Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4th Quarter Biology Reviewer
Uploaded by
Tortellini0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesThe document summarizes key aspects of the digestive system and genetics. It describes the main parts and functions of the digestive system, including ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination. It also outlines Mendel's laws of heredity from his experiments with pea plants, including the law of segregation, the law of independent assortment, and how Punnett squares can predict offspring genotypes from parental alleles. Genetics is defined as the study of heredity and the passing of traits from parents to offspring.
Original Description:
Original Title
4th-Quarter-Biology-Reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key aspects of the digestive system and genetics. It describes the main parts and functions of the digestive system, including ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination. It also outlines Mendel's laws of heredity from his experiments with pea plants, including the law of segregation, the law of independent assortment, and how Punnett squares can predict offspring genotypes from parental alleles. Genetics is defined as the study of heredity and the passing of traits from parents to offspring.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pages4th Quarter Biology Reviewer
Uploaded by
TortelliniThe document summarizes key aspects of the digestive system and genetics. It describes the main parts and functions of the digestive system, including ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination. It also outlines Mendel's laws of heredity from his experiments with pea plants, including the law of segregation, the law of independent assortment, and how Punnett squares can predict offspring genotypes from parental alleles. Genetics is defined as the study of heredity and the passing of traits from parents to offspring.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
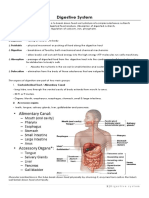
Digestive System * There is no digestion of carbohydrates in the
Digestion- process of breaking down food by stomach
mechanical and enzymatic action *Chyme- thick mixture of food and gastric
Functions: fluid
1. Ingestion- allows food to enter the Chemical Digestion:
digestive tract and have mastication 1. Gastric Juice- secreted by glands in
(chewing) occurs and the resulting food the stomach walls into the stomach cavity
is swallowed a) Mucus- protects stomach lining
Tongue- manipulates food during b) Hydrochloric Acid- kills harmful
mastication bacteria
Amylase- enzyme in saliva c) Pepsinogen- breaks down
Bolus- ball-like mixture of food and saliva proteins
Salivary Glands- parotid, submandibular, -Pepsin when in contact with HCI
sublingual gland secrete most of the -provides acidic environment for
saliva in the oral cavity proteases (break down proteins into
*Saliva- 99.5% water and 0.5% dissolved amino acids)
substances including aylase enzyme 5. Absorption- begins in the stomach with
Teeth- adapted for mechanical digestion or water and alcohol being absorbed
mastication directly into bloodstream
2. Propulsion- movement of food along the -takes place in the walls of small intestine
digestive tract -large intestine is involved in absorption of
Esophagus- serves to carry the food from water and vitamins B and K
pharynx to stomach by peristalsis movement Small Intestine
*Peristalsis- series of alternating contractions Duodenum- smallest section; stomach
and relaxations of smooth muscle empties here
3. Digestion Jejunum- middle section; most of nutrients
a) Mechanical- physical breakdown of present in food are absorbed
food into smaller particles Ileum- absorb products of digestion that were
Mouth- teeth, tongue, palates not absorbed by jejunum
Esopagus- peristalsis Large Intestine- further breaks down food
Stomach- muscular churning action residues
S. Intestine- bile and peristalsis -absorbs most residual water, electrolytes,
b) Chemical- reactions aided by and vitamins
enzymes chemically break down -eliminates stool
food particles 6. Elimination
Stomach- pouch-like organ designed for Defacation- eliminating undigested material
food storage (2-4 hrs) passing rectum and anus
- contains rugae (series of ridges that If constipation frequently takes place, it
make up the interior wall of the causes ill-health and increases the risk of
stomach) contracting colon cancer
4. Secretion- enzymes and digestive fluids If the colon retains its contents too long,
secreted by the digestive tract and its the fecal matter becomes dried out and
accessory organs to facilitate chemical compresses into hard masses causing
digestion constipation and haemorrhoids
Bianca Andrea A. Pielago
8-Auburn
Pancreas- aids in digestion by producing Law of Segregation- Each individual has two
digestive enzymes (break down proteins, fats, factors for each trait
and carbohydrates) -The factors segregate during gamete
-produce insulin and glucagon hormones formation
(regulate blood sugar and carbohydrate -Each gamete contains only one factor from
metabolism) each pair of factors
Liver- produces bile -Fertilization gives each new individual two
Gallblader- small sac; stores and concentrates factors for each trait
bile secreted by liver
Patterns of Mendelian’s Experiment
Heredity-
Heredity- passing of traits from parent to
offspring
Traits-
Traits- characteristics that are inherited
hair color, height, blood type, susceptibility to
a certain disease (diabetes, depression,
obesity, breast cancer)
Genetics-
Genetics- the study of heredity
Gregor Mendel-
Mendel- Father of Genetics
-Austrian monk who formulated fundamental
laws of heredity in early 1860s
Law of Independent Assortment- Pairs of
alleles for different traits separate
independently of one another during gamete
formation (meiosis).
