - MatmatchRaznovrsni KutakNo ratings yet
- UTCHEM Tech Doc PDFDocument256 pagesUTCHEM Tech Doc PDFpasha khanNo ratings yet
- Emx20Clc: General DataDocument3 pagesEmx20Clc: General Dataأبو زينب المهندسNo ratings yet
- Foam TypesDocument12 pagesFoam TypesRolaxNo ratings yet
- Sample - Solution Manual Diffusion, Mass Transfer in Fluid Systems 3rd Edition E. L. CusslerDocument10 pagesSample - Solution Manual Diffusion, Mass Transfer in Fluid Systems 3rd Edition E. L. CusslerGlasst Innovacion 2019No ratings yet
- Motion in Two Dimensions: Constant Velocity Constant AccelerationDocument53 pagesMotion in Two Dimensions: Constant Velocity Constant Accelerationabdullah naseerNo ratings yet
- Requirements For Pressure Relief ValvesDocument1 pageRequirements For Pressure Relief ValvesshuzaoNo ratings yet
- Image Guided RadiotherapyDocument15 pagesImage Guided Radiotherapyana43245100% (1)
- Wind LoadDocument13 pagesWind LoadHimani NagarNo ratings yet
- KR-241 Settler Vent CompressorDocument15 pagesKR-241 Settler Vent CompressorSreekanthMylavarapuNo ratings yet
- In Situ Study Improvement Soft Ground Using Stone Columnfor Railway EmbankmentDocument17 pagesIn Situ Study Improvement Soft Ground Using Stone Columnfor Railway EmbankmentDeepak avinashNo ratings yet