Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supp WNL.0000000000000892 Figure E-1
Supp WNL.0000000000000892 Figure E-1
Uploaded by
Sap0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageThis document provides a diagnostic approach for patients presenting with a humeroperoneal pattern of weakness that may indicate Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD). The approach involves considering factors like inheritance pattern, the presence or absence of cardiac involvement and joint laxity, and genetic testing results to determine if the patient has mutations linked to collagen VI, lamin A/C, emerin, nesprin, or other genes associated with forms of EDMD. Negative genetic testing may warrant further genome sequencing to identify the underlying cause.
Original Description:
Original Title
supp_WNL.0000000000000892_Figure_e-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a diagnostic approach for patients presenting with a humeroperoneal pattern of weakness that may indicate Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD). The approach involves considering factors like inheritance pattern, the presence or absence of cardiac involvement and joint laxity, and genetic testing results to determine if the patient has mutations linked to collagen VI, lamin A/C, emerin, nesprin, or other genes associated with forms of EDMD. Negative genetic testing may warrant further genome sequencing to identify the underlying cause.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageSupp WNL.0000000000000892 Figure E-1
Supp WNL.0000000000000892 Figure E-1
Uploaded by
SapThis document provides a diagnostic approach for patients presenting with a humeroperoneal pattern of weakness that may indicate Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD). The approach involves considering factors like inheritance pattern, the presence or absence of cardiac involvement and joint laxity, and genetic testing results to determine if the patient has mutations linked to collagen VI, lamin A/C, emerin, nesprin, or other genes associated with forms of EDMD. Negative genetic testing may warrant further genome sequencing to identify the underlying cause.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
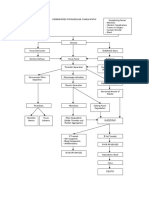
Humeroperoneal
pattern of weakness
Early cardiac involvement, No cardiac involvement, laxity
no joint laxity of joints, protuberant calcanei
Consider genetic testing for mutations in
Inheritance pattern
collagen VI (Bethlem or Ullrich myopathy)
Autosomal Positive collagen Negative collagen
X-linked*
dominant* VI mutation VI mutation
Consider genetic Consider genetic Autosomal recessive,*
Autosomal dominant,*
testing for mutations testing for mutations neonatal or
age at onset variable
in lamin A/C in emerin (XR-EDMD) congenital onset
Negative Bethlem myopathy Ullrich myopathy
Consider genetic testing
for mutations in nesprin
Muscle biopsy
1 and 2 and TMEM43/
LUMA (EDMD3, 4, 5)
Negative
Myofibrillar myopathy with reducing Myofibrillar Nonspecific
bodies, or X-linked inheritance myopathy features
Consider genetic testing Consider genetic testing
for mutations in FHL1 for mutations in desmin
Negative Consider genome- or exome-wide screening
or next-generation sequencing
Figure e-1. Diagnostic approach to patients with a humeroperoneal pattern of weakness and suspected muscular
dystrophy (Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy)
* Autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked inheritance may be responsible in sporadic cases. EDMD = Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy.
You might also like
- Anemia ChartDocument1 pageAnemia ChartBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General Biology Ii - KmbsDocument5 pagesReviewer in General Biology Ii - KmbsKSNo ratings yet
- Methods of Hybrid Seed ProductionDocument16 pagesMethods of Hybrid Seed ProductionSantosh Badiger UHS19UG4508No ratings yet
- Nephrotic Nephritic SyndromsDocument4 pagesNephrotic Nephritic SyndromsKimiwari100% (2)
- DIC PathophysiologyDocument1 pageDIC Pathophysiologykathy100% (1)
- Devpsych Reviewer 1Document56 pagesDevpsych Reviewer 1Joshua MalloNo ratings yet
- Languagecert Iesol Reading & Writing Expert Level - C1 Practice Paper 5HUDocument13 pagesLanguagecert Iesol Reading & Writing Expert Level - C1 Practice Paper 5HUAnita BódiNo ratings yet
- Supp WNL.0000000000000892 Figure E-2Document1 pageSupp WNL.0000000000000892 Figure E-2SapNo ratings yet
- Genetics-Modes of Inheritance and Mnemonics For AD, AR and X-Linked DzsDocument2 pagesGenetics-Modes of Inheritance and Mnemonics For AD, AR and X-Linked DzsAviv RobinovNo ratings yet
- DevPsy 1 PrenatalDocument6 pagesDevPsy 1 PrenatalIvy Marie ToyonganNo ratings yet
