Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 9 - Animal Transport
Uploaded by
Hashtag []Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9 - Animal Transport
Uploaded by
Hashtag []Copyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 9: ANIMAL TRANSPORT 1.
Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium
(RA)
Circulatory systems
2. Deoxygenated blood enters the right ventricle
The circulatory system ensures that blood flows (RV)
around the body, providing vital nutrients to the 3. Deoxygenated blood is pumped by the RV to
cells that need them and taking away metabolic the lungs (to become oxygenated)
waste products. The system consists of a pump, 4. Oxygenated blood enters the left atrium (LA)
blood vessels, and valves. 5. Oxygenated blood enters the left ventricle
(LV)
Single circulation means that the blood passes
6. Oxygenated blood is pumped by the LV to the
through the heart just once. Fishes have a single
rest of the body
circulation system.
7. Body cells use up the oxygen for respiration
Double circulation means that the blood passes and cause the blood to become deoxygenated
through the heart twice. Mammals have a double 8. Deoxygenated blood returns to the heart and
circulation system. the cycle repeats
The double circulation system is more efficient Heart structure & function
because it maintains a higher blood pressure
The right side of the blood contains deoxygenated
compared to a single circulation system. Moreover,
blood, which is pumped to the lungs for
it enables the separation of oxygenated and
oxygenation. The oxygenated blood returns to the
deoxygenated blood which is a crucial aspect of gas
left side of the heart, where it pumps it to the rest of
exchange and respiration.
the body.
Blood flow around the body
All mammals use a double circulation system. It is
important to understand how the blood flows
through the body.
IGCSE BIOLOGY COMPLETE STUDY GUIDE
Heart Function Muscular differences
structure Ventricles have a thicker muscular wall compared to
Atrium The right and left atrium contracts to the atria because the ventricles must pump blood
pump blood into the right and left through a greater distance than the atria.
ventricles respectively
With that same logic, the walls of the left ventricle
Ventricles The right ventricle contracts to pump are thicker than the right ventricle. This is because
blood to the lungs (for oxygenation) the left ventricle must generate more force in order
to pump the blood through a greater distance (to the
The left ventricle contracts to pump
rest of the body) compared to the right ventricle (to
blood to the rest of the body
the lungs).
Pulmonary Carries blood away from the right
artery ventricle to the lungs Veins vs arteries
Sometimes students associate arteries with
Pulmonary Carries blood from the lungs to the
veins left atrium oxygenated blood, and veins with deoxygenated
blood.
Aorta Large artery which carries oxygenated
blood from the left ventricle to the However, this is inaccurate. Afterall, the pulmonary
rest of the body veins carry oxygenated blood and the pulmonary
arteries contain deoxygenated blood.
Vena cava Large vein which carries
deoxygenated blood from the body The true definition of veins and arteries are as
back to the heart (into the right follows
atrium)
● Arteries carry blood away from the heart
Valves Valves prevent the backflow of blood, ● Veins carry blood towards the heart
and ensure that it always flows in one
direction This rule always applies, as you can see from a few
examples here.
Semilunar valves are found within
arteries (aorta & pulmonary artery) ● Vena cava is a vein because it returns blood
to the heart
Atrioventricular valves are found in ● Pulmonary artery is an artery because it
between the atrium and ventricles on
carries blood away from the heart
both sides of the heart. They prevent
the backflow of blood into the atria ● Pulmonary vein is a vein because it carries
when the ventricles contract blood to the heart
● Aorta is an artery because it carries blood
Septum Separates deoxygenated blood (right away from the heart
side) from oxygenated blood (left
side)
IGCSE BIOLOGY COMPLETE STUDY GUIDE
Coronary heart disease Some risk factors for developing coronary heart
disease are
Like all other muscles, the heart muscles themselves
need a supply of blood too in order to function. The ● Poor diet
artery that supplies the heart muscles with blood is ● Stress
called the coronary artery. ● Smoking
● Genetics
● Age
● Gender
The treatment of coronary heart disease can be by
medication or surgery.