-the inheritance of one trait has no influence
on the inheritance of another trait.
Bianca Andrea A. Pielago
8-Auburn
Punnett Square- All possible genotypes of
Alleles- allternative forms of a gene that code sperm are lined up on one axis, and all
for a trait possible genotypes of eggs are lined up on
the other axis
-Every possible combination of alleles (zygote
genotypes) placed within the squares
Principle of Dominance
Mendel’s Monohybrid Cross
Note: Sorry po kung kulang pa ito.
Video link (Mendelian Genetics and Punnet
Squares)----
https://www.youtube.com/watch?
v=3f_eisNPpnc&t=453s
Dihybrid Cross
Bianca Andrea A. Pielago
8-Auburn
You might also like
- DLaboratory Actiivty 5 - Integumentary System AnswerDocument6 pagesDLaboratory Actiivty 5 - Integumentary System AnswerSYDNEY JILL ACHAINo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMDocument21 pagesChapter 9 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMAlexander Santiago ParelNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Endocrinology For Gynaecologist SDocument356 pagesReproductive Endocrinology For Gynaecologist SFebey Arie Mulya100% (1)
- MRI BRAIN FINAL DR Shamol PDFDocument306 pagesMRI BRAIN FINAL DR Shamol PDFDrSunil Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Higher Center - Dr. BarbonDocument5 pagesHigher Center - Dr. BarbonMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- The Normal and Pathological Fetal Brain - Ultrasonographic FeaturesDocument316 pagesThe Normal and Pathological Fetal Brain - Ultrasonographic FeaturesBharti Pant GahtoriNo ratings yet
- Word Part: Word Part Meaning Example(s) Meaning of Example(s)Document6 pagesWord Part: Word Part Meaning Example(s) Meaning of Example(s)Anonymous zdHKF34HNo ratings yet
- Grade12 Year Notes by E.C Mabuza 1Document186 pagesGrade12 Year Notes by E.C Mabuza 1luyandakelebohile34100% (5)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Circulatory Systemnoronisa talusobNo ratings yet
- Inserto TSHDocument10 pagesInserto TSHyandros666No ratings yet
- Digestive System: 1. Mouth 2. Pharynx (Throat)Document5 pagesDigestive System: 1. Mouth 2. Pharynx (Throat)Usita, Zackary, T.No ratings yet
- Food PathDocument7 pagesFood PathLovelle SanchezNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestive Systemhimig the melodyNo ratings yet
- Digestive ReviewerDocument1 pageDigestive ReviewerJay Ivan Milen GamboaNo ratings yet
- Digestion Rev Horses ProteinDocument8 pagesDigestion Rev Horses ProteinKyle Gwyneth BobierNo ratings yet
- Nutrition ReviewerDocument11 pagesNutrition ReviewerNicole Angela MoralesNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDigestive SystemGabrielle Anne CarlosNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Document3 pagesDigestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Kaikiyi Sykay PachecoNo ratings yet
- General Biology: 1. Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology: 1. Digestive SystemJuno Merdien GarciaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System TransesDocument5 pagesDigestive System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- Anaphy FinalsDocument20 pagesAnaphy FinalsHazel Anne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition and Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesAnimal Nutrition and Digestive SystemJan Alixia BasilioNo ratings yet
- 6.1. D.2. - PRES - Digestion and AbsorptionDocument45 pages6.1. D.2. - PRES - Digestion and AbsorptionPhilip ForintonNo ratings yet
- Patho - Digestive SystemDocument17 pagesPatho - Digestive SystemLinda XueNo ratings yet
- General Zoology LabDocument3 pagesGeneral Zoology Labgerlyn duranNo ratings yet
- Characteristic of Life: The Breaking Down of CompoundsDocument5 pagesCharacteristic of Life: The Breaking Down of CompoundsHanz GadongNo ratings yet
- Transes Biochem DigestionDocument4 pagesTranses Biochem DigestionPia Louise100% (1)
