Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CA-1500 SM #3 Electronics
Uploaded by
jakab.m.atilaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CA-1500 SM #3 Electronics
Uploaded by
jakab.m.atilaCopyright:
Available Formats
To Cover Page
SECTION 3 ELECTRONICS
3.1 PCB LOCATIONS............................................................................................................... 1
3.2 BLOCK DIAGRAM .............................................................................................................. 2
3.3 PCB NO. 1246 (STM DRIVE, PU CONTROL) ................................................................... 3
3.4 PCB NO. 2121 (PRE-AMPLIFIER) ..................................................................................... 6
3.5 PCB NO. 2122 (PRE-AMPLIFIER, LED DRIVE) ................................................................ 7
3.6 PCB NO. 2136 (STM DRIVER, SAMPLER CONTROL, TEMPERATURE CONTROL,
PRESSURE MONITOR) ............................................................................................................... 9
3.7 PCB NO. 2137 (LIQUID SURFACE SENSOR) ................................................................ 13
3.8 PCB NO. 2138 (PRE-AMPLIFIER FOR CHROMOGENIC UNIT).................................... 16
3.9 PCB NO. 3052 (I/O) .......................................................................................................... 18
3.10 PCB NO. 4079 (POWER SUPPLY BOARD) .................................................................... 25
3.11 PCB NO. 4088 (POWER SUPPLY) .................................................................................... 26
3.12 PCB NO. 6364 (CPU) ....................................................................................................... 28
3.13 PCB NO. 9270 (Y-AXIS RELAY) ...................................................................................... 36
3.14 PCB NO. 9271 (Z-AXIS RELAY) ...................................................................................... 37
3.15 PCB NO. 9272 (STAT SENSOR) ..................................................................................... 38
3.16 CA-1500 POWER SUPPLY UNIT .................................................................................... 39
CA-1500 S/M December 2000 Revised
SECTION 3 ELECTRONICS
3.1 PCB LOCATIONS
PCB No. 1246 STM drive, PU control PCB No. 3052 I/O
PCB No. 2121 Pre-amplifier PCB No. 4079 Power supply
PCB No. 2122 Pre-amplifier, LED drive PCB No. 4088 Power supply
STM drive, Sampler control, PCB No. 6364 CPU
PCB No. 2136 Temperature control, PCB No. 9172 LED
Pressure monitor PCB No. 9270 Y-axis relay
PCB No. 2137 Liquid sensor PCB No. 9271 Z-axis relay
PCB No. 2138 Pre-amplifier (Chromogenic) PCB No. 9272 STAT sensor
*PCB No. 9271 locates on the Catcher Unit (Up-Down Drive Mechanism No. 1).
CA-1500 S/M 3-1 December 2000 Revised
STAT PCB No. 9272
Holder Unit
PCB No. 2121
XYZ Motor
CA-1500 S/M
Pre-Amplifier XYZ Mechanism
Driving Circuit
Scattered Light
Detector Block Driving Circuit Sample/ Liquid Sensor:
Arm Mechanism
A/D Conversion Driving Circuit Reagent Arm PCB No. 2137
PCB No. 2122 PCB No. 1246
Transmitted PCB No. 2138 PCB No. 2136
Sensors
Data Logger
Light Detector Pre-Amplifier
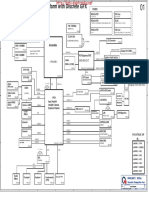
3.2 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Driver Interface
Block
Syringe
Syringe Unit
Driving Circuit
LCD
Lamp Unit
CPU
Halogen Lamp
Driving Circuit
Touch Panel
3-2
Rack Shift Rack Shift
Driving Circuit Mechanism
FD
Solenoid
PCB No. 3052
Solenoid Valve
HD Driving Circuit Valves
PCB No. 6364
Heater
Temperature
Serial Interface
Control Circuit
Peltier
Power Compressor
PCB No. 4079
Supply
PCB No. 4088 Vacuum Pump
Circuit
Power Supply Unit Pneumatic Unit
December 2000 Revised
3.3 PCB NO. 1246 (STM DRIVE, PU CONTROL)
3.3.1 Functions
(1) Drives the motor of each unit.
(2) This PCB relays various sensor outputs.
3.3.2 Descriptions
(1) Stepping Motor Drive (Constant-Current Drive, Constant-Voltage Drive)
The motor is driven according to the motor control signal from the M-I/O (PCB No. 3052) and the
ENB signal from the CPU (PCB No. 6364).
1) Constant-Current Drive
8 channels, +30 VDC, 2-phase drive (1, 2 phase excitation is also possible.)
Reagent Arm (X, Y), Sample Arm (X, Y), Catcher (X, Y), CP Drive x 2
2) Constant-Voltage Drive
3 channels , +12 VDC, 1, 2-phase drive
Reagent Arm (Z), Sample Arm (Z), Catcher (Z)
(2) DC Motor Drive
1 channel (Stirring motor of the catcher), +1.2 VDC
The motor ON/OFF status is controlled according to the control signal from the CPU.
(3) Serial/Parallel Conversion of Control Signal from the CPU
The serial control signal from the CPU is converted into a parallel signal, and sent to each drive
element.
(4) Relay of each Sensor Output
This PCB relays the output from motor limit position sensors, the liquid surface detection board
(liquid surface detection signal and pipette crash signal), and from trash box sensors to the
M-I/O, and relays the parallel/serial converted signal to the CPU. The sensor signal line has a
noise-reduction filter circuit.
(5) This PCB outputs Pneumatic Unit Control Signal and the Chromogenic Unit Halogen Lamp
Control Signal from the M-I/O.
(6) Power Supply
1) Motor : +30 VDC, +12 VDC, +5 VDC
2) Logic : +5 VDC
3) Analog : +15 VDC
CA-1500 S/M 3-3 December 2000 Revised
3.3.3 Block Diagram
3.3.4 Adjustment and Test Point
None.
CA-1500 S/M 3-4 December 2000 Revised
3.3.5 Assembly Drawing
CA-1500 S/M 3-5 December 2000 Revised
3.4 PCB NO. 2121 (PRE-AMPLIFIER)
3.4.1 Functions
(1) This PCB amplifies the first stage detection signals at 4 channels.
(2) This PCB switches and outputs the detection signals of Channel 1 to Channel 8.
(3) Two levels of gain can be switched with the analog switch.
3.4.2 Descriptions
(1) Pre-Amplifier
This PCB has 4 channels of pre-amplifier circuit, which correspond from Channel 5 to Channel 8
of the detecting unit. The pre-amplifier circuits are the same as those of the PCB No. 2122.
(2) Multiplexer
The pre-amplifier signals (of Channels 1 to 8) pass through the low-pass filter, and enter the
multiplexor M7 (Hi-508-5). The signal of each channel is sequentially output according to the
channel selection signal (A0, A1, A2) from the I/O board (PCB No. 3052).
