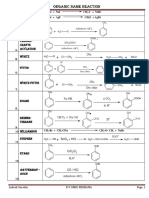
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test Series-Try These
Uploaded by
Pratham ZalaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test Series-Try These
Uploaded by
Pratham ZalaCopyright:
Available Formats
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 1
Dear Teachers/ students,
This test series consists of 05 unsolved
question papers of physics – class XII.
I have put in lot of efforts in preparing
each question paper and hereby ensure that
questions were selected from almost each &
every concept.
In every question paper students find all
types of questions viz., direct, derivations,
diagram based & challenging questions for
high achievers.
I sincerely advice the students to solve
these question papers only after thorough
revision.
I hope this will surely benefit the students
appearing CBSE board examination this year
2023.
Thank you.
All the Best.
Regards,
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA
PGT PHYSICS
NOTE: SOLUTIONS WILL BE SHARED VERY SOON.
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 2
Class: XII SESSION : 2022-2023
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA NO.2 BELAGAVI CANTT.,
SUBJECT: PHYSICS - SET-1
MM: 70 Time Allowed: 3 hours.
General Instructions:
(1) There are 35 questions in all. All questions are compulsory
(2) This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D and Section
E. All the sections are compulsory.
(3) Section A contains eighteen MCQ of 1 mark each, Section B contains seven questions of two
marks each, Section C contains five questions of three marks each, section D contains three
long questions of five marks each and Section E contains two case study -based questions of
4 marks each.
(4) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in section B, C, D
and E. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
(5) Use of calculators is not allowed.
SECTION -A
1 What will be the value of electric field at the centre of the electric dipole 1M
a)Zero
b)Equal to the electric field due to one charge at centre
c)Twice the electric field due to one charge at centre
d) Half the value of electric field due to one charge at centre
2 A parallel plate air capacitor has a capacitance 18 µF. If the distance between the plates is 1M
tripled and a dielectric medium is introduced, the capacitance becomes 72 µF. The dielectric
constant of the medium is
a)4 b)9 c)12 d)2
3 Point charge q moves from point P to point S along the path PQRS (figure) in a uniform electric 1M
field E pointing parallel to the positive direction of the x-axis. The co-ordinates of the point
P, Q, R and S are (a, b, 0), (2a, 0, 0), (a, –b, 0) and (0, 0, 0) respectively. The work done by
the field in the above process is :
4 In the circuit diagram, calculate the electric current through branch BC: 1M
a) 4 amp b) 2 amp c) 5 amp (d) 10 amp
5 In a certain region of space, electric field 𝐸⃗ and magnetic field 𝐵
⃗ are perpendicular to each 1M
other. An electron enters perpendiculary to both the fields and moves undeflected. The
velocity of electron is
𝐸 𝐵
a) b) c)𝐸⃗ ×𝐵
⃗ d)𝐸⃗ .𝐵
⃗
𝐵 𝐸
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 3
6 Figure shows a square loop ABCD with edge length a. The resistance of the 1M
wire ABC is r and that of ADC is 2r. The value of magnetic field at the center
of the loop O is :-
7 The variation of magnetic susceptibility(χ) with temperature for a diamagnetic substance is 1M
best represented by
(a) b)
© (D)
8 If both the number of turns and core length of an inductor is doubled keeping other factors 1M
constant, then its self-inductance will be-
(a) Unaffected B)Doubled C) Halved D) Quadrant
9 An AC voltage source of variable angular frequency ω and fixed amplitude V connected in 1M
series with a capacitance C and an electric bulb of resistance R (inductance zero). When ω
is increased
(a) The bulb glows dimmer (b) The bulb glows brighter
(c) Net impedance of circuit is unchanged
(d) Total impedance of the circuit increases
10 The figure shows variation of R, XL and XC with frequency f in a series L, C, R circuit. Then 1M
for what frequency point, the circuit is inductive.
(a) A (b) B (c) C (d) A and B
11 If E and B represent electric and magnetic field vectors of the electromagnetic wave, the 1M
direction of propagation of electromagnetic wave is along.
(a) E b)B c) B x E d) E x B
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 4
12 Ray diverging from a point source on a wave front are: 1M
(a)cylindrical (b)spherical (c)plane (d)cubical
13 The photoelectric work function for a metal surface is 4.14 ev .The cut-off wavelength 1M
for this is:
(a)4125Å (b) 2062.5Å (c)3000Å (d)6000Å
14 Which spectral series of hydrogen lie in UV region? 1M
(a) Paschen (b) Lyman (c) Brackett (d) Balmer
15 Binding energy of hydrogen nucleus is 1M
a) -13.6 eV b) 13.6 eV c) 0 d) 6.8 eV
16 ASSERTION- When a plane wavefront is refracted through a convex lens, the emerging 1M
wavefront is spherical.
REASON- The central part of the plane wavefront travels through the greatest thickness of
convex lens and is, therefore, slowed down the most. The marginal parts of the wavefront
travel through a minimum thickness of the lens and are, therefore, slowed down the least.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of
assertion
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of
assertion
© If assertion is true but reason is false
(d) If both the assertion and reason are false
17 Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). 1M
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given
below.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b) Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c) A is true but R is false
d) A is false and R is also false
A : The process of photoelectron emission and thermionic emission of electrons is different.
R : Photoelectric emission does not depend upon temperature, whereas thermionic emission
is temperature dependent.
18 Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). 1M
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given
below.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b) Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c) A is true but R is false
d) A is false and R is also false
A: Semiconductors do not obey Ohm’s law.
R: In semiconductors the rate of flow of charge not only depends on the applied electric field
but also on the availability of charge carriers.
SECTION – B (2 M QUESTIONS)
19 A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges (Q). Show that the 2M
system of three charges will be in equilibrium. If q=-Q/4
20 (a) What happens if a bar magnet is cut into two pieces: (i) transverse to its length, (ii) along 2M
its length
(b) Magnetic field arises due to charges in motion. Can a system have
magnetic moments even though its net charge is zero?
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 5
21 The magnetic field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given by 2M
𝑩𝒚 =(2×𝟏𝟎𝟕 )T sin(0.5×𝟏𝟎𝟑 x+1.5×𝟏𝟎𝟏𝟏 t)
(a) What is the wavelength and frequency of the wave?
(b) Write an expression for the electric field.
22 A small bulb is placed at the bottom of a tank containing water to a depth of 80 cm. What is 2M
the area of the surface of water through which light from the bulb can emerge out? Refractive
index of water is 1.33.(Consider the bulb to be a point source.)
23 a) In a single slit diffraction, the width of the slit is made double the original width. How does 2M
this affect the size and intensity of the central diffraction band?
b) In what way is diffraction from each slit related to the interference pattern in a double slit
experiment?
24 A 12.5 eV electron beam is used to bombard gaseous hydrogen at room temperature. What
series of wavelengths will be emitted?
(OR)
From the relation R= R0A1/3, where R0 is a constant and A is the Mass Number of a Nucleus, 2M
Show That the Nuclear Matter Density Is Nearly Constant (i.e., Independent of A).
25 Suppose a pure Si crystal has 5 x 1028 atoms m-3. It is doped by 1 ppm concentration of 2M
pentavalent ARSENIC (As). Calculate the number of electrons and holes. Given that ni = 1.5
x 1016 m-3.
SECTION – C (3 M QUESTIONS)
26 A long straight solid metal wire of radius R carries a current I uniformly distributed over its 3M
circular cross section. Find the magnetic field at a distance r from the axis of wire (i) inside
(ii) outside the wire.
27 Two concentric circular coils, one of small radius r1 and the other of large radius r2, such 3M
that r1 << r2, are placed co-axially with centres coinciding. Obtain the mutual inductance of
the arrangement.
28 (a)When an AC source is connected to an ideal inductor 3M
show that the average power supplied by the source over
a complete cycle is zero.
(b)A lamp is connected in series with an inductor and an
AC source. What happens to the brightness of the lamp
when the key is plugged in and an iron rod is inserted
inside the inductor? Explain.
(OR)
A device 'X' is connected to an AC sources V=V0 sin ωt. The variation of voltage, current and 3M
power in one cycle is in the following graph:
(i) Identify the device 'X'.
(ii) Which of the curves A, B and C represent the voltage, current and the power
consumed in the circuit? Justify your answer.
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 6
29 a) Discuss briefly how wave theory of light cannot explain the features of photoelectric effect. 3M
b) Do all the electrons that absorb a photon come out as photo electrons?
OR
a) All the photo electrons are not emitted with same energy. The energy of photo electrons are 3M
distributed over a certain range why?
b) Radiation of frequency 1015 Hz is incident on two photosensitive surface P and Q. There is
no photosensitive from surface P. Photoemission occurs from surface Q but photoelectrons
have zero kinetic energy. Explain these observations and find the value of work function for
surface Q.
30 a)Find the shortest wavelength present in the Paschen series of Spectral lines? 3M
b) Define the distance of closest approach. An α-particle of kinetic energy K is bombarded on
a thin gold foil. The distance of the closest approach is r. What will be the distance of closest
approach for an α-particle of double the kinetic energy?
SECTION – D (5 M QUESTIONS)
31 i) State Gauss’s theorem. 5M
ii) Using Gauss’ law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite
plane sheet is independent of the distance between from it.
iii) How is the field directed, if (a) The sheet is positively charged,(b) Negatively charged?
(OR)
i) Derive the expression for the electric potential due to an electric dipole at a point on its 5M
axial line.
ii) Two identical parallel plate capacitors A and B are
connected to battery of V volts with the switch S is closed.
