Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 6206059040699580929
Uploaded by
Arunima halderOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5 6206059040699580929
Uploaded by
Arunima halderCopyright:
Available Formats
ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS
1. Growth in plants is largely restricted to specialised 8. Consider the following statements.
regions of active cell division, which are called
(a) Phloem fibres are made up of sclerenchy-matous
(1) Permanent (2) Meristems cells
(3) Both (1) & (2) (4) Xylem
(b) Phloem parenchyma are generally present in
2. Tissue that produce woody axis and appear later monocots
than primary meristem is called
(c) The first formed primary phloem consists of
(1) Apical meristem
narrow sieve tube and is referred to as
(2) lntercalary meristem
protophloem and the later formed phloem has
(3) Secondary meristem bigger sieve tubes and is referred to as
(4) Both 1 and 2 metaphloem
3. Example of lateral meristern/s is/are :- Which statement(s) is/ are false ?
(A) Intrafascicular cambium (Fascicular vascular
(l)Onlya (2) Onlyb
cambium)
(3)Onlyc (4) a , b , and c
(B) Interfascicular cambium
(C) Cork cambium 9. The outside of the epidermis is often covered with
(1) Only A (2) Only B a waxy thick layer, called
(3)OnlyC (4) All A, B and C (1) Hypoderrnis (2) Cuticle
4. Permanent tissue, having all cells similar in structure (3) Root hair (4) Ste m hair
and function is called 10. Cuticle is absent in
(1) Simple tissue
(1) Roots (2) Dicot Stem
(2) Complex tissue (3) Leaves (4) Monocot stem
(3)Cambium 11. Parenchymatous cells with large intercellular spaces
(4) Apical meristem which occupy the central portion of the stem
5. Which of the following statement is incorrect for constitute
parenchyma? (1) Cortex (2)Pith
(1) Cells are generally isodiametric
(3) Hypoderrnis (4) Epidermis
(2) Their cell walls are thin and made up of cellulose 12. In grasses, certain adaxial epidermal cells along the
(3) They perform various functions like veins modify themselves into large, empty, colourless
photosynthesis, storage etc.
cells. These cells are called :-
(4) Their cell walls are thick and lignified
(1) Bulliform cells (2) Starch sheath cells
6. Collenchyma cells are much thickened at the comers
(3) Companion cells (4) Complimentary cells
due to deposition of :-
13. In dicot stem, the cells of cambium present between
(1) Cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin
primary xylem and primary phloem is the
(2) Cellulose , hemicellulose, pectin
(1) lnterfascicular cambium
(3) Cellulose, suberin
(2) Vascular cambium
(4) Suberin, ligin (3) Intra fascicular cambium
7. Sclereids are present in (4) Cork cambium
(A) Fruit wall of nuts 14. By the activity of cambium ring, the cells cut off
(B) Pulp of guava, pear and sapota toward pith, mature into
(C) Seed coat of legume (1) Secondary phloem
(1) Only A (2) Only B (2) Primary xylem
(3) Only C (4) All A, B and C (3) Secondary xylem
(4) Primary phloem
15. During secondary growth in dicot stem, At some 24. Collenchyma is consist of cells which are much
places, the cambium forms a narrow band of thickened at the corners due to deposition of