(3) Analog Switch
The output signal from the multiplexer M7 is amplified without reversing, and is sent to the I/O
board (PCB No. 3052). The analog switch M4 (Hi3-201-5) switches the amplification ratio
between High and Low gains according to the control signal from the I/O board. Amplification
ratio of High gain is 7.4, and that of Low gain is 1.1.
3.4.3 Block Diagram
3.4.4 Adjustment and Test Point
None.
CA-1500 S/M 3-6 December 2000 Revised
3.4.5 Assembly Drawing
3.5 PCB NO. 2122 (PRE-AMPLIFIER, LED DRIVE)
3.5.1 Functions
(1) This PCB amplifies the first stage of detection signals at 4 channels.
(2) This PCB drives the LEDs at a constant current.
3.5.2 Descriptions
This PCB provides the pre-amplifier circuits for Channel 1 to Channel 4, and drives the LEDs for
Channel 1 to Channel 8. This PCB provides the following functions:
(1) Pre-Amplifier Circuit
The Photo-Diode (S1133-05) detects the scattered light from Channel 1 to Channel 4 of the
detecting unit. The generated current is converted into a voltage by Current-Voltage Convertor
Circuit (M1) and amplified by Amplifier 1 (M2) with a gain of 4.9 times.
The highpass filters cut off the noise overlapping with the DC signal, and output to PCB No.
2121.
(2) Constant-Current LED Drive Circuit (M4)
The light source LEDs for Channel 1 to Channel 8 of the detecting unit are driven at a constant
current.
CA-1500 S/M 3-7 December 2000 Revised
3.5.3 Block Diagram
3.5.4 Adjustment and Test Point
None.
CA-1500 S/M 3-8 December 2000 Revised
3.5.5 Assembly Drawing
3.6 PCB NO. 2136 (STM DRIVER, SAMPLER CONTROL,
TEMPERATURE CONTROL, PRESSURE MONITOR)
3.6.1 Functions
(1) This PCB drives the motor of each unit.
(2) This PCB relays various sensor outputs.
(3) This PCB performs A/D conversion for temperature control and temperature monitoring.
(4) This PCB performs A/D conversion for pressure monitor.
(5) This PCB drives the solenoid valves.
(6) This PCB drives the stat indicator and sample plate indicator.
3.6.2 Descriptions
(1) Stepping Motor Drive (Constant-current drive, Constant-voltage drive)
The motor is driven according to the motor control signal from the M-I/O (PCB No. 3052) and the
ENB signal from the CPU (PCB No. 6364).
1) Constant-Current Drive
6 channels, +12 VDC, 1, 2-phase drive
Volumetric syringe for samples, Volumetric syringe for reagents, Lamp unit filter drive,
Sampler rack shift, Sampler feed-in, and Sampler feed-out.
(2) DC Motor Drive
2 channels: Hopper motor (+12 VDC), Feeder motor (+5 VDC)
(3) Serial/Parallel Conversion of CPU Control Signal
The serial control signal from the CPU is converted into a parallel signal, and sent to each drive
element.
(4) Temperature Control : 4 channels
Heater temperature (3 channels) and Peltier element (1 channel) are controlled with the
thermistor.
A room temperature monitor circuit (1 channel) is also provided.
CA-1500 S/M 3-9 December 2000 Revised
The thermistor’s output voltage is sent to the CPU through the A/D convertor. The CPU
calculates a temperature using the conversion formula specified in the program. The control
signal from the CPU controls each heater, and the Peltier element.
1) 37°C (Proportional control): Scattered light detecting unit, Transmitted light detecting
unit, and Reagent pipette.
2) 15°C (ON/OFF control) : Cooler unit
(5) Pressure Monitor : 3 channels (2.2 kg/cm2, 1.0 kg/cm2, and 400 mmHg).
Each pressure sensor’s output voltage is sent to the CPU through the A/D convertor.
(6) Solenoid Valve ON/OFF Control : 24 channels
The solenoid valve ON/OFF status is controlled according to the control signal (+12 VDC) from
the CPU.
(7) Relay of Each Sensor Output
This PCB relays each motor limit position sensor’s output; float switch sensor’s output for each
chamber, and the external bottle; output of the sample tube sensor in the hopper (for detecting
the dummy sample tube); output of the sample tube sensor in the feeder; light-shield cover
sensor’s output; and the sampler sensor’s output to the M-I/O. It then relays the parallel/serial
converted signal to the CPU.
A noise reduction filter circuit is provided for sensor input.
(8) Output of Stat Sample indicator/Sample Plate indicator Control Signals
(9) Operation Stop Switch Monitor : 1 channel
(10) Stat Sample Holder Lock Drive
(11) Latch Circuit for Sampler Tube Position Sensor’s Output
(12) Power Supply
1) Motor : +30 VDC, +12 VDC, +5 VDC
2) Logic : +5 VDC
3) Analog : ±15 VDC
4) Temperature control : +28 VDC, +12 VDC, 100 VAC
CA-1500 S/M 3-10 December 2000 Revised
3.6.3 Block Diagram
3.6.4 Adjustment and Test Point
See Section 4.
CA-1500 S/M 3-11 December 2000 Revised
3.6.5 Assembly Drawing
CA-1500 S/M 3-12 December 2000 Revised
3.7 PCB NO. 2137 (LIQUID SURFACE SENSOR)
3.7.1 Functions
(1) Liquid surface detection is performed based on a capacitance change.
(2) The PCB relays signals from various sensors, motors, and the reagent pipette heater to the
Y-axis relay board.
3.7.2 Descriptions
(1) Liquid Surface Detecting Function
The sensor detects the liquid surface of samples, reagents and buffer, and outputs detection
signal. The detecting sensitivity can be switched between High and Low gains so that the liquid
surface detection can be performed with both open and closed blood collection tubes.
At least 50 µL of samples and reagents can be detected in the sample/reagent cooling unit.
At least 200 µL of samples can be detected in a blood collection tube in the sampler.
To detect a micro sample in an open blood collection tube, and to prevent a liquid surface
detection error when a closed blood collection tube is used, the detecting sensitivity can be
switched between HIGH gain and LOW gain in the program.
1) Oscillator circuit
400 kHz ceramic oscillator (CSB400J) and transistor (2SC1815GR)
Since the liquid surface sensor board is separately provided for both the sample arm and
reagent arm, their oscillator circuits interfere with each other. To eliminate malfunction
caused by interference, the oscillator circuits can be turned ON/OFF.
2) Oscillator output interrupt circuit
Analog switch using FET (2SK30)
3) Limiter
The oscillator waveform is clipped in the range of 1.2 V p-p through the diode (1SS133).
