Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment Econ Entrep
Uploaded by
EJ RaveloOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment Econ Entrep
Uploaded by
EJ RaveloCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Earl Justine V.
Ravelo Subject: Economics
Grade/Section: 12 ABM (A)
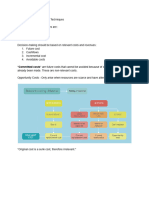
1. Definition of
a. Elasticity- is a method of measuring the likelihood of one economic factor
affecting another, such as when the price of an item affects consumer
demand or when supply affects how much something costs. Elasticity is
driven by the principles of supply and demand, meaning the higher the
demand for an item, the more elastic its price is. The elasticity dynamic is also
affected by the number of alternative options in the market. In other words,
when people have plenty of similar options, price elasticity will be lower.
b. Demand Elasticity- occurs when the price of a good or service affects
consumer demand. If the price goes down just a little, consumers will buy a
lot more. If prices rise just a bit, they'll stop buying as much and wait for prices
to return to normal. To emphasize, this is a degree to which changes in a
good’s price affect the quantity demanded by consumers. The demand for a
product can be elastic or inelastic.
2. Types of Demand Elasticity
a. Elastic
b. Inelastic
c. Unitary o unit elastic
d. Perfectly elastic
e. Perfectly Inelastic Demand
Name: Earl Justine V. Ravelo Subject: Entrepreneurship
Grade/Section: 12 ABM (A)
Four Ms of Production
The most critical factor in the whole production system are the inputs and
the transformation process. Their quality determines the quality of the
output. It is also known as “garbage in, garbage out” or GIGO in the
parlance of computer technology.
A. Manpower- simply refers to the human workforce involved in the
manufacture of products. It is considered as the most critical and
important factor of production. The entrepreneur must determine,
acquire, and match the most qualified employees with the jobs at the
most appropriate time period.
Some of the manpower criteria that must be highly considered by the
entrepreneur are as follows:
1. Educational qualifications and experience required for the job.
2. Status of employment, whether permanent or temporary.
3. Number of workers required for the job.
4. Skills and expertise required for the job.
5. Appropriate time the worker is needed.
6. Conduct of background checking and issuance of payments.
7. Amount of salary or wages and to other mandatory benefits.
8. Availability of potential workers in the community.
B. Method or production method, refers to the process or technique of
converting raw materials to finished products. The raw materials
undergoes several stages before it is completed and becomes ready
for delivery to the target customers.
The selection of the method of production is dependent on some
factors, namely,
1. Product to produce
2. Mode of production
3. Manufacturing equipment to use
4. Required skills to do the work.
C. Machine- refers to the manufacturing equipment used in the
production of goods or delivery of services.
In the process of selecting the type of equipment to purchase, the
entrepreneur may consider the following important elements:
1. Types of products to be produced
2. Production system to be adopted
3. Cost of the equipment
4. Availability of spare parts in the local market
5. Efficiency of the equipment
6. The skills required in running the equipment
D. Materials-simple refers to the raw needed in the production of a
product. Materials basically form part of the finished product. For
example, wood or lumber is a raw materials used to produce a table
or a chair. In case raw materials are of poor quality, the finished
product will be poor quality as well.
