Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrolysis
Electrolysis
Uploaded by
MUHAMMAD ISA ALI 109270 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageThe document discusses electrolysis and the processes that occur at the anode and cathode during different electrolysis reactions. It provides examples of electrolysis of barium chloride, copper sulfate, and molten aluminum oxide. For barium chloride, chlorine gas forms at the anode if concentrated, and oxygen forms if dilute. For copper sulfate, copper deposits on the cathode, copper dissolves from the anode if copper electrodes are used, and colorless gas forms at the anode with carbon electrodes. For molten aluminum oxide, aluminum forms at the cathode, oxygen forms at the anode, and graphite electrodes are used.
Original Description:
Original Title
electrolysis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses electrolysis and the processes that occur at the anode and cathode during different electrolysis reactions. It provides examples of electrolysis of barium chloride, copper sulfate, and molten aluminum oxide. For barium chloride, chlorine gas forms at the anode if concentrated, and oxygen forms if dilute. For copper sulfate, copper deposits on the cathode, copper dissolves from the anode if copper electrodes are used, and colorless gas forms at the anode with carbon electrodes. For molten aluminum oxide, aluminum forms at the cathode, oxygen forms at the anode, and graphite electrodes are used.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageElectrolysis
Electrolysis
Uploaded by
MUHAMMAD ISA ALI 10927The document discusses electrolysis and the processes that occur at the anode and cathode during different electrolysis reactions. It provides examples of electrolysis of barium chloride, copper sulfate, and molten aluminum oxide. For barium chloride, chlorine gas forms at the anode if concentrated, and oxygen forms if dilute. For copper sulfate, copper deposits on the cathode, copper dissolves from the anode if copper electrodes are used, and colorless gas forms at the anode with carbon electrodes. For molten aluminum oxide, aluminum forms at the cathode, oxygen forms at the anode, and graphite electrodes are used.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
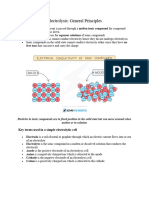
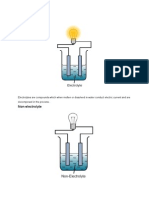
ANODE:
anion
positve
forms non metal(except hydrogen)
attracts negative charged ions
Negative ions (anions) in the electrolyte move towards the anode where they lose
electrons
CATHODE
cathion
negative
forms metals or hydrogen
Positive ions (cations) in the electrolyte move towards the cathode where they gain
electrons
For a concentrated solution of barium chloride, the Cl- ions are
discharged more readily than the OH- ions, so chlorine gas is produced at the
anode.
If the solution is dilute however only the OH- ion is discharged and so oxygen
would be formed.
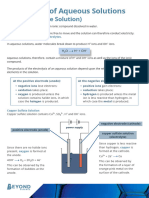
observations during electrolysis of aqueous copper(II)sulfate:
copper metal is deposited on the cathode in a reddish pink colour
if copper electrodes then copper anode dissloves.
observations during electrolysis of aqueous copper(II)sulfate with carbon
electrodes:
at anode: colorless gas forms
electrlyte: blue color fades beacause copper ions removed (at negative ele ctrode)
cathode: pink solid forms
As the copper ions from the electrolyte get discharged, the blue colour of copper
sulphate becomes paler
and finally, a colourless sulphuric acid is formed by the combination of H+ and
SO42− ions in the
electrolyte.
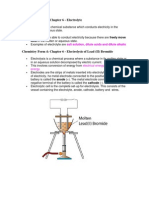
electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide:
cryolite is added to oxide to extract pure aluminium to reduce energy costs
cathode: Al(3+) +3e → Al (reduced) product= liquid aluminium
anode: 2O(2-)→O(2)-4e (oxidised) peoduct= oxygen
graphite elctrodes as they can conduct electricity
aluminium collected at bottom
aluminium and aluminium oxide both are liquid during this process
the positive carbpn electrodes lose mass during this process and needs regular
replacement.