4) Oscillator waveform amplifier circuit
Non-inverting amplifier circuit (gain: 22) using operational amplifier (AD847)
5) Buffer circuit
6) Wave detection circuit
Wave detection using diode
7) Differentiation circuit
Highpass filter using C and R
8) Differential waveform amplifier circuit
Operational amplifier (LF356)
9) Gain switching circuit
Analog switch
10) Comparator circuit
Zener diode (RD4.7JSB3) and comparator (LM393)
11) Latch circuit
D flip-flop (SN74LS74)
(2) Pipette Crash Detection Circuit
Digital transistor (DTC114YF)
(3) Signal Relay Function
The pipette crash signal, reagent pipette heater control signal, thermistor signal for monitoring the
reagent pipette heater temperature, and sample arm/reagent arm home position sensor signal
are relayed to the Y-axis relay board. Also, the control signals are relayed to the sample
arm/reagent arm Z-axis motors.
CA-1500 S/M 3-13 December 2000 Revised
3.7.3 Block Diagram
3.7.4 Adjustment and Test Point
See Section 4.
3.7.5 Interface Specification
(1) Connections with Relay Board : 20-pole tape cable
• Power supply (+15 V, +5 V)
• Pipette crash detection signal
• Liquid surface detection signal
• Arm Z-axis home position sensor signal
• Arm Z-axis motor signal
• Liquid sensor limit signal
• Oscillator circuit ON/OFF signal
• HIGH/LOW gain switching signal (for the sample arm only)
• Reagent pipette heater power supply (for the reagent arm only)
• Thermistor signal (for the reagent arm only)
(2) Connections with Z-Axis Stepping Motor (6 pins)
(3) Connections with Z-Axis Home Position Sensor (3 pins): +5 V, SIG, GND
(4) Pipette (Liquid surface sensor) (4 pins) : SIG, GUARD SHIELD, GND SHIELD
(5) Pipette Crash Switch (2 pins)
(6) Thermistor Heater Shielded Cable (6 pins)
CA-1500 S/M 3-14 December 2000 Revised
3.7.6 Assembly Drawing
3.7.7 Cap Detection Function (with Cap Piercer Unit)
On CA-1500, both closed (capped) collection tubes and open tubes can be set in a sample rack for cap
piercing sampling. The detection sensitivity is automatically switched between low and high.
1. The sensitivity for cap detection is set at low.
2. The cap detection is done at approx. 41 mm down from the upper end position of Sample Arm.
3. If cap is detected, the piercer goes down to aspirate sample. After sample aspiration, returns to
high sensitivity.
4. If no cap is detected at the above position, then the sensitivity is automatically switched to high.
The Sample Arm goes up approx. 10 mm, then goes down to aspirate the sample.
Note that Micro Mode analysis is impossible in closed sampling.
Table 3-7-1: Sensitivity Switching
Normal Mode Micro Mode
without CACP Unit high high
with CACP Unit low (cap detection) Æ high
using closed tubes low (sample aspiration) Æ high *Probe Crash error at cap detection
with CACP Unit low (cap detection) Æ high
using open tubes high (sample aspiration) Æ high
Information: PCB No. 2137 was once modified for Cap Piercing capability (ECR 398F071).
The modified PCB is labeled with “9807”, and used on CA-1500 S/N A1054 and
thereafter. The old PCB should not be used on the CA-1500 with CP Unit, since
sample aspiration error will be caused.
CA-1500 S/M 3-15 December 2000 Revised
3.8 PCB NO. 2138 (PRE-AMPLIFIER FOR CHROMOGENIC UNIT)
3.8.1 Functions
(1) Pre-amplifier board for detection Channels 1 to 4 of the chromogenic unit
3.8.2 Descriptions
(1) Pre-Amplifier Circuit
The photo-diode detects the transmitted light of Channels 1 to 4 of the chromogenic substance
detection unit, and generates a small current. The current - voltage convertor circuit converts the
current into a voltage. The detection signal passes through the DC amplifier circuit, and then it is
output to the I/O board.
3.8.3 Block Diagram
CA-1500 S/M 3-16 December 2000 Revised
3.8.4 Adjustment and Test Point
None.
3.8.5 Assembly Drawing
CA-1500 S/M 3-17 December 2000 Revised
3.9 PCB NO. 3052 (I/O)
3.9.1 Functions
This PCB is the I/O board intended for motor control, serial control, and data input.
3.9.2 Descriptions
(1) The conventional two PCBs (PCB No. 1231 (M-I/O) and PCB No. 3045 (Data Logger)) are
combined into this board.
(2) This PC board provides a 64-pin VME bus (DIN connector) as the system bus.
(3) I/O
1) Asynchronous serial communication port (2 channels)
CH1 : Not used
(With the conventional board, this channel is used as current loop port for
temperature adjustment.)
CH2 : For sampler (RC-232C port)
CH3 : For ID (bar code) reader (RC-232C port)
2) Synchronous serial communication port (2 channels)
Synchronous serial input port
Synchronous serial output port
3) Parallel I/O port (16 channels)
One SM0006 chip is provided for asynchronous serial communication, synchronous
serial communication, and parallel input/output.
4) Stepping motor (18 channels)
One SM0006 chip and nine SM0009 chips are provided for stepper motor control.
(4) Data Logger
1) The memory uses 256-Kbit SRAM, providing 512 bytes for each channel. Data on
offset, gain, channel and write pointers for each channel, and 12-bit analysis data are
stored here.
2) The A/D convertor’s buffer size is 504 bytes for each channel. The buffer can store up to
252 segments of 12-bit A/D conversion data (2 bytes for each).
3) The A/D conversion data input is executed at 100 ms intervals for 25.2 seconds. The
ring buffer overwrites input data after the input time exceeds this period.
4) An arbitration function is provided to make access to the sequencer (PLC) and host
computer. Data can be read at any time.
The time-series memory provides a RD pointer for data reading management.
5) An 8-bit write port is provided to start/stop the sequencer.
