Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Second Periodical Test 1
Uploaded by
mary-ann escala0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesThis document contains a science test with multiple choice and word scramble questions about human and plant reproduction, as well as marine biology topics like estuaries, salinity, mangroves, and abiotic and biotic factors in ecosystems. It was given to students in the District of Dauis in the Philippines' Department of Education. The test covers material taught in the second periodical test in science.
Original Description:
Original Title
science-second-periodical-test-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a science test with multiple choice and word scramble questions about human and plant reproduction, as well as marine biology topics like estuaries, salinity, mangroves, and abiotic and biotic factors in ecosystems. It was given to students in the District of Dauis in the Philippines' Department of Education. The test covers material taught in the second periodical test in science.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesScience Second Periodical Test 1
Uploaded by
mary-ann escalaThis document contains a science test with multiple choice and word scramble questions about human and plant reproduction, as well as marine biology topics like estuaries, salinity, mangroves, and abiotic and biotic factors in ecosystems. It was given to students in the District of Dauis in the Philippines' Department of Education. The test covers material taught in the second periodical test in science.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region VII, Central Visayas
Division of Bohol
District of Dauis
SECOND PERIODICAL TEST IN SCIENCE V
Read carefully. Choose the best answer.
1.What do you call the process of the union of the egg cell and sperm cell?
1. fertilization 2. Implantation 3. Menstruation 4. Ovulation
2. What part of the male reproductive system serves s a passageway for the sperm cells from the testes to the
seminal vesicle?
1. prostate glands 2. Scrotum 3. Urethra 4. vas deferens
3. Where does fertilization occur?
1. cervix 2. fallopian tube 3 Uterus 4. Vagina
4. What part of the female reproductive system m releases the egg cell?
1. cervix 2 ovary 3 oviduct 4. Vagina
5. How many days does a normal menstrual cycle occur?
1. 7 days 2. 14 day 3. 21 days 4. 28 days
6. Where does the baby (fetus) grow and develop inside the mother?
1. fallopian tube 2. Ovary 3. Stomach 4. Uterus
7. What is the function of the male reproductive system in human reproduction?
1. It produces hormones called testosterone.
2. It is responsible for the deepening of male’s voice.
3. It provides hormones to develop male characteristics
4. It produces sperm cells needed to fertilize egg cells to produce new human being.
8. Why does the scrotum and testes maintain low temperature?
1. to stock sperm cells 3. To produce sperm cells
2. to protect sperm cells 4. To provide sperm cells with sac like pouch for protection
9. . Which of the following changes in puberty does NOT occur in males?
1. enlargement of sex organs 3. Pubic hair growth
2. growth of spurts 4. Hips become round and wide
10. Which of the following is TRUE about the uterus?
1. it is where fertilization takes place 3. It is where fertilized egg grows and develop
2. It is where the baby passes through during birth 4. It is where the sperm cell finds and fertilizes
An egg inside the mother’s body
11. Which of the following organism can reproduce through binary fission?
1. sea anemone 2. Fish 3. Frog 4. Lizard
12. This process happens when the sperm cells are released into the body of the female and become fertilized
1. asexual fertilization 2. External fertilization 3. Internal fertilization 4. Incubation
13. Which of the following organisms is NOT included in the group?
1. fish 2. Hydra 3. Frog 4. Butterfly
14. Which is NOT an example of asexual reproduction?
1. binary fission 2. Budding 3. Fertilization 4. Regeneration
15. It is described as the time between fertilization and the birth of the live young.
1. gestation 2. Incubation 3. Internal fertilization 4. External fertilization
16. What kind of fertilization happens when eggs are released by the female to the environment and is
fertilized by the sperm of the male
1. asexual 2. External fertilization 3. Internal fertilization 4. Sexual
17. What kind of reproduction involves only one parent?
1. asexual 2. External fertilization 3. Internal fertilization d. sexual
18. How does sexual reproduction happen in animals?
1. When sperm cell and egg cell unite 3. When 2 sperm cells unite with 1 egg cell
2. when 2 sperm cells unite with 2 egg cells 4. When sperm cell unites with another sperm cell
19. Chicks are hatched from eggs. Goats are born alive and look like its parents. Frogs undergo many changes
as they grow. What do these observation prove?
1. All animals are born alive. 3. Different animals move in different ways
2. All animals are hatched from eggs. 4. Different animals reproduce in different ways
20. Why is reproduction important to living organism?
1. It controls the body parts 3. It collects and removes wastes
2. it converts food into nutrients 4. It ensures continued existence of the organisms.
