Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Product
Chemistry Product
Uploaded by
Prince Dhanani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesThe document describes the relationship between wavelength and color for different elements. It defines wavelength and frequency of electromagnetic radiation, noting that wavelength is measured in meters and frequency in Hertz. It provides the equations showing that the speed of light equals wavelength times frequency, and that photon energy equals Planck's constant times frequency.
Original Description:
chemistry program with pregnant women
Original Title
chemistry product
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the relationship between wavelength and color for different elements. It defines wavelength and frequency of electromagnetic radiation, noting that wavelength is measured in meters and frequency in Hertz. It provides the equations showing that the speed of light equals wavelength times frequency, and that photon energy equals Planck's constant times frequency.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesChemistry Product
Chemistry Product
Uploaded by
Prince DhananiThe document describes the relationship between wavelength and color for different elements. It defines wavelength and frequency of electromagnetic radiation, noting that wavelength is measured in meters and frequency in Hertz. It provides the equations showing that the speed of light equals wavelength times frequency, and that photon energy equals Planck's constant times frequency.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Element Colour Wavelength(nm)
Barium Light Green 535
Calcium Orange Red 622
Copper Bluish Green 492
Lithium Pink 597
Potassium Light Lilac 423
Sodium Yellow 587
Strontium Red or Crimson 701
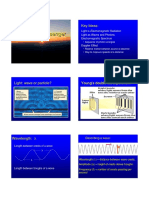
Electromagnetic radiation is composed of perpendicular
waves oscillating in the electric and magnetic fields
(through space or matter). These waves are characterized
by their wavelength (λ) and frequency (ν). Wavelength is
defined as the distance between successive crests (or
troughs) on a wave, and is measured in meters. Frequency
is defined as the number of waves that pass a given point
every second, and is measured in 1/seconds, or Hertz
(Hz).
All electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light (c),
or 2.998×108m/s. The relationship between the wavelength,
frequency and speed of an electromagnetic wave is given by the
equation:
c=λ×ν
Electromagnetic radiation also occurs as discreet packets of energy
(or quanta) called photons. The energy per photon (in Joules) is
given by the equation
Ephoton=h×ν
Here, hh is Planck’s constant, which has a value of 6.626×10−34J.
Visible light is the most familiar example of electromagnetic
radiation. Differences in the wavelengths of visible light are
manifested as different colors
You might also like
- Chem Experiment No 2Document3 pagesChem Experiment No 2Abigail Cristine VelascoNo ratings yet
- Combined Analytical SlidesDocument249 pagesCombined Analytical SlidesDanso MichaelNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry IIDocument14 pagesAnalytical Chemistry IIMike Chris HolysticksNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - Electromagnetic Radiation PDFDocument13 pagesCH 2 - Electromagnetic Radiation PDFNidhi PatelNo ratings yet
- Electron Energy and LightDocument6 pagesElectron Energy and LightAliou KoneNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation PDFDocument6 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation PDFGhaus100% (1)
- CHE029 Spectroscopic-AnalysisDocument6 pagesCHE029 Spectroscopic-AnalysisCarla Mae OlvenarioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 PPIDocument21 pagesLecture 11 PPIabeehazakeeshNo ratings yet
- Flame Tests and Atomic SpectraDocument3 pagesFlame Tests and Atomic SpectraImmanuel LashleyNo ratings yet
- Basic Instrumental Analysis CHM260: An Introduction To Spectroscopic Methods of AnalysisDocument65 pagesBasic Instrumental Analysis CHM260: An Introduction To Spectroscopic Methods of AnalysisNurhayati HasanahNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument32 pagesChapter Threemiesoabdela57No ratings yet
- Alternate Light Source Imaging Forensic Photography TechniquesDocument99 pagesAlternate Light Source Imaging Forensic Photography Techniquesjadrio1556No ratings yet
- 3 CC1Document6 pages3 CC1marianNo ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument28 pagesSpectrosPraveen Kumar AvvaruNo ratings yet
- Grade8 Science Colors of LightDocument35 pagesGrade8 Science Colors of LightCatherine Yorong PedranoNo ratings yet
- #1 Instrumental PDFDocument40 pages#1 Instrumental PDFMahmoud RedaNo ratings yet
- Student Notes: Clinchem1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentDocument9 pagesStudent Notes: Clinchem1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentMelody Jane PardilloNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum - Lecture 1Document14 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum - Lecture 1Mvita HenocNo ratings yet
- E01 Handbook IntroductionDocument12 pagesE01 Handbook IntroductionAlexander Quebra Madeira NemchinovNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 1Document15 pagesUnit 1 1tehreemshakirchNo ratings yet