The switch is now opened and the free space between the
plates of the capacitors is filled with a dielectric of dielectric
constant K. Find the ratio of the total electrostatic energy
stored in both capacitors before and after the introduction
of the dielectric.
32 i)Derive an expression for drift velocity of electrons in a conductor. Hence deduce ohms law. 5M
ii) A wire whose cross-sectional area is increasing linearly from its one and two others, is
connected across the battery of we volts. which of the quantities remain constant in the wire.
(OR)
(I)Can the EMF of a cell be less than it's terminal voltage? If yes, give reasons? 5M
(ii)Plot the graph showing the variation of terminal potential difference across the cell of emf
(E) and internal resistance (r) are with current drawn from it using this graph how does one
determine the EMF of a cell.
(iii)Three cells of emf E, 2E, 5E having internal resistances r, 2r, 3r , variable resistance R
shown in the figure. Find the expression for current. Plot a graph for variation of current with
R.
33 5M
a) Define power of a lens. Write its units. Deduce the relation for two thin lenses
kept in contact coaxially.
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 7
b) The image obtained with a convex lens is erect and its length is four times the length of
the object. If the focal length of the lens is 20 cm, calculate the object and image distances.
(OR)
(i) Draw a neat labelled ray diagram of a compound microscope. Explain briefly its working. 5M
Obtain an expression for its magnification when the final image is formed at LDDV?
(ii) Why must both the objective and the eyepiece of a compound microscope have short focal
lengths?
CASE STUDY BASE QUESTIONS ::SECTION – E: 8 X 1 = 8 8M
34 When two light waves of the same frequency and having zero or constant phase difference
travelling in the same direction superpose each other, the intensity in the region of
superposition gets redistributed, becoming maximum at some points and minimum at others.
This phenomenon is called interference of light. The two sources of light are said to be
coherent only when the phase difference between the light waves produced by them is zero
or constant. The point at which two waves are in phase or if trough of one wave coincides
with the trough of other or crest of one wave coincides with the crest of other then the
resultant intensity produced at that point will be larger and amplitude also maximum. Such
points are the points where ‘constructive interference’ takes place. While there are some
points where two light waves are not in phase with each other and crest of one wave coincides
with the trough of other and vice versa due to which resultant intensity at that point is
minimum and amplitude also get decreased. Such points are the points where ‘destructive
interference’ takes place.
For constructive interference, the path difference is equal to integral multiple of wavelengths
and resultant intensity will be maximum at that points. While for destructive interference,
the path difference is (n + 1/2) multiple of wavelengths and where resultant intensity is zero.
i) What are coherent sources ?
ii) How coherent sources are obtained in YDSE?
iii) Give any two conditions to obtain sustained interference pattern?
iv) Draw the intensity distribution curve in case of interference of light?
v) How does the fringe width in interference change if red light is replaced by blue
light?
35 P-N junction is a semiconductor diode. It is obtained by bringing p-type semiconductor in
close contact with n-type semiconductor. A thin layer is developed at the p-n junction which
is devoid of any charge carrier but has immobile ions. It is called depletion layer. At the
junction a potential barrier appears which does not allow the movement of majority charge
carriers across the junction in the absence of any biasing of the junction.
If p-side of p-n junction is connected to positive terminals of external battery and n-side is
connected to negative terminal of external battery, then the p-n junction is said to be forward
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 8
biased. If n-side of p-n junction is connected to positive terminals of external battery and p-
side is connected to negative terminal of external battery, then the p-n junction is said to be
reverse biased. The p-n junction offers low resistance when forward biased and high
resistance when reverse biased.
i) The current in the circuit shown in the figure is
a. 20 A b)2 x 10-3 A c) 200 A d) 2 x 10-4 A
ii) Define diffusion and drift in the context of semiconductor junction diode? ( 2M)
iii) Define minority carrier injection?
iv) How does the potential barrier change during reverse bias?
THE END :: ALL THE BEST
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 9
Class: XII SESSION : 2022-2023
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA NO.2 BELAGAVI CANTT.,
SUBJECT: PHYSICS - SET-2
MM: 70 Time Allowed: 3 hours.
General Instructions:
(1) There are 35 questions in all. All questions are compulsory
(2) This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D and Section
E. All the sections are compulsory.
(3) Section A contains eighteen MCQ of 1 mark each, Section B contains seven questions of two
marks each, Section C contains five questions of three marks each, section D contains three
long questions of five marks each and Section E contains two case study -based questions of
4 marks each.
(4) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in section B, C, D
and E. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
(5). Use of calculators is not allowed.
SECTION -A
1 Force between A and B is F. If 75% charge of A is transferred to B then force between A 1M
and B is :
F
(1) (2) 4F (3) F 4) None
4
2 Capacitance between points A and B is 1M
a)4 µF b)12/7 µF
c)1/4 µF d)7/12 µF
3 Five capacitors of 10 F capacity each are connected to a DC 1M
potential of 100V as shown in the adjoining figure. Find charge
in 10μF capacitor :-
(1) 100 µC (2) 500 µC
(3) 250 µC (4) 300 µC
4 We use alloy for making of resistors, because they have 1M
Temp. coefficient Resistivity
(a) Low Low
(b) High High
(c) High Low
(d) Low High
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 10
5 Two particles A and B of masses mA and m B respectively and having the same charge are 1M
moving in a plane. A uniform magnetic field exists perpendicular to this plane. The speed of
the particles is vA and vB respectively, and the trajectories are as shown in the figure. Then
A) mAvA < mBvB
B) mAvA >mBvB
C) mA <mB and vA <vB
D) mA = mB and vA = vB
6 Current flows due north in a horizontal transmissionline. Magnetic field at a point P 1M
vertically above it directed
(1) North wards (2) South wards (3) Toward east
(4) Towards west
7 The area of B-H loop for soft iron as compared to that of steel 1M
is
a)More b)Less c)Equal d)Zero
8 Two identical circular coils A and B are kept in a horizontal tube side by side without 1M
touching each other. If the current in coil A increases with time, in response, the coil B.
(a) is attracted by A
(b) is repelled by A
(c) is not effected
(d) rotates
9 The r.m.s. voltage of the wave form shown is 1M
(a) 10 V (b) 7 V (c) 6.37 V (d) 12 V
10 When AC source is connected across series R-C combination, the ac- current may lead 1M
AC voltage by
(a) 0° (b) 180° (c) 30° (d) 90°
11 The ratio of contributions made by the electric field and magnetic field components to 1M
the intensity of an EM wave is
A)c:1 B)c2:1 C) 1:1 D) √c:1
12 In a single diffraction pattern observed on a screen placed at ‘D’ m ,distance from the slit 1M
of width ‘d’ m ,the ratio of the width of the central maxima to the width of other
secondary maxima is :
a.2:1 b.1:2 c.1:1 d.3:1
13 IfE1,E2,E3, E4, are the respective kinetic energies of electron, deuteron, proton and 1M
neutron having same De Broglie wavelength. Select the correct order in which those
values would increase:
(a)E1,E3,E4,E2
(b)E2,E4,E1,E3
(c)E2,E4,E3,E1
(d)E3,E1,E2,E4
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 11
14 What is the order of velocity of electron in a hydrogen atom in ground state. 1M
(a) 106 ms-1 (b) 102 ms-1 (c) 1010 ms-1 (d) 109 ms-1
15 Two nucleons are at a separation of 1 fm. The net force between 1M
them is F1 if both are neutrons, F2 if both are protons, and F3 if
one is a proton and the other is a neutron
(1) F1 > F2 > F3
(2) F2 > F1 > F3
(3) F1 = F3 > F2
(4) F1 = F2 > F3
16 Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). 1M
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given
below.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b) Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c) A is true but R is false
d) A is false and R is also false
ASSERTION: The speed of light, sound waves, water waves in a medium is independent
of the nature of the source or intensity (so long it is low).
REASON : Speed of the waves in a medium depends on wavelength.
17 Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). 1M
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given
below.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b) Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c) A is true but R is false
d) A is false and R is also false
ASSERTION : If a stationary nucleus emits an -particle, the de Broglie wavelengths of
the daughter nucleus and the-particle are equal.
REASON: The magnitudes of the linear momenta of the daughter nucleus and the -
particle are the same.
18 Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). 1M
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given
below.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b) Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c) A is true but R is false
d) A is false and R is also false
ASSERTION : Germanium is preferred over silicon for making semi-conductor devices:
REASON : Energy gap for Ge is more than that of Si.
SECTION – B ( 2M QUESTIONS)
19 A dipole, with a dipole moment of magnitude p, is in stable equilibrium in an 2M
electrostatic field of magnitude E. Find the work done in rotating this dipole to its
position of unstable equilibrium.
20 A coil of N turns and radius R carries a current I. It is unwound and rewound to make a 2M
square coil of side a having same number of turns N. Keeping the current I same, find
the ratio of the magnetic moments of the square coil and the circular coil.
21 2M
In a plane electromagnetic wave, the electric field oscillates sinusoidally at a frequency
of 2.0×𝟏𝟎𝟏𝟎 Hz and amplitude 48𝑽𝒎−𝟏
(a) What is the wavelength of the wave?
(b) What is the amplitude of the oscillating magnetic field?
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 12
22 A beam of light converges at a point P. Now a lens is placed in the path of the convergent beam 2M
12cm from P. At what point does the beam converge if the lens is (a) a convex lens of focal length
20cm, and (b) a concave lens of focal length 16cm?
23 What is the shape of the wavefront in each the following cases: 2M
(a) Light diverging from a point source
(b) emerging out of a convex lens when a point source is placed at its focus.