21. Which of the following is NOT needed by plants for their growth and development?
1. fire 2. Nutrients 3 sunlight 4. Water
22. Which part of the plant cannot undergo vegetative propagation?
1. stem 2. Fruit 3. Leaves 4. roots
23. What type of pollination happens when pollen grains from the anther are transferred to the stigma of a
flower that belongs to the same plant?
1. across-pollination 2. Auto-pollination 3. Cross-pollination 4. Self-pollination
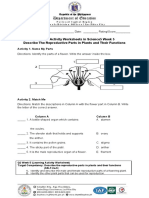
24. Which is NOT a female part of a flower?
1. filament 2. Pistil 3. Ovary 4. Stigma
25. Which part of a flower becomes the seed?
1. ovum and anther 2. Ovum and ovary 3. Ovum and ovule 4. Ovum and style
26. Which part of the flower produces the pollen ?
1. anther 2. Ovary 3. Pistil 4. Stamen
27. Which of the following examples is a tuber?
1. guava plant 2. Mango plant 3. Orange plant 4. Potato plant
28. Which parts f the flower are needed in pollination?
1. calyx and anther 2. Pistil and stamen 3. Pistil and petals 4. Sepals and petals
29. What would happen when a butterfly sips nectar from a flower?
1. Flower could wilt 3. Stamen could develop a tube.
2. Pistil could break. 4. Pollen could fall on the stigma
30. What happens during cross-pollination?
1. the pollen grains transfer from the anther to the stigma of the same plant’s flower
2. the pollen grains transfer from the anther to the stigma of a flower that belongs to another plant of the
Same kind
3. the pollen grains transfer from the anther to the stigma of another plant of the different kind
4. none of the above mentioned
II, Unscramble the letter in Column B to form the word being described in Column C . Write your answer on
your answer sheet.
COLUMN A COLUMN B COLUMN C
_______________31, TUESARISE “ nurseries of the seas”
_______________32. NIALSIYT amount of salt in water
_______________33. NAGMEVOR trees which grow in saltwater areas
_______________34 PUREMEATTER hotness or coldness of water
_______________35 SEAWV movement of the surface of the water
_______________36 LATED a body of water that can also be an estuary
_______________37 SSYECOTME the relationship between biotic and abiotic factors in a certain
Place
_______________38. SHARKBIC the type of water in estuaries
_______________39. ICIBOAT nonliving factors in the environment
_______________40. DIALTTREIN area which is directly affected by tides
Answer key science 2nd periodical test
1. 1 11. 1 21 1 31. ESTUARIES
2. 4 12. 3 22 2 32 SALINITY
3. 2 13. 2 23 4 33. MANGROVE
4 2 14 3 24 1 34 TEMPERATURE
5 4 15. 1 25 3 35 WAVES
6. 4 16 2 26 1 36 DELTA
7 4 17 1 27 4 37 ECOSYSTEM
8, 3 18 1 28 2 38 BRACKISH
8, 4 19 4 29 4 39 ABIOTIC
10. 3 20. 4 30 2 40 INTERTIDAL
You might also like
- GAPS Paper Plant Physio and Rep.Document4 pagesGAPS Paper Plant Physio and Rep.Aryan KhandkaNo ratings yet
- 4th P.test Sci - Grade 8Document4 pages4th P.test Sci - Grade 8Leonie Cruz ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Origin Nature and Evolution of Protoplasmic Individuals and Their Associations: Protoplasmic Action and ExperienceFrom EverandThe Origin Nature and Evolution of Protoplasmic Individuals and Their Associations: Protoplasmic Action and ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Comparing The Stages in A Life Cycle ofDocument36 pagesComparing The Stages in A Life Cycle ofReychelle GutierrezNo ratings yet
- EM - Bio - G13 - T2 - I, II PP - 2020Document18 pagesEM - Bio - G13 - T2 - I, II PP - 2020Sumaiya RizanNo ratings yet
- Biology Passing Package 2Document73 pagesBiology Passing Package 2Ankith Raj100% (2)
- Test 2 (NEETprep 2020 Test Series)Document28 pagesTest 2 (NEETprep 2020 Test Series)SUDHANSHU PANWARNo ratings yet
- UNIT6Document14 pagesUNIT6James OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument60 pagesAsexual and Sexual ReproductionJerome DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Biology Worksheets - XIIDocument188 pagesBiology Worksheets - XIIlatishabasilNo ratings yet
- Ncert Page Wise Q Plant Growth Regulatorsplant Growth RegulatorsDocument22 pagesNcert Page Wise Q Plant Growth Regulatorsplant Growth RegulatorsSagarNo ratings yet
- Biology Passing Package For Ii PucDocument38 pagesBiology Passing Package For Ii PucRishi Kesh100% (1)
- Class XII BiologyDocument189 pagesClass XII BiologyVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Chapter-1 Reproduction in OrganismsDocument10 pagesReproduction Chapter-1 Reproduction in OrganismsSharafaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Quantification MCQsDocument3 pagesBacterial Quantification MCQsMahi ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Revision 4 - Ordinary Level Biology-EdexcelDocument3 pagesRevision 4 - Ordinary Level Biology-Edexceleugene_970418755No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Module Activities Q2Document11 pagesEarth and Life Science Module Activities Q2Francine ValdezNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionDocument18 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionAutumn JJ100% (3)
