Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem Set Buoyancy
Problem Set Buoyancy
Uploaded by
The Daily QuotesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem Set Buoyancy
Problem Set Buoyancy
Uploaded by
The Daily QuotesCopyright:
Available Formats
Saint Mary’s University
Bayombong, Nueva Vizcaya Fluid Mechanics
School of Engineering, Architecture and Information Technology ENGR. JTA, RMP, MSCE
Buoyancy
SHOW YOUR SOLUTIONS WITH PROPER UNITS.
STORE VALUES. ROUND & BOX YOUR FINAL ANSWER.
PROBLEM SOLVING
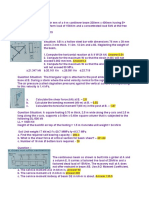
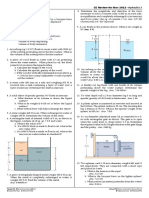
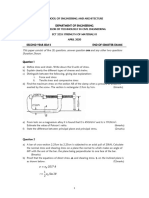
Situation 1. A metal cube 300mm on a side and weighing 1,500 N is lowered into a tank containing a layer of water over
a layer of mercury.
a. Determine the position of the block from the bottom when it has reached equilibrium.
b. Determine the buoyant force contribute by the mercury.
c. Determine the buoyant force contributed by the water.
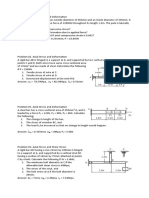
Situation 2. A block of wood (SG=0.70) floats in a fluid having a specific gravity of 1.25. The block has a uniform cross
sectional area of 0.49 square meters. If the thickness of the block is 25cm.
a. Determine the draft.
b. Determine the buoyant force acting on the block.
c. What maximum additional load can the block carry so that it is at the verge of sinking?
Situation 3. A ball weighs 7120N in air and 4780N when weigh in water. Determine the radius of the ball and calculate its
density.
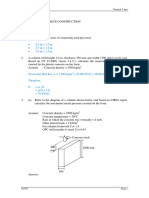
Situation 4. The rectangular concrete block measures 0.4m x 0.4m x 3m is lowered into the sea for an underwater
construction project. ɣc=23.6 kN/m3.
a. Determine the tension in the rope when it is suspended in air.
b. Determine the tension in the rope when it is submerged in water.
You might also like
- Answer: 250Mm, 0.74mpa, 2.75M: Reinforced Concrete - Lecture03 - August2019Document5 pagesAnswer: 250Mm, 0.74mpa, 2.75M: Reinforced Concrete - Lecture03 - August2019hazelNo ratings yet
- 603Document7 pages603jessa marie sayconNo ratings yet
- Hyd 3Document1 pageHyd 3Jocelyn CabarlesNo ratings yet
- Hyd - 6Document2 pagesHyd - 6SamNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No1Document1 pageProblem Set No1Ritsu TainakaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set DamsDocument1 pageProblem Set DamsThe Daily QuotesNo ratings yet
- ID Number: Subject: Strength of Materials 24 Day: LMS Online QuizDocument4 pagesID Number: Subject: Strength of Materials 24 Day: LMS Online QuizMikhail Roy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Activity No. 1Document6 pagesIrrigation Activity No. 1Jeiel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- PRE - Board Examination in Structural Engineering and ConstructionDocument11 pagesPRE - Board Examination in Structural Engineering and ConstructiongemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.4 Poissons RatioDocument11 pagesChapter 2.4 Poissons Ratiogillianminano9No ratings yet
- Civil Engineering November 2020 Review Innovations Strength of Materials 2Document2 pagesCivil Engineering November 2020 Review Innovations Strength of Materials 2Kervin Manila100% (1)
- Assignment #2Document3 pagesAssignment #2Amr M. AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Nov 2023 Preboard 2 Hge - DONEDocument6 pagesNov 2023 Preboard 2 Hge - DONEengr.jaysoncapadosamariNo ratings yet
- 1 2 PressureDocument22 pages1 2 PressuretrojanfrpNo ratings yet
- 2022 Nov Finalpreboard HydgeoDocument6 pages2022 Nov Finalpreboard HydgeoIrah BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Set 2Document3 pagesHydraulics Set 2cielo_cetd3670100% (1)
- Review Module 62 (GH10) Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsDocument2 pagesReview Module 62 (GH10) Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsJoenem AbenojaNo ratings yet
- ProblemSet 3Document1 pageProblemSet 3The Daily QuotesNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument4 pagesStrength of MaterialsAbi Nesh100% (1)
- Ce 603 Set CDocument12 pagesCe 603 Set CJade Paul D. BesanaNo ratings yet
