Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 03
Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 03
Uploaded by
darshan8422Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 03
Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 03
Uploaded by
darshan8422Copyright:
Available Formats
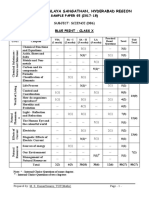
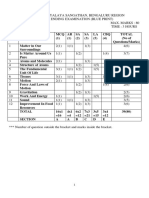
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
SAMPLE PAPER 03 FOR SESSING ENDING EXAM (2017-18)
SUBJECT: SCIENCE (086)
BLUE PRINT : CLASS IX
Practical
VSA SA – I SA – II LA Unit
UNIT Chapter (1 mark) (2 marks) (3 marks) (5 marks)
Based Total
Total
Questions
Matter in our
Matter - Its Nature
-- -- 3(1) -- 2(1) 5(2)
surroundings
and Behaviour
Is Matter around us
-- -- 3(1)* -- 2(1) 5(2)
pure
23(7)
Atoms and Molecules -- -- 3(1) 5(1) -- 8(2)
Structure of the Atom -- -- -- 5(1)* -- 5(1)
The Fundamental unit
Organisation in the
-- -- 3(1) 5(1) -- 8(2)
of life
Living World
Tissues 1(1) -- -- 5(1)* -- 6(2)
20(7)
Diversity in living
-- -- 3(1)* -- -- 3(1)
organisms
Why Do we fall ill 1(1) -- -- -- 2(1) 3(2)
Motion -- -- 3(1) -- 2(1)* 5(2)
Motion, Force and
Force and Laws of
-- -- 3(1) -- 2(1) 5(2)
motion
Work
Gravitation -- -- -- 5(1) -- 5(1) 27(9)
Work and Energy -- -- 3(1)* 5(1) -- 8(2)
Sound -- 4(2) -- -- -- 4(2)
Environment
Our
Natural Resources -- -- 6(2) -- -- 6(2) 6(2)
Food; Food
Production
Improvement un Food
-- 2(1) -- -- 2(1) 4(2) 4(2)
Resources
Total 2(2) 6(3) 30(10) 30(6) 12(6) 80(27) 80(27)
Note: * - Internal Choice Questions of same chapter.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 1 -
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
SAMPLE PAPER 03 FOR SESSING ENDING EXAM (2017-18)
SUBJECT: SCIENCE MAX. MARKS : 80
CLASS : IX DURATION : 3 HRS
General Instructions:
1. All questions are compulsory.
2. The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
3. All questions of Section-A and Section-B are to be attempted separately.
4. There is an internal choice in three questions of three marks each and two question of five marks.
5. Question number 1 to 2 in Section-A are one mark question. These are to be answered in one word or in
one sentence.
6. Question numbers 3 to 5 in Section-A are two marks questions. These are to be answered in about 30
words each.
7. Question numbers 6 to 15 in Section-A are three marks questions. These are to be answered in about 50
words each.
8. Question numbers 16 to 21 in Section-A are five marks questions. These are to be answered in about 70
words each.
9. Question numbers 22 to 27 in Section-B are questions based on practical skills and are two marks
questions.
SECTION – A
1. Write the criteria used for the classification of organisms as proposed by Whittaker.
2. Why is rabies virus called neurotrophic in nature?
3. (a) Which wave property determines (i) Loudness, (ii) Pitch?
(b) How are wavelength and frequency related to speed of sound waves?
4. The successive crest and trough of a wave 30 cm apart. Find the wavelength. Also, find the
frequency of wave if 10 crests and 10 troughs are produced in 2s.
5. Differentiate between kharif and rabi crops. Mention the months in which these are sown. Give
one example of each.
6. State Law of Conservation of Energy and express it in the form of an equation for a body of
mass m falling from a point A at height h, above the ground at (a) A, (b) B at a height from
ground, (c) C.
OR
Define power. State commercial unit and SI unit of electrical energy. An electric heater of 400 W
works for 2 hours. Find the electrical energy units consumed in a day.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 2 -
7. (a) Define matter and write its three states.