24 The energy of the electron in the ground state of hydrogen is -13.6 eV. Calculate the energy 2M
of the photon that would be emitted, if electron was to make a transition corresponding to
the emission of the first line of the Lyman series of the H-atom.
(OR)
A heavy nucleus X of mass number 240 and binding energy per nucleon 7.6MeV is split, 2M
into two fragments Y and Z of mass numbers 110 and 130 the binding energy of nucleons
in Y and Z is 8.5MeV per nucleon. Calculate the energy Q released per fission in MeV.
25 A) C, Si and Ge have same lattice structure. Why is C insulator while Si and Ge intrinsic 2M
semiconductors?
B) Can we take one slab of p-type semiconductor and physically join it to another n-type
semiconductor to get p-n junction?
SECTION – C (3M QUESTIONS)
26 Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer and explain its working. What is 3M
the function of radial magnetic field inside the coil?
27 (a) Obtain the expression for the magnetic energy stored in a solenoid in terms of 3M
magnetic field B, area A and length l of the solenoid.
(b) How does this magnetic energy compare with the electrostatic energy stored in a
capacitor?
28 (i)The given graphs (a) and (b) represent the variation of the opposition offered by the circuit 3M
element to the flow of alternating current, with frequency of the applied emf. Identify the
circuit element corresponding to each graph
(ii)Write the expression for the impedance offered by the series combination of the above
two elements connected across the AC source. Which will be ahead in phase in this circuit,
voltage (or) current?
OR
A)Determine the value of phase difference between the current and the voltage in the 3M
given series LCR circuit.
b) Calculate the quality factor of a series LCR circuit with L=2.0H, C=2μF and R=10Ω.
c) Resonance frequency of a circuit is ν . If the capacitance is made 4 times the initial
value, then by how many times the resonance frequency will become?
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 13
29 a)Write Einstein's photoelectric equation and mention which important features in 3M
photoelectric effect can be explained with the help of this equation.
b)The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons gets doubled when the wavelength of
light incident on the surface changes from ′λ1′ to ′λ2′. Derive the expressions for the
threshold wavelength ′λ0′ and work function for the metal surface.
OR
Define the term cut-off frequency in photoelectric emission. The threshold frequency of a 3M
metal is f.
When the light of frequency 2f is incident on the metal plate, the maximum velocity of
photo- electron is v1. When the frequency of the incident radiation is increased to 5f, the
maximum velocity of photoelectrons is v2. Find the ratio v1:v2 .
30 3M
a)Find the ratio between the wavelengths of the 'most energetic' spectral lines in the
Balmer and Paschen series of the hydrogen spectrum.
b) The ground state energy of a H-atom is - 13.6 eV. If an electron makes a transition from
an energy level - 0.85 eV to -1.51 eV, then calculate the wavelength of the spectral line
emitted. To which series of hydrogen spectrum does this wavelength belong?
SECTION – D (5M QUESTIONS)
31 a) Derive expression for the torque on an electric dipole in a uniform electric field? 5M
b) What happens if the electric field is non uniform in the above case?
c) What would happen if the electric field E is increasing (i) parallel to P and anti
parallel to P ?
(OR)
a)Two charges 3 ×10-8 C and -2 ×10-8 C are located 15 cm apart. At what point on the 5M
line joining the two charges is the electric potential zero? Take the potential at infinity to
be zero.
b) The given graph shows the variation of charge q versus potential difference V for two
capacitors C1, and C2. Both the capacitors have same plate separation but plate area of
C2 is greater than that C1. Which line (A or B) corresponds to C1 and why?
32 a)Obtain a relation between electric current and drift velocity? 5M
b)On the basis of electron drift, drive an expression for resistivity of a conductor in terms
of number density of free electrons and relaxation time. On what factors does resistivity of
a conductor depend?
(OR)
a) State Kirchoff’s laws? 5M
b) Obtain the balancing condition of wheatstone’s bridge with a neat circuit diagram?
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 14
33 a)With the help of a ray diagram explain the working of Astronomical telescope for normal 5M
adjustment? Obtain the expression for its magnifying power?
b)An astronomical telescope when in normal adjustment has magnifying power 5. If the
distance between the two lenses is 24 cm, find the focal length of both the lenses?
(OR)
a)With the help of a ray diagram , explain the construction and working of a reflecting type 5M
telescope? Mention its magnifying power?
b)State some important advantages of a reflecting type telescope over a refracting type
telescope?
SECTION – E (8M) (CASE STUDY BASE QUESTIONS) 4 X 2= 8
34 The experiment produces a bright central maximum that is flanked on both 4M
sides by secondary maxima, with the intensity of each succeeding secondary maximum
decreasing as the distance from the center increases. Figure 4 illustrates this point with a
plot of beam intensity versus diffraction radius. Note that the minima occurring between
secondary maxima are located in multiples of π.
This experiment was first explained by Augustin Fresnel who, along with
Thomas Young, produced important evidence confirming that light travels in waves. From
the figures above, we see how a coherent, monochromatic light emitted from point is
diffracted by aperture d.
i) What is the basic difference between diffraction and interference of light?
ii) How does the angular separation between fringes in single slit diffraction experiment
change when the distance of separation between the slit and screen doubled?
iii) What is the condition for first minima in case of diffraction due to a single slit?
iv)A single slit diffraction pattern is completely immersed in water without changing any
other parameter. How is the width of central maximum affected?
35 A pure semiconductor germanium or silicon, free of every impurity is called intrinsic 4M
semiconductor. At room temperature, a pure semiconductor has very small number of
current carriers (electrons and holes). Hence its conductivity is low.
When the impurity atoms of valance five or three are doped in a pure semiconductor, we
get respectively n- type or p- type extrinsic semiconductor. In case of doped
semiconductor.𝑛𝑒 𝑛ℎ = 𝑛𝑖2 Where 𝑛𝑒 and 𝑛ℎ are the number density of electron and hole
charge carriers in a pure semiconductor. The conductivity of extrinsic semiconductor is
much higher than that of intrinsic semiconductor.
(i) Which of the following statements is not true?
a) The resistance of intrinsic semiconductor decreases with increase of
temperature.
b) Doping pure Si with trivalent impurities gives p- type semiconductors.
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 15
c) The majority charges in n- type semiconductors are holes.
d) All of the above.
(ii) The impurity atoms with which pure Si should be doped to make a p- type
semiconductor is
a) Phosphorus B)Boron C) Arsenic D)Antimony
(iii)Holes are majority charge carriers in
a) Intrinsic semiconductors B)n – type semiconductor
b) p- type semiconductors D)Metals
(iv) At absolute zero, Si acts as
a) Non- metal B)Metal C) Insulator D)None of these
THE END :: ALL THE BEST
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 16
Class: XII SESSION : 2022-2023
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA NO.2 BELAGAVI CANTT.,
SUBJECT: PHYSICS - SET-3
M M: 70 Time Allowed: 3 hours.
General Instructions:
(1) There are 35 questions in all. All questions are compulsory
(2) This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D and Section
E. All the sections are compulsory.
(3) Section A contains eighteen MCQ of 1 mark each, Section B contains seven questions of two
marks each, Section C contains five questions of three marks each, section D contains three
long questions of five marks each and Section E contains two case study -based questions of
4 marks each.
(4) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in section B, C, D
and E. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
(5). Use of calculators is not allowed.
SECTION -A
1 The ratio of electric flux through surfaces S 1 and S2 is: 1M
(1) 1 : 1 (2) –3 : 1 (3) 3 : 1 (4) –1 : 3
2 The electric potential V at any point (x, y, z) is given by V = 3x², where x is in meters 1M
and V in volts. The electric field at the point (1 m, 0,2 m) is
(a) 6 V/m along -X-axis (b) 6 V/m along +X-axis
(c) 1.5 V/m along -X-axis (d) 1.5 V/m along + X-axis
3 Four capacitors with capacitances C1= 1µF,C2 = 1.5 µF, C3 = 2.5 µF and C4 = 0.5 µF 1M
are connected as shown and are connected to a 30 volt source. The potential difference
between points B and A is :-
(1) 5 V (2) 9 V (3) 10 V (4) 13 V
4 A cell supplies a current of 0.9 A through a 2 resistor and a current of 0.3 A through 1M
7 resistor. The internal resistance of the cell is
(a) 2.0 (b) 1.5 (c) 1.0 (d) 0.5
5 To convert a moving coil galvanometer into an ammeter of given range, we must connect: 1M
a) A suitable low resistance in series
b) A suitable low resistance in parallel
c) A suitable high resistance in parallel
d) A suitable high resistance in series
6 An infinitely long, straight conductor AB is fixed and a current 1M
is passed through it. Another movable straight wire CD of finite
length and carrying current is held perpendicular to it and
released. Neglect weight of the wire.
(1) The rod CD will move upwards parallel to itself
(2) The rod CD will move downward parallel to itself
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 17
(3) The rod CD will move upward and turn clockwise at the same time
(4) The rod CD will move upward and turn anti-clockwise at the same time
7 A bar magnet AB with magnetic moment M is cut into two equal parts perpendicular 1M
to its axis. One part is kept over the other so that end B is exactly over A. What will
be the magnetic moment of the combinations formed?
