Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Diagnostic Bacteriology
Uploaded by
Hana Lunaria0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageOriginal Title
Introduction to Diagnostic Bacteriology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageIntroduction To Diagnostic Bacteriology
Uploaded by
Hana LunariaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
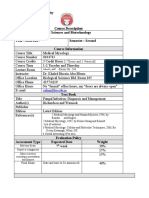
Clinical
Bacteriology
LECTURE/ SECOND SEMESTER
INTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSTIC BACTERIOLOGY
LESSON INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES: What is Microbiology?
After studying this chapter, the students should be able
to:
Define microbiology, medical microbiology and
diagnostic microbiology.
Define terms related to infectious process and
disease transmission.
Outline some of the contributions of
Leeuwenhoek, Pasteur, and Koch to
Microbiology.
GENERAL DEFINITIONS
1. Microbiology- Branch of biology which deals with
the study of living organisms that are small to be
seen by the naked eye.
- Biology is the study of living organisms.
- Micro means small.
2. Medical Microbiology- a branch of medical
science which deals with the study of medically
important microorganisms specifically their role in
human disease which includes diagnosis,
treatment, and prevention of infectious diseases.
- We will be focusing more on medically
important microorganisms
- Our focus is the microorganisms that could
be able to cause disease on humans and
also animals.
3. Diagnostic microbiology- a branch of medical
microbiology that focuses on the laboratory
identification of medically important bacteria by
phenotypical and genotypical characterization
including antibiotic susceptibility testing.
- When we say bacteriology, Logi means
study.
- We will be focusing in the laboratory
identification of bacteria most especially
the medically important bacteria.
- Once na alam natin yung laboratory
identification, next is antibiotic
susceptibility testing.
- Remember in treating bacteria, we’re going
to use antiobiotics.
LUNARIA,HANA LAZO BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE
You might also like
- Microbiome Therapeutics: Personalized Therapy Beyond Conventional ApproachesFrom EverandMicrobiome Therapeutics: Personalized Therapy Beyond Conventional ApproachesNar Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Mic 1 - Microbiology and Parasitology (Lecture) Assignment No. 1: Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesMic 1 - Microbiology and Parasitology (Lecture) Assignment No. 1: Introduction To MicrobiologyRica AngelesNo ratings yet
- Micpar Week 1Document4 pagesMicpar Week 1Jlysa BatulanNo ratings yet
- PONCE - Module 1 - BSN-2 - A18Document7 pagesPONCE - Module 1 - BSN-2 - A18Ponce Kristel Mae ONo ratings yet
- General Microbiology - Introduction - 1Document3 pagesGeneral Microbiology - Introduction - 1Harsha N KumarNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument37 pagesIntroductionnanakwame5769No ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical Microbiology and Immunology 25th October 2022 2Document35 pagesIntroduction To Medical Microbiology and Immunology 25th October 2022 2wildoNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document7 pagesModule 1mirai desuNo ratings yet
- MICRO-102 (Assignment# 1)Document6 pagesMICRO-102 (Assignment# 1)hely shahNo ratings yet
- Introduction in Medical Microbiology June 2020 Online ClassDocument9 pagesIntroduction in Medical Microbiology June 2020 Online Classjames rukenyaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Pathology ArticleDocument6 pagesMicrobiology and Pathology ArticlesamwilliamsNo ratings yet
- STM 211 Belels 2024Document8 pagesSTM 211 Belels 2024belelmusa86.mhmbNo ratings yet
- Why Study MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesWhy Study MicrobiologyRica AngelesNo ratings yet
- Methodological Instructions - Module 2Document60 pagesMethodological Instructions - Module 2Frt TrfNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Microbiology Notes FinalDocument111 pagesFundamental of Microbiology Notes Finalshi vaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microbiology: Size Which IncludesDocument1 pageIntroduction To Microbiology: Size Which IncludesShweta ChevleNo ratings yet
- 02.02.24-Basic Microbiology-Lecture-1Document38 pages02.02.24-Basic Microbiology-Lecture-1ashik rahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction and HistoryDocument37 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction and HistoryAkbar SaleemNo ratings yet
- Micro AssignmentDocument3 pagesMicro AssignmentClement GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Notes On Microbiology - BiologyDocument83 pagesNotes On Microbiology - BiologyRajaDeepak VermaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To MicrobiologygraanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology The ScienceDocument14 pagesMicrobiology The ScienceWaad ShamailehNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument10 pagesMicrobiologyCabdullaahi CabdiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - History and Introduction To Microbiology-1Document33 pagesLecture 1 - History and Introduction To Microbiology-1stancyzuluNo ratings yet
