Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetics I Quiz - Coursera Answers 2
Uploaded by
FarooqOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genetics I Quiz - Coursera Answers 2
Uploaded by
FarooqCopyright:
Available Formats
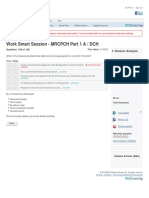
10/20/22, 4:27 PM Genetics I Quiz | Coursera
Genetics I Quiz
Back Due Oct 16, 11:59 PM PKT
Graded Quiz • 30 min
Introduction Try again once you are ready
Inheritance, Genetic Scales, and Retake the assignment in 8h
Grade Latest Submission To pass 70% or
Cell Division
Inheritance II
received 60% Genetics I Quiz
Grade 40% higher
Quiz • 30 min
Video: Basic Single-Gene Inheritance
(G)
15 min
Video: X-Linked Inheritance and 1. Imagine that you Submit
have twoyour
childhood
assignment
friends of average strength who exercised an average amount. They decide 1 / 1 point
Independent Assortment (S) Try again
to exercise heavily for many years to build up their strength, and in the end, they are so strong that they win
16 min Due Oct 16, 11:59 PM PKT Attempts 1 every 8 hours
Olympic gold medals in weightlifting. They get married and have kids. Assuming their kids exercise an average
Retake the quiz in 8h
Reading: Supplemental Materials, amount, the kids will most likely be:
Genetics I
10 min
Correct Receive grade Your grade
Practice Quiz: Genetics Problem Set View Feedback
1 To Pass 70% or higher 60% We keep your highest score
6 questions
Quiz: Genetics I Quiz
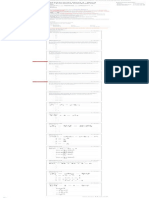
10 questions 2. Which of the following outcomes would be a direct consequence of blending inheritance? 0 / 1 point
Like Dislike Report an issue
Incorrect
3. Based on the material covered in the videos, what effect would a mutation in an intron have on the expression of 0 / 1 point
a gene?
Incorrect
4. Cancers are commonly caused by mutations that arise somewhere in the body and lead to uncontrolled cell 1 / 1 point
division and growth within our bodies. Why don’t the majority of these cancer mutations spread into our
offspring?
Correct
5. Envision the end-products of mitosis and meiosis (not considering fertilization). Which of these end-products can 0 / 1 point
exhibit "recessivity" of genes?
Incorrect
6. You are studying the inheritance of earlobe attachment (a free-hanging earlobe is dominant over an attached 1 / 1 point
earlobe) in your family. Assuming that this trait is inherited by alleles at a single gene on chromosome 14, which
of the following observations is NOT possible under normal circumstances:
Correct
7. Polydactyly (having an extra finger on your hand) is inherited as an autosomal (not on the X-chromosome) 0 / 1 point
dominant trait. Imagine you know two people, John and Sue, with polydactyly, each of whom had fathers with
polydactyly but whose mothers had 5-fingers. John and Sue get married and have children. What fraction of their
children are expected to inherit this trait?
Incorrect
8. Red-green color blindness is associated with a recessive mutation on the X-chromosome. Which of the following 0 / 1 point
scenarios is NOT possible with respect to color blindness?
Incorrect
9. Imagine a cross between these two individuals: GgHh and GGHh. If the two genes (represented by G and H) assort 0 / 1 point
independently, what will the offspring proportions be?
Incorrect
10. When studying genetics, "pedigrees" are often used which indicate the genotype or phenotype of specific 1 / 1 point
individuals in a family and their relationships (parents are drawn above offspring). Squares are male, and circles
are female. Yellow shapes typically depict an unaffected (or healthy) individual whereas black shapes mean an
affected (or diseased) individual. Imagine that the pedigree here depicts inheritance of a simple autosomal single-
gene disease in a family. What do we know about the genotype of individual 1 for the disease causing gene?
[Click here for a text version of the image below.]