Start/Stop signal (Bit 0) : 1: Start, 0: Stop
CA-1500 S/M 3-18 December 2000 Revised
3.9.3 Block Diagram
CA-1500 S/M 3-19 December 2000 Revised
3.9.4 Connector Pin Assigns
(1) J11: Control of STM13 to STM18, 52-pin Straight Header
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
1A VCC 1B VCC
2A STM13_L1 (CW) 2B STM14_L1 (CW)
3A STM13_L2 (CCW) 3B STM14_L2 (CCW)
4A STM13_S0b 4B STM14_S0b
5A STM13_S1b 5B STM14_S1b
6A STM13_S2b 6B STM14_S2b
7A STM13_S3b 7B STM14_S3b
8A GND 8B GND
9A VCC 9B VCC
10A STM15_L1 (CW) 10B STM16_L1 (CW)
11A STM15_L2 (CCW) 11B STM16_L2 (CCW)
12A STM15_S0b 12B STM16_S0b
13A STM15_S1b 13B STM16_S1b
14A STM15_S2b 14B STM16_S2b
15A STM15_S3b 15B STM16_S3b
16A GND 16B GND
17A VCC 17B VCC
18A STM17_L1 (CW) 18B STM18_L1 (CW)
19A STM17_L2 (CCW) 19B STM18_L2 (CCW)
20A STM17_S0b 20B STM18_S0b
21A STM17_S1b 21B STM18_S1b
22A STM17_S2b 22B STM18_S2b
23A STM17_S3b 23B STM18_S3b
24A STM15_ENB 24B STM16_ENB
25A STM17_ENB 25B STM18_ENB
26A GND 26B GND
(2) J10: Control of STM7 to STM12, 52-pin Straight Header
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
1A VCC 1B VCC
2A STM7_L1 (CW) 2B STM8_L1 (CW)
3A STM7_L2 (CCW) 3B STM8_L2 (CCW)
4A STM7_S0b 4B STM8_S0b
5A STM7_S1b 5B STM8_S1b
6A STM7_S2b 6B STM8_S2b
7A STM7_S3b 7B STM8_S3b
8A GND 8B GND
9A VCC 9B VCC
10A STM9_L1 (CW) 10B STM10_L1 (CW)
11A STM9_L2 (CCW) 11B STM10_L2 (CCW)
12A STM9_S0b 12B STM10_S0b
13A STM9_S1b 13B STM10_S1b
14A STM9_S2b 14B STM10_S2b
15A STM9_S3b 15B STM10_S3b
16A GND 16B GND
17A VCC 17B VCC
18A STM11_L1 (CW) 18B STM12_L1 (CW)
19A STM11_L2 (CCW) 19B STM12_L2 (CCW)
20A STM11_S0b 20B STM12_S0b
21A STM11_S1b 21B STM12_S1b
22A STM11_S2b 22B STM12_S2b
23A STM11_S3b 23B STM12_S3b
24A STM9_CLKB 24B N. C.
25A STM9_DIRB 25B N. C.
26A GND 26B GND
CA-1500 S/M 3-20 December 2000 Revised
(3) J9: Control of STM1 to STM6, 52-pin Straight Header
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
1A VCC 1B VCC
2A STM1_L1 (CW) 2B STM2_L1 (CW)
3A STM1_L2 (CCW) 3B STM2_L2 (CCW)
4A STM1_A 4B STM2_A
5A STM1_B 5B STM2_B
6A STM1_Ab 6B STM2_Ab
7A STM1_Bb 7B STM2_Bb
8A GND 8B GND
9A VCC 9B VCC
10A STM3_L1 (CW) 10B STM4_L1 (CW)
11A STM3_L2 (CCW) 11B STM4_L2 (CCW)
12A STM3_A 12B STM4_S0b
13A STM3_B 13B STM4_S1b
14A STM3_Ab 14B STM4_S2b
15A STM3_Bb 15B STM4_S3b
16A GND 16B GND
17A VCC 17B VCC
18A STM5_L1 (CW) 18B STM6_L1 (CW)
19A STM5_L2 (CCW) 19B STM6_L2 (CCW)
20A STM5_S0b 20B STM6_S0b
21A STM5_S1b 21B STM6_S1b
22A STM5_S2b 22B STM6_S2b
23A STM5_S3b 23B STM6_S3b
24A STM5_CLKb 24B N. C.
25A STM5_DIRb 25B N. C.
26A GND 26B GND
CA-1500 S/M 3-21 December 2000 Revised
(4) J8: Bus Signal, 64-pin DIN Connector (2-row, Male)
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
1A VCC 1B GND
2A IACK/ 2B N. C.
3A N. C. 3B N. C.
4A N. C. 4B IRQ3b
5A N. C. 5B N. C.
6A SYSRESET/ 6B GND
7A N. C. 7B N. C.
8A N. C. 8B N. C.
9A N. C. 9B N. C.
10A N. C. 10B N. C.
11A AB [15] 11B AB [14]
12A AB [13] 12B AB [12]
13A AB [11] 13B AB [10]
14A AB [9] 14B AB [8]
15A AB [7] 15B AB [6]
16A AB [5] 16B AB [4]
17A AB [3] 17B AB [2]
18A AB [1] 18B GND
19A SYSCLK 19B GND
20A AS/ 20B WRITE/
21A UDS/ 21B IOARDS/
22A LDS/ 22B DTACKb
23A N. C. 23B N. C.
24A N. C. 24B N. C.
25A N. C. 25B N. C.
26A N. C. 26B N. C.
27A DB [7] 27B DB [6]
28A DB [5] 28B DB [4]
29A DB [3] 29B DB [2]
30A DB [1] 30B DB [0]
31A GND 31B GND
32A VCC 32B VCC
(5) J7: Built-in Bar Code Reader Control, 14-pin MIL-compatible Right-angle Header
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
1 F. G. 8 GND
2 GND 9 RTS
3 RxD 10 N. C.
4 GND 11 DTR
5 TxD 12 N. C.
6 VCC 13 GND
7 CTS 14 DSR
(6) J6: Sampler Transfer Control, 10-pin MIL-compatible Straight Header
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
1 F. G. 6 GND
2 GND 7 RTS
3 RxD 8 N. C.
4 GND 9 DTR
5 TxD 10 N. C.
CA-1500 S/M 3-22 December 2000 Revised
(7) J5: Analog Power Supply
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
1 A+15V 3 A–15V
2 AGND
(8) J4: Detector Control for Chromogenic Substance Method, 16-pin MIL-compatible Straight
Header
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
1 A+15V 9 SIG6
2 A–15V 10 GND
3 SIG3 11 SIG7
4 AGND 12 GND
5 SIG4 13 SIG8
6 VCC 14 GND
7 SIG5 15 N. C.
8 VCC 16 N. C.
(9) J3: Detector Control for Bioactivity Method, 26-pin MIL-compatible Straight Header
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
1 A+15V 14 VCC
2 A–15V 15 HGAINb
3 A+15V 16 VCC
4 A–15V 17 LGAINb
5 SIG1 18 GND
6 AGND 19 SEL0b
7 SIG2 20 GND
8 AGND 21 SEL1b
9 SEL0b 22 GND
10 VCC 23 SEL2b
11 SEL1b 24 GND
12 VCC 25 HGAINb
13 SEL2b 26 LGAINb
(10) J2: General-purpose I/O, 40-pin MIL-compatible Straight Header
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
1 VCC 21 VCC
2 SIN_CLK 22 IOP [6]
3 VCC 23 VCC
4 SIN_LATCH 24 IOP [7]
5 N. C. 25 VCC
6 SIN_DATA 26 IOP [8]
7 GND 27 VCC
8 GND 28 IOP [9]
9 VCC 29 VCC
10 IOP [0] 30 IOP [10]
11 VCC 31 VCC
12 IOP [1] 32 IOP [11]
13 VCC 33 VCC
14 IOP [2] 34 IOP [12]
15 VCC 35 VCC
16 IOP [3] 36 IOP [13]
17 VCC 37 VCC
18 IOP [4] 38 IOP [14]
19 VCC 39 VCC
20 IOP [5] 40 IOP [15]
CA-1500 S/M 3-23 December 2000 Revised
(11) J1: Driver Control, 14-pin MIL-compatible Straight Header (3M J3598-6002FL)
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
1 SOUT_CLK 8 VCC
2 GND 9 SIN_CLK
3 SOUT_DATA 10 GND
4 VCC 11 SIN_LATCH
5 SOUT_LATCH 12 VCC
6 GND 13 SIN_DATA
7 SOUT_ENb 14 GND
3.9.5 Setting and Adjustment
See Section 4.
