Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guide For Making A Lab Report
Uploaded by
johnosborneOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Guide For Making A Lab Report
Uploaded by
johnosborneCopyright:
Available Formats
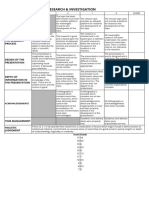
FORMAT FOR THE LAB REPORT
Type the lab report in a digital document. No Abstract is required. Write the report in the past or passive
tense. Use full sentences whenever possible, and also use sub-headings, numbered sections and bullet
points. Footnote all your sources of information and make a complete bibliography.
The Lab Report is a form of communication, so note the three C's: CLARITY, COHERENCE and
CONCISENESS.
TITLE (Page)
Include essential information: date, your name, students in your group, title of the investigation, written as
a question to be researched
Use the title and date as a repeating page header in the lab report.
PLANNING
Introduction
Purpose or setting or background: Why undertake this investigation? What is the general area of
interest? What do you hope to find out?
Research question or problem: A statement of the problem to be investigated - the research
question.
Hypothesis: A testable ‘if-then’ statement, followed by a justification.
Prediction: Brief statement of the general procedure and method employed to answer the research
question and test the hypothesis, with expected results
ACTION
A description of how the investigation was carried out. The goal is that the investigation is described in
such a way that another researcher could follow these instructions and obtain comparable results. The
design of the investigation should be able to achieve statistically useful, quantitative results.
Method
Materials & Equipment
Variables - variables table, incl. how controlled variables are handled
Risk Assessment & Safety
Ethical and environmental considerations
Results
Results should be tabulated and then treated - graphed and/or statistically manipulated - and described.
Results may be qualitative but should always be quantitative.
Raw Results Tables - titles; units of measurement; clarity.
Treatment of results
Statistical manipulation.
Graphing - all graphs should have a title and a brief sentence or two of explanation.
Statements drawing attention to patterns, trends and relationships (but not discussion).
Errors and limitations
● Systematic errors
● Random errors
● Quantifying the errors
EVALUATION
Conclusions: A simple statement of support for, or rejection of, the hypothesis.
Discussion: Justification for the conclusion, supported by summaries of the results and analysis of
results.
Interpretation and implications: What is the meaning of these results and conclusions?
Proposals for extension: questions which need further investigation.
Modifications and improvements: how the errors and limitations listed previously could be reduced or
eliminated - be scientific and exact in this section.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
This should be a complete list of all resources and references used, including all that have been footnoted.
Follow the APA 5th Edition convention for citing.
You might also like
- Biology Ia - Format For The Lab Report: TITLE (Page)Document1 pageBiology Ia - Format For The Lab Report: TITLE (Page)John OsborneNo ratings yet
- Guide Lab Report Experimental BiologyDocument4 pagesGuide Lab Report Experimental BiologyjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Tesis de Grado in ScienceDocument5 pagesStructure of The Tesis de Grado in ScienceJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Guide To Preparing The Estudio de CasoDocument5 pagesGuide To Preparing The Estudio de CasojohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Grade Project - Caso de EstudioDocument5 pagesStructure of The Grade Project - Caso de EstudiojohnosborneNo ratings yet
- FST 511Document15 pagesFST 511fadijidavid3No ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes: Mark Hero S. CabusaoDocument21 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes: Mark Hero S. CabusaoMark Hero Cabusao50% (2)
- 2 Research Paper Writing Lesson 1Document24 pages2 Research Paper Writing Lesson 1King LeonidasNo ratings yet
- Format of Research PaperDocument6 pagesFormat of Research PaperAmiel PandaNo ratings yet
- Guide To Preparing and Writing The Final DissertationDocument5 pagesGuide To Preparing and Writing The Final DissertationJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Format of Research Paper: A. Purpose B. Procedure Used C. Results D. ConclusionDocument2 pagesFormat of Research Paper: A. Purpose B. Procedure Used C. Results D. Conclusionemm morNo ratings yet
- Steps in Conducting A Research (2) Amira (1) 11Document24 pagesSteps in Conducting A Research (2) Amira (1) 11mohammad202020585No ratings yet
- Parts of A Research PaperDocument23 pagesParts of A Research PaperLyanne BejenNo ratings yet
- Reports - Practical Reports - Sep - 2017Document3 pagesReports - Practical Reports - Sep - 2017Thabsile Mbhele KamaNgcolosiNo ratings yet
- Marketing ResearchDocument15 pagesMarketing ResearchAsraar Ahmed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Suggested Format For Idea Research ProjectDocument3 pagesSuggested Format For Idea Research ProjectSarah ClarkNo ratings yet
- IMRAD For Diss Workshop 1Document6 pagesIMRAD For Diss Workshop 1Luis RamosNo ratings yet
- Type of Report: Research ReportDocument47 pagesType of Report: Research ReportrzainNo ratings yet
- Capstone FormatDocument4 pagesCapstone FormatRyann Zandueta ElumbaNo ratings yet
- IA TemplateDocument4 pagesIA TemplateYesid Vargas DiazNo ratings yet
- Sample Lab Assignment ReportDocument1 pageSample Lab Assignment ReportFarhad Hossain TamzidNo ratings yet
- Formal ReportDocument3 pagesFormal ReportVideo ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Chapters 4 and 5 of ResearchDocument2 pagesChapters 4 and 5 of ResearchApple Marivic SalemNo ratings yet
- Writing STS ReportDocument4 pagesWriting STS ReportSairam CNo ratings yet
- Writing STS ReportDocument4 pagesWriting STS ReportS ArtNo ratings yet
- Lab Report GuideDocument4 pagesLab Report GuideJefrelyn Eugenio MontibonNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Presentation of The Scientific ReportDocument4 pagesGuidelines For Presentation of The Scientific ReportsstavrosNo ratings yet
- EmailsDocument4 pagesEmailsMohamed Amine IddirNo ratings yet
- Lab Report TemplateDocument8 pagesLab Report TemplateAbdul SamadNo ratings yet
- Velocity Lab-Danika StreckoDocument5 pagesVelocity Lab-Danika Streckoapi-292000448No ratings yet
- Parts of A Research PaperDocument20 pagesParts of A Research Paper01dianaleeNo ratings yet
- General Information For Authors: 2. Materials and MethodsDocument2 pagesGeneral Information For Authors: 2. Materials and MethodsSantosh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Conflict Article Summary and Powerpoint GuidelinesDocument3 pagesConflict Article Summary and Powerpoint GuidelinesCarla WolfeNo ratings yet
- Outline For Research Reports and Proposals Using Apastyle 1Document2 pagesOutline For Research Reports and Proposals Using Apastyle 1rajashree97No ratings yet
- Title of Your Project: GWDD Candidate: Your Name Supervisor: Supervisor Name BME Sponsor: Sponsor Name or N/ADocument1 pageTitle of Your Project: GWDD Candidate: Your Name Supervisor: Supervisor Name BME Sponsor: Sponsor Name or N/ARobert JenkinsNo ratings yet
- Journal Template - IRIFairDocument6 pagesJournal Template - IRIFairakaiokeininiNo ratings yet
- Report Writing and PresentationDocument16 pagesReport Writing and PresentationVeroen SiddharthNo ratings yet
- Components of A Research PaperDocument6 pagesComponents of A Research PaperMark Alvin Jay CarpioNo ratings yet
- Format For Manuscript of RP2 FYP2Document1 pageFormat For Manuscript of RP2 FYP2Nurwani HussinNo ratings yet
- Research FormatDocument6 pagesResearch FormatAshley May LugoNo ratings yet
- Writing The Research ReportDocument22 pagesWriting The Research ReportMairah KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 & 7: Results and DiscussionDocument29 pagesLesson 6 & 7: Results and DiscussionJ i n100% (1)
- How To Make An Investigatory ProjectDocument2 pagesHow To Make An Investigatory ProjectCecille TagayNo ratings yet
- SCT111 - Notes On Lecture 1, LAB Report WritingDocument2 pagesSCT111 - Notes On Lecture 1, LAB Report WritingPriscilla OpokuNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem Quarter 4Y 2022 2023Document6 pages2nd Sem Quarter 4Y 2022 2023Ray Angilo DiazNo ratings yet
- Lab Report GuidelinesDocument2 pagesLab Report GuidelinesAdel Al-EnaziNo ratings yet
- Guideline To Laboratory Report Writing PDFDocument2 pagesGuideline To Laboratory Report Writing PDFIjal JaminNo ratings yet
- Quantitative MethodsDocument16 pagesQuantitative Methodspseudo dwadadadNo ratings yet
