Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Extracted Pages From File - 5ec533c798843
Uploaded by
Mubarak AL-GrafiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Extracted Pages From File - 5ec533c798843
Uploaded by
Mubarak AL-GrafiCopyright:
Available Formats
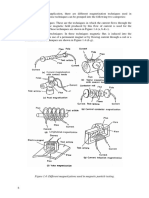
The applications of visual testing include:
(1) Checking of the surface condition of the test specimen.
(2) Checking of alignment of mating surfaces.
(3) Checking of shape of the component.
(4) Checking for evidence of leaking.
(5) Checking for internal side defects.
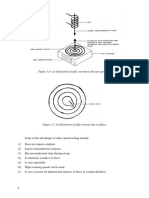
1.1.4. Liquid penetrant testing (PT)
This is a method which can be employed for the detection of open-to-surface discontinuities
in any industrial product which is made from a non-porous material. This method is widely used
for testing of non-magnetic materials. In this method a liquid penetrant is applied to the surface of
the product for a certain predetermined time, after which the excess penetrant is removed from
the surface. The surface is then dried and a developer is applied to it. The penetrant which
remains in the discontinuity is absorbed by the developer to indicate the presence as well as the
location, size and nature of the discontinuity. The process is illustrated in Figure 1.2.
Penetrants used are either visible dye penetrant or fluorescent dye penetrant. The inspection
for the presence of visible dye indications is made under white light while inspection of presence
of indications by fluorescent dye penetrant is made under ultraviolet (or black) light under
darkened conditions. The liquid penetrant processes are further sub-divided according to the
method of washing of the specimen. The penetrants can be: (i) water-washable, (ii) post-
emulsifiable, i.e. an emulsifier is added to the excess penetrant on surface of the specimen to
make it water-washable, and (iii) solvent removable, i.e. the excess penetrant is needed to be
dissolved in a solvent to remove it from the test specimen surface. In order of decreasing
sensitivity and decreasing cost, the liquid penetrant processes can be listed as:
(1) Post emulsifiable fluorescent dye penetrant.
(2) Solvent removable fluorescent dye penetrant.
(3) Water washable fluorescent dye penetrant.
(4) Post emulsifiable visible dye penetrant.
(5) Solvent removable visible dye penetrant.
(6) Water washable visible dye penetrant.
Some of the advantages of liquid penetrant testing are as follows:
(1) Relatively low cost.
(2) Highly portable NDT method.
(3) Highly sensitive to fine, tight discontinuities.
(4) Fairly simple method.
(5) Can be used on a variety of materials.
(6) All surface discontinuities are detected in one operation, regardless of orientation.
You might also like
- 1.1.4. Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)Document3 pages1.1.4. Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)Tee Klong RungNo ratings yet
- 2 2Document11 pages2 2RAJESH. RNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant InspDocument5 pagesDye Penetrant InspVysakh VasudevanNo ratings yet
- Often Referenced StandardsDocument18 pagesOften Referenced StandardssriramNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant InspectionDocument5 pagesDye Penetrant Inspectionrajasekar21No ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant TestingDocument64 pagesLiquid Penetrant TestingLeon Heart FCNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant Testing ModuleDocument59 pagesLiquid Penetrant Testing ModuleDITANo ratings yet
- Module1 Testing and Flaw Detection of Materials and ComponentsDocument12 pagesModule1 Testing and Flaw Detection of Materials and ComponentsHari GovindNo ratings yet
- NDT Lecture05 2015Document39 pagesNDT Lecture05 2015Miruna Clinciu100% (1)