- SP01 - Atomic Theory To Bohr - PresentationDocument29 pagesSP01 - Atomic Theory To Bohr - PresentationMarianNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Optics Ebook FinalDocument38 pagesFundamentals of Optics Ebook FinalSuman RachaNo ratings yet
- Remote Sensing Essentials: Electromagnetic Spectrum, Solar Reflection and Thermal EmissionDocument18 pagesRemote Sensing Essentials: Electromagnetic Spectrum, Solar Reflection and Thermal EmissionTrambak BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Week-1 Module-4 EM Spectrum Solar Reflection and Thermal Emission Remote SensingDocument18 pagesWeek-1 Module-4 EM Spectrum Solar Reflection and Thermal Emission Remote SensingAKASH MAURYANo ratings yet
- Optics and Optical Communication: Amanuel Admassu, Mtu-EceDocument70 pagesOptics and Optical Communication: Amanuel Admassu, Mtu-EceAmanuel AdmassuNo ratings yet
- The Visible SpectrumDocument4 pagesThe Visible Spectrumjambadilla.eduNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Introduction To Spectrometry 2013-14Document16 pagesUnit 5 Introduction To Spectrometry 2013-14Dianna WattNo ratings yet
- Visible Light-Based Human Visual System Conceptual ModelDocument8 pagesVisible Light-Based Human Visual System Conceptual ModelingenieurmechanicalNo ratings yet
- Atomic Emission Line SpectraDocument10 pagesAtomic Emission Line SpectraDCNo ratings yet
- 12 Electron Energy and Light-SDocument6 pages12 Electron Energy and Light-SSelma CedilloNo ratings yet
- Radiation 1Document37 pagesRadiation 1guna sekaranNo ratings yet
- Dipartimento Di Fisica Universita' Della Calabria Corso Di Laurea Magistrale in Fisica A.A. 2016/2017Document12 pagesDipartimento Di Fisica Universita' Della Calabria Corso Di Laurea Magistrale in Fisica A.A. 2016/2017Diego Blady HaroNo ratings yet
- Light Propagation in Optical Fiber: Light Thought of As A WaveDocument6 pagesLight Propagation in Optical Fiber: Light Thought of As A WaveMona SayedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Analytical MethodsDocument104 pagesChapter 4 Analytical MethodsCL SanchezNo ratings yet
- UV HandoutDocument9 pagesUV HandoutGezem GigantoNo ratings yet
- Uv Vis Spectroscopy QuestionsDocument6 pagesUv Vis Spectroscopy QuestionsFahra Aqilla AzzurahNo ratings yet
- Spectro Photo Me TryDocument3 pagesSpectro Photo Me TryAshley Nicole DelizoNo ratings yet
- Flame Color of MetalsDocument3 pagesFlame Color of MetalsDyan Rioja50% (2)
- UV Spectroscopy:: Empirical Approach To Molecular StructuresDocument56 pagesUV Spectroscopy:: Empirical Approach To Molecular StructuresTehmina HanifNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 16 - Electronic SpectrosDocument24 pagesLecture Note 16 - Electronic SpectrosTbsbi P.No ratings yet
- Light Electromagnetic Radiation: Optics: The Study of LightDocument52 pagesLight Electromagnetic Radiation: Optics: The Study of LightsariNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet/Visible Light Absorption Spectrophotometry (UV-Vis)Document63 pagesUltraviolet/Visible Light Absorption Spectrophotometry (UV-Vis)MiftahAinulMardiahNo ratings yet
- Instrumental Analysis: Spectrophotometric MethodsDocument32 pagesInstrumental Analysis: Spectrophotometric MethodsMarie PetalcorinNo ratings yet
- Optical PropertiesDocument36 pagesOptical PropertiesJoseph GabuyaNo ratings yet
- CCh3 Introduction To Radient Energy2Document71 pagesCCh3 Introduction To Radient Energy2Habtamu MollaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Fundamental of Remote SensingDocument50 pagesLecture 5 Fundamental of Remote SensingAddo MawuloloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Fall-2022-2023-C411Document25 pagesChapter 1-Fall-2022-2023-C411hesham khaledNo ratings yet
- Infrared SpectrosDocument50 pagesInfrared SpectrosmohammedabubakrNo ratings yet
- Uv, Vis 1Document71 pagesUv, Vis 1مروه العمرNo ratings yet
- Invse Square LawDocument10 pagesInvse Square LawBEDELE KNOWLEDGENo ratings yet
- Iub Pha404 Autumn 2022 AasDocument40 pagesIub Pha404 Autumn 2022 AasTanvir FahimNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument30 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumyeloalmasenNo ratings yet
- Optical MethodsDocument12 pagesOptical Methodsjosquim01No ratings yet
- Introduction To Aerial Photographic Systems: Ies / Cee / For / Gle 301Document30 pagesIntroduction To Aerial Photographic Systems: Ies / Cee / For / Gle 301JJNo ratings yet
- The Quantum-Mechanical Model of The Atom: Lecture PresentationDocument54 pagesThe Quantum-Mechanical Model of The Atom: Lecture PresentationIrene SumbilloNo ratings yet
- Light The Messenger: Key IdeasDocument4 pagesLight The Messenger: Key IdeasabdishakurNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 5 - SPECTROPHOTOMETRYDocument2 pagesPerformance Task 5 - SPECTROPHOTOMETRYKeith BagangNo ratings yet
- SCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLDocument42 pagesSCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLErick Wangila WanyonyiNo ratings yet
- Optics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyFrom EverandOptics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Optical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandOptical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet