Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Food-borne diseases - causes, types and prevention
Uploaded by
I Made Yoga Satria Anggara0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views10 pagesFood-borne diseases are a more accurate term than food poisoning or ptomaine poisoning to describe illness associated with food consumption. Food-borne diseases can be caused by living organisms like bacteria, parasites, and viruses in food, or by toxins produced by bacteria before consumption. Some common types of food-borne diseases are caused by bacteria like Salmonella, E. coli, Shigella, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus through foods such as poultry, salads, dairy products, and shellfish. Thorough cooking, clean handling practices, and refrigeration can help prevent food-borne illnesses.
Original Description:
Original Title
06.Foodborne Diseasess
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFood-borne diseases are a more accurate term than food poisoning or ptomaine poisoning to describe illness associated with food consumption. Food-borne diseases can be caused by living organisms like bacteria, parasites, and viruses in food, or by toxins produced by bacteria before consumption. Some common types of food-borne diseases are caused by bacteria like Salmonella, E. coli, Shigella, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus through foods such as poultry, salads, dairy products, and shellfish. Thorough cooking, clean handling practices, and refrigeration can help prevent food-borne illnesses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views10 pagesFood-borne diseases - causes, types and prevention
Uploaded by
I Made Yoga Satria AnggaraFood-borne diseases are a more accurate term than food poisoning or ptomaine poisoning to describe illness associated with food consumption. Food-borne diseases can be caused by living organisms like bacteria, parasites, and viruses in food, or by toxins produced by bacteria before consumption. Some common types of food-borne diseases are caused by bacteria like Salmonella, E. coli, Shigella, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus through foods such as poultry, salads, dairy products, and shellfish. Thorough cooking, clean handling practices, and refrigeration can help prevent food-borne illnesses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Food poisoning and ptomaine poisoning – these
terms are often loosely applied to illness
Associated with the consumption of food.
A more accurate term to use for illness associated
with the consumption of food are
FOOD-BORNE DISEASES.
.
Food borne diseases may be subdivided into :
1. Food-borne infections- Where the disease is produced by living
organisms such as certain bacteria,parasites,viruses,etc.
entering the body with food,
2. Food poisoning or food intoxication- where the disease
is produced by substances called toxins or poisonous agents in the
before consumption.
Ptomaine's are toxic chemical substances
produced by certain bacteria during
The decomposition of foods such as during the
decaying of meats, ripening of fruits
And the aging of cheese. There is reason to
believe that true
Ptomaine poisoning is very rare or does not
actually occur.
BACTERIAL PARASITIC
1. Typhoid 1. Ascariasis
2. Cholera 2. Amoebiasis
3. Bacillary Dysentery 3. Trichinosis
4. Salmonella infection 4. others
5. Others
Bacterial Plant and animals Chemical
1.Staphylococcus 1. Some mushrooms 1. Arsenic
2. C. Botulium 2. Some mussels 2. Lead
3.Streptococcus 3. Certain herbs 3. Cadmium
4. Some fishes 4. Cyanide
5. Others 5. Antimory
6. Nitrites
7. DDT.ETC
1. Bacterial
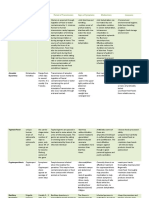
NAME ETIOLOGICAL FOODS USUALLY PREVENTIVE
AGENT INVOLVED PROCEDURES
SALMONELLOS Members of Poultry, salads. Poultry Cooking of food
IS Salmonella family dressing,duck eggs, thoroughly; strict
e.g S.Enteridis warmed leftover foods. personal
paratyphi newcastl;e cleanliness in food
aertrycke and preparation,
others. refrigeration of
moist foods during
storage periods