3.9.6 Assembly Drawing
J11 J10 J9
STM#13-18 STM#7-12 STM#1-6
S1
T-VME BUS
DIP
SW
J13 J8
ID J7
Detector
J6
Sampler
J12 Parallel (Chromo)
J1 J2 J3 J4 J5
Serial Detector Power
CA-1500 S/M 3-24 December 2000 Revised
3.10 PCB NO. 4079 (POWER SUPPLY BOARD)
3.10.1 Functions and Descriptions
After the full-wave rectification at the bridge diode, the rectified voltage passes through the
smoothing circuit with an electrolytic capacitor.
Thus, +30 VDC and +28 VDC power supplies are provided to drive the stepping motor and
thermal module.
This board also relays 100 VAC to the +12 V switching regulator, lamp unit switching power
supply and PCB No. 1246.
3.10.2 Block Diagram
PCB No.4079
F1 TP1
+30V
AC 27V 4.5A
F2 J3
J1
TP2 +28V
AC 24V 5.0A TP3
AC100V
F3 TP4
AC
F4 TP5 100V
AC 100V 3.0A J2
J4 AC
TP6 100V
3.10.3 Assembly Drawing
CA-1500 S/M 3-25 December 2000 Revised
3.11 PCB NO. 4088 (POWER SUPPLY)
3.11.1 Functions
(1) Power supply board incorporated in the CA-1500 power supply unit.
(2) Inputs AC power from the power supply transformer to provide the DC power supplies for the
analog, halogen lamp, and LCD circuits.
(3) Relays 100 VAC to the compressor, switching regulator and the heater of the detecting unit.
(4) The ON/OFF status of the halogen lamp and compressor power supplies is controlled with the
relays of the driver board.
3.11.2 Descriptions
This PCB provides the following power supply outputs:
(1) For Analog : ±15 ±0.6 VDC (Rated current: 0.4 A)
(2) For Halogen Lamp : +6 ±0.2 VDC (Rated current: 1.67 A), 2.8 A max. (Over-current protection
circuit)
This power supply is controlled with the relay (control signal from the PCB
No. 1246 driver board), which is normally ON.
(3) For LCD : +34 ±2 VDC (Rated current 0.022 A max.)
(4) Relay of Compressor Power Supply : 100 VAC (Rated current 1.0 A)
The ON/OFF status of this power supply is controlled with the relay (control
signal from the PCB No. 1246 driver board).
(5) Relay of Switching Regulator and 100 VAC Heater Power Supply
(Rated current: 2.6 A)
A fuse is provided in all the AC input lines of the above power supplies.
CA-1500 S/M 3-26 December 2000 Revised
3.11.3 Block Diagram
3.11.4 Adjustment and Test Point
See Section 4.
CA-1500 S/M 3-27 December 2000 Revised
3.11.5 Assembly Drawing
3.12 PCB NO. 6364 (CPU)
3.12.1 Functions
This PC board is intended for main CPU and basic I/O (HDD, FDD, Display, External output, etc.)
control.
3.12.2 Descriptions
(1) CPU
1) CPU : MC68EC020 25 MHz
2) ROM : 256 K words (4-Mbit EPROM)
3) RAM : 8 Mbytes (Fixed)
4) BBURAM : 256 Kbytes (1 Mbit × 2)
5) Calendar clock : RTC62421
6) Timer : 82C54
7) Serial interface : MB89371 (Debugger connection)
(2) Basic I/O
1) HDD : SCSI interface
2) FDD : 3 modes
3) Serial interface : MB89371 RS-232C (× 2)
4) Parallel interface : Centronics (× 2)
5) Key interface : Parallel 128 keys (Max.)
6) Buzzer
7) Display function : 640 × 480 dot dual-scan STN color LCD control
Image memory 16 Mbits
(3) Auxiliary Extended Function
Add-on board mountable via a 64-pole T-VME bus
CA-1500 S/M 3-28 December 2000 Revised
(4) Display
1) General specifications
(a) Application
Compatible with dual-scan STN color LED
(b) Screen structure
640 × 480 dots (R: Red, G: Green, B: Blue, I: Brightness), 6 screens
(c) Image memory
Multi-port DRAM + General-purpose DRAM
2) Block Diagram
CA-1500 S/M 3-29 December 2000 Revised
3.12.3 Block Diagram
CA-1500 S/M 3-30 December 2000 Revised
3.12.4 Connector Pin Assigns
(1) J1: LCD Upper Half Screen Control (Right-angled)
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J1-1 FLM J1-8 UD0
J1-2 M J1-9 UD1
J1-3 DISP OFFb J1-10 UD2
J1-4 CL1 J1-11 UD3
J1-5 VSS J1-12 UD4
J1-6 CL2 J1-13 UD5
J1-7 VSS J1-14 UD6
J1-15 UD7
(2) J2: LCD Lower Half Screen Control (Right-angled)
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J2-1 LD0 J2-8 LD7
J2-2 LD1 J2-9 VDD
J2-3 LD2 J2-10 VSS
J2-4 LD3 J2-11 VDD
J2-5 LD4 J2-12 VEE
J2-6 LD5 J2-13 VEE
J2-7 LD6 J2-14 VO
(3) J3: Touch Panel Control(Flat)
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J3-1 SD6 J3-10 KD2
J3-2 SD7 J3-11 KD1
J3-3 SD8 J3-12 KD0
J3-4 SD9 J3-13 SD5
J3-5 KD7 J3-14 SD4
J3-6 KD6 J3-15 SD3
J3-7 KD5 J3-16 SD2
J3-8 KD4 J3-17 SD1
J3-9 KD3 J3-18 SD0
(4) J4: Brightness adjustment VR (Side)
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J4-1 VEE (CW side) J4-3 VSS (CCW side)
J4-2 VO (Wiper terminal)
(5) J5: LCD invertor control (Side)
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J5-1 GND J5-5 VR B
J5-2 VFL (DC+12V) J5-6 N. C.
J5-3 CNT J5-7 GND
J5-4 VR A
(6) J6: Communication with a Handheld Bar code Reader, D-SUB 9-pin, Male,
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J6-1 N. C. J6-6 DSR
J6-2 RxD J6-7 RTS
J6-3 TxD J6-8 CTS
J6-4 DTR J6-9 N. C.