- DevPsy 1 PrenatalDocument6 pagesDevPsy 1 PrenatalChristian 07No ratings yet
- DevPsy 1 PrenatalDocument6 pagesDevPsy 1 PrenatalChristian 07No ratings yet
- DevPsy 1 PrenatalDocument7 pagesDevPsy 1 PrenatalninamaedamilesNo ratings yet
- SKEMADocument1 pageSKEMAnadhilaNo ratings yet
- What If?: Aberrations in Cell CycleDocument7 pagesWhat If?: Aberrations in Cell CycleJasper CasayuranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Principle of Inheritance and Variation PDFDocument54 pagesChapter 4 - Principle of Inheritance and Variation PDFdeepunymNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance IDocument1 pageChromosomal Basis of Inheritance IFiqahhyNo ratings yet
- Combinepdf 7Document129 pagesCombinepdf 7Joe JosephNo ratings yet
- Gemistocytes: Gemistocytic AstrocytomaDocument4 pagesGemistocytes: Gemistocytic AstrocytomaRojales FrancisNo ratings yet
- Genetics Diy-LectureDocument14 pagesGenetics Diy-LectureRoselyn LacernaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - KaryotypingDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 - KaryotypingNajah HanimNo ratings yet
- Maternal Notes PrelimDocument13 pagesMaternal Notes PrelimyueNo ratings yet
- Patterns of InheritanceDocument26 pagesPatterns of InheritanceVidhya NairNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Lecture 07Document7 pagesCytogenetics Lecture 07Dianne NolascoNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Junction Disorders: Myasthenia GravisDocument20 pagesNeuromuscular Junction Disorders: Myasthenia GravisIzabella MihályNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of IUFD: FertilizationDocument1 pagePathophysiology of IUFD: FertilizationWilson Carandang100% (1)
- Pedigree Analysis in Human GeneticsDocument6 pagesPedigree Analysis in Human GeneticsGela ReyesNo ratings yet
- (GYNE) Menopause-Dr. Palaypayon (M. ALdana Med 2021)Document10 pages(GYNE) Menopause-Dr. Palaypayon (M. ALdana Med 2021)adrian kristopher dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Menopause: Cagayan Valley Medical Center Department of Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument37 pagesMenopause: Cagayan Valley Medical Center Department of Obstetrics and GynecologySofia Kezia Apostol CabaroNo ratings yet
- Genetics Trans 4Document4 pagesGenetics Trans 4Jeztin Faye Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Biology Module 6 6365a8ada060c PDFDocument13 pagesBiology Module 6 6365a8ada060c PDFTanisha PatelNo ratings yet
- Integrativeactivity2 JennifercristalpDocument22 pagesIntegrativeactivity2 JennifercristalpJenniferNo ratings yet
- MUTATIONS Science (Lasttopic)Document2 pagesMUTATIONS Science (Lasttopic)geecyjane YguintoNo ratings yet
- Biology KaryotypeDocument4 pagesBiology KaryotypeAlyana Grace GuquibNo ratings yet
- Topic - Primary Ovarian Insufficiency 2564Document12 pagesTopic - Primary Ovarian Insufficiency 2564Decha SaechoenNo ratings yet
- Plasma Cell Dyscrasias Testing Algorithm PDFDocument1 pagePlasma Cell Dyscrasias Testing Algorithm PDFolesyaNo ratings yet
- 10 Patterns of Inheritance 160215185228Document26 pages10 Patterns of Inheritance 160215185228CHERI-ANN SEVILLANo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of AgingDocument2 pagesBiochemistry of AgingKaedehara KazuhaNo ratings yet
- Approach To BleedingDocument7 pagesApproach To BleedingMunish DograNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument4 pagesConnective TissuePaola Elizabeth González MartínezNo ratings yet
- Biology of Spermatogenesis: Paulo Navarro CostaDocument11 pagesBiology of Spermatogenesis: Paulo Navarro CostaMuhammadIrfanHamkaNo ratings yet
- A Listing of Major Genetic and Chromosomal DisordersDocument5 pagesA Listing of Major Genetic and Chromosomal DisordersAndersonEladseetNo ratings yet
- The Invariant Lineage of C. Elegans: 1090 Cells Cell Death!Document28 pagesThe Invariant Lineage of C. Elegans: 1090 Cells Cell Death!Antoaneta PapNo ratings yet
- AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT INHERITANCE - Traditional Patterns of Inheritance 2Document4 pagesAUTOSOMAL DOMINANT INHERITANCE - Traditional Patterns of Inheritance 2Yan Yee TanNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts!: and Huran HealthDocument9 pagesKey Concepts!: and Huran HealthANUPRIYA PARTHIBAN M.SC. HUMAN GENETICSNo ratings yet
- Heredofamilial and Congenital Glomerular Disorders: Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. GlassockDocument7 pagesHeredofamilial and Congenital Glomerular Disorders: Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. GlassockdoraNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary A: 7 Genetics - I)Document7 pagesVocabulary A: 7 Genetics - I)Tius LenaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument4 pagesDocumentALi AL-kwafiNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Inheritance Chapter 7 EmerysDocument23 pagesPatterns of Inheritance Chapter 7 Emerysmenahil.zaidi.s23No ratings yet
