Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PS - Week 6 - 4TH Quarter
PS - Week 6 - 4TH Quarter
Uploaded by
FionOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PS - Week 6 - 4TH Quarter
PS - Week 6 - 4TH Quarter
Uploaded by
FionCopyright:
Available Formats
Name:
Section/Strand:
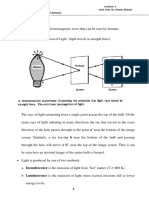
Test Yourself
Answer the question completely.
Instruction: Explain the following Physical Optics terms.
Physical Optics terms Description
Scintillation When exposed to an ionizing radiation event, a scintillator emits a
brief pulse of light (such as an x-ray or gamma ray or alpha particle).
The total energy of a light pulse is normally directly proportional to
the energy of incident ionizing radiation, making it useful as an
energy-dispersive radiation detector in spectroscopy.
Constructive interference Constructive interference can be used to enhance a signal and make
detection easier; for example, an interferometer can be used to
measure the diameter of a star.
Electromagnetic wave An electromagnetic wave is a wave made up of perpendicularly
oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Electromagnetic waves are
energy photons that travel through space carrying electromagnetic
radiation. They do not require any physical medium to spread. This
means that they can travel even in a vacuum.
Activity
Name: Grade/Section:
Activity #1
Directions: Make a collage about the different Atmospheric Optics events
Explanation about the Collage:
This collage consists of different atmospheric optics events. We have rainbows, eclipses,
aurora borealis, and many more. Atmospheric optical phenomena occur when visual
events occur in the Earth's atmosphere as a result of light reflection, refraction, and
diffraction by solid particles, liquid droplets, and other atmospheric elements.
You might also like
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itFrom EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itNo ratings yet
- Unified Field Theory in a Nutshell1: The Quest for the Theory of EverythingFrom EverandUnified Field Theory in a Nutshell1: The Quest for the Theory of EverythingNo ratings yet
- Tour of The Ems Tagged v7Document36 pagesTour of The Ems Tagged v7Mark CaoNo ratings yet
- Lighting Handbook 2Document263 pagesLighting Handbook 2Boris TepavacNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument17 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAviation/Space History Library100% (4)
- 1.1 Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument17 pages1.1 Electromagnetic SpectrumShreyas SvNo ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument21 pagesSpectrosAman Rathore100% (1)
- CBSE XII Chemistry Project Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsDocument21 pagesCBSE XII Chemistry Project Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsRichie SinghNo ratings yet
- Laser Scanner TechnologyDocument22 pagesLaser Scanner TechnologyEng M G ElkhateebNo ratings yet
- Ps - Week 6 - 4th QuarterDocument3 pagesPs - Week 6 - 4th QuarterFionNo ratings yet
- Reyhan Qomara - Assignment 1 Optical Engineering Class DDocument5 pagesReyhan Qomara - Assignment 1 Optical Engineering Class DReyhan QomaraNo ratings yet
- Zwinkels - 2015 - Light Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument9 pagesZwinkels - 2015 - Light Electromagnetic SpectrumFirda SyavieraNo ratings yet
- Phy 104 Atomic SpectraDocument24 pagesPhy 104 Atomic SpectraAisha abba HabibNo ratings yet
- Opt 212 Physical OpticsDocument77 pagesOpt 212 Physical OpticsEshiramhe AugustineNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction in CrystalDocument67 pagesX-Ray Diffraction in CrystalAnonymous BW2VsFifi9No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Introduction To RadiationDocument36 pagesChapter 3 Introduction To Radiationhailemicael mesfinNo ratings yet
- Description: Electromagnetic Radiation Charged ParticlesDocument8 pagesDescription: Electromagnetic Radiation Charged ParticlesfaithNo ratings yet
- Light: Waves in Empty SpaceDocument7 pagesLight: Waves in Empty Spacejean magdayNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument15 pagesChemSachin RaiNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document16 pagesSession 2KithminiNo ratings yet
- CBSE XII Chemistry/Physics Project Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsDocument21 pagesCBSE XII Chemistry/Physics Project Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsshantanurNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsDocument21 pagesSpectroscopy and Its Applicationspkkalai112No ratings yet
- HAFTA XRD-1-dönüştürüldüDocument26 pagesHAFTA XRD-1-dönüştürüldüKatrina Ranee RamosNo ratings yet
- 14 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovDocument16 pages14 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovKVP LyricsNo ratings yet