- Gastro NotesDocument11 pagesGastro NotesMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Digestion and AbsorptionDocument45 pagesUnit 3. Digestion and AbsorptionDiana HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Summary of Digestion: C. Gastrointestinal Hormones 1. GastrinDocument5 pagesSummary of Digestion: C. Gastrointestinal Hormones 1. GastrinIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal TractDocument5 pagesGastrointestinal TractMalayao, Philip Jude M.No ratings yet
- Animal NutritionDocument8 pagesAnimal NutritionSofi ParkNo ratings yet
- 6.1: Types of Nutrition 6.2: Balanced Diet 6.3: Malnutrition 6.4:digestion Process 6.5:process of Absorption & AssimilationDocument48 pages6.1: Types of Nutrition 6.2: Balanced Diet 6.3: Malnutrition 6.4:digestion Process 6.5:process of Absorption & AssimilationHuang Zheng XianNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 6 & 7 NUTRISI TERNAK DASARDocument45 pagesPertemuan 6 & 7 NUTRISI TERNAK DASARsyintiaNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument2 pagesScience NotesSofia JeonNo ratings yet
- DR Felix Anatomy and Digestion Whole Page NOTESDocument103 pagesDR Felix Anatomy and Digestion Whole Page NOTESEmpowering YouthNo ratings yet
- Digestive Systems: Goal (Learning Objective) Pre-Lesson PreparationDocument6 pagesDigestive Systems: Goal (Learning Objective) Pre-Lesson PreparationArvin ManaloNo ratings yet
- GB2 Lesson-3.1 NutritionDocument74 pagesGB2 Lesson-3.1 NutritionMyla Concepcion RigonanNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: GastrologyDocument14 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease: GastrologyMarie Jennifer ParilNo ratings yet
- Sistim Pencernakan: Zaenal M. SOFRO Bagian Ilmu Faal FK - UGMDocument30 pagesSistim Pencernakan: Zaenal M. SOFRO Bagian Ilmu Faal FK - UGMDesi Dwi CahyantiNo ratings yet
- Book 11 AnimalNutrition2021 Adapted 2Document11 pagesBook 11 AnimalNutrition2021 Adapted 2assf7235No ratings yet
- BIODocument12 pagesBIOvinjireh caasiNo ratings yet
- Medtech Git Upper and LowerDocument72 pagesMedtech Git Upper and LowerBabe YamonganNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument4 pagesDigestionMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument16 pagesAnaphy ReviewerBr1nfoNo ratings yet
- Lab Ex 3 CDocument7 pagesLab Ex 3 Cs.manuel.kyrraaliahNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316 LectureDocument34 pagesNCMB 316 LecturePatrisha May MahinayNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesDigestive SystemRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument1 pageThe Digestive SystemAlexa VeraNo ratings yet
- Digestive System FINALDocument43 pagesDigestive System FINALSean Lorenzo TumacderNo ratings yet
- L - 6 Life Processes - Heterotrophic NutritionDocument7 pagesL - 6 Life Processes - Heterotrophic NutritionNotImmortalNo ratings yet
- What Type of System Is This?Document17 pagesWhat Type of System Is This?Gabriela Ruiz ColínNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument8 pagesDigestive System NotesDale Gil JuliaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument6 pagesDigestive System NotesZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesDocument5 pagesDigestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- QUIZ Sheet of PaperDocument33 pagesQUIZ Sheet of PaperGab FgilzcheNo ratings yet
- Science - Revised Notes 4TH QTRDocument4 pagesScience - Revised Notes 4TH QTRG13 Luzaran, Princess Migumi, R.No ratings yet
- Lea 417 510 2011Document121 pagesLea 417 510 2011Oliver TalipNo ratings yet
- 11B16 - (Digestion and Absorption) - Solutions V1.2Document2 pages11B16 - (Digestion and Absorption) - Solutions V1.2Gaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Final: Gluconeogenesis - When The Liver and KidneysDocument43 pagesFinal: Gluconeogenesis - When The Liver and KidneysRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Metabolism (Ncm-216)Document10 pagesMetabolism (Ncm-216)Sofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Physiology: Department of Physiology CHS, UniosunDocument59 pagesGastrointestinal Physiology: Department of Physiology CHS, UniosunTeeNo ratings yet
- Digestion & AbsorptionDocument13 pagesDigestion & AbsorptionU Than HanNo ratings yet
- Animal Digestive System: Food Water Medicine (If Needed) Food NutritionDocument7 pagesAnimal Digestive System: Food Water Medicine (If Needed) Food NutritionRstu Cordillera PnptsNo ratings yet