(b) Explain how these states of matter arise due to variation in the characteristics of the particles.
OR
(a) Why does the water kept in an earthen pot become cool in summer?
(b) Draw a well labelled diagram showing sublimation of camphor.
(c) Convert: 340 K to degree Celsius.
8. Draw labelled diagram of the apparatus used to separate a mixture of two immiscible liquids.
9. Define mass number and atomic number. How are these represented around the symbol of an
element? The mass number and atomic number of an isotope of uranium (U) are 235 and 92
respectively. Calculate the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom.
10. What is xylem? Name the four elements of xylem and write one function of each.
11. List in the tabular form any three differences between the Aves and the Mammalia group.
OR
List some adaptations of reptiles towards terrestrial mode of life.
12. (a) Define average speed.
(b) A bus travels a distance of 120 km with a speed of 40 km/h and returns with a speed of 30
km/h. Calculate the average speed for the entire journey.
13. Car A of mass 1500 kg travelling at 25 m/s collides with another car B of mass 1000 kg
travelling at 15 m/s in the same direction. After collision, the velocity of car A becomes 20 m/s.
Calculate the velocity of car B after collision.
14. Water is meant by RRR of water bodies. Explain in brief.
15. What is Nitrogen fixation? Mention two differences between nitrification and denitrification
processes. Name the organisms involved in these processes.
16. Verify by calculating the following:
(a) Number of molecules in 100 g of NH3 is more than 100 g of N2 [Atomic mass of N = 14 u, H
= 1 u]
(b) 60 g of carbon and 60 g of magnesium elements have a molar ratio 2 : 1 [Atomic mass of C =
12 u, Mg = 24 u].
17. (a) Explain why did Rutherford select a gold foil in his alpha scattering experiments?
(b) What observations in a scattering experiment led Rutherford to make the following
observations:
(i) Most of the space in an atom is empty.
(ii) Nucleus is positively charged.
(c) Mention any two drawbacks of Rutherford’s model.
OR
(a) The average atomic mass of a sample of an element X is 16.2 u. What are the percentage of
isotope 816X and 818X in the sample.
(b) On the basis of Thomson’s model of an atom explain how the atom is neutral as a whole.
18. (a) Differentiate between acceleration due to gravity and universal gravitational constant. Derive
a relation between ‘g’ and ‘G’.
(b) State universal law of Gravitation.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 3 -
19. Given below is a diagrammatic sketch of electron microscopic view of an animal cell :
(a) Label the parts indicated by lines as 1 to 10.
(b) Give two reasons to support that it is an animal cell.
(c) How many mitochondria are shown in the diagram?
20. (a) Explain the formation of complex permanent tissue in plants. Mention two types of complex
tissues and write their functions.
(b) How simple permanent tissues are different from complex permanent tissues?
OR
What are neurons? Where are they found in the body? What functions do they perform in the
body of an organism?
21. (a) Define work. Give SI unit of work. Write an expression for positive work done.
(b) Calculate the work done in pushing a cart through a distance of 50 m against the force of
friction equal to 250 N. Also state the type of work done.
(c) Sarita lives on 3rd floor of building at the height of 15 m. She carries her school bag
weighting 5.2 kg from the ground floor to her house. Find the amount of work done by her and
identity the force against which she has done work (g = 10 ms–2)
SECTION – B
22. (i) Arrange the following substances in increasing order of force of attraction between the
particles: (a) water (b) hydrogen (c) sand
(ii) Why does the temperature remain constant at the melting point?
23. Although Archana has been suffering from cold and cough she decided to appear for her class
test. Classmates seated close to her had an exposure to the infection being carried by Archana.
However, only one of them actually suffered from cold and cough. Explain, what prevented rest
of those classmates catching cold and cough in spite of their exposure to the infection.