The entrepreneur may consider the following important factors in the
selection of raw materials;
1. Cost
2. Quality
3. Availability
4. Credibility of suppliers
5. Waste that the raw materials may produce
You might also like
- Purchase Good Assessment USAMA KHALIDDocument9 pagesPurchase Good Assessment USAMA KHALIDUsama AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Guide to Contract Pricing: Cost and Price Analysis for Contractors, Subcontractors, and Government AgenciesFrom EverandGuide to Contract Pricing: Cost and Price Analysis for Contractors, Subcontractors, and Government AgenciesNo ratings yet
- Materials Enabled Designs: The Materials Engineering Perspective to Product Design and ManufacturingFrom EverandMaterials Enabled Designs: The Materials Engineering Perspective to Product Design and ManufacturingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Consulting Interview Case Preparation: Frameworks and Practice CasesFrom EverandConsulting Interview Case Preparation: Frameworks and Practice CasesNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions On Demand Estimation LatestDocument6 pagesPractice Questions On Demand Estimation Latestimylviva100% (2)
- Report in Production ManagementDocument6 pagesReport in Production ManagementNheil Coping BeteNo ratings yet
- For Example, Nikon Cameras Plan and Establish Special Lines For Each Model and Manufacture Huge Quantities For The Global Market. Here, TheDocument7 pagesFor Example, Nikon Cameras Plan and Establish Special Lines For Each Model and Manufacture Huge Quantities For The Global Market. Here, Themohit jainNo ratings yet
- Managerial EcnomiccsDocument7 pagesManagerial EcnomiccsEzam ShahNo ratings yet
- Material ManagementDocument33 pagesMaterial ManagementAsif UniaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument30 pagesIntroductionBlessious Joseph LandoyNo ratings yet
- Demand Forecasting MEDocument26 pagesDemand Forecasting MEmanslikeNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Opportunities and Selection Process: Unit IiDocument35 pagesEntrepreneurial Opportunities and Selection Process: Unit IiAnkush YedaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Opportunity Seeking Screening and SeizingDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Opportunity Seeking Screening and SeizingMaica A. Agliam100% (1)
- Ducusin Janna P. Om Chapter 1Document3 pagesDucusin Janna P. Om Chapter 1Jessie jorgeNo ratings yet
- MSL Vol2 MSL 2012 98Document26 pagesMSL Vol2 MSL 2012 98rnaganirmitaNo ratings yet
- Factors To Consider in ProductDocument1 pageFactors To Consider in ProductkuselvNo ratings yet
- Material ControlDocument14 pagesMaterial ControlKavana DNo ratings yet
- Decision Making: The Elements of DecisionDocument11 pagesDecision Making: The Elements of DecisionsidrabatoolNo ratings yet
- Demand Forecasting and Techniques: TR PandeyDocument26 pagesDemand Forecasting and Techniques: TR PandeyNiharika Satyadev JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Notes (PM) by SSDocument17 pagesUnit 3 Notes (PM) by SSupadhyaypriyam.50No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document14 pagesChapter 5Cyra JimenezNo ratings yet
- Potential For Profit: 1. Most Critical CriteriaDocument4 pagesPotential For Profit: 1. Most Critical CriteriaprodandanliviuNo ratings yet
- Purchasing Process, Enablers Documents Used in Purchasing BCOM YERA TWODocument10 pagesPurchasing Process, Enablers Documents Used in Purchasing BCOM YERA TWOZediNo ratings yet
- Stores Location & LayoutDocument7 pagesStores Location & LayoutVinay SinghNo ratings yet
- Entrep ScriptDocument8 pagesEntrep ScriptJamelleNo ratings yet
- MATH322-f Week 1 and 2Document62 pagesMATH322-f Week 1 and 2Jordan RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Recognize A Potential MarketDocument26 pagesRecognize A Potential MarketRalph LatosaNo ratings yet
- 4ms of ProductionDocument3 pages4ms of ProductionJarred HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Market ForcesDocument73 pagesModule 3 - Market ForcesShamanth GowdaNo ratings yet
- Entrep Q4 - Module 5Document10 pagesEntrep Q4 - Module 5Paula DT PelitoNo ratings yet
- Material Cost & ValuationDocument71 pagesMaterial Cost & ValuationRiya KesarwaniNo ratings yet
- M1 CPR MoralesDocument4 pagesM1 CPR Moralesmedwin moralesNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Quarter 2 - LAS 1Document10 pagesEntrepreneurship: Quarter 2 - LAS 1Shaine GiliNo ratings yet
- Section B, C AND E NotesDocument29 pagesSection B, C AND E NotesCorrinaNo ratings yet
- Explain The Meaning of The Term Demand ForecastingDocument7 pagesExplain The Meaning of The Term Demand ForecastingzbenipalNo ratings yet
- Sources of Opportunities Hand OutDocument2 pagesSources of Opportunities Hand OutTanya Jane PeñarandaNo ratings yet