(a)Zero (b)M/4 (c)M (d)3M/4
8 The instantaneous magnetic flux linked with a coil is given by = (5t3-100t+300) Wb. 1M
The emf induced in the coil at time t = 2s is
(a)-40 V (b) 40 V (c) 140 V (d) 300 V
9 The core of a transformer is laminated, so as to 1M
(a) make it light weight (b) make it robust and strong
(c) increase the secondary voltage (d) reduce energy loss due to eddy current
10 A resistor of 20Ω is connected to a source of an alternating potential, 1M
V = 200sin(100πt). The time taken by current to change from its peak value to rms value
is
(a) 0.2s (b) 0.25s (c) 25 × 10-3 s (d) 2.5 × 10-3s
11 Frequency of a wave is 6 x 10 Hz. The wave is
10 1M
(a) Radio wave (b) Microwave (c) X-ray (d) none of these
12 The interference is produced by two waves of intensity ratio 16:9,the ratio of maximum 1M
and minimum intensities in interference pattern is :-
(a)4:3 (b)49:1 (c)25:7 (d)256:81
13 Which of the following has maximum stopping potential when metal is illuminated by 1M
visible light?
(a)Blue (b)Yellow (c)Violet (d)Red
14 The energy level diagram of an element is given, which transition corresponds to the 1M
emission of a spectral line of wave length 102.7 nm
(a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D
15 If the nuclear radius of 27Al is 3.6 Fermi, the approximate nuclear radius of 64Cu in 1M
Fermi is
a) 2.4 b) 1.2 c) 4.8 d) 3.6
16 Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). 1M
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given
below.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b) Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c) A is true but R is false
d) A is false and R is also false
A: When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, it loses some speed but it
doesn't imply a reduction in the energy carried by the light wave.
R: Energy carried by a wave depends on the amplitude of the wave and not on the
speed of wave propagation.
17 Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). 1M
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given
below.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b) Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c) A is true but R is false
d) A is false and R is also false.
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 18
A : A photon cannot transfer all of its energy to an isolated electron.
R : When energy of a photon is more than 1.02 MeV, it can materialize into two
particles called electron and positron.
18 Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). 1M
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given
below.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b) Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c) A is true but R is false
d) A is false and R is also false
ASSERTION: To make p type semiconductor, pentavalent impurity like phosphorus is
mixed with Si.
REASON : Pentavalent impurity produces free electrons.
SECTION – B ( 2 M questions)
19 Consider two hollow concentric spheres, S1and S2, enclosing 2M
charges 2Q and 4Q respectively as shown in the figure.
(i) Find out the ratio of the electric flux through them.
(ii) How will the electric flux through the sphere S1change, if a medium of dielectric
constant ′ϵr′ is introduced in the space inside S1in place of air? Deduce the necessary
expression.
20 Show diagrammatically the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence of (i) 2M
- paramagnetic and (ii) diamagnetic substances. How does one explain this distinguishing
feature?
21 Answer the following questions: 2M
(a) It is necessary to use satellites for long distance TV transmission.Why?
(b) Optical and radiotelescopes are built on the ground but X-ray astronomy is
possibleonly from satellites orbiting the earth.Why?
22 Use the mirror equation to show that an objectplaced between f and 2f of a concave 2M
mirrorproduces a real image beyond 2f.
23 In Young’s double-slit experiment using monochromatic light of wavelength λ The 2M
intensity of light at a point on the screen where path difference is λ, is K units. What is
the intensity of light at a point where path difference is λ/3?
24 Explain in brief, why Rutherford's model cannot account for the stability of an atom? 2M
(OR)
Explain the processes of nuclear fission and nuclear fusion by using the plot of binding 2M
energy per nucleon (BE/A) versus the mass number A.
25 Draw the circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier and state how it works? 2M
SECTION – C (3 M questions)
26 Two long straight parallel conductors carrying steady current I1 and I2 are 3M
separated by a distance d. Explain briefly with the help of a suitable
diagram how the magnetic field due to one in conductor acts on the other.
Hence, deduce the expression for the force acting between the two
conductors. Mention the nature of this force.
27 Define mutual inductance between two long coaxial solenoids. Find out the expression 3M
for the mutual inductance of inner solenoid of length / having the radius r, and the
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 19
number of turns n, per unit length due to the second outer solenoid of same length and
n, number of turns per unit length.
28 State its principle of working of a transformer with the help of a diagram. Mention 3M
various energy losses in this device.
OR
A step up transformer is operated on a 2.5 kV line. It supplies a load with 20 A . The 3M
ratio of the primary winding to the secondary winding is 10:1. If the transformer is 90%
efficient, calculate
i) the power output ii) the voltage and iii) the current in the secondary.
29 A) Why is the wave nature of matter not more apparent to our daily observations? 3M
B) Two mono chromatic beams A and B of equal intensity I, hit a screen. The number of
photons hitting the screen by beam A is twice that by beam B. Then what inference can
you make about their frequencies?
C) A photon and electron have got the same de Broglie wavelength. Explain which has
greater total energy.
OR
A) What consideration led de-Broglie to suggest that material particles can also show 3M
wave property?
B) Photoelectric currents at distances r1 and r2 of light source from photoelectric cell
are I1 and I2 respectively. The value of (I1/I2) will be?
C) Write the expression for the Broglie wavelength associated with a charged particle
having charge 'q' and mass 'm', when it is accelerated by a potential V.
30 Find the ratio of energies of photons produced due to transition of an electron of H- 3M
atom from its
(i) Second permitted energy level to the first level and
(ii) The highest permitted energy level to the first permitted level.
SECTION – D (5 M questions)
31 a) Define dipole moment of an electric dipole ? State its SI unit? 5M
b)Derive an expression for the electric field “E” due to a dipole of length “ 2a” at a point,
distance “r”, from the centre of the dipole , on the axial line.
c) Draw a graph of ‘E’ versus ‘r’. ( r>>>a).
(OR)
a) State Gauss’s theorem in electrostatics? 5M
b)Using Gauss’s theorem , deduce the expression for the electric field due to a uniformly charged spherical
conducting shell of radius R at a point i) outside and ii) inside the shell.
c)If the electric flux through a closed surface is zero, is it necessary that field due to the charge inside the
closed surface zero?
32 a) A cell of emf “ e” and internal resistance “r’ connected across an external resistance 5M
“R’ . Plot a graph showing the variation of potential difference”(V)’ across R versus” R”.
b) The figure shows a plot of terminal voltage V versus the current I of a given cell.
Calculate emf of the cell and internal resistance of the cell from the graph.
(OR)
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 20
a) On what basic conservation laws are Kirchhoff current law and voltage law based? 5M
b)Calculate the value of resistance in the circuit shown in the figure, so that current in
the circuit is 0.2. What would be the potential difference between points A and B?
c) Calculate the current drawn from the battery in given network.
33 a) State the assumptions on which Huygen’s principle of secondary wavelets is based. 5M
Describe briefly Huygen’s construction for the propagation of wavefronts in a medium?
b) Derive the laws of reflection of light on the basis of Huygen’s theory of light?
(OR)
a)Draw and explain the graph showing the variation of intensity in the interference 5M
pattern in Young’s double slit experiment?
b) Show that the phenomenon of interference of light is in accordance with the law of
conservation of energy?
c)What is the ratio of slit widths if the amplitudes of light waves from them have a ratio
of 2 : 1.
CASE STUDY BASE QUESTIONS ::SECTION – E: 4 X 2 = 8
34 In the astronomical telescope , the focal lengths of the objective and eyepiece are 100 cm 4M
and 5 cm respectively. If the telescope is focussed on a scale 2m from the objective , the
final image is formed at 25 cm from the eyepiece. Then
i. Magnification of the eyepiece is
A) 2 B) 4 C) 6 D) 8
ii. Magnification of telescope is
A) 6 B) 12 C) 18 D) 24
iii. Length of the telescope is
A) 154.5 cm B) 172 cm C) 196.4 cm D) 204.2 cm
iv. Focal length of objective and eyepiece of telescope are 200cm and 4 cm respectively.
What is the length of telescope for normal adjustment?
A) 196 cm B) 204 cm C) 250 cm D)225 cm.
v. An astronomical telescope has an objective of focal length 100 cm and an eye piece of
focal length 5 cm. The final image of a star is seen 25 cm from the eyepiece. The
magnifying power of the telescope is
A) 20 (B) 22 (C) 24 (D) 2
35 A p-n junction ia an interface or a boundary between two semiconductor material types, 4M
namely the p-type and n-type, inside a semiconductor . In a semiconductor, the p-n
junction is created by the method of doping. P-N junctions are elementary “ building
blocks” of semiconductor electronic devices such as diodes, transistors, solar cells,
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 21
LEDs, and integrated circuits. They are active sites where the electronic action of the
devices takes place.
i. For the same order of doping, why does n-type semiconductor exhibit larger conductivity than p-type
semiconductor?
ii. Give one application of P-N junction diodes.
iii. Why does a potential barrier set up across the P-N junction?
OR
What are the two types of biasing in p-n junction diode? Draw the respective diagrams?
THE END:: ALL THE BEST
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 22
Class: XII SESSION : 2022-2023
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA NO.2 BELAGAVI CANTT.,
SUBJECT: PHYSICS - SET-4
MM: 70 Time Allowed: 3 hours.
General Instructions:
(1) There are 35 questions in all. All questions are compulsory
(2) This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D and Section
E. All the sections are compulsory.
(3) Section A contains eighteen MCQ of 1 mark each, Section B contains seven questions of two
marks each, Section C contains five questions of three marks each, section D contains three
long questions of five marks each and Section E contains two case study -based questions of
4 marks each.
(4) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in section B, C, D
and E. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
(5). Use of calculators is not allowed.