24. Silver iodide, AgI is a yellow crystalline solid. But when it is exposed to sunlight, it forms solid
grey silver and iodine. Why? Give one practical application of this reaction and write the
equation also.
25. Name the various techniques or practices used for achieving sustainable agriculture.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 4 -
26. Find the displacement of a body whose velocity time graph is shown below:
OR
Even when a body covers equal distances in equal time intervals, its velocity can be variable.
Comment giving an example.
27. In the below experimental set-up, a student gives the card a sharp and fast horizontal flick with a
finger.
(i) What will happen to the coin?
(ii) State reason for your answer.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 5 -
You might also like
- Folio Radioactivity Ting 5Document16 pagesFolio Radioactivity Ting 5akunaruto92100% (3)
- Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02Document5 pagesScience Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02darshan8422No ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesScience Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01rajman1990No ratings yet
- 1095549296science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01Document5 pages1095549296science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01Abhishek JhaNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03Document6 pagesScience Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03darshan8422No ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020Document7 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Document6 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Gowtham LNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument8 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Document6 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020CharuNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 04 For Board Exam 2020Document7 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 04 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Document5 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03hweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Sample Paper 01 For See 2021 1Document8 pagesScience Class Ix Sample Paper 01 For See 2021 1Alina SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2020Document7 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01hweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document3 pagesScience Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Anonymous TvppppNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02Document5 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Sample Paper 02 For See 2021 1Document8 pagesScience Class Ix Sample Paper 02 For See 2021 1Alina SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2019Document5 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2019KamalNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 08 For Board Exam 2019Document5 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 08 For Board Exam 2019Kamal0% (1)
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 08 For Board Exam 2018Document5 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 08 For Board Exam 2018BHARAT kommanaNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173100% (1)
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173No ratings yet
- Merge 01Document7 pagesMerge 01nrupesh.kumar.mohanty28031No ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01Document3 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01garNo ratings yet
- Science Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document4 pagesScience Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Blue Print 1 Class XI Half Yearly 23Document1 pagePhysics Blue Print 1 Class XI Half Yearly 23Nilima Aparajita SahuNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2018Document5 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2018Maruti AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Science Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02sparsh bagalNo ratings yet
- Science Class VII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01Document4 pagesScience Class VII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01soni.satindraNo ratings yet
- Biology Blue PrintDocument1 pageBiology Blue Printaniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- Chemistry Class Xii Blue Prints For Board Exam 2023Document1 pageChemistry Class Xii Blue Prints For Board Exam 2023aniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01hweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document4 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03hweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03Document4 pagesScience Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03Kajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Document3 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Physics Blue Print 1 Class XI Half Yearly 23Document1 pagePhysics Blue Print 1 Class XI Half Yearly 23banarjeerupali4No ratings yet