- Mehedi Assignment IntroDocument12 pagesMehedi Assignment Intromssakib2003No ratings yet
- Modulus Infection - 2019 - DescriptionDocument45 pagesModulus Infection - 2019 - Descriptionrafael rubinovNo ratings yet
- Importance of MicrobiologyDocument10 pagesImportance of MicrobiologyAbdul QadirNo ratings yet
- Plains of Mamre InstituteDocument5 pagesPlains of Mamre InstituteAbel NimolNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry CoursepackDocument34 pagesBiochemistry Coursepackanonymous squash0% (1)
- Biochemistry - Meaning & ScopeDocument2 pagesBiochemistry - Meaning & ScopeBasudev GoswamiNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument11 pagesMicrobiologyKaleem AfridiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microbiology For Ipc 1Document134 pagesIntroduction To Microbiology For Ipc 1charitygyasi2002No ratings yet
- Introduction To Micro - MD - 2023Document112 pagesIntroduction To Micro - MD - 2023Tall tunaNo ratings yet
- Module in Micro & paraDocument6 pagesModule in Micro & paraAlpha-z PrinNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesMicrobiologyreg speckNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument30 pages1 Introduction To MicrobiologyrazAn swNo ratings yet
- Basic Microbiology Lecture 1Document15 pagesBasic Microbiology Lecture 1Md Loby MahmudNo ratings yet
- Micro para LecDocument3 pagesMicro para LecKristine Angie RamosNo ratings yet
- Biosecurity. BiotherrorismDocument3 pagesBiosecurity. BiotherrorismReshuNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences PDFDocument64 pagesLife Sciences PDFChris HemsworthNo ratings yet
- FFFFFFF FFFFFFF FFFFFFFFDocument16 pagesFFFFFFF FFFFFFF FFFFFFFFJonathan SaveroNo ratings yet
- Micro BioDocument8 pagesMicro BioElma SolderoNo ratings yet
- Assigment MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesAssigment MicrobiologyFu'e AbdumalikNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument11 pagesMicrobiologyPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- Cabornay MC3 1stDocument22 pagesCabornay MC3 1stDaisy RoseteNo ratings yet
- Introduction of MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesIntroduction of MicrobiologyRahul PalsNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument14 pagesMicrobiology and ParasitologyLleana TanNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument11 pagesMicrobiologyEdy SaindarNo ratings yet
- Pure MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesPure MicrobiologyElla Mharie Muñasque GabijanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument14 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To MicrobiologyRealyn FababaerNo ratings yet
- G102933a2019 20iENG PDFDocument9 pagesG102933a2019 20iENG PDFJeof Bethafin OrtezaNo ratings yet
- PD2Document15 pagesPD2DrShobhit RajNo ratings yet
- What Is MicrobiologyDocument13 pagesWhat Is MicrobiologyShifa RazaNo ratings yet
- The Microbiology Companion ReviewDocument12 pagesThe Microbiology Companion Reviewogangurel100% (1)
- Overview of The Scope of MicrobiologyDocument10 pagesOverview of The Scope of MicrobiologySivalakshmi GuruselvanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology World Magazine Issue4Document33 pagesMicrobiology World Magazine Issue4ritter kinsellaNo ratings yet
- Branches of BiologyDocument7 pagesBranches of BiologyDeane Marc TorioNo ratings yet
- The Hashemite University Faculty of Science: Salma@hu - Edu.joDocument3 pagesThe Hashemite University Faculty of Science: Salma@hu - Edu.joOdurNo ratings yet
- Bsczo 302Document237 pagesBsczo 302Irb azNo ratings yet
- Definition, Scope and Significance of MicrobiologyDocument6 pagesDefinition, Scope and Significance of Microbiologykrixiededios7No ratings yet
- Worksheet #1 MicroscopeDocument1 pageWorksheet #1 MicroscopeHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic ContinuationDocument5 pagesNucleic ContinuationHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- Bact211 Lec Week 2 Taxonomy and ClassificationDocument6 pagesBact211 Lec Week 2 Taxonomy and ClassificationHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- CRWTDocument20 pagesCRWTHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminologies and AbbreviationDocument4 pagesMedical Terminologies and AbbreviationHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- Tangina Mo Basahin Mo AkoDocument4 pagesTangina Mo Basahin Mo AkoHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- ANACHEM - ChromatographyDocument6 pagesANACHEM - ChromatographyHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- Health Care System PDFDocument6 pagesHealth Care System PDFHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- Planning and Conducting ClasssesDocument6 pagesPlanning and Conducting ClasssesHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument7 pagesLipidsHana LunariaNo ratings yet