SECTION -A
1 Four charges are placed at the circumference of a dial clock as shown in figure. If the 1M
clock has only hour hand, then the resultant force on a charge q0 placed at the centre,
points in the direction which shows the time as:–
(1) 1:30 (2) 7:30(3) 4:30 (4) 10:30
2 On bringing an electron near to other electron, the potential energy of the system 1M
a) decreases b) increases c)remains same d)becomes zero
3 Two parallel plate capacitors X and Y, have the same area of plates and same separation 1M
between plates. X has air and Y with dielectric of constant 2, between its plates. They
are connected in series to a battery of 12 V. The ratio of electrostatic energy stored in X
and Y is
a)4:1 b)1:4 c)2:1 d)1:2
4 From the graph between current I and voltage V shown below, identify the portion 1M
corresponding to negative resistance
(a) AB (b) BC (c) CD (d) DE
5 A circular coil of radius ‘a ‘carries an electric current. The magnetic field due the coil at 1M
a point on the axis of the coil located at a distance r from centre of the coil, such that
r>>a varies as
1 1 1 1
a) b) 2c) 3d) 3/2
𝑟 𝑟 𝑟 𝑟
6 Three long, straight and parallel wires carryingcurrents are arranged as shown in figure. 1M
The forceexperienced by 10 cm length of wire Q is
(1) 1.4×10–4 N towards the right
(2) 1.4×10–4 N towards the left
(3) 2.6 × 10–4 N to the right
(4) 2.6×10–4 N to the left
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 23
7 For making electromagnets, steel is preferred over soft iron as it has high retentivity 1M
as well as high coercivity . The susceptibility of a ferro magnetic material is “χ”
at27°C. At what temperature will it’s susceptibility be “0.5 χ”
(a)54°C(b)327°C (c)600°C (d)237°C
8 A copper disc of radius 0.1m is rotated about its normal axis with 10 rps in a uniform 1M
magnetic field of 0.1 T with its plane perpendicular to the filed. The emf induced across
the radius of the disc is
a) Π x 10 V b) 2π x 10 V c) π x 10-2 V d) 2π x 10-2 V
9 Which of the following combination should be selected for better turning of an L.C.R 1M
circuit used for communication?
(a) R=25Ω,L=1⋅5H,C=45μF (b) R=20Ω,L=1⋅5H,C=35μF
(c) R=25Ω,L=2⋅5H,C=45μF (d) R=15Ω,L=3.5H,C=30μF
10 If E = 200Volt, R = 25 , L=2H and C=2μF and the frequency is variable then the current 1M
at f = 0 and f = will be respectively –
(1) 0A, 8A (2) 8A, 0A(3) 8A, 8A (4) 0A, 0A
11 The nature of electromagnetic wave is :- 1M
(1) longitudinal (2) longitudinal stationary
(3) transverse (4) transverse stationary.
12 The angular fringe width does not depend upon :- 1M
(1) Wavelength (2) Distance between slits (d)
(3) Distance between slits and screen (D)
(4) Ratio D/d
13 If kinetic energy of an electron is increased by 4% then percentage change in de-Broglie 1M
wavelength: -
(1) decreases by 2% (2) decreases by 1%(3) increases by 5% (4) None of these
14 The de-Broglie wavelength of an electron in first Bohr’s Orbit is 1M
(a) equal to ¼ of circumference of orbit
(b) equal to ½ of circumference of orbit
(c) equal to twice of circumference of orbit
(d) equal to the circumference of orbit
15 A nuclear fission is said be critical when multiplication factor or K is 1M
a) K=1 b)K>1 c) K<1 d)K=0
16 Assertion: A white source of light during interference forms only white and black 1M
fringes.
Reason: Width of fringe is inversely proportional to the wavelength ofthe light used.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is the correct explanation of
assertion
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation
of assertion
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false
(d) If both the assertion and reason are false
17 1M
ASSERTION : There is almost no time-lag between the incidence of light and the
emission of photoelectrons.
REASON : A photon transfers almost all its energy to a single electron in a metal.
a) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is the correct explanation of
assertion
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation
of assertion
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false
(d) If both the assertion and reason are false.
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 24
18 ASSERTION: In forward biasing current starts when minimum voltage of battery 1M
becomes equal to knee voltage.
REASON: Up to knee voltage barrier potential of diode prevents the motion of holes and
electrons.
a) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is the correct explanation of
assertion
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation
of assertion
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false
(d) If both the assertion and reason are false
SECTION – B( 2M QUESTIONS)
19 A hemispherical body is placed in a uniform electric field E. what is the flux associated 2M
with the curved surface, if the field is
(i) Parallel to base? Ii) Perpendicular to base?
20 (i) How does a diamagnetic material behave when it is cooled at a very low 2M
temperature?
(ii) Why does a paramagnetic sample display greater magnetization when
cooled? Explain.
21 a)Why are microwaves considered suitable for radar systems used in aircraft 2M
navigation?
b)Name the electromagnetic wave used in LASIK eye surgery and why?
22 Two thin lenses are in contact and thefocal length of the combination is 80 cm. If the 2M
focallength of one lens is 20 cm, then what would be the power of the other lens?
23 Determine the angular separation between central maximum and first order maximum 2M
of the diffraction pattern due to a single slit of width 0.25mm when light of wavelength
5890 A0 is incident normally on it?
24 The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is -13.6 eV. 2M
(i) What is the kinetic energy of an electron in the 2nd excited state ?
(ii) What is the potential energy of an electron in the 3rd excited state?
(OR)
Calculate the energy in the below fusion reaction 2M
2
1H + 21H 3
2He + n,
Where Average BE of 21H
= 2.23 MeV and that of 32He = 7.73 MeV.
25 Assuming that the resistance of the meters are negligible, what will be the readings of 2M
the ammeters A1 and A2 in the circuit shown in figure.
SECTION – C(3 M QUESTIONS)
26 (i) write the expression for the force F acting on a particle of mass m and charge q moving 3M
with velocity v in a magnetic field B. Under what conditions will it move in (a) A circular
path (b)A helical path
(ii) Show that the kinetic energy of the particle moving in magnetic field remains
constant.
27 a) Can a straight wire act as an inductor? 3M
b) How can the self-inductance of a given coil having N number of turns, area of cross-
section “A” and length “l” be increased?
c) If a coil is removed from a magnetic field (i) slowly and (ii) rapidly, then in which case,
more work will be done?
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 25
28 A device X is connected across an AC source of voltage V = V0 sin ωt. The current through 3M
𝜋
X is given as I = I0 sin(ωt + ).
2
i) Identify the device X and write the expression for its reactance.
ii) Draw graphs showing variation of voltage and current with time over one cycle of AC,
for X.
iii) How does reactance of the device X vary with frequency of the AC? Show this variation
graphically.
(OR)
A series L-C-R circuit with L = 0.12H, C = 480nF, R = 23Ω is connected to a 230V variable 3M
frequency supply.
i) What is the source frequency for which current amplitude is maximum? Obtain this
maximum value.
ii) What is the source frequency for which average power absorbed by the circuit is
maximum? Obtain the value of maximum power.
iii) For which frequency of the source is the power transferred to the circuit half the
power at resonant? What is the current amplitude at these frequencies?
29 Monochromatic light of frequency 6.0 × 1014 Hz is produced by a laser 3M
Thepoweremittedis2.0×10-3 W.
A) What is the energy of a photon in the light beam?
B) How many photons per second, on an average, are emitted by the source?
(OR)
Mono chromatic light of wavelength 632.8 nm is produced by a helium-neon laser. The 3M
power emitted is 9.42 mW.
a) Find the energy and momentum of each photon in the light beam,
b) How many photons per second, on the average, arrive at a target irradiated by this
beam? (Assume the beam to have uniform cross-section which is less than the target
area) , and
c) How fast does a hydrogen atom have to travel in order to have the same momentum
as that of the photon?
30 a) State Bohr’s quantization condition in terms of de- Broglie wavelength? 3M
b) If the wave number of spectral line of Brackett series of hydrogen is ( 9/ 400) times the Rydberg’s
constant, then find the quantum number of the state from which the transition has taken place?
SECTION – D (5 M QUESTIONS)
31 a) Define dipole moment of an electric dipole ? State its SI unit? 5M
b)Derive an expression for the electric field “E” due to a dipole of length “ 2a” at a point,
distance “r”, from the centre of the dipole , on the equatorial line.
c) Draw a graph of ‘E’ versus ‘r’. ( r>>>a).
(OR)
a) State Gauss’s theorem in electrostatics? 5M
b)Using Gauss’s theorem , deduce the expression for the electric field due to a thin infinitely long straight
line of charge, with a uniform charge density of λ C/m.
c) Draw a graph showing the variation of electric field with distance in the above case?
32 Two cells of emf E1 and E2 , and internal resistance r1 and r2 respectively are connected in parallel as 5M
shown.
Deduce expressions for the (i) equivalent emf of the
combination (ii) the equivalent resistance of the combination and
(iii) the potential difference between the points A and B.
(OR)
a)What are “polar” and “non-polar” dielectrics? Explain how do they behave when p[laced 5M
in an external electric field?
b)Show that the electric field at the surface of a charged conductor is proportional to its
charge density?
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 26
c)A battery of 10V is connected to a capacitor of capacity 0.1F. The battery is now
removed and this capacitor is connected to a second uncharged capacitor. If the charge
distributes equally on these two capacitors, find the total energy stored in the two
capacitors. Further, compare this energy with the initial energy stored in the first
capacitor.
33 a) State the assumptions on which Huygen’s principle of secondary wavelets is based. 5M
Describe briefly Huygen’s construction for the propagation of wavefronts in a medium?
b) Verify mathematically ,the laws of refraction of light on the basis of Huygen’s theory
of light when light travels from denser to a rarer medium?