- CBSE Class 11 Biology MCQs - Set 6 PDFDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology MCQs - Set 6 PDFsarimfayyazNo ratings yet
- Arlene Amaro Science-4-CotDocument7 pagesArlene Amaro Science-4-CotARLENE T. AMARONo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 5: "Where Do I Begin?"Document28 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 5: "Where Do I Begin?"Freya Joy Mercado - Santos90% (10)
- 102 Incourse Test 2013Document17 pages102 Incourse Test 2013Sam CuthbertNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Sexual and Asexual ReproductionDocument17 pages4.1 Sexual and Asexual ReproductionRoza Roza100% (1)
- Life Cycle of Spore-Bearing PlantsDocument15 pagesLife Cycle of Spore-Bearing PlantsMia ManaayNo ratings yet
- English Medium (Science) Grade 10-Unit Test 8Document5 pagesEnglish Medium (Science) Grade 10-Unit Test 8The NaNi ShowNo ratings yet
- Identify The Letter of The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument5 pagesIdentify The Letter of The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionMara LabanderoNo ratings yet
- Biology Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesBiology Important QuestionsLlamNo ratings yet
- Ncert Page Wise Q Animal KingdomDocument14 pagesNcert Page Wise Q Animal KingdomAleen KhanNo ratings yet
- G5-Science HYE Compiled Revision Worksheet With Answer KeyDocument23 pagesG5-Science HYE Compiled Revision Worksheet With Answer KeyRevanth kumarNo ratings yet
- QTR 2 Module 4 ReproductionDocument10 pagesQTR 2 Module 4 ReproductionNick BantoloNo ratings yet
- High Yielding Test Series - Part Test 5: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Document24 pagesHigh Yielding Test Series - Part Test 5: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718DR. SAYAJI KASHIDNo ratings yet
- Mode of Reproduction in Butterflies and Mosquitoes: By: Eloisa A. Rivera, Ed.DDocument39 pagesMode of Reproduction in Butterflies and Mosquitoes: By: Eloisa A. Rivera, Ed.DCatherine Dimailig100% (1)
- Mini Research ReportDocument25 pagesMini Research ReportArifahNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Reproductive System TESTDocument5 pagesSCIENCE Reproductive System TESTMegan CabahugNo ratings yet
- 5B-Wilby Yanwar Syah Putra-150510220300Document3 pages5B-Wilby Yanwar Syah Putra-150510220300Wilby YanwarNo ratings yet
- Botany - Section A: AIIMS Level Test (05-Jun) Full SyllabusDocument22 pagesBotany - Section A: AIIMS Level Test (05-Jun) Full SyllabusANUP MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Class 8 Reproduction in Animals Notes of LessonDocument11 pagesClass 8 Reproduction in Animals Notes of LessonSanthosh 456No ratings yet
- Biology Home Work Class 12 Science: Submitted by Suyam RokaDocument22 pagesBiology Home Work Class 12 Science: Submitted by Suyam RokaSafin RokaNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 Learning Activity Sheets (LAS) 2Document13 pagesScience: Quarter 2 Learning Activity Sheets (LAS) 2Angeilyn RodaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 5 - Q2 - Mod3Document24 pagesSCIENCE 5 - Q2 - Mod33tj internetNo ratings yet
- ?ihnsj901o - Pointers To ReviewDocument8 pages?ihnsj901o - Pointers To Reviewdwxgf5zwwgNo ratings yet
- SU WORKSHEET - 1st QT GR 8 ScienceDocument2 pagesSU WORKSHEET - 1st QT GR 8 ScienceLea Bondoc LimNo ratings yet
- Bio 2 QuizDocument21 pagesBio 2 QuizMae P ArcipeNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal ReproductionDocument7 pagesPlant and Animal Reproductionstephruth constantinoNo ratings yet
- Homework For Xii ADocument4 pagesHomework For Xii AAtish Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- Test 12 (Class 11) - Type Bio SCANDocument6 pagesTest 12 (Class 11) - Type Bio SCANSaurav sharmaNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce - Notes-Class 10Document11 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce - Notes-Class 10Varshini PeraNo ratings yet
- II PU Biology Practical Viva Question and AnswersDocument6 pagesII PU Biology Practical Viva Question and AnswersHoly GhostNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science: ReproductionDocument9 pagesGrade 7 Science: ReproductionJerry De Leon TaayNo ratings yet
- Animal Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument21 pagesAnimal Reproduction and DevelopmentEmerald SugotNo ratings yet
