Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Team 10 Phenol Process Senior Design
Team 10 Phenol Process Senior Design
Uploaded by
Fabi OneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Team 10 Phenol Process Senior Design
Team 10 Phenol Process Senior Design
Uploaded by
Fabi OneCopyright:
Available Formats
Phenol Production Process Design
Team 10 – Tiffany Robinson, Daniel Harrell, Dillian Beechler
Organizational Problem Key Economic Results Safety Considerations
ABC Corporation’s resins production unit wants to carry out a study estimate of a plant Total cost per pound of product $0.857/lb
to produce phenol as a raw material at a cheaper cost than the current market price of Component Hazards Toxicity/Dangers
$0.64/lb. The production rate of concern is 190,000 metric tons per year. Total Capital Investment (TCI) $183 MM
Flammable, harmful if swallowed or contacted with skin,
Total annual operating costs $299 MM/yr Acetone
irritant
Basic Flow Diagram and Process Background
Process Economics Cumene
Flammable, toxic, harmful if swallowed or contacted
with skin, irritant, carcinogen, hazardous to
Capital Investment Summary environment
Flammable, toxic, harmful if swallowed or contacted
AMS
with skin, irritant, hazardous to environment
Oxidizing, toxic, corrosive, harmful if swallowed or
CHP
contacted with skin, irritant, hazardous to environment
Combustible, corrosive, harmful if swallowed or
Phenol
contacted with skin, irritant
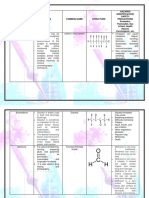
The phenol production process is based on the oxidation and cleavage of cumene.
Oxidation of Cumene (Hock process)[1]: Major Hazards
C6 H5 CH CH3 2 + O2 → C6 H5 C CH3 2 OOH Equipment Installed Cost
1 • Oxygen concentration in oxidation reactor
C6 H5 CH CH3 2 + O2 → CH3 2 C6 H3 CH2 OH
2 • CHP distillation column reboiler
Cleavage reactions to produce phenol and acetone/AMS by-products[1]: • Cleavage reactor
CH3 2 C6 H3 CH2 OH → C6 H4 C2 H3 CH3 + H2 O
C6 H5 C CH3 2 OOH → C6 H5 OH + CH3 COCH3 General Safety
AMS and acetone are by-products of the reactions that are sold for credit. In addition to • Training
the credit received from by-products, there is also fuel credit obtained from the vent in • Proper PPE
the process. Finally, water is the only waste in the process and will be sent to a • Protective systems and alarms
wastewater treatment facility. • Routine inspection and monitoring of process
HYSYS Process Flow Diagram Environmental Considerations
Utilities Cost Summary
Environmental pollution is a major concern for all industrial plants, such as the phenol
production plant. Proper disposal is imperative for maintaining the wellbeing of the
surrounding environment.
For the phenol production process the streams of concern are:
• Vent from 2nd stage separator
• Vent from partial condenser
• Wastewater from acetone-water separation train
The process is comprised of six main steps that include the following:
References
[1] Ullman’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 5th ed., 1985.
[2] The Essential Chemical Industry: Online. 2015. Via http://www.essentialchemicalindustry.org/chemicals/phenol.html
• Cumene oxidation to hydroperoxide [3] Perry, R. H., & Green, D. W. (2008). Perry's chemical engineers' handbook. New York: McGraw-Hill. Table 2-2.
• Cumene hydroperoxide concentration Economic Conclusions [4] University, Safety Officer in Physical Chemistry at Oxford (2005). "Safety (MSDS) data for cumene hydroperoxide".
• Cumene hydroperoxide decomposition/cleavage Retrieved 2015-03-13.
• Cleavage effluent neutralization The production cost for the design process exceeds the current market price of $0.64/lb [5] Richard J. Lewis, Richard J. Lewis (Sr.), Hazardous chemicals desk reference, Publisher Wiley-Interscience, 2008, ISBN 0-
• Product fractionation/purification of phenol and makes the implementation of the design impractical. Unless new 470-18024-2, ISBN 978-0-470-18024-2, 1953 pages
[6] "Cumene".
• Effluent treatment alternative methods or adjustments to optimize the process are determined, executing National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). 4 December 2014. Retrieved 24 February
2015.
the process design is not economically viable. Therefore, it is not recommended that
this design be implemented.