- How To Write Chapter 5Document4 pagesHow To Write Chapter 5Ricky GumanadNo ratings yet
- Master's Thesis WritingDocument35 pagesMaster's Thesis WritingProfetiza Iquiña-MaatubangNo ratings yet
- How Write A Lab ReportDocument2 pagesHow Write A Lab Reportapi-344568500No ratings yet
- Appreciating Research: Why Do It? What Are Its Benefits?Document22 pagesAppreciating Research: Why Do It? What Are Its Benefits?ReignNo ratings yet
- Outline of The Research ReportDocument3 pagesOutline of The Research ReportAnalyn QuinagoranNo ratings yet
- Writing A PaDocument2 pagesWriting A PaSalim AngoNo ratings yet
- Format For PT3-1Document13 pagesFormat For PT3-1RAIN HEART VASQUEZNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document6 pagesModule 7Earl averzosaNo ratings yet
- Research & the Analysis of Research Hypotheses: Volume 2From EverandResearch & the Analysis of Research Hypotheses: Volume 2No ratings yet
- ChatGPT Guide to Scientific Thesis Writing: AI Research writing assistance for UG, PG, & Ph.d programsFrom EverandChatGPT Guide to Scientific Thesis Writing: AI Research writing assistance for UG, PG, & Ph.d programsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Earth SystemsDocument9 pagesLesson 1 Earth SystemsjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Rubric Ozone Campaign Planning &preparationDocument1 pageRubric Ozone Campaign Planning &preparationjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- APES Eco-ColumnsDocument6 pagesAPES Eco-ColumnsjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- How Medellin Is Beating The Heat With Green CorridorsDocument5 pagesHow Medellin Is Beating The Heat With Green CorridorsjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Seed Germination Introduction & PlanningDocument2 pagesSeed Germination Introduction & PlanningjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- APES Eco-ColumnsDocument6 pagesAPES Eco-ColumnsjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Evaluation Rubric Objective 3Document2 pagesDiagnostic Evaluation Rubric Objective 3johnosborneNo ratings yet
- The Lab ReportDocument2 pagesThe Lab ReportjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Evaluation September 2023Document16 pagesDiagnostic Evaluation September 2023johnosborneNo ratings yet
- Objectives 4 & 5 Diagnostic Evaluation Sept 2023Document4 pagesObjectives 4 & 5 Diagnostic Evaluation Sept 2023johnosborneNo ratings yet
- Reintroduction of Cheetahs in Kuno NP, IndiaDocument5 pagesReintroduction of Cheetahs in Kuno NP, IndiajohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Will The Gulf Stream Really Collapse by 2025Document2 pagesWill The Gulf Stream Really Collapse by 2025johnosborneNo ratings yet
- Rubric Assignment 2 MEDIA REPORTDocument2 pagesRubric Assignment 2 MEDIA REPORTjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- The Lab ReportDocument2 pagesThe Lab ReportjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Introduction Preparation Apes 2023-2024Document4 pagesIntroduction Preparation Apes 2023-2024johnosborneNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Learning PresentationDocument44 pagesAir Pollution Learning PresentationjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Statistics (0.0) : IB Diploma BiologyDocument44 pagesStatistics (0.0) : IB Diploma BiologyJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- 23 Most Important Things To Know About WaterDocument6 pages23 Most Important Things To Know About WaterjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Handbook Bio StatDocument305 pagesHandbook Bio StatADWINDT100% (1)
- Details of Assessment Estudio de CasoDocument5 pagesDetails of Assessment Estudio de CasojohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Water Infographic Assignment June 2023Document2 pagesWater Infographic Assignment June 2023johnosborneNo ratings yet
- Journal Year 9 La Hesperia 2018 MayDocument6 pagesJournal Year 9 La Hesperia 2018 MayJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Atmospheric PollutionDocument5 pagesUnit 7 Atmospheric PollutionjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Energy From Liquid Alcohols & HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesEnergy From Liquid Alcohols & HydrocarbonsjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Lab: Comparing Energy From Different Hydrocarbon CompundsDocument7 pagesLab: Comparing Energy From Different Hydrocarbon CompundsjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Rubric Campaign Unit 6 Topic 13Document14 pagesRubric Campaign Unit 6 Topic 13johnosborneNo ratings yet