J6-5 GND
CA-1500 S/M 3-31 December 2000 Revised
(7) J7: Communication with the Host Computer, D-SUB 9-pin, Male
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J7-1 N. C. J7-6 DSR
J7-2 RxD J7-7 RTS
J7-3 TxD J7-8 CTS
J7-4 DTR J7-9 N. C.
J7-5 GND
(8) J8: DP Control, D-SUB 25-pin, Female
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J8-1 STRB J8-14 N. C.
J8-2 D [0] J8-15 FAULT
J8-3 D [1] J8-16 INIT
J8-4 D [2] J8-17 N. C.
J8-5 D [3] J8-18 GND
J8-6 D [4] J8-19 GND
J8-7 D [5] J8-20 GND
J8-8 D [6] J8-21 GND
J8-9 D [7] J8-22 GND
J8-10 ACK J8-23 GND
J8-11 BUSY J8-24 GND
J8-12 PE J8-25 GND
J8-13 SLCT
(9) J9: GP Control, D-SUB 25-pin, Female
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J9-1 STRB J9-14 N. C.
J9-2 D [0] J9-15 FAULT
J9-3 D [1] J9-16 INIT
J9-4 D [2] J9-17 N.C.
J9-5 D [3] J9-18 GND
J9-6 D [4] J9-19 GND
J9-7 D [5] J9-20 GND
J9-8 D [6] J9-21 GND
J9-9 D [7] J9-22 GND
J9-10 ACK J9-23 GND
J9-11 BUSY J9-24 GND
J9-12 PE J9-25 GND
J9-13 SLCT
CA-1500 S/M 3-32 December 2000 Revised
(10) J10: FDD Control, 34-pin MIL-compatible Socket
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J10-1 GND J10-18 DIRECTION
J10-2 MODE_SEL J10-19 GND
J10-3 GND J10-20 STEP
J10-4 N. C. J10-21 GND
J10-5 GND J10-22 WRITE DATA
J10-6 N.C. J10-23 GND
J10-7 GND J10-24 WRITE DATA
J10-8 INDEX J10-25 GND
J10-9 GND J10-26 TRACK 00
J10-10 DRV SELECT 0 J10-27 GND
J10-11 GND J10-28 WRITE PROTECT
J10-12 N. C. J10-29 GND
J10-13 GND J10-30 READ DATA
J10-14 N. C. J10-31 GND
J10-15 GND J10-32 SIDE1 SELECT
J10-16 MOTOR ON J10-33 GND
J10-17 GND J10-34 READY
(11) J11: HDD Control, 50-pin MIL-compatible Socket
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J11-1 GND J11-26 TERMPWR
J11-2 SD [0] J11-27 GND
J11-3 GND J11-28 GND
J11-4 SD [1] J11-29 GND
J11-5 GND J11-30 GND
J11-6 SD [2] J11-31 GND
J11-7 GND J11-32 ATN
J11-8 SD [3] J11-33 GND
J11-9 GND J11-34 GND
J11-10 SD [4] J11-35 GND
J11-11 GND J11-36 BSY
J11-12 SD [5] J11-37 GND
J11-13 GND J11-38 ACK
J11-14 SD [6] J11-39 GND
J11-15 GND J11-40 RST
J11-16 SD [7] J11-41 GND
J11-17 GND J11-42 MSG
J11-18 SDP J11-43 GND
J11-19 GND J11-44 SEL
J11-20 GND J11-45 GND
J11-21 GND J11-46 C/D
J11-22 GND J11-47 GND
J11-23 GND J11-48 REQ
J11-24 GND J11-49 GND
J11-25 N. C. J11-50 I/O
(12) J12: Power Supply, 12-pin Straight Header
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J12-1 DC5V J12-7 GND
J12-2 DC5V J12-8 GND
J12-3 DC5V J12-9 GND
J12-4 DC5V J12-10 GND
J12-5 DC12V J12-11 GND (12V)
J12-6 DC34V J12-12 GND
CA-1500 S/M 3-33 December 2000 Revised
(13) J13: Bus Signal, 64-pin DIN Connector, 2-row, Female
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J13-1A VCC J13-1B GND
J13-2A INTACKb J13-2B INT [7] b
J13-3A INT [6] b J13-3B INT [5] b
J13-4A INT [4] b J13-4B INT [3] b
J13-5A INT [2] b J13-5B INT [1] b
J13-6A RESETb J13-6B GND
J13-7A AB [23] J13-7B AB [22]
J13-8A AB [21] J13-8B AB [20]
J13-9A AB [19] J13-9B AB [18]
J13-10A AB [17] J13-10B AB [16]
J13-11A AB [15] J13-11B AB [14]
J13-12A AB [13] J13-12B AB [12]
J13-13A AB [11] J13-13B AB [10]
J13-14A AB [9] J13-14B AB [8]
J13-15A AB [7] J13-15B AB [6]
J13-16A AB [5] J13-16B AB [4]
J13-17A AB [3] J13-17B AB [2]
J13-18A AB [1] J13-18B GND
J13-19A S_CLK J13-19B GND
J13-20A Asb J13-20B WRITEb
J13-21A UDSb J13-21B IOARDSb
J13-22A LDSb J13-22B DTACKb
J13-23A DB [15] J13-23B DB [14]
J13-24A DB [13] J13-24B DB [12]
J13-25A DB [11] J13-25B DB [10]
J13-26A DB [9] J13-26B DB [8]
J13-27A DB [7] J13-27B DB [6]
J13-28A DB [5] J13-28B DB [4]
J13-29A DB [3] J13-29B DB [2]
J13-30A DB [1] J13-30B DB [0]
J13-31A GND J13-31B GND
J13-32A VCC J13-32B VCC
(14) J17 : Battery backup ON (ON when connected)
(15) J19: Power Supply for FDD (Top)
Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. Signal Name
J19-1 5V J19-3 GND
J19-2 GND
3.12.5 Setting and Adjustment
See Section 4.
CA-1500 S/M 3-34 December 2000 Revised
3.12.6 Assembly Drawing
Inverter
J1 J2 J3 J4 J5
LCD LCD Contrast
Touch
(upper (lower VR
Panel J6 Sequence
half) half)
T-VME BUS
VR1
J7 HOST
J13
S1 Bz
S2
J9 GP
D2 D3 TP1 TP2
Battery GND VCC
J17
FDD J8 DP
J12 J11 J19 J10
Power HDD FDD Power
CA-1500 S/M 3-35 December 2000 Revised
3.13 PCB NO. 9270 (Y-AXIS RELAY)
3.13.1 Functions
(1) This PCB relays various control signals from the driver board to the Y-axis motors and sensors.
The control signals from the driver are relayed to the liquid surface sensor board or the Z-axis
relay board.
3.13.2 Descriptions
(1) This PCB is the Y-axis relay board that provides the following functions:
1) Relay of the Y-axis motor control signal
2) Relay of the Y-axis home position sensor signal
(2) The control signals from the driver board and various sensor signals are relayed to the liquid
surface sensor board or Z-axis relay board.