Medication Blood thinning medication is used to
reduce chance of forming blood
Plaque is a fatty, waxy substance that forms deposits clots, thereby reducing the chance of
a heart attack
in artery walls. This causes the artery lumen to
become narrower. Surgical Stents are a tube shaped device
which is placed inside the coronary
artery to physically hold it open
Angioplasty uses a spherical balloon
that can be inflated once it is inside
the artery to force it to open
A bypass is the process of making a
separate “new” artery to allow for an
alternative blood path that the heart
can use to receive blood (rather than
solely relying on the coronary
artery)
Heart activity
The heart rate is the rate at which the heart beats.
There are a few different ways in which this can be
measured.
Coronary heart disease describes the buildup of
plaque in specifically the coronary artery, which ● Pulse rate
causes vascular narrowing and limits the blood flow This is the most common way to measure the
to the heart. A complete blockage may occur if a heart rate.
blood clot gets jammed inside the artery, which
leads to a heart attack. ● Listening to heart valves closing
IGCSE BIOLOGY COMPLETE STUDY GUIDE
By using a stethoscope, it is possible for Sometimes blood can travel directly from the
doctors to listen to the closing of heart valves arterioles to venules without going through the
to measure heart rate. capillaries via shunt vessels, which directly connect
the arterioles and venules. Shunt vessels therefore
● Electrocardiogram (ECG)
act as an alternative pathway for blood to flow
With each heartbeat, an electrical signal through.
travels through the heart. This signal causes
Refer to the diagram below which demonstrates the
the heart to contract and pump blood.
relationship between the different blood vessels
An electrocardiogram detects these electrical mentioned above.
signals to derive accurate measurements of
heart activity.
Physical activity increases the energy demand in
muscles such as the arms and legs. With an
increased rate of respiration, the blood must travel
quicker to supply the muscles of oxygen and
nutrients, whilst removing the waste products such
as carbon dioxide. It is for this reason that the heart
rate goes up with exercise, in order to meet the
respiratory demands of the body.
Blood vessels
Types of blood vessels
You must know the structures of each of these blood
Blood vessels are tubular structures used for
vessels.
carrying blood throughout the body.
1. Arteries
The arteries carry blood directly from the heart (at
● Thick muscular walls to withstand
high pressures). As these arteries get closer to the
blood being carried at high pressures
tissues and organs that need the blood, they begin
● Narrow lumen which expands as
to branch out into smaller vessels called the
blood pulsates through which
arterioles. The arterioles then branch into even
maintains the blood pressure
narrower vessels called the capillaries.
● Valves absent (not necessary since
It is at the level of the capillaries that oxygen and backflow will not happen when blood
nutrients leave the blood and enter the tissues, is carried at such high pressures)
while waste products such as carbon dioxide leave 2. Arterioles
the tissues and enter the blood. The blood therefore ● Muscular and elastic walls which can
becomes deoxygenated. constrict and dilate in order to
regulate blood flow
The capillaries begin to join together to form larger
tubes called the venules, which then join to form >> See chapter 15: Coordination and
veins which are even larger.
IGCSE BIOLOGY COMPLETE STUDY GUIDE
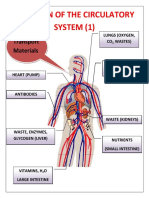
response : Homeostasis ● Pulmonary vein - transports oxygenated
blood from the lungs to the left atrium
3. Capillaries
● Thin walls (one cell thick) to allow for Kidneys
rapid diffusion of nutrients and wastes ● Renal artery - transports oxygenated blood to
● Tiny lumen (size of single RBC) to the kidneys
allow blood cells to pass as closely to ● Renal vein - transports deoxygenated blood
the walls as possible to allow for rapid away from the kidneys
diffusion
● Valves absent (not necessary because Liver
backflow of blood cannot happen due ● Hepatic artery - transports oxygenated blood
to extremely small lumen) to the liver
4. Venules ● Hepatic vein - transports deoxygenated blood
● Thinner walls than arterioles away from the liver
5. Veins ● Hepatic portal vein - transports blood from
● Thin walls with minimal muscle and intestines, spleen, pancreas and gallbladder
elastic fibers (thick walls not necessary to the liver
since blood is traveling at low
pressures) Blood
● Large lumen to reduce blood flow Components of blood
resistance
● Valves to ensure that blood does not The blood is made up of a mixture of:
backflow ● Plasma
6. Shunt vessels ● Red blood cells (RBCs)
● Like arterioles, the elastic walls can ● White blood cells (WBCs)
constrict and dilate in order to regular ● Platelets
blood flow
The plasma makes up about 50% of blood. It is a
Blood vessels of various organs yellowish liquid that all other blood components are
Heart dissolved in.