(OR)
a) Define” coherent sources” ? 5M
b) Write any two conditions for obtaining sustained and observable interference pattern?
c) A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths, 650 nm and 520 nm. Is used to obtain
interference fringes in a Young’s double-slit experiment.What is the least distance from
the central maximum where the bright fringes due to both the wavelengths coincide?
The distance between the two slits is 2 mm and the distance between the plane of the
slits and the screen is 120 cm.
CASE STUDY BASE QUESTIONS ::SECTION – E:4 X 2 = 8
34 Consider two lenses A and B of focal length f1 and f2placed in contact with each other. 4M
Let the object be placed at a point O beyond the focus of the first lens A. The first lens
produces an image at I1. Since image I1 is real, it serves as a virtual object for the second
lens B, producing the final image at I. It must, however, be borne in mind that formation
of image by the first lens is presumed only to facilitate determination of the position of
the final image. In fact, the direction of rays emerging from the first lens gets modified
in accordance with the angle at which they strike the second lens. Since the lenses are
thin, we assume the optical centres of the lenses to be coincident. Let this central point
be denoted by P. The two lens-system is regarded as equivalent to a single lens of focal
length F.
1. Two lenses of power +10D and –5D are placed in contact. Where should the object be
held from the lens so as to obtain a virtual image of magnification 2?
(A) 5 cm (B) –5cm (C) 10 cm (D) –10 cm
2. The plane faces of two identical plano-convex lenses, each having focal length of 40
cm, are placed against each other to form a usual convex lens. The distance from this
lens at which an object must be placed to obtain a real, inverted image with
magnification '–1' is
(A) 80 cm (B) 40 cm (C) 20 cm (D) 160 cm
3. Two thin lenses of focal lengths 20 cm and –20 cm are placed in contact with each
other. The combination has a focal length equal to
(A) Infinite (B) 50 cm (C) 60 cm (D) 10 cm
4. If a convex lens of focal length 80 cm and a concave lens of focal length 50 cm are
combined together, what will be their resulting power
A) + 6.5 D (B) – 6.5 D (C) + 7.5 D (D) – 0.75 D
35 When the diode is forward biased, it is found that beyond forward voltage V = Vk, called 4M
knee voltage, the conductivity is very high. At this value of battery biasing for p-n
junction ,the potential barrier is overcome and the current increases rapidly with
increase in forward voltage. When the diode is reverse biased, the reverse bias voltage
produces a very small current about a few microamperes which almost remains constant
with bias. This small current is reverse saturation current.
(I) In which of the following figures, the p-n diode is forward biased.
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 27
(II) Based on the V-I characteristics of the diode, we can classify diode as
a) bi-directional device (b) ohmic device
(c) non-ohmic device (d) passive element
(III) The V-I characteristic of a diode is shown in the figure. The ratio of forward to reverse bias
resistance is
(a) 100 (b) 106 (c) 10 (d) 10-6
(IV) In the case of forward biasing of a p-n junction 25 diode, which one of the following figures
correctly depicts the direction of conventional current (indicated by an arrow mark)?
(V) If an ideal junction diode is connected as shown, then the value of the current I is
(a) 0.013 A (b) 0.02 A (c) 0.01 A (d) 0.1 A
THE END :: ALL THE BEST
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 28
Class: XII SESSION : 2022-2023
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA NO.2 BELAGAVI CANTT.,
SUBJECT: PHYSICS - SET-5
MM: 70 Time Allowed: 3HRS
.
General Instructions:
(1) There are 35 questions in all. All questions are compulsory
(2) This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D and Section
E. All the sections are compulsory.
(3) Section A contains eighteen MCQ of 1 mark each, Section B contains seven questions of two
marks each, Section C contains five questions of three marks each, section D contains three
long questions of five marks each and Section E contains two case study -based questions of
4 marks each.
(4) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in section B, C, D
and E. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
(5)Use of calculators is not allowed.
SECTION -A
1 The surface charge densities on the surface of two charged spherical conductors of1
radii R1 and R2 are equal. The ratio of electric intensities on the surfaces are 1M
a)R12/R22 b)R22/R12 c)R1/R2 d)1 :1
2 For the arrangement of charges shown in the figure, potential is zero at – 1M
(1) A, B and C (2) D, B and E(3) B only (4) A, B, C, D, and E
3 In the figure, the equivalent capacitance between points A and B is 1M
a)4 µF b)2.5 µF c)2 µF d)0.25 µF
4 In the adjoining circuit, the galvanometer G shows zero deflection. If the batteries 1M
A and B have negligible internal resistance, the value of the resistor R will be :-
(1) 500 (2) 1000 (3) 200 (4) 100
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 29
5 Currents of 10 A and 2 A are flowing in opposite directions through two parallel 1M
wires A and B respectively. If the wire A is infinitely long and wire B is 2 m long,
then force on wire B which is situated at 10 cm from A, is
a) 8×10-5 T b) 6×10-5 T c) 4×10-5 T d) 2×10-5 T
6 Two wires of same length are shaped into a square and a circle if they carry same 1M
current, ratio of magnetic moment is:
a) 2: π b) π:2 c)π:4 d)4: π
7 A short bar magnet of magnetic moment 0.4 J/T is placed in a uniform magnetic 1M
field of 0.16 T. The magnet is in stable equilibrium when the potential energy is
1. -0.064 J 2. Zero 3.-0.082 J 4. 0.064J
8 Two different wire loops are concentric and lie in the same 1M
plane. The current in the outer loop (l) is clockwise and
increases with time. The induced current in the inner loop.
1. Is clockwise 2. Is zero
3. Is counter clockwise
4. Has a direction that depends on the ratio of the loop radii.
9 A power transmission line feeds input power at 2300 V to a step down transformer 1M
with its primary windings having 4000 turns. What should be the number of turns
in the secondary in order to get output power at 230 V?
(a) 600 (b) 550 (c) 400 (d) 375
10 In an AC circuit, the instantaneous values of emf and current are V = 200Sin(314t)V 1M
and I=Sin (314t+π/3)A. Find average power consumed.
(a) 200W (b) 100W(c) 50W (d) 25W
11 An EM wave of intensity “I” falls on a surface and completely absorbed. Pressure 1M
on the surface will be:-
(1) I/C (2) I/2C (3) 2I/C (4) I/3C
12 Four light waves are represented by 1M
(i) y = a1 sin 𝜔t(ii) y = a2 sin (ωt +)(iii) y = a1 sin 2ωt(iv) y = a2 sin (2ω t +)
Interference fringes may be observed due to superposition of
(1) (i) and (ii), (iii) and (iv)(2) (i) and (iii), (iii) and (iv)
(3) (ii) and (iv), (iii) and (iv)(4) (iii) and (iv) only.
13 A l00 watt light source is emitting radiations of wavelength 5000Å. The rat e of 1M
emission of photons is of the order of:
(1) 1040 (2) 1020(3) 1010 (4) 105
14 Energy levels A, B, C of a certain atom correspond to increasing values of energy 1M
i.e., EA < EB < EC. If λ1, λ 2, λ 3 are the wavelengths of radiation corresponding to
the transition C to B, B to A and C to A respectively, which of the following relation
is correct ?
15 The above is a plot of binding energy per nucleon Eb, against the nuclear mass M; 1M
A, B, C, D, E,F correspond to different nuclei.
Consider four reactions :-
(i) A + B → C + (ii) C → A + B +
(iii) D + E → F + (iv) F → D + E +
where is the energy released. In which reactions
is “” positive?
(1) (ii) and (iv) (2) (ii) and (iii)(3) (i) and (iv) (4) (i) and (iii).
16 ASSERTION : In the wave picture of light, intensity of light is determined by the 1M
square of the amplitude of the wave.
REASON : In the photon picture of light, for a given frequency, intensity of light is
determined by the number of photons per unit area.
a) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is the correct explanation of
assertion .
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 30
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct
explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If both the assertion and reason are false.
17 ASSERTION: Work function of aluminium is 4.2 eV. Emission of electrons will be 1M
possible by two photons, each of 2.5 eV energy, striking the electron of aluminium.
REASON: Energy of a photon can be less than the work function of the metal, for
photoelectron emission.
a) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is the correct explanation of
assertion .
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct
explanation of assertion .
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false .
(d) If both the assertion and reason are false.
18 ASSERTION : In reverse biased condition a p-n junction diode does not conduct. 1M
REASON : In reverse biased condition a diode has zero resistance.
a) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is the correct explanation of
assertion .
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct
explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If both the assertion and reason are false.
SECTION – B (2 M QUESTIONS)
19 Two small identical electrical dipoles AB and CD each of dipole moment pare kept 2M
at an angle of 1200 as shown in the figure. What is the resultant dipole moment of
this combination? If this system is subjected to electric field (E) directed
along +X direction, what will be the magnitude and direction of the torque acting
on this?
20 The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 0.9853. Identify the type of magnetic 2M
material. Draw the modification of the field pattern on keeping a piece of this
material in a uniform magnetic field.
21 A) Identify the electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths vary as(a) 10–12m <λ<10–8m 2M
(b) m<λ <10–1m.
B) Write one use for each.
22 A ray of light is incident at an angle of60° on one face of a rectangular glass slab of 2M
thickness0.1 m and refractive index 1.5. Calculate the lateral shiftproduced.
23 In a single slit diffraction experiment , first minimum of red light(660 nm) 2M
coincides with the first maximum of some other wavelength “λ”. Calculate “λ”?