3.13.3 Block Diagram
3.13.4 Adjustment and Test Point
None.
3.13.5 Assembly Drawing
CA-1500 S/M 3-36 December 2000 Revised
3.14 PCB NO. 9271 (Z-AXIS RELAY)
3.14.1 Functions
(1) This PCB is the Z-axis relay board for the reaction tube transfer unit.
(2) Relays various control signals from the driver board through the Y-axis relay board.
3.14.2 Descriptions
This PCB is the Z-axis relay board, and provides the following functions:
1) Input of the Z-axis sensor signal
2) Relay of the Z-axis motor control signal
3) Relay of the catcher stirring motor drive signal
3.14.3 Block Diagram
3.14.4 Adjustment and Test Point
None.
3.14.5 Assembly Drawing
CA-1500 S/M 3-37 December 2000 Revised
3.15 PCB NO. 9272 (STAT SENSOR)
3.15.1 Outline
(1) This PCB is the sensor board for the STAT holder unit.
3.15.2 Functions and Operations
5 sensors are mounted on this board to detect sample tube set in the STAT holder.
3.15.3 Block Diagram
3.15.4 Adjustment and Test Point
None.
3.15.5 Assembly Drawing
CA-1500 S/M 3-38 December 2000 Revised
3.16 CA-1500 POWER SUPPLY UNIT
3.16.1 Functions and Descriptions
This PCB supplies power to each electric circuit. This unit is composed of:
(1) AC inlet with Line Filter
(2) Power supply PCB (PCB No. 4079, PCB No. 4088)
(3) Power Transformer (PT-096, PT-097)
(4) +15V Switching Regulator (R25U-15)
3.16.2 Performance Specification
Input Voltage: AC 117 V ± 10%, 50/60 Hz
AC 220 V ± 10%, 50/60 Hz
AC 230 V ± 10%, 50/60 Hz
AC 240 V ± 10%, 50/60 Hz
Output Voltage: 100 VAC (for Detecting Unit heater)
100 VAC (for Pneumatic Unit control)
+15 VDC (for Reagent Pipette heater)
+28 VDC (for Cooler Unit peltier element)
+30 VDC (for Constant-current drive motor)
Catcher-X, Catcher-Y, Sample Pipette-X, Sample Pipette-Y,
Reagent Pipette-X, Reagent Pipette-Y, CP Unit
+12 VDC (for Constant- voltage drive motor)
Catcher-Z, Sample Pipette-Z, Reagent Pipette-Z, Lamp Unit,
Sample Volumetric Syringe, Reagent Volumetric Syringe,
Rack Feed-in, Rack Shift, Rack Feed-Out
+12 VDC (for Solenoid Valve drive)
+5 VDC (for CPU power supply)
±15 VDC (for analog power supply)
+6 VDC (for Chromogenic Unit Lamp power supply)
+34 VDC (for LCD drive)
+12 VDC (for Fan)
3.16.3 Block Diagram
CA-1500 S/M 3-39 December 2000 Revised
3.16.4 Transformer Power PT-096 (100/117V)
Rated primary voltage: 100/117 V, 50/60 Hz (N.A.)
Rated secondary 33 16 16 12 100 26 24
voltage VAC VAC VAC VAC VAC VAC VAC
Rated primary current 0.09 A 0.4 A 0.4 A 2.8 A 3.3 A 4.5 A 7.5 A
Rated primary current: 6.0 A or less
Voltage fluctuation: 10% or less
Voltage deviation: ±3%
Thermal protection: Melt down at 132°C
Pin No.
Pin No.
Thermal Fuse blue
0V 1 1
Sec. 1 blue 33V 0.09A
blue 2
orange
4
black 16V 0.4A
Sec. 2 3
orange 16V 0.4A
brown 5
100V 2
Primary green
6
Sec. 3 green 12V 2.8A
7
grey
1
Sec. 4 grey 100V 3.3A
red 2
117V 3
red
1
Sec. 5 red 26V 4.5A
4
brown
3
Sec. 6 brown 24V 7.5A
6
3.16.5 Transformer Power PT-097 (220/230/240V)
Rated primary voltage: 220/230/240 V, 50/60 Hz (N.A.)
Rated secondary 33 16 16 12 100 26 24
voltage VAC VAC VAC VAC VAC VAC VAC
Rated primary current 0.09 A 0.4 A 0.4 A 2.8 A 3.3 A 4.5 A 7.5 A
Rated primary current: 3.0 A or less
Voltage fluctuation: 10% or less
Voltage deviation: ±3%
Thermal protection: Melt down at 132°C
Pin No.
Pin No.
Thermal Fuse blue
0V 1 1
Sec. 1 blue 33V 0.09A
blue 2
orange
4
black 16V 0.4A
Sec. 2 3
orange 16V 0.4A
orange 5
green
Primary
220V 2
6
Sec. 3 green 12V 2.8A
7
grey
1
Sec. 4 grey 100V 3.3A
green 2
230V 3
red
1
Sec. 5 red 26V 4.5A
4
brown
3
yellow Sec. 6 brown 24V 7.5A
240V 4 6
CA-1500 S/M 3-40 December 2000 Revised
You might also like
- Section 3 Electronics: To CoverDocument15 pagesSection 3 Electronics: To CoverAlvaro Restrepo GarciaNo ratings yet
- T0757 3312 Barcode Scanner AppnoteDocument3 pagesT0757 3312 Barcode Scanner Appnotejainmalik4294No ratings yet
- Circuit AL 880Document50 pagesCircuit AL 880Environ PrintersNo ratings yet
- Start Up Sigma Solon LDDocument7 pagesStart Up Sigma Solon LDJesus Checa100% (1)
- LP Series: Service ManualDocument38 pagesLP Series: Service ManualPedro GuilarteNo ratings yet
- JVC KD r430 PDFDocument13 pagesJVC KD r430 PDFAleksNo ratings yet
- DSAZIHA100078408Document20 pagesDSAZIHA100078408Rjati devamNo ratings yet
- U010C-Lost Communication With Turbocharger/Supercharger Control ModuleDocument11 pagesU010C-Lost Communication With Turbocharger/Supercharger Control ModuleAshley GymanNo ratings yet
- SEMIKRON Application-Note Gate Driver Basics EN 2021-07-22 Rev-01Document20 pagesSEMIKRON Application-Note Gate Driver Basics EN 2021-07-22 Rev-01erode els erodeNo ratings yet
- Laptek Breaker MCCDocument2 pagesLaptek Breaker MCCenergiprimer.sintangNo ratings yet
- Sc900a PDFDocument23 pagesSc900a PDFgoguNo ratings yet
- Ak09911 PDFDocument18 pagesAk09911 PDFrallu. ralucaNo ratings yet
- Sensorless Position Control of Brushed DC Motor Using Ripple Counting Technique 00003049ADocument50 pagesSensorless Position Control of Brushed DC Motor Using Ripple Counting Technique 00003049AAli ErNo ratings yet
- PanasonicDP 130 150 PDFDocument132 pagesPanasonicDP 130 150 PDFxerox1025No ratings yet
- Design Guide For The 428B TTA System: Y H L CDocument18 pagesDesign Guide For The 428B TTA System: Y H L Cmichael guereroNo ratings yet