You might also like
- Environmental Impacts and Aspects RegisterDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Impacts and Aspects RegisterSlobodan Jankovic100% (1)
- Rain Water HarvestingDocument30 pagesRain Water Harvestingkaran100% (1)
- Food Plant UtilitiesDocument5 pagesFood Plant UtilitiesPiyush Moradiya67% (3)
- Cod Procedure For HACH DR 2800Document8 pagesCod Procedure For HACH DR 2800Berliana Cahya NingtiasNo ratings yet
- Anthony Hower, Julia Kim, and Stan Kim - Lab 9Document8 pagesAnthony Hower, Julia Kim, and Stan Kim - Lab 9Anthony HowerNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Substances Policy - Assessment Chemical Hazard and Risk AssessmentDocument4 pagesHazardous Substances Policy - Assessment Chemical Hazard and Risk Assessmenthussymian06No ratings yet
- Activity 2. Warning Signs That You Should Know in The LaboratoryDocument3 pagesActivity 2. Warning Signs That You Should Know in The LaboratoryMaryaa Luwizaa Allauigan0% (1)
- CO-001 Gloss Aerosol Paint All ColoursDocument4 pagesCO-001 Gloss Aerosol Paint All ColoursKamil GrzybowskiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Register October 2020Document5 pagesChemical Register October 2020Khaled AnwarNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification in GoodyearDocument4 pagesHazard Identification in GoodyearReksa Indika SuryaNo ratings yet
- CO-015 Diesel Fuel - RedDocument4 pagesCO-015 Diesel Fuel - RedKamil GrzybowskiNo ratings yet
- Inorg Chem AssignmentDocument5 pagesInorg Chem AssignmentRose RatacNo ratings yet
- U1l4s Hazardous MatDocument2 pagesU1l4s Hazardous MatpmcisissengueNo ratings yet
- Chemical Hazard Risk AssessmentDocument1 pageChemical Hazard Risk AssessmentBEA FRANCINE DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Innovative Pharmaceutical Sciences and ResearchDocument18 pagesInternational Journal of Innovative Pharmaceutical Sciences and Researchoja karnilaNo ratings yet
- 8.3.19 Synthesis of Zeolite Using Fly Ash and Its Application For The Treatment of Industrial Waste WaterDocument20 pages8.3.19 Synthesis of Zeolite Using Fly Ash and Its Application For The Treatment of Industrial Waste WaterAmit HanatNo ratings yet
- DAPAR, Sophia Pacaldo, Alec SOMOZA, TrexiaDocument6 pagesDAPAR, Sophia Pacaldo, Alec SOMOZA, TrexiaSophia Marie DaparNo ratings yet
- MSDS H2O2 Thai Food GradeDocument2 pagesMSDS H2O2 Thai Food GradeArdita ElliyantiNo ratings yet
- Envi Sci 1Document1 pageEnvi Sci 1TRISHAANN RUTAQUIONo ratings yet
- Common Names Iupac Name Uses Possible Toxicity: AminesDocument4 pagesCommon Names Iupac Name Uses Possible Toxicity: AminesDan FruelNo ratings yet
- Sub Module 4&5Document8 pagesSub Module 4&5angelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- Prospero Jerome A. Intano May 23, 2019 BSA 101 Environmental Science Block #4 AssignmentDocument2 pagesProspero Jerome A. Intano May 23, 2019 BSA 101 Environmental Science Block #4 AssignmentIntano Prospero JeromeNo ratings yet
- SOFW - Eco Friendly Ingredients For Biodegradable Cosmetic ProductsDocument6 pagesSOFW - Eco Friendly Ingredients For Biodegradable Cosmetic ProductsDaniela DimasNo ratings yet
- HT RA 162 and HT RA 162 1working With Wet and Dry Cement and Concrete Products RedactedDocument10 pagesHT RA 162 and HT RA 162 1working With Wet and Dry Cement and Concrete Products RedactedMohamed KatouraNo ratings yet
- HT RA 162 and HT RA 162 1working With Wet and Dry Cement and Concrete Products RedactedDocument10 pagesHT RA 162 and HT RA 162 1working With Wet and Dry Cement and Concrete Products RedactedjohnNo ratings yet
- Wingstay LDocument2 pagesWingstay LChandra SagarNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Surfaktan Di IndustriDocument27 pagesAplikasi Surfaktan Di IndustriDzaki AssuhudNo ratings yet