parenchyma, which passes through the secondary (1) Cellulose only
xylem and secondary phloem in radial directions. (2) Hemicellulose only
These are called :- (3) Pectin only
(1) Sap wood (4) Pectin, cellulose and hemicellulose
(2) Heart wood 25. Regarding to collenchyma find out the incorrect
(3) Secondary medullary rays statement
(4) Primary medullary rays (1) It's cell walls show pecto-cellulosic unlignified
16. Bark that is formed early in the season is called thickenings
(2) lntercellular spaces are generally absent
(1) Late bark (2) Soft bark
(3) Provide mechanical support to petiole of a leaf
(3) Hard bark (4) Ring bark
(4) Found in the form of a layer below epidermis in
17. At certain regions, the phellogen cuts off closely rnonocots
arranged parenchymatous cells on the outer side 26. Match the following :-
instead of cork cells. These are called :-
(a) Parenchyma (i) Pericycle of root
(1) Phellem (2) Periderm
(b) Collenchyma (ii) Hypodermis of dicot
(3) Bark (4) Complimentary cells stem
18. The cells of secondary cortex are :- (c) Sclerenchymatous (iii) Peocyde of stem
(1) Sclerenchymatous (2) Parenchymatous fibres of linum
(d) Sclerenchymatous (iv) Pulp of pear
(3) Collenchymatous (4) Meristematic
sclereids
19. In dicot root, the vascular cambium is.
a b C d
(1) Primary in origin
(1) ii iii iv
(2) Completely secondary in origin
(2) iv iii ii
(3) Both primary and secondary in origin (3) ii iv iii
(4) Neither primary nor secondary in origin (4) iii ii iv
20. Which of the following is primary meristem? 27. Obliterated central lumen (cavity) is the characteristic
(1) Apical meristem (2) lntercalary meristem feature of
(3) Lateral meristem (4) both 1 and 2 (1) Tracheids (2) Vessels
21. Select odd one with respect to origin :-
(3) Xylem fibres (4) Xylem parenchyma
(1) Interfascicular cambium
28. Select out the incorrect statement regarding to xylem
(2) Cork cambium
(1) On the basis of origin xylem is differentiated into
(3) Vascular cambium in dicot roots
primary xylem and secondary xylem .
(4) Intrafascicular cambium
22. During the formation of primary plant body, specific (2) On the basis of development, secondary xylem
regions of the apical meristem donot produce :- is differentiated into protoxylem & metaxylem
(1) Dermal tissues (2) Ground tissue (3) In stems, protoxylem lies towards centre and
(3) Bark (4) Vascular tissue metaxylem towards periphery
23. Cells of parenchyma are generally isodiamelric but (4) In roots, metaxylem lies towards centre &
different in shape. Which of the following is not a protoxylem towards periphery
shape of parenchyma :- 29. Phloem fibres are generally present in :-
(1) Spherical (2) Fibrous
(1) Primary phloem (2) Secondary phloem
(3) Oval (4) Elongated
(3) Protophloem (4) Metaphloem
:SU. u assmcauon or vanous tissue system 1s based on '1b. I he activity ot cambium rs under the control ot :-
(1) Structure (2) Location (1) Phloem activity (2) Physiological factors
(3) Type of cells (4) Both1&2 (3) Environmental factors (4) Both 2 and 3
31. The innermost layer of cortex of dicot root is 37. Regarding to wood find out the wrong statement :-
characterised by presence of suberin thickening.
This suberin thickening occurs on (1) Vessels of spring wood have wider cavities
(1) Radial walls (2) Transverse wall (2) Vessels of autumn wood have wider cavities
(3) Tangential wall (4) Both 1&3 (3) Spring wood is lighter in colour
32. The parenchymatous cells lies between xylem & (4) Autumn wood has a higher density
phloem of root is known as 38. Match the following
(1) Cambium (2) Conjunctive tissue (a) Early wood 0) Innermost mass
(3) Pith (4) Pericycle of wood
(b) Late wood (ii) Wood just inner lo
33. Regarding to stele which of the following statement vascular cambium
is correct ?
(c) Heart wood (iii) Low density
(1) All the tissues lies inner to pericycle (d) Sap wood (iv) High density
(2) All the tissues lies inner to endodermis a b C d
(3) All the tissues lies inner to hypoderrnis (1) iii iv i ti
(4) All the tissues lies inner to epidermis (2) iii iv ii i
34. Due to continuous growth of secondary xylem (3) iv iii ti i
which of the following get crushed gradually (4) iv iii i ti
(1) Primary phloem 39. Impervious nature of cork for water is due to
deposition of which chemical ?
(2) Earlier formed secondary phloem
(1) Llgnin (2) Suberin
(3) Either 1 or 2
(3) Pectin (4) Hemicellulose
(4) both 1 and 2
40. During secondary growth in root, cambium ring arises
35. After secondary growth what is the actual future of from
primary xylem ?