- Phy Chem EngDocument3 pagesPhy Chem Engnrupesh.kumar.mohanty28031No ratings yet
- Xi PhysicsDocument1 pageXi PhysicsjollygalileoNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document3 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03hweta173No ratings yet
- Class 9th CBSE Blue PrintDocument2 pagesClass 9th CBSE Blue PrintYash BawiskarNo ratings yet
- SCIDocument2 pagesSCIDeepika KarraNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Viii Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 03Document3 pagesMaths Class Viii Periodic Test 02 Exam Sample Paper 03Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- Blue Print For Common Physics Exams PDFDocument2 pagesBlue Print For Common Physics Exams PDF2007.satyamjaiswalNo ratings yet
- Blue Print CHEMISTRY SEE 2023-24 AGRA REGIONDocument2 pagesBlue Print CHEMISTRY SEE 2023-24 AGRA REGIONVanshNo ratings yet
- Physics 11Document2 pagesPhysics 11RishabhNo ratings yet
- BP Xi Physics See23-24Document2 pagesBP Xi Physics See23-24ashishkrsingh4565No ratings yet
- Null 3Document1 pageNull 3class6supertech6No ratings yet
- Science BP PB1Document1 pageScience BP PB1ashly BTS (sushi)No ratings yet
- BP Maths Ix See 2022 23Document1 pageBP Maths Ix See 2022 23Chirag PadhiyarNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Blueprint, See, XiDocument1 pageBlueprint, See, XikavisanjurohillaNo ratings yet
- Earth-Abundant Materials for Solar Cells: Cu2-II-IV-VI4 SemiconductorsFrom EverandEarth-Abundant Materials for Solar Cells: Cu2-II-IV-VI4 SemiconductorsNo ratings yet
- 9th - PS-Lesson Plan BookDocument39 pages9th - PS-Lesson Plan Bookmadhumita.kothawalaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument14 pagesAtomic StructureApeksha MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Modul Pecutan Kimia SPM 2021Document25 pagesModul Pecutan Kimia SPM 2021Nuan Ting NgNo ratings yet
- Chang Problems Chapter 2Document10 pagesChang Problems Chapter 2ChaNo ratings yet
- Atoms Ions & Isotopes Study Guide AnswersDocument2 pagesAtoms Ions & Isotopes Study Guide AnswersNevaeh DouglasNo ratings yet
- 9701 s06 QP 1Document26 pages9701 s06 QP 1G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Radiopharmaceuticals: James P. Jimenez, RPHDocument36 pagesRadiopharmaceuticals: James P. Jimenez, RPHArk Olfato ParojinogNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics-1Document22 pagesModern Physics-1Minato NamikazeNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry and Applications of RadioactivityDocument15 pagesNuclear Chemistry and Applications of RadioactivityAnusha KhadkaNo ratings yet
- NucleiDocument3 pagesNucleijaisinghrajput2146No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument7 pagesPhysicsChaN.deDiosNo ratings yet
- 9701 s14 QP 22Document12 pages9701 s14 QP 22Abhin SfNo ratings yet
- Matter and Stoichiometry Chm092 June 2014Document223 pagesMatter and Stoichiometry Chm092 June 2014ida hadiNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics P7 Radioactivity Past Paper QuestionsDocument23 pagesAQA Physics P7 Radioactivity Past Paper Questionsis7112No ratings yet
- 1st Nine Weeks Exam ReviewDocument5 pages1st Nine Weeks Exam Reviewapi-233187566No ratings yet
- NuclearDecaySEDocument6 pagesNuclearDecaySEvasean329No ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics Summary Notes: Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesNuclear Physics Summary Notes: Atomic StructureShelly AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 5070 ChecklistDocument5 pagesChemistry 5070 ChecklistObby-GiftMwambaKachecheNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging The Requisites 5Th Edition Janis P Omalley Full ChapterDocument67 pagesNuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging The Requisites 5Th Edition Janis P Omalley Full Chapteralan.feliciano162100% (5)
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument11 pagesNuclear Physicsvaigundh vaiNo ratings yet
- 06 0620 42 3RP - InddDocument4 pages06 0620 42 3RP - InddIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument13 pagesUnit 1 Multiple ChoiceJinJinKiraieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Matter and StoichiometryDocument223 pagesChapter 1 - Matter and StoichiometryJatjediNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atomic Structure Multiple ChoiceDocument13 pages1.1 Atomic Structure Multiple ChoiceAmmaarah PatelNo ratings yet
- Origin of ElementsDocument27 pagesOrigin of ElementsJoanna Ruth SeproNo ratings yet
- Week 16Document14 pagesWeek 16Harry Jhonley LabisteNo ratings yet
- Humans - An Unauthorized Biography - 1st Edition (2016)Document133 pagesHumans - An Unauthorized Biography - 1st Edition (2016)Fujion Kambra100% (1)
- Matter and Substances.: 4.1 Changes in The States of Matter. Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument15 pagesMatter and Substances.: 4.1 Changes in The States of Matter. Kinetic Theory of MatterElly EllynaNo ratings yet
- 4CH0 1C ChemistryDocument28 pages4CH0 1C ChemistryAbrar JahinNo ratings yet