1. Bacterial
NAME ETIOLOGICAL FOODS USUALLY PREVENTIVE
AGENT INVOLVED PROCEDURES
Dysentery Various species of Moist foods, dairy Strict persomnal
shigella-sonne products, water cleanliness and food
flexner and others contamininated with preparation,
carries and cases refrigeration of moist
foods during storage
periods, cooking of
foods prior to serving
Typhoid Fever Salmonella typhosa Moist foods,dairy Pasteurization of milk
products, water,shellfish, and other dairy
salad contaminate with products,
excreta from carrier, certtification of
direct or indirect shellfish,
cholerination of
water, prohibiting
carriers from
handling food
1. Bacterial
NAME ETIOLOGICAL FOODS USUALLY PREVENTIVE
AGENT INVOLVED PROCEDURES
streptococcus Certain strains of Foods contaminated with Strict persomnal
hermolytic rodent cleanliness and food
preparation,
refrigeration of moist
foods during storage
periods, cooking of
foods prior to serving
Typhoid Fever Salmonella typhosa Moist foods,dairy Pasteurization of milk
products, water,shellfish, and other dairy
salad contaminate with products,
excreta from carrier, certtification of
direct or indirect shellfish,
cholerination of
water, prohibiting
carriers from
handling food
You might also like
- Grammar, Vocabulary and Pronunciation TestDocument3 pagesGrammar, Vocabulary and Pronunciation TestHoàng TháiNo ratings yet
- Food Service, Sanitation - Safety in HealthCare InstitutionsDocument19 pagesFood Service, Sanitation - Safety in HealthCare Institutionsshannon c. lewisNo ratings yet
- Juanito's Kitchen Safety ManualDocument62 pagesJuanito's Kitchen Safety ManualJessan Sinadhan LimosneroNo ratings yet
- Food Borne IllnessesDocument18 pagesFood Borne IllnessesMaria AbigailNo ratings yet
- Lum Bang Activity 1Document4 pagesLum Bang Activity 1Hoshi KwonNo ratings yet
- Food Poisoning or Foodborne Illness: Oli Veporchorgani CsDocument11 pagesFood Poisoning or Foodborne Illness: Oli Veporchorgani Csmarie parfanNo ratings yet
- Table Biological HazardDocument2 pagesTable Biological HazardStanislava Kanjevac100% (1)
- Food Safety at Sea - Hygiene SenseDocument24 pagesFood Safety at Sea - Hygiene SenseNaveen DalaniduNo ratings yet
- Microbes and More - Creative LPDocument28 pagesMicrobes and More - Creative LPAshleigh LynNo ratings yet
- Bahaya Biologis Dan Penyakit Bawaan Makanan: Pertemuan 4Document29 pagesBahaya Biologis Dan Penyakit Bawaan Makanan: Pertemuan 4Ratih PurwasihNo ratings yet
- Common Foodborne PathogensDocument3 pagesCommon Foodborne PathogensO PNo ratings yet
- Applied BacteriologyDocument4 pagesApplied BacteriologyTreshia SusonNo ratings yet
- 5.2.2 (4) Nea Food Safety Bulletin Issue 4Document7 pages5.2.2 (4) Nea Food Safety Bulletin Issue 4Seyha L. AgriFoodNo ratings yet
- Foodborne IllnessesDocument30 pagesFoodborne IllnessesNicoel100% (6)
- Risk Management QuirinotibredelacruzruizDocument16 pagesRisk Management Quirinotibredelacruzruiztibreshaannmae25No ratings yet
- Datasheet: Pathogenic Bacteria:: Campylobacter JejuniDocument2 pagesDatasheet: Pathogenic Bacteria:: Campylobacter JejuniDutch CharmingNo ratings yet
- Listeriosis: Powered by Estland Food Control AuthorityDocument1 pageListeriosis: Powered by Estland Food Control AuthorityMCHADNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tract Pathogens and Microbiology AssignmentDocument8 pagesGastrointestinal Tract Pathogens and Microbiology AssignmentWame Cynthia KNo ratings yet
- Food SafetyDocument14 pagesFood SafetyROCZAN GRIEGONo ratings yet
- Food and Milk SanitationDocument6 pagesFood and Milk SanitationBianca CordovaNo ratings yet
- Outbreak of S. Weltevreden Linked To Fermented Cashew Nut Cheese in Victoria, BCDocument8 pagesOutbreak of S. Weltevreden Linked To Fermented Cashew Nut Cheese in Victoria, BCLeila RochaNo ratings yet
- FCM 1.8 - Food and Waterborne DiseasesDocument21 pagesFCM 1.8 - Food and Waterborne DiseasesZazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2mason.rudd05No ratings yet
- Food PoisoningDocument30 pagesFood PoisoningFitz BaniquedNo ratings yet