(1) Tissues located below phloem bundles
(1) Converts into secondary xylem
(2) Portion of pericycle tissue above proloxylem
(2) Remains more or less intact in or around the (3) Endodermis
centre
(4) Both 1 and 2
(3) Converts into secondary phloem
(4) Gets crushed
ANSWERS KEY
::lue 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
~ns. 2 3 4 1 4 2 4 2 2 1 2 1 3 3 3 2 4 2 2 4
::lue 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
~ns. 4 3 2 4 4 1 3 2 2 4 4 2 2 4 2 4 2 1 2 4
You might also like
- Plant Form and FunctionDocument32 pagesPlant Form and FunctionPaula SanicoNo ratings yet
- Plant AnatomyDocument63 pagesPlant AnatomyRabin Bajagain.No ratings yet
- Practice Test 11 - BotanyDocument7 pagesPractice Test 11 - BotanyLoma somNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Class Test - AAMIR-SirDocument9 pagesAnatomy Class Test - AAMIR-Sirkrishnavy2000No ratings yet
- PDF ZoologeDocument3 pagesPDF ZoologeShruti YadavNo ratings yet
- NEET Test Series 5Document24 pagesNEET Test Series 5Willis ChekovNo ratings yet
- XI - CBSE - Worksheet - 3 - Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument3 pagesXI - CBSE - Worksheet - 3 - Anatomy of Flowering PlantsRajasekar Karuppannan100% (1)
- 0) LT PACE-5 - PAPER With Key - 23.07.2023 - 1290861 - 2023 - 07 - 24 - 11 - 37Document24 pages0) LT PACE-5 - PAPER With Key - 23.07.2023 - 1290861 - 2023 - 07 - 24 - 11 - 37vulurakashsharma2005No ratings yet
- Biology Day-12Document1 pageBiology Day-12anvith srinivasNo ratings yet
- Jb5-Anatomy of Flowering Plant (Final)Document8 pagesJb5-Anatomy of Flowering Plant (Final)anvith srinivasNo ratings yet
- 2 Growth 17Document1 page2 Growth 17raoaamir3434No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants DPP 01of Lecture 2 Arjuna NEET 2024Document3 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants DPP 01of Lecture 2 Arjuna NEET 2024z5476259No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument19 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantsLol Boi100% (1)
- Animal Tissue - 3: Location FunctionDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissue - 3: Location FunctionKb AshishNo ratings yet
- Target DPP TestDocument4 pagesTarget DPP TestAnirudh GururajanNo ratings yet
- Tissue - NSEJS-Primo Race.Document5 pagesTissue - NSEJS-Primo Race.Kanchan Shirbhate0% (1)
- Target DPP Test: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Document5 pagesTarget DPP Test: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Deep SapuiNo ratings yet
- Test - 01 - Cell Unit of Life - Biology - 01-11-2023 - TestDocument4 pagesTest - 01 - Cell Unit of Life - Biology - 01-11-2023 - TestHarsh BadoniyaNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument12 pagesAnatomysriNo ratings yet
- Output 231016 141817-52-63Document12 pagesOutput 231016 141817-52-63123No ratings yet
- Incoming JR Aiims S60 & Neet MPL (Batch-1&2) NWT - 13 Paper (29-08-2021)Document18 pagesIncoming JR Aiims S60 & Neet MPL (Batch-1&2) NWT - 13 Paper (29-08-2021)Mission NEET 2022No ratings yet
- 01 Animal Tissue DPPDocument16 pages01 Animal Tissue DPPRuchi DandaleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of AngiospermsDocument1 pageAnatomy of AngiospermsAditiNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue - 1Document3 pagesAnimal Tissue - 1Kb AshishNo ratings yet
- Target Test: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Document8 pagesTarget Test: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718VARUN KUMAR V SNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues - DPP (00-00-2022)Document14 pagesAnimal Tissues - DPP (00-00-2022)mahir malikNo ratings yet
- 62fa78438e1dc400189315a9 ## Short Practice Test 01 Zoology TestDocument4 pages62fa78438e1dc400189315a9 ## Short Practice Test 01 Zoology Testaayush.tripathi0101No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants &animal Tissues-Q.pDocument8 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants &animal Tissues-Q.pchp8615742No ratings yet
- SR Elite, SR Aiims s60 & SR Neet MPL Neet Part Test - 4 Paper - 22!01!19Document20 pagesSR Elite, SR Aiims s60 & SR Neet MPL Neet Part Test - 4 Paper - 22!01!19Pankaj JakharNo ratings yet
