Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Taxonomy Is The Method by Which Biologist Organize Living Things Into Groups
Uploaded by
Insanity 123Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Taxonomy Is The Method by Which Biologist Organize Living Things Into Groups
Uploaded by
Insanity 123Copyright:
Available Formats
Taxonomy is the method by which biologist organize living things into groups
Taxa is the group of organisms in taxonomy
Aristotle created a classification system called the great chain of being.
The term species was used to refer to a particular type of organism. The term Genus was
used to refer to a more general grouping of organisms that share certain traits.
The most influential early classification system was developed by Carolus Linnaeus “Father
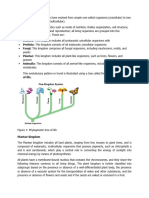
of Taxonomy”. He divided all nature into 3 kingdoms:
Animal
Vegetable
Mineral.
The taxa are:
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
In Binomial Nomenclature The two words in the name are the genus name and the
Species name. Example: Homo sapiens
Examples of added taxa include:
Subphylum
Superfamily
Domain
Phylogenetic classification
Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a group of genetically related organisms. A
phylogeny is usually represented by a tree diagram called a phylogenetic tree.
The most common method of incorporating information into phylogenetic trees is called
cladistics. Cladistics depicts hypotheses about how organisms are related, based on traits
if ancestor and descendent species
A diagram showing evolutionary relationships within one or more clades is called a
cladogram.
Traits inherited form a common ancestor are called ancestral traits. Traits that evolved
since two groups shared a common ancestor called derived traits.
A classification of organisms on the basis of such relationships is called a phylogenetic
classification.
Phylogenetic classification
1. Treats all levels of a cladogram as equivalent.
2. Places no limit on the number of levels in a cladogram
3. Primary goal is to show the process of evolution
4. It is limited to organisms that are related by ancestry.
5. Does not include a method for making species,
Linnean classification
1. Treat each taxa uniquely and has a special name or each.
2. Has fixed numbers and types of taxa.
3. Primary goal is to group species based on similarities in physical traits.
4. Can include any organisms without regard to ancestry
5. Has a method for giving unique names to species
You might also like
- Agri - Fishery Module Notes 2 Plant TaxonomyDocument3 pagesAgri - Fishery Module Notes 2 Plant TaxonomyGale ViernesNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy 1Document27 pagesTaxonomy 1Rouie john dizonNo ratings yet
- Classification: Essential Question Why Is It Important To Place Living Things Into Categories?Document45 pagesClassification: Essential Question Why Is It Important To Place Living Things Into Categories?Martin TisherNo ratings yet
- Macro TaxonomyDocument58 pagesMacro TaxonomyLimos, Gilcyanne M.No ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Classification of Animals NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 4-Classification of Animals Notesapi-195601294No ratings yet
- Miller/Tupper: Zoology 11e Instructor's Manual: Chapter SummaryDocument3 pagesMiller/Tupper: Zoology 11e Instructor's Manual: Chapter SummaryCaesar Franz RuizNo ratings yet
- LHT 4th Q Week 4.2Document5 pagesLHT 4th Q Week 4.2Katherine AudienciaNo ratings yet
- SystematicsDocument28 pagesSystematicsMishal FatimaNo ratings yet
- Living World Class 11nthDocument12 pagesLiving World Class 11nthraghavNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy. Thamanna KM. S1 MSC MBDocument24 pagesTaxonomy. Thamanna KM. S1 MSC MBAleetta SelestineNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument39 pagesClassificationAl-Bien TadoNo ratings yet
- Paper:: Plant Systematics Exam::mid Term Subject::plant Systematics Name::m.jebraeel Semester::2nd Portal Id::16071 Programme::m.sc BotanyDocument30 pagesPaper:: Plant Systematics Exam::mid Term Subject::plant Systematics Name::m.jebraeel Semester::2nd Portal Id::16071 Programme::m.sc BotanySajid RehmanNo ratings yet
- Classifying OrganismsDocument2 pagesClassifying OrganismshomamunfatNo ratings yet
- CH 26 Bio Vocab Campbell ReeceDocument3 pagesCH 26 Bio Vocab Campbell ReecebevancouverNo ratings yet
- Classification of OrganismDocument35 pagesClassification of OrganismJnll JstnNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and Phylogeny of AnimalsDocument46 pagesTaxonomy and Phylogeny of Animalsjaypasco79No ratings yet
- Phylogeny The Tree of Life Myp Class LectureDocument46 pagesPhylogeny The Tree of Life Myp Class LectureSamar El-MalahNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Organisms: The Varity of LifeDocument2 pagesDiversity of Organisms: The Varity of LifeKha RenNo ratings yet