- Dye Penetrant InspectionDocument5 pagesDye Penetrant Inspectionrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant InspectionDocument5 pagesDye Penetrant InspectiontechzonesNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant PresentationDocument98 pagesLiquid Penetrant PresentationAkhil Balachandran100% (9)
- General Knowledge: Specific ObjectivesDocument33 pagesGeneral Knowledge: Specific ObjectivesJahan ZebNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Surface Gears MethodsDocument12 pagesModule 2 Surface Gears MethodsNAVEEN H V MENo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant Inspection: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument59 pagesDye Penetrant Inspection: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaPratik Karekar0% (1)
- PT 2Document91 pagesPT 2safeer ahmadNo ratings yet
- LPTDocument22 pagesLPTPratik SalveNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant Inspection 3Document24 pagesLiquid Penetrant Inspection 3Taha KhanNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant Inspection - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesDye Penetrant Inspection - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaviswamanoj100% (1)
- EXPERIMENT No.: - Liquid Penetrant TestDocument6 pagesEXPERIMENT No.: - Liquid Penetrant TestVandan GundaleNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant InspectionDocument15 pagesDye Penetrant InspectionUwaiz Qurni IINo ratings yet
- Nondestructive Evaluation (NDE)Document14 pagesNondestructive Evaluation (NDE)Zahir Rayhan JhonNo ratings yet
- DPTDocument10 pagesDPTShabbir HassanNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant Inspection (DPI) - Liquid Penetrant Inspection (LPI) - Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)Document9 pagesDye Penetrant Inspection (DPI) - Liquid Penetrant Inspection (LPI) - Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)ISHITA ROY CHOUDHURYNo ratings yet
- NDT Lecture NotesDocument16 pagesNDT Lecture Notesupender100% (2)
- Dye Penetration TestingDocument4 pagesDye Penetration TestingMahrukh JavedNo ratings yet
- PTDocument217 pagesPTkhaled saadnehNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant TestingDocument20 pagesLiquid Penetrant Testingajayghosh3140No ratings yet
- Penetrant RaportDocument6 pagesPenetrant RaportMeritan BaballariNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant InspectionDocument6 pagesDye Penetrant InspectionHabib ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant TestingDocument20 pagesLiquid Penetrant TestingsanjibkrjanaNo ratings yet
- Penetrant Non Destructive Testing. Theory and Application?Document3 pagesPenetrant Non Destructive Testing. Theory and Application?SimranAhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge: 1.1 Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) 1.1.1 Definition and Nature of NDT TechnologyDocument44 pagesGeneral Knowledge: 1.1 Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) 1.1.1 Definition and Nature of NDT TechnologyMirza Safeer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant Testing PDFDocument20 pagesLiquid Penetrant Testing PDFgueridiNo ratings yet
- Dye PenetrantDocument17 pagesDye Penetrantsen_subhasis_58No ratings yet
- PT 001Document18 pagesPT 001ziyadhelaly998No ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Junagadh: Liquid Penerant TestingtDocument16 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Junagadh: Liquid Penerant TestingtArvind DedunNo ratings yet
- LPT Study Material LatestDocument53 pagesLPT Study Material LatestManish SinghNo ratings yet
- PT Level IIDocument161 pagesPT Level IIJerry100% (5)
- Experiment No.3 Dye Penetration TestDocument4 pagesExperiment No.3 Dye Penetration TestChristian D. AllanaNo ratings yet