● Vena cava - a large vein that delivers Red blood cells have hemoglobin which binds with
deoxygenated blood to the right atrium oxygen for transport around the body.
● Aorta - a large artery that delivers White blood cells are a part of the immune system
oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to that helps to destroy pathogens. There are two types
the rest of the body of white blood cells
Lungs 1. Phagocytes - WBCs that engulf and digest
● Pulmonary artery - transports deoxygenated pathogens via phagocytosis
blood from the heart to the lungs 2. Lymphocytes - WBCs which produce
antibodies
IGCSE BIOLOGY COMPLETE STUDY GUIDE
>> See chapter 10: Diseases and immunity
Lastly, the platelets are substances that form blood
clots which act to prevent blood loss. At the site of
damage, platelets immediately stick together and
release chemical signals which attract nearby cells
and clump them together. A series of chemical
reactions take place, including the important
reaction:
Fibrinogen → Fibrin
Fibrin forms a threat which forms a mesh that traps
RBCs to establish a thick clot. The clot seals off the
damaged site.
IGCSE BIOLOGY COMPLETE STUDY GUIDE
You might also like
- CN111 CardioVascular SystemDocument43 pagesCN111 CardioVascular SystemSydney AchaiNo ratings yet
- How the Circulatory System Transports Substances Around the BodyDocument31 pagesHow the Circulatory System Transports Substances Around the BodyGeonardo100% (3)
- CardioVascular SystemDocument26 pagesCardioVascular SystemSamir KadiyaNo ratings yet
- Animal Transport - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Document14 pagesAnimal Transport - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Zhi En LeeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument34 pagesCirculatory SystemMHAR CHRISTOPHER MAMASIGNo ratings yet
- 024-Premedical Circulatory SystemDocument31 pages024-Premedical Circulatory Systemchealzea asuncsionNo ratings yet
- Thecirculatorysystem 130618021608 Phpapp01Document70 pagesThecirculatorysystem 130618021608 Phpapp01Mikel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument24 pagesCardiovascular Systemjimjose antonyNo ratings yet
- Transport in HumansDocument6 pagesTransport in HumansJason Ng100% (5)
- Circulatory System Explained in 40 CharactersDocument22 pagesCirculatory System Explained in 40 CharactersJheyrick Casipe BaliguatNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: How Blood Transports Oxygen and NutrientsDocument4 pagesCirculatory System: How Blood Transports Oxygen and NutrientsShanice BedecirNo ratings yet
- Animal Transport 1Document13 pagesAnimal Transport 1Feranmi AkinboboyeNo ratings yet
- Life Processes, Class XDocument31 pagesLife Processes, Class XPiyushNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 f3Document101 pagesChapter 3 f3Ghanapathi RamanathanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory systemDocument15 pagesCirculatory systemsafiealrahman.2009No ratings yet
- Transport in Animals (1)Document12 pagesTransport in Animals (1)Jedidiah DickNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Intro To Circulation 2014 2Document51 pagesTissues and Intro To Circulation 2014 2Chantae JulienNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System in Man: A Concise Guide to the Heart and Blood FlowDocument54 pagesThe Circulatory System in Man: A Concise Guide to the Heart and Blood FlowStudent ResearchNo ratings yet
- Circulatory_System_in_Humans_Document4 pagesCirculatory_System_in_Humans_petra.t.ayalNo ratings yet
- This Powerpoint Is Hosted On Please Visit For 100's More Free PowerpointsDocument21 pagesThis Powerpoint Is Hosted On Please Visit For 100's More Free PowerpointsMisbakhul MunirNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: Ronmar T. Riňo Abegail Bersamin Maila C. TamondongDocument30 pagesThe Circulatory System: Ronmar T. Riňo Abegail Bersamin Maila C. TamondongKelly Troy Alano100% (12)