- Phylogenetic SystematicsDocument6 pagesPhylogenetic SystematicsSakshi IssarNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-8-Q4-M-4.1 TaxonomyDocument2 pagesSCIENCE-8-Q4-M-4.1 TaxonomyDesiree de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and SystematicsDocument22 pagesTaxonomy and SystematicsHyun JiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Taxonomy PPT, 2024Document49 pagesPrinciples of Taxonomy PPT, 2024GAMECHU MULUNEHNo ratings yet
- B7 Classification ReadingDocument3 pagesB7 Classification ReadingMatt StromNo ratings yet
- Systematic BiologyDocument42 pagesSystematic BiologyYlane LeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 Microbial TaxonomyDocument14 pagesLecture1 Microbial TaxonomyJonathan NathanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Taxonomy of InsectDocument6 pagesUnit 5: Taxonomy of InsectAravind SrivasthavNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Microbial WorldDocument16 pagesDiversity of Microbial WorldAfrin IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Plant TaxonomyDocument7 pagesPlant TaxonomySiaNo ratings yet
- The Act, Process, or Result of Classifying. A Category or Class. Biology The Systematic Grouping of Organisms Into Categories On The Basis of Evolutionary or Structural Relationships Between ThemDocument6 pagesThe Act, Process, or Result of Classifying. A Category or Class. Biology The Systematic Grouping of Organisms Into Categories On The Basis of Evolutionary or Structural Relationships Between ThemsadiaNo ratings yet
- TaxonomyDocument46 pagesTaxonomyMyra MonicaNo ratings yet
- Purpose of Taxonomy in BiologyDocument7 pagesPurpose of Taxonomy in BiologytboylingweNo ratings yet
- Intro To Csec BioDocument5 pagesIntro To Csec BioJagdeesh Gosine100% (1)
- Chapter 16 Reconstructing and Using Phylogenetic TreesDocument4 pagesChapter 16 Reconstructing and Using Phylogenetic Treesapi-272677238No ratings yet
- Wa0000Document19 pagesWa0000Muzammil LiaketNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Bio320 PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Bio320 PDFNurul Amirah HossainNo ratings yet
- Each Name Must Refer To Only One Species Everyone Must Use The Same NameDocument9 pagesEach Name Must Refer To Only One Species Everyone Must Use The Same NameWe the people Lesson 9No ratings yet
- Taxonomy - Importance, History and Development and Binomial Nomenclature - Definitions of Biotype, Sub-Species, Species, Genus, Family and OrderDocument4 pagesTaxonomy - Importance, History and Development and Binomial Nomenclature - Definitions of Biotype, Sub-Species, Species, Genus, Family and OrderRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 SCDocument5 pagesChapter 7 SCapi-523871804No ratings yet
- Animal Taxonomy, Phylogeny and Organization: Duration75 Min Grade: 4 CCSS, NgssDocument25 pagesAnimal Taxonomy, Phylogeny and Organization: Duration75 Min Grade: 4 CCSS, Ngssbread genieNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Systematic Zoology Course Information and Specification 11Document29 pagesLecture 1 - Systematic Zoology Course Information and Specification 11English SpeakingNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument45 pagesHepatitisReza MajidiNo ratings yet
- Presentation Phenon N CategoryDocument19 pagesPresentation Phenon N CategorySohaib NasirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 OutlineDocument11 pagesChapter 25 OutlineEvelyn KimNo ratings yet
- Pieris Homo Lathyrus Sapiens OdoratusDocument1 pagePieris Homo Lathyrus Sapiens OdoratusjennieNo ratings yet
- UNIT III. Taxonomy and Systematics-1Document41 pagesUNIT III. Taxonomy and Systematics-1Dion PamittanNo ratings yet
- A. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCDocument1 pageA. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCHannah 晗❾No ratings yet
- Lecture-2&3 Taxonomic Ranks, Phylogenetic TreeDocument52 pagesLecture-2&3 Taxonomic Ranks, Phylogenetic TreejayashreeNo ratings yet
- CBSE 11th Sample BIOLOGY 1Document17 pagesCBSE 11th Sample BIOLOGY 1ALEENA KANNINo ratings yet
- Document 3Document12 pagesDocument 3Sanaya ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Systematics Based On Evolutionary Relationship 1Document13 pagesSystematics Based On Evolutionary Relationship 1Keith Penaso100% (3)
- Invertebrados 2Document17 pagesInvertebrados 2reyes.sammyNo ratings yet
- Angio Classi Systems Material MSC Sem - IIDocument9 pagesAngio Classi Systems Material MSC Sem - IIAtta Ul Mustafa ZainNo ratings yet
- CH 03 BiodiversityDocument9 pagesCH 03 BiodiversityZain NoorNo ratings yet
- Module1 and 2 - Introduction To SystematicsDocument19 pagesModule1 and 2 - Introduction To SystematicsZai AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Classification of BiodiversDocument2 pagesClassification of Biodiverssathish1992No ratings yet
- Education: ScienceDocument14 pagesEducation: ScienceLamiche EdalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Animal Kingdom: Definition of ZoologyDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Animal Kingdom: Definition of ZoologyFabiana GarridoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Animal Kingdom: Definition of ZoologyDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Animal Kingdom: Definition of ZoologyPepe CaramésNo ratings yet