- SR Elite, SR Aiims S60 & SR Neet MPL Neet Part Test - 4 Paper - 22-01-19 - PDFDocument20 pagesSR Elite, SR Aiims S60 & SR Neet MPL Neet Part Test - 4 Paper - 22-01-19 - PDFPankaj JakharNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Practice Sheet 01Document6 pagesAnimal Tissue Practice Sheet 01subhash devpalNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of Life DPP 02 (Of Lec 06)Document3 pagesCell The Unit of Life DPP 02 (Of Lec 06)sairajkhedkar69No ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Practice - NEET - EnglishDocument18 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Practice - NEET - EnglishEducation PointNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of Life, Cell Cycle and Cell Division - Practice Sheet 02 - Yakeen NEET 2024Document5 pagesCell - The Unit of Life, Cell Cycle and Cell Division - Practice Sheet 02 - Yakeen NEET 2024ankitfrutyNo ratings yet
- NEET UG Biology Plant Anatomy Plant TissuesDocument13 pagesNEET UG Biology Plant Anatomy Plant TissuesNigar MoinNo ratings yet
- Uits 2Document45 pagesUits 2Firoj AhmedNo ratings yet
- Yakeen NEET (2024) Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesYakeen NEET (2024) Morphology of Flowering Plantsmedical ChyNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 01 BotanyDocument3 pagesPractice Test 01 Botanybhupendranaik330No ratings yet
- BotanyDocument6 pagesBotanyGirish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom1Document10 pagesAnimal Kingdom1kevxin.johnNo ratings yet
- M CAPS 01 - (RM) Zoology PDFDocument3 pagesM CAPS 01 - (RM) Zoology PDFUmar FarooqueNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument6 pages2.1. Anatomy of Flowering PlantsjohnnyNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue - 2: Location FunctionDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissue - 2: Location FunctionKb AshishNo ratings yet
- ViewpdfDocument9 pagesViewpdfChannappa C SNo ratings yet
- Kinematics IIDocument3 pagesKinematics IINeetaiimsjipmer Ipe720/720No ratings yet
- 02-05-2021 Long TermDocument17 pages02-05-2021 Long TermGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- 1GROWTH16Document1 page1GROWTH16raoaamir3434No ratings yet
- L. Ulothrix, Shows (L) Is: of in WaterDocument1 pageL. Ulothrix, Shows (L) Is: of in Waterabin s100% (1)
- Botany - QP WITH ANSWERDocument4 pagesBotany - QP WITH ANSWERSyamala NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantDocument21 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantNalla Raghuram ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Plant Anmol SirDocument24 pagesAnatomy of Plant Anmol SirKhushi PathakNo ratings yet
- DIPASREE - ROYCHOWDHURYAnatomy Short Questions2020-08-22Anatomy Short Questions 22-8-2020Document11 pagesDIPASREE - ROYCHOWDHURYAnatomy Short Questions2020-08-22Anatomy Short Questions 22-8-2020Nigar MoinNo ratings yet
- 2002 PDFDocument4 pages2002 PDFjp techNo ratings yet
- II ME NRP B SS 05. Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesII ME NRP B SS 05. Anatomy of Flowering PlantsAmit RavindhraNo ratings yet
- 1 Biology CD Solutions-M2Document10 pages1 Biology CD Solutions-M2raseemsha2No ratings yet
- LT-23 SPL (G-1) Morphology of Animals - 04-09-21Document6 pagesLT-23 SPL (G-1) Morphology of Animals - 04-09-21orisNo ratings yet
- Dropper Test Paper: Biology Nugas Classes By: G.K. Nugas 'Main Market, Sector-13, HUDA, Hisar / Mob. 8529147033Document7 pagesDropper Test Paper: Biology Nugas Classes By: G.K. Nugas 'Main Market, Sector-13, HUDA, Hisar / Mob. 8529147033UV JANGRANo ratings yet
- NEET Test Series 43Document28 pagesNEET Test Series 43anitalakshmi32No ratings yet
- M CAPS 02 - Botany (PMTcorner - In) PDFDocument3 pagesM CAPS 02 - Botany (PMTcorner - In) PDFbipin100% (1)
- CC 3Document4 pagesCC 3Praveen ReddyNo ratings yet
- SR Elite, Aiims S60, MPL & LTC Neet Grand Test - 1 Paper (29-05-2022)Document28 pagesSR Elite, Aiims S60, MPL & LTC Neet Grand Test - 1 Paper (29-05-2022)srsoumyaranjantareiNo ratings yet
- Alternate: AlstoniaDocument4 pagesAlternate: AlstoniaArunima halderNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision Check List, by MentorfazeelDocument1 pagePhysics Revision Check List, by MentorfazeelArunima halderNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Final Check List by MentorfazeelDocument1 pageChemistry Final Check List by MentorfazeelArunima halderNo ratings yet