- Cbcs FormatDocument1 pageCbcs Formats s kattiNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Battery - 2Document4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Battery - 2Aileen AntipoloNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument4 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksMadan PanditNo ratings yet
- Midterm 2 - Version BDocument4 pagesMidterm 2 - Version BcapturemrahNo ratings yet
- Hgeeeeeapr 24Document6 pagesHgeeeeeapr 24arjiiicryptNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 With KTCDocument6 pagesQuiz 1 With KTCacurvz2005100% (1)
- Tutorials Pad Footing Nta 5 (2012&2013)Document3 pagesTutorials Pad Footing Nta 5 (2012&2013)Host FredyNo ratings yet
- Sw3 Answer KeyDocument1 pageSw3 Answer KeyPati DukaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 9-1Document1 pageTutorial Sheet 9-1Sumit GhoshNo ratings yet
- Seatwork - DamsDocument4 pagesSeatwork - Damsplm.riveralarissaNo ratings yet
- Ce 602 Set CDocument9 pagesCe 602 Set CJade Paul D. BesanaNo ratings yet
- Ect 3255 Strength of Materials Ii 2Document3 pagesEct 3255 Strength of Materials Ii 2Joseph WambuiNo ratings yet
- Strength December2019Document13 pagesStrength December2019Lester John PrecillasNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Cambridge O LDocument5 pagesPressure, Cambridge O LSuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- RCTut03ans Rev1Document5 pagesRCTut03ans Rev1myint phyoNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 1 Marking SchemeDocument12 pagesPhysics Form 1 Marking SchemeOkumu KevinsNo ratings yet
- Advanced Physics Paper 1Document8 pagesAdvanced Physics Paper 1Java JimmyNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics EngineeringDocument3 pagesHydraulics EngineeringRon Christian Pardilla RicohermosoNo ratings yet
- 10bt30301-Strength of MaterialsDocument1 page10bt30301-Strength of Materialsvinay MurakambattuNo ratings yet
- Refresher 1 Marjes - HGEDocument38 pagesRefresher 1 Marjes - HGEMark Joseph Castrodes LinogaoNo ratings yet
- 2021 Nov Final Preboard HydgeoDocument7 pages2021 Nov Final Preboard HydgeoMacatangay Mhorien100% (1)
- ECW 231 Tutorial and Answers Buoyancy Sept19Document5 pagesECW 231 Tutorial and Answers Buoyancy Sept19hairinnisaNo ratings yet
- Apr 2024 Preboard 1 HgeDocument3 pagesApr 2024 Preboard 1 HgeChrisjohn Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Prestress ConcreteDocument19 pagesPrestress ConcreteAbdulrhman Abduelgassim OsmanNo ratings yet
- Box Girder Design BriefDocument6 pagesBox Girder Design Briefsanusi69No ratings yet
- Pretest Physics For EngineersDocument10 pagesPretest Physics For EngineersIrish NaragNo ratings yet
- 2022NOV HPGE UnlockedDocument4 pages2022NOV HPGE UnlockedKristelle V. TorrealbaNo ratings yet
- Ri Preboard - April - 2023 - Hge PDFDocument6 pagesRi Preboard - April - 2023 - Hge PDFRichelle Faye VillaverdeNo ratings yet
- CE6302-Mechanics of Solids PDFDocument15 pagesCE6302-Mechanics of Solids PDFsarre mamoudouNo ratings yet
- Homework Problems 21-28 PDFDocument2 pagesHomework Problems 21-28 PDFebrahem_sahil5188No ratings yet
- Hpge Practice ProblemsDocument14 pagesHpge Practice ProblemsJayson Pagal100% (1)
- 16 Fluid Mechanics Review Notes 1 PDFDocument4 pages16 Fluid Mechanics Review Notes 1 PDFDoben CañebaNo ratings yet
- Strength July2019Document13 pagesStrength July2019Aj OstiqueNo ratings yet
- Ii Mech Mos DescDocument1 pageIi Mech Mos DescGuru MaheshNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1From EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Magnetic Fields, Special Relativity and Potential Theory: Elementary Electromagnetic TheoryFrom EverandMagnetic Fields, Special Relativity and Potential Theory: Elementary Electromagnetic TheoryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lec 10 LeadingDocument9 pagesLec 10 LeadingThe Daily QuotesNo ratings yet
- Lec 11 ControllingDocument10 pagesLec 11 ControllingThe Daily QuotesNo ratings yet
- Assign HydrauDocument2 pagesAssign HydrauThe Daily QuotesNo ratings yet
- Problem Set DamsDocument1 pageProblem Set DamsThe Daily QuotesNo ratings yet
- ProblemSet 3Document1 pageProblemSet 3The Daily QuotesNo ratings yet
- Capstone Research ProposalDocument9 pagesCapstone Research ProposalThe Daily QuotesNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 StaffingDocument8 pagesLec 7 StaffingThe Daily QuotesNo ratings yet