24 The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is -13.6 eV. If an electron makes a 2M
transition from an energy level-1.51 eV to - 3.4 eV, then calculate the wavelength
of the spectral line emitted and name the series of hydrogen spectrum to which it
belongs.
(OR)
Draw a plot of potential energy between a pair of nucleons as a function of their
separation. Mark the regions where potential energy is (i) positive and (ii) negative.
25 Draw the energy band diagrams of – i) P type and ii) N- type semiconductor. 2M
SECTION – C( 3 M questions)
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 31
26 A) Use Biot -Savert’s law to derive the expression for the magnetic field on the axis 3M
of a current carrying circular loop of radius R.
b) Draw the magnetic field lines due to a circular wire carrying current (I).
27 Figure shows a rectangular conductor PQRS in which the conductor PQ is free to 3M
move in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to the plane of the paper. The
field extends from x = 0 to x = b and is zero for x > b.
Assume that only the arm PQ possesses resistance r.When the arm PQ is pulled
outward from x = 0 to x = 2b and is then moved backward to x = 0 with constant
speed v.
Sketch the variations of magnetic flux linked, the induced emf and the force
necessary to pull the arm with distance 0 ≤ x ≤ 2b.
28 i)Find the value of the phase difference between the current and the voltage in the 3M
series L-C-R circuit shown below. Which one leads in the phase, current or voltage?
ii) Without making any other change, find the value of the additional capacitor ‘C’,
to be connected in parallel with the capacitor C, in order to make the power factor
of the circuit unity.
(OR)
50
A resistor of 400 Ω, an inductor of 5/π H and a capacitor of µ𝐹 are connected in 3M
𝜋
series across a source of alternating voltage of 140 sin100πt V. Find the
voltage(rms) across the resistor, the inductor and the capacitor. Is the algebraic
sum of these voltage more than the source voltage? If yes, resolve the paradox.
29 A)Show that the wave length of electro magnetic radiation is equal to the de-Broglie 3M
wave length of its quantum (photon)
B)The work function of a certain metal is 4.2 eV. Will this metal give photo electric
emission for incident radiation of wavelength 330nm?
c)The photo electric cut-off voltage in a certain experiment is 1.5V What is the
maximum kinetic energy of photo electrons emitted?
(OR)
A)The given graph shows the variations of photo-electric current(I) versus applied 3M
voltage (V) for two different photosensitive materials and for two different intensities of
the incident radiations. Identify the pairs of curves that correspond to different
materials but same intensity of incident radiation:
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 32
b)Show graphically ,the variation of the de-Broglie wave length (λ) with the
potential (V) through which an electron is accelerated from rest.
30 The electron, in a hydrogen atom, initially in a state of quantum number n 1 makes 3M
a transition to a state whose excitation energy , with respect to the ground state ,
is 10.2 eV.
If the wavelength , associated with the photon emitted in this transition, is 487.5
nm, find the i) Energy in eV and
ii) Value of the quantum number n1 of the electron in its initial state.
(OR)
The energy levels of an atom are as shown in figure. (a) Which one of these 3M
transitions will result in the emission of photon of wave length 275nm? (b) Which
transition corresponds to emission of radiation of maximum wave length?
SECTION – D ( 5 M questions)
31 a) Derive expression for the torque acting on an electric dipole placed in a uniform 5M
electric field?
b) Two identical charges , Q each, are kept at a distance r from each other. A third charge “q” is
placed on the line joining the above two charges such that all the three charges are in equilibrium.
What is the magnitude , sign and position of the charge “q”?
(OR)
a) Show that the conservative electric field is equal to the negative gradient of electric potential. 5M
b) Figure shows some equipotential surfaces. Calculate the magnitude and
direction of the electric field ?
32 a) Obtain expression for the capacity of a parallel plate capacitor filled with a 5M
dielectric of specific inductive capacity “k” and thickness t < d ( d is the separation
between the plates).( area of each plate is “A”.
b) Where is the energy stored in a capacitor? Derive an expression for the energy
density of an electric field?
(OR)
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 33
a) 36 cells each of internal resistance 0.5 ohm and emf 1.5 Volt each are used to send current 5M
through an external circuit of 2 ohm resistance. Find the best mode of grouping them and the
current through the external circuit?
b) Plot a graph showing temperature dependence of resistivity for typical
semiconductor. how is this behaviour explained?
c) How does the internal resistance of a cell vary with increase in temperature?
33 a)Derive the following relation for a real image formed by a convex refracting surface 5M
when the object is placed in rarer medium. Also write the assumptions and sign
convention used.
𝑛2 𝑛1 𝑛2−𝑛1
- =
𝑣 𝑢 𝑅
b) Calculate the radius of curvature of an equi-concave lens of refractive index 1.5,
when it is kept in a medium of refractive index 1.4, to have a power of –5D ? If the
same lens immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.33 calculate its power.
(OR)
a) Sketch the refracted wave front for the incident plane wave front of light from a 5M
distant object passing through a convex lens.
b) In the diffraction due to a single slit experiment, the aperture of the slit is 3 mm.
If monochromatic light of wavelength 620 nm is incident normally on the slit,
calculate the separation between the first order minima and the 3rd order maxima
on one side of the screen. The distance between the slit and the screen is 1.5 m.
c) Describe any two characteristic features which distinguish between interference
and diffraction phenomena.
CASE STUDY BASE QUESTIONS ::SECTION – E: 4 X 2 = 8
34 Read the following paragraph and answer the questions 4M
ABC is a right angled prism kept in air. A ray (1) is
incident on the face AB along the normal. Another
ray (2) is incident on the face AB such that it
emerges normally from the face AC. Then
(i) The minimum value of refractive index of the
material of the prism for which the ray (1) undergoes
total internal reflection on the face AC is
a) 2 b) 2 c) 1.5 d)2.2
(ii) The angle of incidence of the ray (2) on the Face AB is
a )00 b) 450 c) 300 d) 900
(iii) The deviation suffered by the light ray(2) is
(a) 600 B) 450 C) 300 D) 900
(iv) For which colour the refractive index of material of the prism is least?
(v) Draw the graph between angle of incidence and angle of deviation for a prism?
35 Read the following paragraph and answer the questions 4M
A P-N junction is the key to all semiconductor devices. When such a junction diode
is made, a depletion layer is formed consisting of immobile ions devoid of their
electrons or holes. This is responsible for a junction potential barrier. By changing
the external applied voltage, junction barrier can be changed. In forward bias, the
barrier is decreased while the barrier increases in reverse bias. Hence, forward bias
current is more while it is very small in reverse biased junction diode.
(i)What is the cause for current in reverse bias of a PN junction diode ?
(ii) Name the two processes, by which PN junction is formed?
(iii) The diodes in the circuit have a forward resistance of 50 Ohm and infinite
backward resistance. Find the current through the 100ohm resistance?
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 34
(OR)
(iii) What will happen to the intrinsic semiconductor, when placed at absolute zero ?