- 4 Intro To Penetrant 03092013 OKDocument27 pages4 Intro To Penetrant 03092013 OKnishant kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Non Destructive Testing - Dye Penetrant InspectionDocument6 pagesNon Destructive Testing - Dye Penetrant InspectionKevin ThomasNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge: 1.1 Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) 1.1.1 Definition and Nature of NDTDocument28 pagesGeneral Knowledge: 1.1 Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) 1.1.1 Definition and Nature of NDTAsad KhanNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrantion Test: Greated byDocument25 pagesLiquid Penetrantion Test: Greated byشمس الضحىNo ratings yet
- Penetrant Testing NotesDocument7 pagesPenetrant Testing NotesHarry FrankNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant InspectionDocument2 pagesDye Penetrant InspectionsuparnaNo ratings yet
- ASNT Sample TestDocument71 pagesASNT Sample Testshabbir626No ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant InspectionDocument3 pagesLiquid Penetrant InspectionrenjisrsNo ratings yet
- Lec7 MaintenancePlanningDocument25 pagesLec7 MaintenancePlanningtarekhadad99No ratings yet
- AC 43.13-1B Section 5 Penetrant InspectionDocument8 pagesAC 43.13-1B Section 5 Penetrant Inspection320338100% (1)
- Inspecting Welds With Liquid PenetrantDocument4 pagesInspecting Welds With Liquid PenetrantHizbul WathanNo ratings yet
- Penetrant Testing: Principles, Techniques, Applications and Interview Q&AFrom EverandPenetrant Testing: Principles, Techniques, Applications and Interview Q&ANo ratings yet
- Current Advances in Drug Delivery Through Fast Dissolving/Disintegrating Dosage FormsFrom EverandCurrent Advances in Drug Delivery Through Fast Dissolving/Disintegrating Dosage FormsNo ratings yet
- Systematic Methods of Water Quality Parameters Analysis: Analytical MethodsFrom EverandSystematic Methods of Water Quality Parameters Analysis: Analytical MethodsNo ratings yet
- Solid-Liquid Filtration: A User’s Guide to Minimizing Cost and Environmental Impact, Maximizing Quality and ProductivityFrom EverandSolid-Liquid Filtration: A User’s Guide to Minimizing Cost and Environmental Impact, Maximizing Quality and ProductivityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chemical Modification of Solid Surfaces by the Use of AdditivesFrom EverandChemical Modification of Solid Surfaces by the Use of AdditivesNo ratings yet
- Fingerprint Development Techniques: Theory and ApplicationFrom EverandFingerprint Development Techniques: Theory and ApplicationNo ratings yet
- NDE Handbook: Non-Destructive Examination Methods for Condition MonitoringFrom EverandNDE Handbook: Non-Destructive Examination Methods for Condition MonitoringKnud G. BøvingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- 597 Business Ideas You Can Start From Home Doing What You LOVE! 230309 133446 2Document1 page597 Business Ideas You Can Start From Home Doing What You LOVE! 230309 133446 2Mubarak AL-GrafiNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From File - 5ec533c79884324Document1 pageExtracted Pages From File - 5ec533c79884324Mubarak AL-GrafiNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From File - 5ec533c79884335Document1 pageExtracted Pages From File - 5ec533c79884335Mubarak AL-GrafiNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From File - 5ec533c7988431Document1 pageExtracted Pages From File - 5ec533c7988431Mubarak AL-GrafiNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From File - 5ec533c79884333Document1 pageExtracted Pages From File - 5ec533c79884333Mubarak AL-GrafiNo ratings yet
- Me 434 NDT 3Document1 pageMe 434 NDT 3Mubarak AL-GrafiNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From File - 5ec533c79884322Document1 pageExtracted Pages From File - 5ec533c79884322Mubarak AL-GrafiNo ratings yet
- Theory and Practice of Non Destructive Testing - Course2Document1 pageTheory and Practice of Non Destructive Testing - Course2Mubarak AL-GrafiNo ratings yet
- Me 434 NDT 1Document1 pageMe 434 NDT 1Mubarak AL-GrafiNo ratings yet