- Questions and AnswersDocument44 pagesQuestions and Answersjamb2316No ratings yet
- Digestive System in Non-RuminantsDocument5 pagesDigestive System in Non-RuminantsTumisang TlhabanoNo ratings yet
- Systems and Their ControlDocument38 pagesSystems and Their ControlsurainiNo ratings yet
- Sci - Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesSci - Digestive SystemClaude de alger ObeliaNo ratings yet
- Genchem 2Document1 pageGenchem 2TortelliniNo ratings yet
- DIY CentrifugeDocument1 pageDIY CentrifugeTortelliniNo ratings yet
- 21st Century LiteratureDocument1 page21st Century LiteratureTortelliniNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter PHYSICAL EDUCATIONDocument2 pages2nd Quarter PHYSICAL EDUCATIONTortelliniNo ratings yet
- Itaewon Crowd Crush DRRRDocument7 pagesItaewon Crowd Crush DRRRTortelliniNo ratings yet
- 21st-Century-2 2 1Document4 pages21st-Century-2 2 1TortelliniNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument5 pagesCell StructureTortelliniNo ratings yet
- The GardenerDocument9 pagesThe GardenerTortelliniNo ratings yet
- Transcranial Magnetic StimulationDocument2 pagesTranscranial Magnetic StimulationCandle Shop FullNo ratings yet
- Maryland Veteran Who Received Genetically Modified Pig Heart TransplaDocument1 pageMaryland Veteran Who Received Genetically Modified Pig Heart Transplaed2870winNo ratings yet
- Albinism Clinical CaseDocument17 pagesAlbinism Clinical CaseJosh Ryan MoletaNo ratings yet
- Cleanse & Restore Kit and ProtocolDocument2 pagesCleanse & Restore Kit and ProtocolEmese MagdásNo ratings yet
- Science G4 Break It DownDocument51 pagesScience G4 Break It DownYourMakatiPad Properties100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan of Integument SystemDocument27 pagesNursing Care Plan of Integument SystemAlfianGafar67% (3)
- Salvagability Giant HydronephrosisDocument14 pagesSalvagability Giant HydronephrosisAndy WijayaNo ratings yet
- 15b - Digestive System Anatomy and Physiology SeriesDocument100 pages15b - Digestive System Anatomy and Physiology SeriesNickson OnchokaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: by - Brett Bennell and Lisa MatzelleDocument27 pagesThe Nervous System: by - Brett Bennell and Lisa MatzelleJames PerianayagamNo ratings yet
- Krok 1 Medicine 2020 Papers MCQ Practice - OnlineKitaabsDocument48 pagesKrok 1 Medicine 2020 Papers MCQ Practice - OnlineKitaabsHarsh NimavatNo ratings yet
- Social Practice of The Language 6Document9 pagesSocial Practice of The Language 6Brenda LizarragaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing - Cardiovascular System DisordersDocument11 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing - Cardiovascular System DisordersSofia LiNo ratings yet
- Physiology (Receptors)Document17 pagesPhysiology (Receptors)Omar NuhicNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Compliance With Standard Criteria For Postero-Anterior (Pa) Chest Radiographs in Parklane Hospital EnuguDocument37 pagesEvaluation of Compliance With Standard Criteria For Postero-Anterior (Pa) Chest Radiographs in Parklane Hospital EnuguLavinia VictorNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption of LipidsDocument21 pagesDigestion and Absorption of LipidsFazal Akbar KhaliliNo ratings yet
- Fibrocystic Breast Disease: Luthfy Winarto Departemen Bedah Sub Div - Onkologi Palembang - 2016Document35 pagesFibrocystic Breast Disease: Luthfy Winarto Departemen Bedah Sub Div - Onkologi Palembang - 2016Afkar30No ratings yet
- B5 Home AssignmentDocument2 pagesB5 Home AssignmentMemoona GullNo ratings yet
- Bio-Zoology - Vol - 2 EM PDFDocument176 pagesBio-Zoology - Vol - 2 EM PDFmuraliNo ratings yet
- 6 Krok GitDocument14 pages6 Krok GitRodriguez Vivanco Kevin DanielNo ratings yet
- FAMORCAN, MAVELLE A. - WEEK 6 PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - gRADE 11Document5 pagesFAMORCAN, MAVELLE A. - WEEK 6 PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - gRADE 11Mavelle FamorcanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument43 pagesEndocrine Systemwieka mawieNo ratings yet