- ESQUEMATICO G2-Samsung NP100 - ByLeo037Document42 pagesESQUEMATICO G2-Samsung NP100 - ByLeo037mateo herediaNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor Driver: Order This Document by SAA1042/DDocument7 pagesStepper Motor Driver: Order This Document by SAA1042/DGalo CárdenasNo ratings yet
- Scala - 14L REV 1.0 (BA41-01335A) - Samsung RV408Document56 pagesScala - 14L REV 1.0 (BA41-01335A) - Samsung RV408kasimkaNo ratings yet
- Xenon Motherboard Theory of OperationsDocument35 pagesXenon Motherboard Theory of Operationsluiz carlos de souzaNo ratings yet
- Ssdac G36Document52 pagesSsdac G36aditya_vyas_13No ratings yet
- Sdram 2M X 16 Bit X 4 Banks: M12L128168A (2L)Document45 pagesSdram 2M X 16 Bit X 4 Banks: M12L128168A (2L)geniunetNo ratings yet
- AS5145H/AS5145A/AS5145B: 1 General DescriptionDocument37 pagesAS5145H/AS5145A/AS5145B: 1 General DescriptionsekoNo ratings yet
- 210 m2 Jet ElectricalDocument47 pages210 m2 Jet ElectricalДмитрий ЗолотковNo ratings yet
- 5527 (C6Pro) Service ManualDocument31 pages5527 (C6Pro) Service ManualncirNo ratings yet
- System Block Diagram: Schematic DiagramsDocument45 pagesSystem Block Diagram: Schematic DiagramsMatias MareNo ratings yet
- Diagrama FWM663Document10 pagesDiagrama FWM663Antonio GomesNo ratings yet
- AS5311 DataheetDocument32 pagesAS5311 DataheetBruno TondinNo ratings yet
- JRC - Installation GuideDocument122 pagesJRC - Installation GuideTrency FernandesNo ratings yet
- SM GP 90 PDFDocument32 pagesSM GP 90 PDFyoppiNo ratings yet
- Fairchild - Semiconductor FAN73611MX DatasheetDocument14 pagesFairchild - Semiconductor FAN73611MX DatasheetDeddy WilopoNo ratings yet
- PGN607 (5805) - Service Manual - With Revise Suggestions Functional DescriptionDocument24 pagesPGN607 (5805) - Service Manual - With Revise Suggestions Functional DescriptionncirNo ratings yet
- Abs535t Service ManualDocument61 pagesAbs535t Service ManualvovchickNo ratings yet
- HP Probook 4520s QUANTA GC9A Rev 1A SchematicsDocument57 pagesHP Probook 4520s QUANTA GC9A Rev 1A SchematicssanathNo ratings yet
- SV6030P Single-Chip 802.11 B/G/N MAC/BB/Radio With SDIO/SPI - SLAVE InterfaceDocument28 pagesSV6030P Single-Chip 802.11 B/G/N MAC/BB/Radio With SDIO/SPI - SLAVE Interfaceapi-432313169No ratings yet
- TV Chassis Fc3g2 Training ManualDocument53 pagesTV Chassis Fc3g2 Training ManualUmar MajeedNo ratings yet
- EV1 SCR Motor ControllerDocument32 pagesEV1 SCR Motor ControllerJShearer95% (20)
- Myray RX DC Block Diagram BD069F 0Document7 pagesMyray RX DC Block Diagram BD069F 0Bartosz OgibowskiNo ratings yet
- AN-1252 Application Note: How To Configure TheDocument12 pagesAN-1252 Application Note: How To Configure Thenguyen thuanNo ratings yet
- L6228PD Motor DriverDocument35 pagesL6228PD Motor DriverArvind WaghNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram t240Document6 pagesSchematic Diagram t240dany weinfeldNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: XR3F-19B160Document9 pagesService Manual: XR3F-19B160Andre VPNo ratings yet
- Fujitsu LifeBook LH530 Quanta FH1 Intel UMA Rev1A SchematicDocument37 pagesFujitsu LifeBook LH530 Quanta FH1 Intel UMA Rev1A SchematicAsep IndraNo ratings yet
- Seccion 2Document42 pagesSeccion 2Joel Allbert PimentelNo ratings yet
- 1327 enDocument80 pages1327 enLuis FelipeNo ratings yet
- 08 - Circuit Description PDFDocument6 pages08 - Circuit Description PDFphetronyo ferreira de oliveiraNo ratings yet
- Manual CD Player Fic FordDocument26 pagesManual CD Player Fic FordMarcelo MulinariNo ratings yet
- Westinghouse Ds 416 PDFDocument28 pagesWestinghouse Ds 416 PDFLuiz_F_A_ViannaNo ratings yet
- MC33742 PDFDocument72 pagesMC33742 PDFfraurNo ratings yet
- SSDC SeriesDocument48 pagesSSDC SeriesCông NguyễnNo ratings yet
- SAPPORO 150 (DAL00) : LA-1911 REV0.3 SchematicDocument58 pagesSAPPORO 150 (DAL00) : LA-1911 REV0.3 SchematicMehmet DemirNo ratings yet
- Tlm-1903 Service ManualDocument40 pagesTlm-1903 Service ManualdaldoggyNo ratings yet
- Preliminary: Revision HistoryDocument48 pagesPreliminary: Revision HistoryElnino HartonoNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: CD Mechanism Module (S10Mp3)Document25 pagesService Manual: CD Mechanism Module (S10Mp3)roto44No ratings yet
- Manual TranstectorDocument6 pagesManual TranstectorHoku's NickNo ratings yet
- Inventory Regarding Reparing CellDocument17 pagesInventory Regarding Reparing CellUsman ZahidNo ratings yet
- Skema l412Document57 pagesSkema l412Marselo M100% (1)
- Chapter 3 ELECTRONICS: Edition: 156Document47 pagesChapter 3 ELECTRONICS: Edition: 156Bagas dwi PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Transistor Electronics: Use of Semiconductor Components in Switching OperationsFrom EverandTransistor Electronics: Use of Semiconductor Components in Switching OperationsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Instruction For UseDocument2 pagesInstruction For Usejakab.m.atilaNo ratings yet
- CA-1500 SM #6 Error MessagesDocument56 pagesCA-1500 SM #6 Error Messagesjakab.m.atilaNo ratings yet
- CA-1500 SM #7 SchematicsDocument6 pagesCA-1500 SM #7 Schematicsjakab.m.atilaNo ratings yet
- CA-1500 SM #2 Hydraulic&MechDocument24 pagesCA-1500 SM #2 Hydraulic&Mechjakab.m.atilaNo ratings yet