- Food Processing MethodDocument9 pagesFood Processing Methodridwan90% (10)
- yaashikaa2016Document9 pagesyaashikaa2016nadela noviaNo ratings yet
- Food Safety and HygieneDocument32 pagesFood Safety and HygieneJulia El SamraNo ratings yet
- Winterbourne Diseases Causative Agent Incubation Period of Transmission Signs of Symptoms Medications MeasuresDocument7 pagesWinterbourne Diseases Causative Agent Incubation Period of Transmission Signs of Symptoms Medications MeasuresJeanie Rose AlduesoNo ratings yet
- Pembetulan Peta Minda SlideDocument3 pagesPembetulan Peta Minda SlideNur Husnina ZawawiNo ratings yet
- lecture 1Document17 pageslecture 1abdisa767No ratings yet
- Food Contamination 1709801411Document19 pagesFood Contamination 1709801411Giang Pham Thi ThuyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 (Part 1)Document28 pagesLesson 2 (Part 1)Yisu HimaaNo ratings yet
- Objectives of This Chapter: Food Biodeterioration and Preservation Food Biodeterioration and PreservationDocument11 pagesObjectives of This Chapter: Food Biodeterioration and Preservation Food Biodeterioration and PreservationQuoc KhanhNo ratings yet
- Factors AffectingDocument17 pagesFactors AffectingVaibhav UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- CKCLEC001 I. Haccp System Flowchart II. Characteristic of Bacteria IllnessDocument4 pagesCKCLEC001 I. Haccp System Flowchart II. Characteristic of Bacteria IllnessGrace de los SantosNo ratings yet
- Basic Food Hygiene Level 1Document77 pagesBasic Food Hygiene Level 1g5nbNo ratings yet
- Sanitation and Safety - Quality AssuranceDocument35 pagesSanitation and Safety - Quality AssuranceLien Mar GastadorNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Fermented Fruits and Vegetables of Asia: A Potential Source of ProbioticsDocument20 pagesReview Article: Fermented Fruits and Vegetables of Asia: A Potential Source of ProbioticsYar ZenaitnasNo ratings yet
- Viral DiseasesDocument6 pagesViral DiseasesValentina CretuNo ratings yet
- 2-1. Bacterial Food Poisoning (Infective)Document53 pages2-1. Bacterial Food Poisoning (Infective)lectureslides22No ratings yet
- FOOD POISONING - ProjectDocument23 pagesFOOD POISONING - ProjectIshika SinghNo ratings yet
- Food preservation methodsDocument2 pagesFood preservation methodsBorela MoniqueNo ratings yet
- Food Processing Aid Means A Substance WhichDocument21 pagesFood Processing Aid Means A Substance WhichHƯƠNG NGUYỄN LÊ NGỌCNo ratings yet
- Types of Food ContaminationDocument13 pagesTypes of Food ContaminationHelena MbangoNo ratings yet
- Toxi Lab Lecture Notes 6-15Document7 pagesToxi Lab Lecture Notes 6-15Micah Lou CalambaNo ratings yet
- Physical, Chemical and Biological HazardsDocument32 pagesPhysical, Chemical and Biological HazardsDaisy ObisoNo ratings yet
- FOOD SAFETY AND SANITATION TIPSDocument12 pagesFOOD SAFETY AND SANITATION TIPSabcdef lunaNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMRisk Management in Applied SafetyDocument3 pagesMIDTERMRisk Management in Applied SafetyAngelita CayabyabNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGICAL SAFETY OF FOODS: KEY FOODBORNE PATHOGENS AND PREVENTIONDocument42 pagesMICROBIOLOGICAL SAFETY OF FOODS: KEY FOODBORNE PATHOGENS AND PREVENTIONRidhu SehgalNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ii Risk Mgt.Document10 pagesChapter Ii Risk Mgt.zionNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Food MicrobiologyDocument6 pagesUnit - 1 Food Microbiologyfarhan79054No ratings yet
- Jurnal - Kelompok 3Document12 pagesJurnal - Kelompok 3Mia FadilahNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach to Managing Food PoisoningDocument2 pagesClinical Approach to Managing Food PoisoningNidya PutriNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Management: Health and Safety DepartmentDocument11 pagesFood Safety Management: Health and Safety DepartmentMasiur HossainNo ratings yet
- FSFCS03Document4 pagesFSFCS03Della StreetleNo ratings yet
- FSM 5 Food Processing Module 3 AmponganDocument5 pagesFSM 5 Food Processing Module 3 AmponganShim EdwardNo ratings yet