- NDT 5Document1 pageNDT 5Mubarak AL-GrafiNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument4 pagesExerciseAshebirNo ratings yet
- Royal Continental, Niger Project - Pi - 3751Document9 pagesRoyal Continental, Niger Project - Pi - 3751ashishvaidNo ratings yet
- MTPDF4 - Module 4 Main PDF LessonDocument35 pagesMTPDF4 - Module 4 Main PDF LessonEunnicePanaliganNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of A High-Speed Shaft Crack: Technicalarticle-Peer-ReviewedDocument12 pagesFailure Analysis of A High-Speed Shaft Crack: Technicalarticle-Peer-RevieweddouglasncamiloNo ratings yet
- Analytical ChemistryDocument5 pagesAnalytical ChemistryChristian FloresNo ratings yet
- Bio Gas Final ProjectDocument75 pagesBio Gas Final ProjectMowafk AlsharabyNo ratings yet
- Polymer Chemistry For B.SC - Sem-6th PDFDocument49 pagesPolymer Chemistry For B.SC - Sem-6th PDFSohel Ansari0% (1)
- A Fatigue Damage Model of Composite Materials PDFDocument5 pagesA Fatigue Damage Model of Composite Materials PDFpanbuNo ratings yet
- 2010developing Psychrometric Chart For Palestine Main Locations Using Matlab Soft Ware Computer ProgramDocument69 pages2010developing Psychrometric Chart For Palestine Main Locations Using Matlab Soft Ware Computer ProgramluqmanNo ratings yet
- Slide 11 Extrusion and Wire DrawingDocument53 pagesSlide 11 Extrusion and Wire Drawingjohn doeNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus, Reactive, PhosVer 3 Method 8048, 02-2009, 9th EdDocument7 pagesPhosphorus, Reactive, PhosVer 3 Method 8048, 02-2009, 9th EdzvjesosNo ratings yet
- Elvacite® 2016 Acrylic Resin: ApplicationsDocument4 pagesElvacite® 2016 Acrylic Resin: ApplicationsPaola Lopez100% (2)
- Poly - Mer: Cartoon Schematic of Polymer MoleculesDocument7 pagesPoly - Mer: Cartoon Schematic of Polymer MoleculesElenaDiSavoiaNo ratings yet
- 8-Heat Transfer-2016 - Ans Key-Master FileDocument12 pages8-Heat Transfer-2016 - Ans Key-Master FileLourdes Cagungun100% (2)
- Toluene Methylation To Para-XyleneDocument164 pagesToluene Methylation To Para-XyleneAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Johnson Rajkot Elite Plus Elite WallDocument148 pagesJohnson Rajkot Elite Plus Elite WallSiddhartha AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 InorgDocument5 pagesQuiz 1 InorgDanielle Lois AbagNo ratings yet
- Material TestingDocument35 pagesMaterial TestinghanyNo ratings yet
- 10 Chapter 16 Composite MaterialsDocument27 pages10 Chapter 16 Composite MaterialsZain FarhanNo ratings yet
- Fire ExtinguisherDocument21 pagesFire ExtinguisherAbdulrahman JradiNo ratings yet
- ANTHE-2020 - (VIII Moving To IX) - (Code-O) - 13-12-2020Document14 pagesANTHE-2020 - (VIII Moving To IX) - (Code-O) - 13-12-2020Lakshman RaiNo ratings yet
- Kyra - 2 Storey Linked Homes Launch at Bandar Bukit RajaDocument26 pagesKyra - 2 Storey Linked Homes Launch at Bandar Bukit RajaSime Darby PropertyNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Simulation of Temperature and Strain Distribution in Al2024 Aluminum Alloy by Friction Stir WeldingDocument5 pagesFinite Element Simulation of Temperature and Strain Distribution in Al2024 Aluminum Alloy by Friction Stir Weldingabhilash sharanNo ratings yet
- Al. Alloy Chemical CompositionDocument9 pagesAl. Alloy Chemical Compositionketan1965No ratings yet
- AttakaDocument6 pagesAttakaM Alim Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Bentogliss 121 enDocument2 pagesBentogliss 121 enAdityaNo ratings yet
- FINAL SIP PRINT OUT Guransh 7sepDocument58 pagesFINAL SIP PRINT OUT Guransh 7sepAmbuj Roy100% (1)
- Ec101 Semi ConductorsDocument68 pagesEc101 Semi ConductorsCaptain Tech8No ratings yet
- Limit States Design in Structural Steel: G.L. Kulak and G.Y. Grondin 9 Edition, 1 Printing 2010Document19 pagesLimit States Design in Structural Steel: G.L. Kulak and G.Y. Grondin 9 Edition, 1 Printing 2010Rania Kanj KiwanNo ratings yet
- Anchor Cage DocumentsDocument13 pagesAnchor Cage DocumentsDan BitcaNo ratings yet