You might also like
- Screenshot 2022-06-19 at 3.39.23 PMDocument47 pagesScreenshot 2022-06-19 at 3.39.23 PMWalaa AdelNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument17 pagesElectrolysisSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesElectrolysisResearch LifeNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of AueqousDocument8 pagesElectrolysis of AueqousSelinawong Win Jing SelinawongNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesElectrolysisSafwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Olevel NotesDocument110 pagesOlevel Notestatendachimbandi1No ratings yet
- Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument51 pagesChemistry - Electrolysisjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- Electrolysis. Olevel ChemistryDocument53 pagesElectrolysis. Olevel ChemistrySaraYasinNo ratings yet
- SS2 Note ElectrolysisDocument7 pagesSS2 Note ElectrolysisIbukun OlaitanNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSI1Document10 pagesELECTROLYSI1jpkaomeNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument10 pagesElectrolysisFaithNo ratings yet
- 584 6 Electrometallurgy Solid: State Example Type of ConductivityDocument2 pages584 6 Electrometallurgy Solid: State Example Type of ConductivityAshish KotwalNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesElectrolysisPrashiNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSIS o Level 2Document33 pagesELECTROLYSIS o Level 2Tom TommmaNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument24 pagesElectrolysisstudent purposesNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument16 pagesElectrochemistryitsshaunboteNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Term MeaningDocument22 pagesElectrolysis: Term MeaningYeen ChengNo ratings yet
- A Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectDocument10 pagesA Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectLij WynterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Electricity and Chemistry: ConductivityDocument13 pagesChapter 5: Electricity and Chemistry: Conductivityapi-181176018No ratings yet
- Electrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01Document20 pagesElectrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01jiivi87No ratings yet
- Electrolysi S Electrolyte Electrode DischargeDocument28 pagesElectrolysi S Electrolyte Electrode Dischargeanwar9602020100% (1)
- Electricity and ChemistryDocument13 pagesElectricity and Chemistrysalman ahsanNo ratings yet
- 6.3 (A) Electrolysis of An Aqueous SolutionDocument18 pages6.3 (A) Electrolysis of An Aqueous SolutionFid AwanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4: Chapter 6 - Electrolyte: Ions in The Molten or Aqueous StateDocument16 pagesChemistry Form 4: Chapter 6 - Electrolyte: Ions in The Molten or Aqueous StateVinayNo ratings yet
- Form 4A Notes: Cations Migrate To The Cathode and Are Reduced by Gaining of ElectronsDocument9 pagesForm 4A Notes: Cations Migrate To The Cathode and Are Reduced by Gaining of ElectronsGono TakaduuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document10 pagesChapter 6Elynn TanNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Notes For SdaDocument13 pagesElectrolysis Notes For Sdatmoatshe96No ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesElectrolysisapi-381901280% (5)
- Chapter 6 Electrochemistry SPMDocument62 pagesChapter 6 Electrochemistry SPMhanifzainol100% (1)
- ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesElectrolysis12 kijNo ratings yet
- Esis 2Document35 pagesEsis 2Amir Abd KadirNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument32 pagesElectrolysischong5683% (6)
- Chemistry f4Document26 pagesChemistry f4Puvaneswari PunisNo ratings yet
- 9 Electrochemistry NotesDocument10 pages9 Electrochemistry Noteskirabo Daniel -connellNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Aqeous Solutions (Copper Sulfate) PosterDocument1 pageElectrolysis of Aqeous Solutions (Copper Sulfate) Posternnilam1308No ratings yet
- Electrochemistr Y: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument30 pagesElectrochemistr Y: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyHaya SweetNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument43 pagesElectrochemistryShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- P.P.Savani Cambridge International School: NotesDocument4 pagesP.P.Savani Cambridge International School: NotesdhruvNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic Refining of CooperDocument2 pagesElectrolytic Refining of CooperAslam PANo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry #2Document8 pagesElectrochemistry #2swcaptain2008No ratings yet
- Preferential Discharge TheoryDocument4 pagesPreferential Discharge TheoryRitesh Mittra33% (3)
- Electricity and ChemistryDocument9 pagesElectricity and ChemistryFrancis EssilfieNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesCSEC Chemistry - ElectrochemistryCornflakes Toasted100% (1)
- ElectroDocument48 pagesElectroMang friesNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Silver SulphateDocument5 pagesElectrolysis of Silver SulphateJackson_de_Roz_6005100% (1)
- IGCSE Chemistry ElectrolysisDocument5 pagesIGCSE Chemistry ElectrolysisdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE CoordSci Electricity and Chemistry L2Document35 pagesIGCSE CoordSci Electricity and Chemistry L2dung luongtuanNo ratings yet
- Presentation KPTDocument79 pagesPresentation KPTNor Fatihah Ab Malek100% (1)
- Chapter 6 ElectrochemistryDocument11 pagesChapter 6 ElectrochemistryAshraf Shaharudin100% (1)
- Chemistry Homework Material (Electrolysis) by Adaugo Olaedo UbahDocument3 pagesChemistry Homework Material (Electrolysis) by Adaugo Olaedo UbahAdaugo UbahNo ratings yet
- New Electrolysis 1Document18 pagesNew Electrolysis 1Rethabile LekgethoNo ratings yet
- Electricity and ChemistryDocument10 pagesElectricity and ChemistrybiancaNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument30 pagesElectrolysisZarrar Hamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis PDFDocument14 pagesElectrolysis PDFBaryaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Extractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesFrom EverandExtractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- WF 3 F 1Document1 pageWF 3 F 1MUHAMMAD ISA ALI 10927No ratings yet
- Q1 IIIDocument1 pageQ1 IIIMUHAMMAD ISA ALI 10927No ratings yet
- Q3Document2 pagesQ3MUHAMMAD ISA ALI 10927No ratings yet
- ListDocument1 pageListMUHAMMAD ISA ALI 10927No ratings yet
- ListDocument1 pageListMUHAMMAD ISA ALI 10927No ratings yet
- Act 3Document2 pagesAct 3MUHAMMAD ISA ALI 10927No ratings yet
- OthelloDocument2 pagesOthelloMUHAMMAD ISA ALI 10927No ratings yet
- He Never Expected Much PoemDocument1 pageHe Never Expected Much PoemMUHAMMAD ISA ALI 10927No ratings yet
- Python String HandlingDocument1 pagePython String HandlingMUHAMMAD ISA ALI 10927No ratings yet