- Purchasing CycleDocument13 pagesPurchasing CyclePoonam Sugand0% (2)
- Topic Two Purchasing Process and Negotiation Full ReaderDocument25 pagesTopic Two Purchasing Process and Negotiation Full ReaderIanNo ratings yet
- Quality ManagementDocument3 pagesQuality ManagementRowena MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Business Plan Preparation:: Sources of Product For BusinessDocument15 pagesUnit-3 Business Plan Preparation:: Sources of Product For BusinessHima VarshaNo ratings yet
- Villon, Rainelle B. 11-BBA-01 Discussion and Review QuestionsDocument20 pagesVillon, Rainelle B. 11-BBA-01 Discussion and Review QuestionsJessie jorgeNo ratings yet
- Solved Assignment 1 PDFDocument36 pagesSolved Assignment 1 PDFsanjana100% (1)
- Supplier SelectionDocument21 pagesSupplier SelectionPriyanka JanaNo ratings yet
- Quality DevelopmentDocument7 pagesQuality Developmentjane85352No ratings yet
- PPT4 The Industry Environment AnalysisDocument31 pagesPPT4 The Industry Environment AnalysisRenee Rose Piñera BulusanNo ratings yet
- A) STEEP Analysis On Finish Line IncDocument3 pagesA) STEEP Analysis On Finish Line IncHuma TariqNo ratings yet
- Las Entrep Q1 M2Document7 pagesLas Entrep Q1 M2Ma. Crisanta A. AntonioNo ratings yet
- MidTermExam CM 1Document10 pagesMidTermExam CM 1Gurlal SinghNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Medical and Business College EeeeDocument8 pagesAddis Ababa Medical and Business College EeeemoadagimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Inventory Control Review and Discussion QuestionsDocument3 pagesChapter 12 Inventory Control Review and Discussion QuestionsDennis MpoNo ratings yet
- Product Manager: Production Planning Personnel Production Control Personnel Inventory Control PersonnelDocument3 pagesProduct Manager: Production Planning Personnel Production Control Personnel Inventory Control PersonnelOyi Lorenzo-LibanNo ratings yet
- The Cost of Production ProcessDocument22 pagesThe Cost of Production ProcessAya Abdel-fadeelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2IanNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document31 pagesPresentation 5Ram BarceloNo ratings yet
- Shabab Full ProjectDocument73 pagesShabab Full Projectkirnan32No ratings yet
- Achieving a Safe and Reliable Product: A Guide to Liability PreventionFrom EverandAchieving a Safe and Reliable Product: A Guide to Liability PreventionNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CH 171Document1 pageCH 171EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- UCSP Reviewer LawDocument6 pagesUCSP Reviewer LawEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Research EnvironmentDocument1 pageResearch EnvironmentEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Sports Article English High School Level Earl Justine RaveloDocument2 pagesSports Article English High School Level Earl Justine RaveloEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing 4th QuarterDocument10 pagesReading and Writing 4th QuarterEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Community Profile and Baseline DataDocument7 pagesCommunity Profile and Baseline DataEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document1 pageCH 2EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Reflect Upon 1Document2 pagesReflect Upon 1EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Mail Merge SampleDocument1 pageMail Merge SampleEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document1 pageCH 4EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Math ChallengeDocument1 pageMath ChallengeEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Abstract ResearchDocument1 pageAbstract ResearchEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document1 pageCH 3EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- 3 RDQRT MTweek 3Document3 pages3 RDQRT MTweek 3EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document1 pageCH 7EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- 4 TH Mathwk 9Document4 pages4 TH Mathwk 9EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- 3 RD MAPEHWK9Document6 pages3 RD MAPEHWK9EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- 3 RD MAPEHWK3Document4 pages3 RD MAPEHWK3EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- 3 RD Mathwk 7Document4 pages3 RD Mathwk 7EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document2 pagesCH 5EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- 3 RD MAPEHWK6Document6 pages3 RD MAPEHWK6EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- 3 RDQRT MTWK 5Document3 pages3 RDQRT MTWK 5EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- 3 RD MAPEHWK7Document7 pages3 RD MAPEHWK7EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Daily