- Xii Biology Practical 2022-23 5 January 23Document35 pagesXii Biology Practical 2022-23 5 January 23Swarup PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Living World - Pyqs: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Document2 pagesLiving World - Pyqs: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Rahul DixitNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animals - RevisionDocument5 pagesReproduction in Animals - RevisionNikhitha SreeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Heredity Variation and InheritanceDocument38 pagesChapter 12 Heredity Variation and InheritanceAngel Mie ReyesNo ratings yet
- 262050-Class 8 - Science - Reproduction in Animals - WS With Ans. - RexyDocument8 pages262050-Class 8 - Science - Reproduction in Animals - WS With Ans. - RexyNeha ParkhiNo ratings yet
- Budding Is A Form of Asexual Reproduction That Results From The Outgrowth of ADocument2 pagesBudding Is A Form of Asexual Reproduction That Results From The Outgrowth of AI Don't Know My NameNo ratings yet
- Question Bank in Biology Class XIIDocument64 pagesQuestion Bank in Biology Class XIIaleena'No ratings yet
- EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE Evolving Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of Evidence (Q2 - LP1) Activity 1Document7 pagesEARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE Evolving Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of Evidence (Q2 - LP1) Activity 1Yvette Ortile NievaNo ratings yet
- Garbage DisposalDocument3 pagesGarbage Disposalmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 and 6 Edited HGDocument2 pagesWeek 5 and 6 Edited HGmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- SCHOOL MEMO NO 001 S 2022 2022 Schools Mid Year Break Activities Final2Document3 pagesSCHOOL MEMO NO 001 S 2022 2022 Schools Mid Year Break Activities Final2mary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- TOS - 1 To 4 EditedDocument4 pagesTOS - 1 To 4 Editedmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Sked of Sanitation and DisinfectionDocument2 pagesSked of Sanitation and Disinfectionmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Summative 4Document2 pagesSummative 4mary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Answer SheetDocument2 pagesAnswer Sheetmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Student Information Data SheetDocument1 pageStudent Information Data Sheetmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Science5 Q2 ST#4Document3 pagesScience5 Q2 ST#4mary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Batangas City: 10 Things People Might Know About My CityDocument1 pageBatangas City: 10 Things People Might Know About My Citymary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Notes Science Modes in ReproductionDocument1 pageNotes Science Modes in Reproductionmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Notes Science Modes in Reproduction PLANTSDocument3 pagesNotes Science Modes in Reproduction PLANTSmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - W5 English5 - CadayDocument4 pagesQ3 - W5 English5 - Cadaymary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WK 6-English 5 - VillaDocument4 pagesQ3 - WK 6-English 5 - Villamary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Elements of Sports WritingDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Elements of Sports Writingmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Q2 LAW Science5 Week5 6 EditedDocument5 pagesQ2 LAW Science5 Week5 6 Editedmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1-ScienceDocument1 pageActivity 1-Sciencemary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- 4th Science MapehDocument1 page4th Science Mapehmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- DisinfectionDocument2 pagesDisinfectionmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- SPG Action Plan-2021-2022Document2 pagesSPG Action Plan-2021-2022mary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- W3 5.EDITED English q4Document8 pagesW3 5.EDITED English q4mary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Research in EnglishDocument10 pagesResearch in Englishmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- First Assessment Learning in SCIENCEDocument4 pagesFirst Assessment Learning in SCIENCEmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- SpellingDocument3 pagesSpellingmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Research in MathDocument12 pagesResearch in Mathmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- TABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS ScienceDocument1 pageTABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS Sciencemary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- E Readers Science June 21Document1 pageE Readers Science June 21mary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Tally BoardDocument3 pagesTally Boardmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- GENSOC ReviewerDocument3 pagesGENSOC ReviewerPatricia San GasparNo ratings yet