- Blood and Circulation PDFDocument47 pagesBlood and Circulation PDFeric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument111 pagesCirculatory SystemYounas Bhatti100% (1)
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemJpaw Kidman100% (1)
- Life Processes - Transportation in Human Beings 1.PptxDocument24 pagesLife Processes - Transportation in Human Beings 1.PptxraghavrungtambwaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory Systemparitosh7_886026No ratings yet
- XI-1 Adinda Caesaria Bunga Astiti Hanin Rialsa Meitha Anindya Raisa CeciliaDocument20 pagesXI-1 Adinda Caesaria Bunga Astiti Hanin Rialsa Meitha Anindya Raisa CeciliaadiriadheeNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument7 pagesTransport in Animalstmoatshe96No ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: (Parts and Functions) Prepared By: Wilfred D. ManingasDocument30 pagesThe Circulatory System: (Parts and Functions) Prepared By: Wilfred D. ManingasAngelica OlivarNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesCardiovascular SystemMayim LouiseNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument67 pagesCirculatory SystemGideon Cavida80% (5)
- القلبDocument11 pagesالقلبNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument6 pagesTransport in Animals2027dpatel.studentNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemGodsend OparaNo ratings yet
- Student Notes - Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesStudent Notes - Circulatory SystemJanith VimukthiNo ratings yet
- Chapter9 Transport in AnimalsDocument77 pagesChapter9 Transport in Animalsyuuu32716No ratings yet
- Copy For Students Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument45 pagesCopy For Students Respiratory and Circulatory SystemKarla AlegreNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 4 - Circulatory SystemJoseeNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLili M.No ratings yet
- Transport in Animals BIOLOGY bySATRIADocument7 pagesTransport in Animals BIOLOGY bySATRIASatria HalimNo ratings yet
- TEAM3 BSN1-J Anatomy Lec Module 10 Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesTEAM3 BSN1-J Anatomy Lec Module 10 Cardiovascular SystemElisha Fleur Cambas GachoNo ratings yet
- Transport System in OrganismsDocument19 pagesTransport System in OrganismsJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- 3.2.2 Blood Circulatory System in HumansDocument19 pages3.2.2 Blood Circulatory System in HumanslovenialawNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory Systemsyrine mendozaNo ratings yet
- 4 - The Circulatory System - PPTDocument110 pages4 - The Circulatory System - PPTRinopro 555No ratings yet
- Circulatory System LabDocument44 pagesCirculatory System LabMarileth CoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument33 pagesCardiovascular SystemJay Anne CorrianoNo ratings yet
- (Lecture 7) The Cardiovascular, Respiratory and Lymphatic SystemDocument32 pages(Lecture 7) The Cardiovascular, Respiratory and Lymphatic SystemKasraSrNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Guide for 10th Grade StudentsDocument52 pagesCirculatory System Guide for 10th Grade StudentsThe Deep Sea IdNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System PDFDocument22 pagesCirculatory System PDFJerry SmithNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument10 pagesTransport in Animalswarona letangNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.2 - Human Circulatory SystemDocument30 pagesTopic 2.2 - Human Circulatory Systembienfrancis.reyes.jhsNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy: The HeartDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy: The HeartSyafiq RozaliNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System ExplainedDocument27 pagesThe Cardiovascular System ExplainedMary100% (1)
- Unit 6 Learning Guide Name: Brandon Au-Young: InstructionsDocument31 pagesUnit 6 Learning Guide Name: Brandon Au-Young: InstructionsBrandonNo ratings yet
- The Heart Pumps Blood CirculationDocument9 pagesThe Heart Pumps Blood CirculationShokefun OlawaleNo ratings yet