- Tujuan: Efek Toksik Tumbuhan RacunDocument10 pagesTujuan: Efek Toksik Tumbuhan RacunCatherina AileenNo ratings yet
- Section 7 ChemicalsDocument8 pagesSection 7 ChemicalsUnais RahmanNo ratings yet
- Basak 2014Document11 pagesBasak 2014ERIKO DARMAWANNo ratings yet
- Chemical Disinfectants Against SARS-CoV-2Document3 pagesChemical Disinfectants Against SARS-CoV-2Dr.Kamlesh BariNo ratings yet
- Open Burning Chemical ListDocument7 pagesOpen Burning Chemical ListsilhouettegurlzNo ratings yet
- Coshh Assessment: Hi-Stick Spray Paint Contract Number:: Substance Properties and Hazards LabelsDocument4 pagesCoshh Assessment: Hi-Stick Spray Paint Contract Number:: Substance Properties and Hazards LabelsSafety ExpertNo ratings yet
- 12 MPotentially MHarmful MIngredients MCommon MCosmetic MProductsDocument2 pages12 MPotentially MHarmful MIngredients MCommon MCosmetic MProductsivanna obayaNo ratings yet
- Rona LynDocument2 pagesRona Lyncesarioronalyn042No ratings yet
- Chemical - Safety - Guide - 1701469217 2023-12-01 22 - 20 - 24Document21 pagesChemical - Safety - Guide - 1701469217 2023-12-01 22 - 20 - 24abdullah shafeiNo ratings yet
- GEM07 Hazardous Waste Management enDocument5 pagesGEM07 Hazardous Waste Management enمحمد سلمانNo ratings yet
- Globally Harmonized SystemDocument1 pageGlobally Harmonized SystemVentas AlbenovaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet TemplateDocument2 pagesSafety Data Sheet TemplateCheyuNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Plastic Bottles: ReferencesDocument1 pageCase Study: Plastic Bottles: ReferencesENo ratings yet
- Case Study: Plastic Bottles: ReferencesDocument1 pageCase Study: Plastic Bottles: ReferencesENo ratings yet
- VOC Reducer StarbetterDocument22 pagesVOC Reducer Starbettermanishsingh811No ratings yet
- Whmis: Workplace Hazardous Materials Information SystemDocument2 pagesWhmis: Workplace Hazardous Materials Information SystemruksarNo ratings yet
- Combustible Liquid and VaporDocument3 pagesCombustible Liquid and VaporShinu DiazNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry.Document1 pageEnvironmental Chemistry.sarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Ojapps - 2020122216323733Document10 pagesOjapps - 2020122216323733brahiman TRAORENo ratings yet
- 01 Module 2.2 Health Hazards Rev 3Document44 pages01 Module 2.2 Health Hazards Rev 3Jeric Dela Cruz QuiminalesNo ratings yet
- Nail Polish BrochurekbbjkkbjbkjDocument2 pagesNail Polish Brochurekbbjkkbjbkjdibb dabNo ratings yet
- Herbicidecomparisontable PDFDocument2 pagesHerbicidecomparisontable PDFOlgalycosNo ratings yet
- MSDS Palm Tree DustDocument13 pagesMSDS Palm Tree Dusterik mulyanaNo ratings yet
- Portfolio - Business ModelDocument3 pagesPortfolio - Business ModelYuanita Kumala DewiNo ratings yet
- CYCOLOY™ FR Resins - C2950 - Asia - MSDSDocument8 pagesCYCOLOY™ FR Resins - C2950 - Asia - MSDSSơn Nguyễn ĐắcNo ratings yet
- Glatt FA 104 Process Technologies To Optimize Detergent Manufacturing en SOFW 2020 10Document5 pagesGlatt FA 104 Process Technologies To Optimize Detergent Manufacturing en SOFW 2020 10joeolaabidakunNo ratings yet
- Chemical Inventory Sheet: Name of Company/Production UnitDocument4 pagesChemical Inventory Sheet: Name of Company/Production UnitNur E Alam NuruNo ratings yet
- Corning Guardiant™ Antimicrobial Particles: WarningDocument1 pageCorning Guardiant™ Antimicrobial Particles: WarningmulysieNo ratings yet
- Ceramides - 2 JurnalDocument54 pagesCeramides - 2 Jurnaldian kaizenNo ratings yet
- Euro Product Excellence RevDocument1 pageEuro Product Excellence Revkoko manjitNo ratings yet
- Professional: The Environmental Impact of DentistryDocument6 pagesProfessional: The Environmental Impact of DentistryAlexandru Codrin-IonutNo ratings yet