- ,al RT/: AxisDocument4 pages,al RT/: AxisArunima halderNo ratings yet
- Mentorfazeel: Ncert Reading MCQ Notes Red Orange Green Number of Revision After Completion of Syllabus (5-7 at Least)Document2 pagesMentorfazeel: Ncert Reading MCQ Notes Red Orange Green Number of Revision After Completion of Syllabus (5-7 at Least)Arunima halderNo ratings yet
- West Bengal Tentative DatesDocument1 pageWest Bengal Tentative DatesArunima halderNo ratings yet
- NEET UG State Wise Schedule - XLSX - NEET UG State Wise ScheduleDocument1 pageNEET UG State Wise Schedule - XLSX - NEET UG State Wise ScheduleArunima halderNo ratings yet
- NEET UG State Counseling - ScheduleDocument1 pageNEET UG State Counseling - ScheduleArunima halderNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument10 pagesDownloadKatrin Choisy D. PascualNo ratings yet
- Eight Married Couples Meet To Lend One Another Some BooksDocument2 pagesEight Married Couples Meet To Lend One Another Some BooksBrahim IdbendrissNo ratings yet
- Jaringan Pada Daun Monokotil Dan Dikotil DitaDocument14 pagesJaringan Pada Daun Monokotil Dan Dikotil DitaDita Linda YaniNo ratings yet
- Describe The Structure and Function of The Five Major Types of Cells Found in Plant TissueDocument3 pagesDescribe The Structure and Function of The Five Major Types of Cells Found in Plant TissueIshaHenryNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument12 pagesAnimal TissuemutiaNo ratings yet
- Plant PartsDocument49 pagesPlant Partsshahzad18400% (1)
- Facts About FruitDocument3 pagesFacts About Fruit2200564No ratings yet
- Monocot Dicot PDFDocument28 pagesMonocot Dicot PDFSunflowerNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2022-PollinationFlowerFruitDocument6 pagesAssignment 2022-PollinationFlowerFruitjaveriaNo ratings yet
- FS-Botanical Names of Common FruitsDocument1 pageFS-Botanical Names of Common FruitsNAYAN JYOTI KALITANo ratings yet
- Botanical Pharmacognosy of AndrographisDocument4 pagesBotanical Pharmacognosy of AndrographisNongton DeBitNo ratings yet
- Macmillan Science Level 3 Pupil S Book Topic 1 PP 8 11Document4 pagesMacmillan Science Level 3 Pupil S Book Topic 1 PP 8 11reema2050reemaNo ratings yet
- Morphology Chart Eng 1Document1 pageMorphology Chart Eng 1angadgneware0% (1)
- Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter-02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument9 pagesClass 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter-02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsVerma AjjuNo ratings yet
- BIO 11 Lect - Botany Part 2 AssignmentDocument2 pagesBIO 11 Lect - Botany Part 2 AssignmentLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
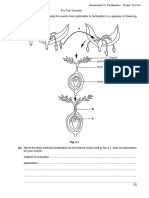
- Assessment 5 Fertilisation in Flowering Plants Flower To FruitDocument2 pagesAssessment 5 Fertilisation in Flowering Plants Flower To Fruitpeterpetty2014No ratings yet
- Points To Remember: Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesPoints To Remember: Morphology of Flowering PlantsMuskan VarlaniNo ratings yet
- Fruitflashcards 817508 PDFDocument6 pagesFruitflashcards 817508 PDFanusyaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Seed PlantsDocument18 pagesEvolution of Seed PlantsMnqobi ZuluNo ratings yet
- Wood DensityDocument2 pagesWood Densitymuhammad saqib IlyasNo ratings yet
- Cassava Catalogue 2016 3rd RevisionDocument62 pagesCassava Catalogue 2016 3rd RevisionDestin Iragi ziringaboNo ratings yet
- Anatomy or Structure of A FruitDocument25 pagesAnatomy or Structure of A FruitCamila SimbajonNo ratings yet
- Cultivar AssociationDocument36 pagesCultivar AssociationEdina Egri-VidékiNo ratings yet
- Summative QuizDocument4 pagesSummative Quizjan ray aribuaboNo ratings yet
- Morfologi DaunDocument34 pagesMorfologi DaunTasyaChNo ratings yet
- Wood PricelistDocument7 pagesWood PricelistSofiaJabadanEspulgarNo ratings yet
- 20170918140947SBC 3023 - TBB 2033beditednew4Document36 pages20170918140947SBC 3023 - TBB 2033beditednew4Leena MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Moving Flower TemplateDocument1 pageMoving Flower Templatennorman2021No ratings yet