- Female Reproduction SystemDocument37 pagesFemale Reproduction SystemSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Intervention MaterialDocument9 pagesStrategic Intervention MaterialHana Karudi100% (1)
- Understanding Fertility and InfertilityDocument37 pagesUnderstanding Fertility and Infertilitygamal attamNo ratings yet
- HumanReproductionLessonFinal Grade 10Document18 pagesHumanReproductionLessonFinal Grade 10Valerie TingalaNo ratings yet
- Sex at The Anatomical LevelDocument46 pagesSex at The Anatomical LevelkavehNo ratings yet
- B7K750 G6-5315 R11 /: ArchitectDocument6 pagesB7K750 G6-5315 R11 /: ArchitectYogaswara AdiputroNo ratings yet
- Artificial Reproductive Technology (ART)Document8 pagesArtificial Reproductive Technology (ART)sagi muNo ratings yet
- Obs MCQs PRIMEsDocument41 pagesObs MCQs PRIMEssk100% (3)
- Name of The Drug Mechani SM of Action Dosage Indicatio NS Contraindica Tions Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of The Drug Mechani SM of Action Dosage Indicatio NS Contraindica Tions Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibilitieshey aadarshaNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 (OB) Module 1BDocument48 pagesNCM 107 (OB) Module 1BAmiel simon NgoNo ratings yet
- Rajah 2 Menunjukkan Peranan Kelenjar Pituitary Sebagai Kelenjar Utama. Hormon Y Bertanggungjwab Untuk Perkembangan Folikel Dalam OvaryDocument3 pagesRajah 2 Menunjukkan Peranan Kelenjar Pituitary Sebagai Kelenjar Utama. Hormon Y Bertanggungjwab Untuk Perkembangan Folikel Dalam OvaryHamirah Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- Secondary Amenorrhea: DR Hanaa AlaniDocument44 pagesSecondary Amenorrhea: DR Hanaa AlaniAakashNo ratings yet
- Female Repro Part3 - GomezDocument53 pagesFemale Repro Part3 - GomezMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)Document10 pagesPolycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)Juliet Amondi100% (1)
- Lesson 1 To 4Document8 pagesLesson 1 To 4Alaiza Maas LanonNo ratings yet
- Maternity Nursing C) The Action of The Doderlein's BacillusDocument11 pagesMaternity Nursing C) The Action of The Doderlein's BacillusLeilah Khan100% (1)
- LS2 Scientific - Critical Thinking JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL PDFDocument91 pagesLS2 Scientific - Critical Thinking JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL PDFNaomae Lagrada VasalloNo ratings yet
- YL Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesYL Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemdrnyolNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument21 pagesLesson PlanRyrl ShinNo ratings yet
- Bed Site Teaching Onko Pak Bah November 2021Document5 pagesBed Site Teaching Onko Pak Bah November 2021Yudistira YunusNo ratings yet
- Histology Male ReproductiveDocument31 pagesHistology Male Reproductivekhiks34No ratings yet
- Reproductive System of CockroachDocument3 pagesReproductive System of Cockroachhui_junNo ratings yet
- HypospadiaDocument45 pagesHypospadiaMartha P100% (1)
- BASTIAN PORTFOLIO-finalDocument71 pagesBASTIAN PORTFOLIO-finaljohnwel anabezaNo ratings yet
- Morning Report PoliDocument16 pagesMorning Report PoliSiti NofriansyahNo ratings yet
- PSY354 Lecture 2 (Anatomy)Document24 pagesPSY354 Lecture 2 (Anatomy)kadiatou konateNo ratings yet
- Oo GenesisDocument20 pagesOo GenesisDinar Yudistira FirdausNo ratings yet
- BIO 282 Male Reproductive System - FINALDocument46 pagesBIO 282 Male Reproductive System - FINALLira PagaraNo ratings yet
- 3 Orris PcosDocument65 pages3 Orris PcosxtineNo ratings yet
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (111)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (598)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseFrom EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- Change Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessFrom EverandChange Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Minds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateFrom EverandMinds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (633)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsFrom EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo ratings yet
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (217)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- How History Gets Things Wrong: The Neuroscience of Our Addiction to StoriesFrom EverandHow History Gets Things Wrong: The Neuroscience of Our Addiction to StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (12)