- Disease Compendium UpdatedDocument9 pagesDisease Compendium UpdatedKing-son LinNo ratings yet
- NOTES - CH 15 - Sex Determination - Linkage - SlideshowDocument59 pagesNOTES - CH 15 - Sex Determination - Linkage - Slideshowkaren milloNo ratings yet
- DEVPSYCH 3 - Forming A New LifeDocument4 pagesDEVPSYCH 3 - Forming A New LifeRedgie G. GabaneNo ratings yet
- Uw - Elseby Notes PediatricsDocument218 pagesUw - Elseby Notes PediatricsIvy QueenNo ratings yet
- 4M GeneticsDocument12 pages4M GeneticsAubrey Justine GaleonNo ratings yet
- Table On Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument2 pagesTable On Chromosomal AbnormalitiesJoanne Mary RomoNo ratings yet
- Inherited ConditionsDocument2 pagesInherited ConditionsNawal RaiNo ratings yet
- Yim Et Al 2018 Disharmonious Patterns of Heterotaxy and IsomerismDocument9 pagesYim Et Al 2018 Disharmonious Patterns of Heterotaxy and IsomerismEizetNo ratings yet
- Pages From Devesh Mishra Hardcopy - Full AppDocument11 pagesPages From Devesh Mishra Hardcopy - Full AppElenaNo ratings yet
- Pokedex PDFDocument348 pagesPokedex PDFMichael Crager50% (4)
- Biology WorkDocument3 pagesBiology WorkGachi Chealsy50% (2)
- Buenafe JC FoodChem Week 11 To 13Document1 pageBuenafe JC FoodChem Week 11 To 13john buenafeNo ratings yet
- 21 - 10th Bio Class - 25 Interbell WS - 21 EngDocument3 pages21 - 10th Bio Class - 25 Interbell WS - 21 EngsajithvariathNo ratings yet
- Mehlmanmedical Hy ImmunoDocument44 pagesMehlmanmedical Hy Immunonav_malhiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance & VariationsDocument59 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance & VariationsChandra VadanNo ratings yet
- Bio-Rad Explorer Crime Scene Investigator PCR Basics Kit:: A Real-Time PCR ExtensionDocument24 pagesBio-Rad Explorer Crime Scene Investigator PCR Basics Kit:: A Real-Time PCR Extensionstuart littlejohnNo ratings yet
- Antoniega, Ken P. Roc-Bio2 - Las 1Document2 pagesAntoniega, Ken P. Roc-Bio2 - Las 1Ken Palermo AntoniegaNo ratings yet
- Phenylketonuria: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2 GradeDocument24 pagesPhenylketonuria: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2 GradeAsfoor gake1No ratings yet
- Whipps Et Al, 2008Document12 pagesWhipps Et Al, 2008joyeeta8No ratings yet
- Muscle Channelopathies - The Nondystrophic Myotonias and Periodic ParalysesDocument17 pagesMuscle Channelopathies - The Nondystrophic Myotonias and Periodic ParalysesCarlos RiquelmeNo ratings yet
- MCR 108Document9 pagesMCR 108Jeahan Farrahdinna A—No ratings yet
- حجية البصمة الوراثية في الاثبات الجنائيDocument62 pagesحجية البصمة الوراثية في الاثبات الجنائيSamrraa100% (1)
- Anaphy Chapter 3 by GetteDocument13 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3 by GetteDUQUE, GEORGETTE FLOREANNE L.No ratings yet
- Inherited - Vs - Aquired - Traits - PPT EditedDocument37 pagesInherited - Vs - Aquired - Traits - PPT EditedNerwin UrbanoNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument2 pagesProteinsSamNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Module Week 14Document12 pagesEarth and Life Module Week 14Austin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Textbook Advances in Radiation Oncology 1St Edition Jeffrey Y C Wong Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Advances in Radiation Oncology 1St Edition Jeffrey Y C Wong Ebook All Chapter PDFjames.jodha155100% (18)
- The Reproductive Biology of Macadamia: Scientia HorticulturaeDocument6 pagesThe Reproductive Biology of Macadamia: Scientia HorticulturaeAna Belen ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Mouse Anti-His 11922416001bulDocument11 pagesMouse Anti-His 11922416001bulAna SmolkoNo ratings yet
- Color The Animal CellDocument6 pagesColor The Animal Cellyuefen tohNo ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCES P2 GR11 MEMO NOV 2023 - EnglishDocument11 pagesLIFE SCIENCES P2 GR11 MEMO NOV 2023 - Englishpumezabalfour8No ratings yet
- 3rd Exam Environmental ScienceDocument12 pages3rd Exam Environmental Sciencesummerswinter47No ratings yet
- Postgraduate Handbook 2016 2017Document105 pagesPostgraduate Handbook 2016 2017Aya AmirNo ratings yet
- Consolidation of Molecular Testing in Clinical VirologyDocument15 pagesConsolidation of Molecular Testing in Clinical VirologyUDI Unidad Diagnostica IntegralNo ratings yet
- Gizmo - RNA Protein Synthesis BIO WORKSHEETDocument7 pagesGizmo - RNA Protein Synthesis BIO WORKSHEEThenry bhoneNo ratings yet
- Botany Research Paper PDFDocument6 pagesBotany Research Paper PDFfyt18efe100% (1)
- Claudia Gonzalez Lima 2020Document76 pagesClaudia Gonzalez Lima 2020Ann LourieNo ratings yet