Lessonlog Day: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Date/Time QuarterDocument6 pagesDaily Lessonlog Day: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Date/Time QuarterEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- 3 RDQRT MTWK 6Document3 pages3 RDQRT MTWK 6EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument7 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- 4THMATHWK10Document4 pages4THMATHWK10EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Daily Lessonlog Day: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Date/Time QuarterDocument5 pagesDaily Lessonlog Day: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Date/Time QuarterEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Ases Post Phil Iri 2019Document3 pagesAses Post Phil Iri 2019EJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Biology I: Multiple Choice Questions 20 Items Name: - SchoolDocument3 pagesBiology I: Multiple Choice Questions 20 Items Name: - SchoolEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Explain The Practical Implication of Various Elasticity of DemandDocument5 pagesExplain The Practical Implication of Various Elasticity of DemandVivek Chaudhary50% (2)
- Shamsuddin Et Al., 2008 - Demand Analyses of Rice in MalaysiaDocument21 pagesShamsuddin Et Al., 2008 - Demand Analyses of Rice in MalaysiaHannah LeeNo ratings yet
- Model - ME4E - Business Economics Answer Key (Revised) - 06 Dec 21Document15 pagesModel - ME4E - Business Economics Answer Key (Revised) - 06 Dec 21PradeepNo ratings yet
- MCQ RRDocument31 pagesMCQ RRTeleTech RKNo ratings yet
- Economics: Guide To Economics For Filipinos by Bernardo VillegasDocument79 pagesEconomics: Guide To Economics For Filipinos by Bernardo VillegasRahel Yemane Embaye TeweldeNo ratings yet
- LQDocument12 pagesLQCharmaine CapaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Pricing DecisionsDocument37 pagesChapter 15 - Pricing DecisionsPRECIOUSNo ratings yet
- Economics Quiz 3Document3 pagesEconomics Quiz 3Pao EspiNo ratings yet
- Economics 2Document267 pagesEconomics 2Sharon AmondiNo ratings yet
- How You Know Rural IndiaDocument78 pagesHow You Know Rural IndiaAadil KakarNo ratings yet
- Name: Prithhiraj Biswas, Roll No: 35, UG First Semester Topic: 1.point ElasticityDocument15 pagesName: Prithhiraj Biswas, Roll No: 35, UG First Semester Topic: 1.point ElasticityPrithhiraj BiswasNo ratings yet
- Economics of CrimeDocument13 pagesEconomics of CrimeAshutosh Shukla100% (1)
- Definition of Economics:: Two Important Economic Conditions That Necessitate The Study of Economics?Document27 pagesDefinition of Economics:: Two Important Economic Conditions That Necessitate The Study of Economics?Navya NarayanamNo ratings yet
- Onion CultivationDocument45 pagesOnion CultivationbnsamyNo ratings yet
- AEA 207 Demand ElasticityDocument35 pagesAEA 207 Demand Elasticitycalvinkileo6No ratings yet
- 2018ies Exam Question Paper-1Document6 pages2018ies Exam Question Paper-1AnjaliPuniaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11 Marketing - 1.2Document334 pagesCHAPTER 11 Marketing - 1.2Joanna GarciaNo ratings yet
- Q1Document2 pagesQ1racquelcamatchoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Implications of Market Pricing in Making Economic DecisionDocument13 pagesLecture 5 - Implications of Market Pricing in Making Economic DecisionLuna LedezmaNo ratings yet
- MGEA02Document14 pagesMGEA02Tim SmetNo ratings yet
- Econ 2106 Principles of MicroeconomicsDocument7 pagesEcon 2106 Principles of MicroeconomicsWalid Asif JanjuaNo ratings yet
- MEC 604 LecturesDocument40 pagesMEC 604 LecturesRoshan KCNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Health Economics and Policy 5th Edition James W Henderson DownloadDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Health Economics and Policy 5th Edition James W Henderson Downloadirisadele7s3x8No ratings yet
- ECO402 Solved Mid Term Corrected by Suleyman KhanDocument15 pagesECO402 Solved Mid Term Corrected by Suleyman KhanSuleyman KhanNo ratings yet
- ECO111 Microeconomics Class: Handed Out: Submission Due: Format: Submission Mode: Hardcopy and Softcopy Email ToDocument10 pagesECO111 Microeconomics Class: Handed Out: Submission Due: Format: Submission Mode: Hardcopy and Softcopy Email ToDo Thu Tra50% (2)
- Question Bank EFM MCQDocument26 pagesQuestion Bank EFM MCQShekhar MishraNo ratings yet
- Re231123123nur Rdssfsfan Final Assignment - ECO101Document4 pagesRe231123123nur Rdssfsfan Final Assignment - ECO101Turhan PathanNo ratings yet
- Bus 1103 Learning Journal Unit 3Document2 pagesBus 1103 Learning Journal Unit 3Mailu Shirl100% (1)
- ECON 101 Basic MicroeconomicsDocument95 pagesECON 101 Basic MicroeconomicsJunnel RamosNo ratings yet