- Peppered MothDocument7 pagesPeppered MothjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Glass or Plastic May 2023 BBCDocument4 pagesGlass or Plastic May 2023 BBCjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Rubric Campaign Unit 6 Topic 13Document14 pagesRubric Campaign Unit 6 Topic 13johnosborneNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Research PaperDocument5 pagesParts of A Research PaperMedelyn TorresNo ratings yet
- M&O Syllabus YT 2023 Spring 0301Document15 pagesM&O Syllabus YT 2023 Spring 0301ZacharyNo ratings yet
- Satyveer Singh Meena and Hanuman PrasadDocument18 pagesSatyveer Singh Meena and Hanuman PrasadYerrolla MadhuravaniNo ratings yet
- Full Download Think Social Psychology 2012 Edition 1st Edition Duff Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Think Social Psychology 2012 Edition 1st Edition Duff Test Bankremonaplain7421427100% (20)
- Statistical Methods For Machine Learning Mini CourseDocument20 pagesStatistical Methods For Machine Learning Mini CourseMaheshkumar Amula100% (2)
- Ahsgs Kol 25012015 Writing An Effective ProposalDocument35 pagesAhsgs Kol 25012015 Writing An Effective ProposalZuridah HanimNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument283 pagesPDFica fitrianaNo ratings yet
- Monograph Format For KNUDocument16 pagesMonograph Format For KNUSayed Ilyas HashimiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HYPOTHESIS TESTINGDocument48 pagesChapter 4 HYPOTHESIS TESTINGWerty Gigz DurendezNo ratings yet
- Exploratory Research in The Social Sciences: What Is Exploration?Document15 pagesExploratory Research in The Social Sciences: What Is Exploration?suhailNo ratings yet
- Four-Pass Loading - Must-Have or Myth PDFDocument9 pagesFour-Pass Loading - Must-Have or Myth PDFRobert KnightNo ratings yet
- Methods and Approaches of Comparative Education: Prepared By: Jastine S. RafaelDocument23 pagesMethods and Approaches of Comparative Education: Prepared By: Jastine S. RafaelJewels GarciaNo ratings yet
- Module Grade 7Document18 pagesModule Grade 7Gregson GucelaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nursing Research Literature ReviewDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Nursing Research Literature Reviewenam professorNo ratings yet
- Research Title and Chapter 1Document89 pagesResearch Title and Chapter 1Marianne Gonzales100% (1)
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsSarath Bhushan Kaluturi85% (13)
- Su, Et Al., 2015 PDFDocument10 pagesSu, Et Al., 2015 PDFelioraNo ratings yet
- Expp211 C1-5Document9 pagesExpp211 C1-5SARAH MARGARETTE PAGLINAWANNo ratings yet
- An Investigation Into The Impact Spinal Manipulation May Have On The Performance of Strength Athletes A Research SurveyDocument10 pagesAn Investigation Into The Impact Spinal Manipulation May Have On The Performance of Strength Athletes A Research SurveyIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Case AnalysisDocument17 pagesCooperative Case AnalysisAkubuike EluwaNo ratings yet
- TJD Slater PDFDocument22 pagesTJD Slater PDFbryan001935No ratings yet
- Research Design and Sampling Methods and Techniques MODIFIEDDocument59 pagesResearch Design and Sampling Methods and Techniques MODIFIEDjaneth pallangyoNo ratings yet
- A Study On Customer Perception On Maruti Suzuki AltoDocument88 pagesA Study On Customer Perception On Maruti Suzuki Altopuneeth h100% (1)
- Journal of Business Theory and PracticeDocument24 pagesJournal of Business Theory and Practiceruksar retiwalaNo ratings yet
- Unit Three. LinguisticDocument5 pagesUnit Three. Linguisticslimane messaoudiNo ratings yet
- A Comparison and Analysis of School Finance PractitionersDocument373 pagesA Comparison and Analysis of School Finance PractitionersKasmiah OtinNo ratings yet
- Full Download Biology Now 2nd Edition Houtman Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Biology Now 2nd Edition Houtman Test Bankbrumfieldridleyvip100% (32)
- 24 Chemistry LessonsDocument299 pages24 Chemistry LessonsTodd92% (13)
- Statistics and Probability 2nd QuarterDocument398 pagesStatistics and Probability 2nd QuarterHeart GullaNo ratings yet
- Planning and Designing LabsDocument3 pagesPlanning and Designing LabsAlicia HaughtonNo ratings yet