- BOSH ReviewDocument8 pagesBOSH Reviewvispomichael6No ratings yet
- PR Bio-Tanning MaterialDocument12 pagesPR Bio-Tanning MaterialÑojib Ëasar ProttoyNo ratings yet
- Green Paper: A Guide To Grass Paper by ModelDocument4 pagesGreen Paper: A Guide To Grass Paper by ModelVenchie Vic FabreoNo ratings yet
- Annex 7: Table To Accompany Text in Chapter 2Document40 pagesAnnex 7: Table To Accompany Text in Chapter 2Dilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- PTT259 Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME)Document15 pagesPTT259 Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME)Nurshaqina Sufian67% (3)
- Best Available Techniques (BAT) For Waste Water and Waste GasDocument667 pagesBest Available Techniques (BAT) For Waste Water and Waste GasHuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Wicomico River Watershed Report 2020 PDFDocument8 pagesWicomico River Watershed Report 2020 PDFapi-251332269No ratings yet
- EFSEC 2013-01 - Compiled PDF Volume IDocument872 pagesEFSEC 2013-01 - Compiled PDF Volume IEric LaBrantNo ratings yet
- Runoff and Peak Flow Estimation - NRCS MethodDocument13 pagesRunoff and Peak Flow Estimation - NRCS MethodSoufiane ELKHALFINo ratings yet
- Bioremediation: by Nathan FordDocument19 pagesBioremediation: by Nathan Fordsonam snehaNo ratings yet
- Paula Jimenez TorresDocument2 pagesPaula Jimenez TorresPaula JiménezNo ratings yet
- Tait Station Low Dam RemovalDocument2 pagesTait Station Low Dam RemovalAnonymous DyzkF1inINo ratings yet
- Dalmau Population and DischargeDocument2 pagesDalmau Population and DischargeTechnowisdom ConsultantsNo ratings yet
- DB6X - Method Statement TemplateDocument13 pagesDB6X - Method Statement TemplateRakan PierwszyNo ratings yet
- POISONED TALK by Raymond WilsonDocument28 pagesPOISONED TALK by Raymond WilsonEffa Ahmad AzamNo ratings yet
- Water Purification MethodsDocument23 pagesWater Purification Methodsboy80% (5)
- Mata Pelajaran: Bahasa Inggris Sat. Pendidikan: SMA Kelas / Program: XII/ IPS (Dua Belas/ IPS)Document13 pagesMata Pelajaran: Bahasa Inggris Sat. Pendidikan: SMA Kelas / Program: XII/ IPS (Dua Belas/ IPS)Jumadil HakimNo ratings yet
- W - WTR - Chapter - Oil Interceptor PDFDocument22 pagesW - WTR - Chapter - Oil Interceptor PDFNajam24No ratings yet
- Enve 208 Experiment 3Document7 pagesEnve 208 Experiment 3mihrican302No ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusVinothNo ratings yet
- Flyer Sewage Sludge DryingDocument6 pagesFlyer Sewage Sludge Dryingkosmc123No ratings yet
- Unit - 1 - Basic Concepts of EIADocument21 pagesUnit - 1 - Basic Concepts of EIAdivyaintworkNo ratings yet
- Air Stripping TowerDocument5 pagesAir Stripping Towerchristian_ignacioNo ratings yet
- Draft Brunswick CDM Smith Report March 2018 220pm PDFDocument68 pagesDraft Brunswick CDM Smith Report March 2018 220pm PDFAnonymous 90jptQ5wANo ratings yet
- City of Malabon UniversityDocument10 pagesCity of Malabon UniversityMikaela HendersonNo ratings yet
- Topic: Water and Land Pollution Its Causes and EffectsDocument45 pagesTopic: Water and Land Pollution Its Causes and Effectsrajivs0911100% (3)
- Environmental Quality (Sewage) Regulations 2009Document29 pagesEnvironmental Quality (Sewage) Regulations 2009YudhisthiraNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment OptionsDocument4 pagesWaste Water Treatment OptionsGreen Action Sustainable Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Apes 1.4-1.8Document2 pagesApes 1.4-1.8Batoul MortadaNo ratings yet
- Innnnnnnnnnn Cho ConDocument68 pagesInnnnnnnnnnn Cho ConKevin Quach 1No ratings yet
- Difference Between Types of Trickling FiltersDocument1 pageDifference Between Types of Trickling FiltersFatima AnwarNo ratings yet