- Lect 8. Cardiovascular SystemDocument35 pagesLect 8. Cardiovascular Systemrukhsanatariq299No ratings yet
- Transport in Animals o Level2018Document12 pagesTransport in Animals o Level2018MuneebNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryDocument73 pagesCardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryAparna RamachandranNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To Methylene Blue Remarkable Hope For Depression, COVID, AIDS Other Viruses, Alzheimer's, Autism, Cancer,... (Mark Sloan) (Z-Library)Document171 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Methylene Blue Remarkable Hope For Depression, COVID, AIDS Other Viruses, Alzheimer's, Autism, Cancer,... (Mark Sloan) (Z-Library)pieterNo ratings yet
- CH 01 Lecture PresentationDocument90 pagesCH 01 Lecture PresentationNie TofuNo ratings yet
- CirculatorySystemSE - Anthony HernandezDocument5 pagesCirculatorySystemSE - Anthony HernandezAnthony Hernandez100% (1)
- Ipertensione Arteriosa PolmonareDocument33 pagesIpertensione Arteriosa PolmonareCarlo MaxiaNo ratings yet
- CH 19 Transport in HumanDocument49 pagesCH 19 Transport in HumanRay PeramathevanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory and Respiratory Test Study Guide Answer KeyDocument3 pagesCirculatory and Respiratory Test Study Guide Answer KeyMae Ann Tomimbang MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Disorders: BY Dr. Birhane H (MD)Document88 pagesHemodynamic Disorders: BY Dr. Birhane H (MD)Biruck BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and HealingDocument15 pagesInflammation and HealingRachel Niu II100% (1)
- 9 Lymphatic SystemDocument64 pages9 Lymphatic SystemM TalhaNo ratings yet
- 1-4 Inflammation PDFDocument58 pages1-4 Inflammation PDFZaidan FailasufaNo ratings yet
- Nat 5 Biology SQ App 2019Document48 pagesNat 5 Biology SQ App 2019muntazNo ratings yet
- Nasaba Magnona Rawan - Cause-Effect Essay Draft 1Document6 pagesNasaba Magnona Rawan - Cause-Effect Essay Draft 1Sami JafarNo ratings yet
- Blood Flow RegulationDocument30 pagesBlood Flow RegulationEka AlpasraNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System IGCSE Biology Notes and Questions 1Document4 pagesCirculatory System IGCSE Biology Notes and Questions 1Muhammad IbraheemNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 11Document7 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 11Atabuddin MondalNo ratings yet
- ATPL Human Performance & LimitationsDocument42 pagesATPL Human Performance & Limitationsjoethompson007100% (7)
- Science: Quarter 1, WK 2 - Module 2Document31 pagesScience: Quarter 1, WK 2 - Module 2Andres Boni85% (13)
- Akbar CurveDocument15 pagesAkbar CurveKashaf ChNo ratings yet
- 4.3.5.A SmokingLeg at Home ModificationDocument5 pages4.3.5.A SmokingLeg at Home ModificationEmily WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Lecithin Book by Carlson WadeDocument195 pagesLecithin Book by Carlson WadeYoBjjNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism (Loria.J)Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism (Loria.J)Justine Mae Loria0% (1)
- Overview of Angiogenesis - Angiogenesis - NCBI BookshelfDocument10 pagesOverview of Angiogenesis - Angiogenesis - NCBI BookshelfDzulfikarFaizinRomasNo ratings yet
- Andrew MouldenDocument7 pagesAndrew Mouldenmika2k01100% (1)
- Anat FisioDocument653 pagesAnat Fisiodenydeniche388No ratings yet
- Massage - Anatomy and Massage Course NotesDocument18 pagesMassage - Anatomy and Massage Course NotesMarcel FagadarNo ratings yet
- E351 Full PDFDocument13 pagesE351 Full PDFajes coolNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2: Basic Cell PhysiologyDocument72 pagesChapter - 2: Basic Cell Physiologyyash ingawaleNo ratings yet
- NCP For HypertensionDocument4 pagesNCP For HypertensionCiariz Charisse83% (6)
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument3 pagesPulmonary EmbolismdeanneadrianoNo ratings yet
- Module Cardiovascular SystemDocument14 pagesModule Cardiovascular SystemVynz Morales CosepNo ratings yet