THE END :: ALL THE BEST
SATISH KUMAR SIVALANKA/XII/PHYSICS 35
You might also like
- Learner Guide For IGCSE Physics 0625Document49 pagesLearner Guide For IGCSE Physics 0625digarte33% (3)
- Section 12a - Class Exercise: Line Distance Protection: Protecting Power Systems For Engineers - PROT 401Document5 pagesSection 12a - Class Exercise: Line Distance Protection: Protecting Power Systems For Engineers - PROT 401Jorge Corrales BarrazaNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument21 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersprismtonicNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument17 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersprismtonicNo ratings yet
- Solution A2 CHE 312ADocument12 pagesSolution A2 CHE 312AMukul ParasharNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024Document9 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024dhitiNo ratings yet
- Post Lab 10Document6 pagesPost Lab 10Focus On ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Book-2 Physcis 312 Senior SecondaryDocument386 pagesBook-2 Physcis 312 Senior SecondaryBalwinder GherhaNo ratings yet
- Pre Board 1 PhysicsDocument6 pagesPre Board 1 PhysicsMohit KumarNo ratings yet
- COMMON PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION 2022-23 PHYSICSDocument11 pagesCOMMON PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION 2022-23 PHYSICSEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Physics XII QP Set 1Document10 pagesPhysics XII QP Set 1meme MachineNo ratings yet
- 2.physics Qp-XiiDocument6 pages2.physics Qp-XiiEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Class XII Physics Sample Question Paper 1Document42 pagesClass XII Physics Sample Question Paper 1OJASisLiveNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersDocument17 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersxkryxxzNo ratings yet
- Class XII Physics Support Material Final-1 - Removed - RemovedDocument70 pagesClass XII Physics Support Material Final-1 - Removed - RemovedIshu RaoNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII PRE BOARD Physics QP 2023-24Document19 pagesCLASS XII PRE BOARD Physics QP 2023-24suprajabhupalanNo ratings yet
- XII Physics QPDocument8 pagesXII Physics QPsinghbharat50726No ratings yet
- 12 - Physics Question Paper (Pre-Board Ii)Document7 pages12 - Physics Question Paper (Pre-Board Ii)VaniceWhilderNo ratings yet
- 14 SQPDocument8 pages14 SQPdipanshu76612No ratings yet
- PM Shri Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper Test 11 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesPM Shri Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper Test 11 For Board Exam 2024maxers.xdNo ratings yet
- Phy201p QPDocument9 pagesPhy201p QPAyush XI-ANo ratings yet
- Class-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-2Document7 pagesClass-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-2kamali.v777No ratings yet
- QP Xii PhysicsDocument9 pagesQP Xii PhysicsSufiyan BelimNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024 Answers 1Document20 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024 Answers 1s15269a.hasini02886100% (1)
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024xkryxxzNo ratings yet
- Physics Exclusive Sample Paper With SolutionDocument25 pagesPhysics Exclusive Sample Paper With SolutionA KNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1Document11 pages12 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1aniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023Document7 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023shagun sinhaNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - XII - Physics2023-24Document6 pagesSAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - XII - Physics2023-24Nandita SharmaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Xii PB-1 QPDocument10 pagesPHYSICS Xii PB-1 QPAyaan HusainNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument18 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersGyan BardeNo ratings yet
- 12 PhysicsDocument8 pages12 Physicsdhritibarak548No ratings yet
- Test paper 8 (answers)Document17 pagesTest paper 8 (answers)ashishgambhir1986No ratings yet
- Common Pre-Board Examination 2022-23 Physics (042) Class XIIDocument6 pagesCommon Pre-Board Examination 2022-23 Physics (042) Class XIIEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Physics PQ2Document7 pagesPhysics PQ2David BamNo ratings yet
- Xii QP Physics VSTDocument5 pagesXii QP Physics VSTkrishnapradhani091No ratings yet
- 1.Qp - Class 12 - PhysicsDocument12 pages1.Qp - Class 12 - PhysicsEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Physics Pre-Board I 2022-23Document6 pagesPhysics Pre-Board I 2022-23Ayushi KayalNo ratings yet
- PB XII Phy QP Nov 2022Document8 pagesPB XII Phy QP Nov 2022Ayushi KayalNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 12 For Board Exam 2024Document5 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 12 For Board Exam 2024xkryxxzNo ratings yet
- QP - Physics - Xii - SPDocument7 pagesQP - Physics - Xii - SPriteshsamrath440No ratings yet
- Xii-Cbse-Physicspreboardexam (03032024) 240303 143620Document8 pagesXii-Cbse-Physicspreboardexam (03032024) 240303 143620sramalingam.ecbNo ratings yet
- Details: General InstructionsDocument9 pagesDetails: General InstructionsAakriti RoyNo ratings yet
- G12 Physics Pre Board - 1 QP With SolutionsDocument25 pagesG12 Physics Pre Board - 1 QP With SolutionsSreshta ReddyNo ratings yet
- Xii Phy Sample Question Paper 01Document9 pagesXii Phy Sample Question Paper 01Aman DhamiNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 2 Word FileDocument12 pagesSample Paper 2 Word FileAtul DubeyNo ratings yet
- XII - PHYSICS - HY - Question - PaperDocument7 pagesXII - PHYSICS - HY - Question - Papernrusinghsamal2006No ratings yet
- Test Paper 8Document8 pagesTest Paper 8rajeshsharma4121No ratings yet
- 7.prelim - Physics-2022-QnDocument10 pages7.prelim - Physics-2022-QnEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- PB Xii (2022 23) Set 1Document4 pagesPB Xii (2022 23) Set 1Uday SinghNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Physics PB I 2023-24Document6 pagesQuestion Paper Physics PB I 2023-24rishirajkaran2006No ratings yet
- CLASS 12 PRE BOARD PAPER PhysicsDocument13 pagesCLASS 12 PRE BOARD PAPER Physicsaditya singhNo ratings yet
- CAMBRIDGE SCHOOL, NOIDA PREBOARD-II 2022-23 PHYSICS (042) SET BDocument7 pagesCAMBRIDGE SCHOOL, NOIDA PREBOARD-II 2022-23 PHYSICS (042) SET BsidharthNo ratings yet
- Class 12 FCT 4 CBSE FinalDocument6 pagesClass 12 FCT 4 CBSE FinalDerekNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper - 12th ClassDocument6 pagesModel Question Paper - 12th ClassIMRAN ANSARINo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07-Dec-2023Document12 pagesAdobe Scan 07-Dec-2023Poovaraahan RaghuveeranNo ratings yet
- PB 2-Xii-Physics-SetDocument6 pagesPB 2-Xii-Physics-Setyadav.uditanshu75525No ratings yet
- Bhavan's Netaji Subhash Physics Pre Board 1Document9 pagesBhavan's Netaji Subhash Physics Pre Board 1niladriputatunda1No ratings yet
- Pre First TermDocument7 pagesPre First TermAawesh BackupsNo ratings yet
- Ques PaperDocument10 pagesQues Papergupta.sg003No ratings yet
- Class XII 2023 2024 Prelims IDocument10 pagesClass XII 2023 2024 Prelims ITanishkha RaajNo ratings yet
- ISC Physics Sem 1 2022Document23 pagesISC Physics Sem 1 2022mbbhadraNo ratings yet
- Class 12 P. T 2Document7 pagesClass 12 P. T 2Adhvai Senthil kumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 06 For Board Exam 2024Document9 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 06 For Board Exam 2024s15089a.shubham14646No ratings yet
- The Metabolic Map Carbohydrates AtfDocument3 pagesThe Metabolic Map Carbohydrates AtfJoax Wayne SanchezNo ratings yet
- MS PB-1 Set 1 (A) Maths XiiDocument8 pagesMS PB-1 Set 1 (A) Maths XiiPratham ZalaNo ratings yet
- Tips For ConversionDocument2 pagesTips For ConversionPratham ZalaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument2 pagesDocumentPratham ZalaNo ratings yet
- Organic Name ReactionsDocument2 pagesOrganic Name ReactionsPratham ZalaNo ratings yet
- Daily Test Planner 2022-23Document1 pageDaily Test Planner 2022-23Pratham ZalaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Population Density and Percentage Frequency by Quadrat Method - Solving The Problems - Botany PracticalsDocument7 pagesDetermination of Population Density and Percentage Frequency by Quadrat Method - Solving The Problems - Botany PracticalsPratham ZalaNo ratings yet
- Organic ExplanationsDocument4 pagesOrganic ExplanationsManjunath NaikNo ratings yet
- Capsule For Low AchieversDocument17 pagesCapsule For Low AchieversPratham Zala100% (1)
- Flash Cards For Bio PracticalsDocument4 pagesFlash Cards For Bio PracticalsPratham ZalaNo ratings yet
- Project Certificate - ACCDocument5 pagesProject Certificate - ACCPratham ZalaNo ratings yet
- Pollination Methods and MechanismsDocument5 pagesPollination Methods and MechanismsPratham ZalaNo ratings yet
- Catalogo AvxDocument109 pagesCatalogo AvxBernardo QuijadaNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Mechanical Universe From Electricity To Modern PhysiDocument600 pagesBeyond The Mechanical Universe From Electricity To Modern PhysipaulinaNo ratings yet
- Neet Physics in 123 Concepts C 11-Unit 2-Units & MeasurementsDocument3 pagesNeet Physics in 123 Concepts C 11-Unit 2-Units & MeasurementssachinNo ratings yet
- Grammar C1Document17 pagesGrammar C1Saida GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document10 pagesModule 3Michael godsonNo ratings yet
- Eee 315 Electrical Machines IiiDocument6 pagesEee 315 Electrical Machines IiiAbkul KunniNo ratings yet
- 7P2 NewKM v2Document3 pages7P2 NewKM v2Muhzina JunaidNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge - Formula, Properties, UnitDocument10 pagesElectric Charge - Formula, Properties, UnitRahul Rawat100% (1)
- Lesson 3 - Mixtures and SolutionsDocument9 pagesLesson 3 - Mixtures and SolutionsMelvyn DarauayNo ratings yet
- Quantifiers Some and AnyDocument2 pagesQuantifiers Some and AnyNataliaEspejelNo ratings yet
- Units and Measurement - Practice Sheet - Arjuna JEE 4.0 2024Document3 pagesUnits and Measurement - Practice Sheet - Arjuna JEE 4.0 2024Kanishq SarkarNo ratings yet
- Coulombs LawDocument13 pagesCoulombs LawChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Rotational MechanicsDocument25 pagesRotational MechanicsUjib DamianNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 08 - (Test Papers) - Prayas JEE 2.0 2024Document9 pagesPractice Test 08 - (Test Papers) - Prayas JEE 2.0 2024vagattursanjayNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument4 pagesExerciseariefnur19No ratings yet
- Ehvac Previous QuestionsDocument4 pagesEhvac Previous QuestionsVenkatNo ratings yet
- Huawei SUN2000 5KTL M1 HC High CurrentDocument2 pagesHuawei SUN2000 5KTL M1 HC High Currentalexe.alexandru90No ratings yet
- Skoog, West, Holler and Crouch 9 Edition (2004)Document78 pagesSkoog, West, Holler and Crouch 9 Edition (2004)jumanaNo ratings yet
- Physics of Thermo-Acoustic Sound GenerationDocument13 pagesPhysics of Thermo-Acoustic Sound GenerationtaNo ratings yet
- Materials For Energy Harvesting at The Forefront of A New WaveDocument5 pagesMaterials For Energy Harvesting at The Forefront of A New WaveShotech EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Technical College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering AC CircuitDocument7 pagesTechnical College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering AC Circuitاياد النعيميNo ratings yet
- HW02 - 2019 Dynamic CharacteristicsDocument1 pageHW02 - 2019 Dynamic CharacteristicsRindra RahmatullohNo ratings yet
- INPhO 2008 - 2020 Indian National Physics OlympiadDocument362 pagesINPhO 2008 - 2020 Indian National Physics OlympiadSubhankar TripathiNo ratings yet
- A Properties of WaterDocument12 pagesA Properties of WaterLouis TambunanNo ratings yet