- Optics 1Document5 pagesOptics 1asopNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Radiation: Interaction of Radiation With MatterDocument49 pages1.1 Radiation: Interaction of Radiation With MatterShiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Afs Ojhar: Project Submitted By: Sumit Anand Class: XII-ADocument17 pagesAfs Ojhar: Project Submitted By: Sumit Anand Class: XII-ASumit AnandNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Spectroscopy: Ricardo O. Louro Oeiras, Outubro 2015Document56 pagesIntroduction To Spectroscopy: Ricardo O. Louro Oeiras, Outubro 2015salvador lopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 X Ray Diffraction in CrystalDocument67 pagesChapter3 X Ray Diffraction in CrystalAymen AnouneeNo ratings yet
- PM289 ch1Document35 pagesPM289 ch1naveedabc986No ratings yet
- SpectroscopyetextDocument23 pagesSpectroscopyetextTejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Physics - Vol 2 Unit - 7: Name: Standard: Section: School: Exam NoDocument9 pagesPhysics - Vol 2 Unit - 7: Name: Standard: Section: School: Exam NoJagan EashwarNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Live Class-3 Teacher NotesDocument22 pagesAtomic Structure Live Class-3 Teacher Notestarun singhNo ratings yet
- RADIATION, SPECTROSCOPY and TELESCOPESDocument19 pagesRADIATION, SPECTROSCOPY and TELESCOPESapi-3744104No ratings yet
- A Level GCSE PhysicsDocument5 pagesA Level GCSE PhysicsKeshav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Physics 12 ADocument13 pagesPhysics 12 ALight yagami is KIRANo ratings yet
- SCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLDocument42 pagesSCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLErick Wangila WanyonyiNo ratings yet
- 64359b020fd8f800181c4e8b - ## - Light - Reflection and Refraction 01: Class Notes - (Udaan 2024)Document14 pages64359b020fd8f800181c4e8b - ## - Light - Reflection and Refraction 01: Class Notes - (Udaan 2024)Lal BhaiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Yogesh Singh Class: Xii B Submitted To: Ms - Sharaddha NarwariyaDocument36 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Yogesh Singh Class: Xii B Submitted To: Ms - Sharaddha NarwariyaSinghnarwariyaNo ratings yet
- Welcome: To The World ofDocument33 pagesWelcome: To The World ofSREEJITH KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Physics 1Document81 pagesPhysics 1sharad_mumNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument11 pagesProjectMehak Parvez HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Pemr PDFDocument11 pagesPemr PDFJoseph NyabugaNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum 1Document11 pagesThe Electromagnetic Spectrum 1Joseph NyabugaNo ratings yet
- Investigation Project PhysicsDocument16 pagesInvestigation Project Physicskartikdutt.08No ratings yet
- Phenomenon of LightDocument5 pagesPhenomenon of LightPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes I 2016Document38 pagesLecture Notes I 2016Edward Baleke SsekulimaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 ReviewerDocument6 pagesGrade 10 ReviewerDino M PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature, Radiation and Matter. Byju'sDocument83 pagesDual Nature, Radiation and Matter. Byju'sGaurav BhandariNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Science Exam ReviewerDocument6 pages1st Term Science Exam ReviewerAndie MorenoNo ratings yet
- Solid State Chapter 2Document75 pagesSolid State Chapter 2Ambreen KhanNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect: Engy DiabDocument34 pagesPhotoelectric Effect: Engy DiabHazem DiabNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter: Can You Recall?Document35 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Matter: Can You Recall?RAVINDRA WAYKOLENo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Chem1101: Chemistry (Eee/Coe)Document11 pagesAtomic Structure: Chem1101: Chemistry (Eee/Coe)Nabil AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Evanescent WaveDocument1 pageEvanescent WaveVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Quantum Physics Part 1Document24 pagesTopic 7 Quantum Physics Part 1coborotNo ratings yet
- Defraction-Of-Light (1) - Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesDefraction-Of-Light (1) - Investigatory ProjectSankar AnanthyaNo ratings yet
- Chem 3052 CHAPTER 1 (Introduction To Spectroscopy)Document22 pagesChem 3052 CHAPTER 1 (Introduction To Spectroscopy)ashenafiNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Activity Sheet WK 2Document2 pagesUcsp Activity Sheet WK 2FionNo ratings yet
- Perdev - Week 6Document3 pagesPerdev - Week 6FionNo ratings yet
- Diass - Week 2 - 3rd QuarterDocument2 pagesDiass - Week 2 - 3rd QuarterFionNo ratings yet
- Oc - Week 3 - 2nd Quarter - Answer SheetDocument2 pagesOc - Week 3 - 2nd Quarter - Answer SheetFionNo ratings yet