- Microbial Food Spoilage DetectionDocument16 pagesMicrobial Food Spoilage Detectionkayla mariNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Hazards: Biological DangersDocument9 pagesFood Safety Hazards: Biological DangersdianNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction FoodDocument14 pages1 Introduction FoodGift NnamukaNo ratings yet
- Fermented Foods for Health: Use the Power of Probiotic Foods to Improve Your Digestion, Strengthen Your Immunity, and Prevent IllnessFrom EverandFermented Foods for Health: Use the Power of Probiotic Foods to Improve Your Digestion, Strengthen Your Immunity, and Prevent IllnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- SITHKOP005 Appendix A Food Production ListDocument60 pagesSITHKOP005 Appendix A Food Production Listsunita dhamijaNo ratings yet
- Century City Mall Events Center PDFDocument11 pagesCentury City Mall Events Center PDFMarielle AbelaNo ratings yet
- FAMILY DEVELOPMENTAL SESSIONS ON Healthy Lifestyle and NutritionDocument66 pagesFAMILY DEVELOPMENTAL SESSIONS ON Healthy Lifestyle and NutritionMariaLea Serrano AlmosuraNo ratings yet
- Peppermint Brownie Cookies RecipeDocument1 pagePeppermint Brownie Cookies Recipejpl.guedes6842No ratings yet
- Manna Diabetes Ebook 2014 PDFDocument51 pagesManna Diabetes Ebook 2014 PDFClaudia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Coconut Butternut Squash Soup Recipe - NYT CookingDocument1 pageCoconut Butternut Squash Soup Recipe - NYT CookingNatallia StaravoitavaNo ratings yet
- Recipes From MalawiDocument8 pagesRecipes From MalawiAna OrriolsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Water ActivityDocument0 pagesFundamentals of Water Activityharish_srinivasan_11No ratings yet
- Makanan Enteral PDFDocument79 pagesMakanan Enteral PDFRizhal HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Q4 Week1 Support Agronomic Crop WorkDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Q4 Week1 Support Agronomic Crop WorkTeodi Alden TegioNo ratings yet
- Eating Well: Snacks For 1-4 Year OldsDocument42 pagesEating Well: Snacks For 1-4 Year OldsAndreea AndreiNo ratings yet
- Free Fupa TipsDocument4 pagesFree Fupa TipsEulenda MhambiNo ratings yet
- Gaining Power from ProteinDocument4 pagesGaining Power from ProteinBryan MorteraNo ratings yet
- Ginger Garlic ExtractDocument21 pagesGinger Garlic Extractkorki77No ratings yet
- Rojo BrunchDocument1 pageRojo Brunchsupport_local_flavorNo ratings yet
- Review of Dessert Plating Guidelines and Cooking ToolsDocument17 pagesReview of Dessert Plating Guidelines and Cooking ToolsBernardito Romero Rejalde Jr.No ratings yet
- Lcif PrintDocument2 pagesLcif Printc moraNo ratings yet
- Table ServiceDocument7 pagesTable ServicenickjanoNo ratings yet
- Summer 2014 Strength ManualDocument28 pagesSummer 2014 Strength ManualHeather Hughes Regalado100% (2)
- Brown Rice-Beyond The Color Reviving A Lost Health Food - A ReviewDocument6 pagesBrown Rice-Beyond The Color Reviving A Lost Health Food - A ReviewDinesh Babu PugalenthiNo ratings yet
- N O Brand Product/Food Item NET Weight/QuantityDocument2 pagesN O Brand Product/Food Item NET Weight/QuantitynorhazlinnaNo ratings yet
- Radisson - JatinDocument84 pagesRadisson - JatinshlokNo ratings yet
- Soal B.ing UtsDocument17 pagesSoal B.ing UtsPutri Nuraini100% (1)
- Rabbit FeedDocument4 pagesRabbit FeedEddy MwachenjeNo ratings yet
- Baar Baar Dinner Menu Pages Final 11.29.17Document2 pagesBaar Baar Dinner Menu Pages Final 11.29.17Daniel MaurerNo ratings yet
- Collins Work On Your Vocabulary - Elementary (PDFDrive) (1) - 44-46Document3 pagesCollins Work On Your Vocabulary - Elementary (PDFDrive) (1) - 44-46Rachel StrehleNo ratings yet
- Taco Soup With Turkey Burger RecipeDocument2 pagesTaco Soup With Turkey Burger RecipeJv ClausNo ratings yet
- FAO-Growing Greener Cities PDFDocument51 pagesFAO-Growing Greener Cities PDFAida Luciana GalindoNo ratings yet
- Everybody at 320 Main Street Is Very Busy TodayDocument5 pagesEverybody at 320 Main Street Is Very Busy TodayAndrea María Guamuch VélizNo ratings yet