Correct
https://www.coursera.org/learn/genetics-evolution/exam/qiS1v/genetics-i-quiz/attempt?redirectToCover=true 1/1
You might also like
- Genetics I Quiz - Coursera Answers 1Document1 pageGenetics I Quiz - Coursera Answers 1Farooq0% (1)
- Molecular Evolution QuizDocument7 pagesMolecular Evolution QuizSchool OthersNo ratings yet
- Genetics Quiz 3Document3 pagesGenetics Quiz 3School OthersNo ratings yet
- Population Genetics II QuizDocument12 pagesPopulation Genetics II QuizSchool OthersNo ratings yet
- Heritability QuizDocument9 pagesHeritability QuizSchool OthersNo ratings yet
- Genetics II QuizDocument8 pagesGenetics II QuizSchool Others0% (2)
- Review Test Submission: Quiz #2Document1 pageReview Test Submission: Quiz #2Unambiguous16No ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Statistics - CourseraDocument1 pageQuiz 1 Statistics - CourseraJavier P. BarreraNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting and The Future of Networking - CourseraDocument1 pageTroubleshooting and The Future of Networking - CourseraPavan PatchikarlaNo ratings yet
- Development and Vaccines PDFDocument52 pagesDevelopment and Vaccines PDFDr-Jahanzaib GondalNo ratings yet
- Count On Me - Bruno MarsDocument5 pagesCount On Me - Bruno MarsWULAN SARI NUR HUDANo ratings yet
- Dynamic Child 1st Edition Manis Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesDynamic Child 1st Edition Manis Solutions Manualarmorerdoleritercunxa100% (21)
- Dwnload Full Dynamic Child 1st Edition Manis Solutions Manual PDFDocument20 pagesDwnload Full Dynamic Child 1st Edition Manis Solutions Manual PDFantiquateouterlyhxhkwv100% (14)
- ASQ-3 at A Glance: A Parent-Completed Child Monitoring System For Social-Emotional BehaviorsDocument1 pageASQ-3 at A Glance: A Parent-Completed Child Monitoring System For Social-Emotional BehaviorsHOA TRƯƠNGNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Child 1st Edition Manis Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesDynamic Child 1st Edition Manis Solutions ManualMrsJenniferCarsonjrcy100% (52)
- Test - UNIT 2 - (Biological Bases of Behavior - States of Consciousness) - QuizletDocument1 pageTest - UNIT 2 - (Biological Bases of Behavior - States of Consciousness) - Quizletavalon.protter08No ratings yet
- Week 8 Mi Lesson Plan SummaryDocument3 pagesWeek 8 Mi Lesson Plan Summaryapi-534129744No ratings yet
- This Is An Overview of Baranya's Performance in Last WeekDocument2 pagesThis Is An Overview of Baranya's Performance in Last WeekBaranya Raj LahkarNo ratings yet
- Piaget's Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentDocument4 pagesPiaget's Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentAbegail Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Quiz - Coursera PDFDocument1 pageWeek 2 Quiz - Coursera PDFAmit Singh100% (2)
- Unit 16 - Week 12: Assignment 12Document3 pagesUnit 16 - Week 12: Assignment 12Debraj ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Quiz #9 AnswersDocument1 pageQuiz #9 AnswersUnambiguous16No ratings yet
- Revision Unit 1Document4 pagesRevision Unit 1cacaitoNo ratings yet
- RLP Caasi PX Sci 10Document9 pagesRLP Caasi PX Sci 10Lyka Jean GaleraNo ratings yet
- Tier 2Document1 pageTier 2api-354945850No ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Graded Exam - Revisión Del IntentoDocument2 pagesUnit 3 - Graded Exam - Revisión Del IntentoJean Daniel MichelNo ratings yet
- Study Planner and Test Planner - Repeater Course (RM) - MEDICAL - 2020-21 (Phase-1) - MinDocument27 pagesStudy Planner and Test Planner - Repeater Course (RM) - MEDICAL - 2020-21 (Phase-1) - MinLalitha MyakeriNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Week 2: Quiz 2Document3 pagesUnit 3 - Week 2: Quiz 2BARANINo ratings yet
- Solved Hi Kinini, I Hope You Are Doing Well I Want Help in The FollowingDocument3 pagesSolved Hi Kinini, I Hope You Are Doing Well I Want Help in The FollowingMesso FrancisNo ratings yet
- (ACV-S05) Week 05 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz (PA) - INGLES III (58145)Document6 pages(ACV-S05) Week 05 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz (PA) - INGLES III (58145)Mylian AlayoNo ratings yet
- (AC-S06) Week 6 - Pre Task - Quiz - Listening Comprehension (PA) - INGLES I (8802)Document5 pages(AC-S06) Week 6 - Pre Task - Quiz - Listening Comprehension (PA) - INGLES I (8802)Denis Milton Ramos PalominoNo ratings yet
- (FNDMATH) Activity Sheet 8 - Graph of Ellipse and Hyperbola and Curve Sketching (1191 - FNDMATH - EC) - FOUNDATION COURSE IN MATHEMDocument1 page(FNDMATH) Activity Sheet 8 - Graph of Ellipse and Hyperbola and Curve Sketching (1191 - FNDMATH - EC) - FOUNDATION COURSE IN MATHEMerwin cahanapNo ratings yet
- Science November 22 Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesScience November 22 Lesson Planapi-513535960No ratings yet
- Wlap Week 8 TruthDocument2 pagesWlap Week 8 TruthAizel Nova AranezNo ratings yet
- English Language For Competitive Exams - Unit 10 - Week 8Document3 pagesEnglish Language For Competitive Exams - Unit 10 - Week 8Niket BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Noc19 Te01 Assignment3Document3 pagesNoc19 Te01 Assignment3Gg HghNo ratings yet
- NTSEDocument12 pagesNTSEAditya Tiwari100% (1)
- Study Guide - Tact Training (Miguel & Kobari-Wright) - BEHV 5618 Section 918 - ABA Foundations, Concepts and Principles 2 (Spring 2023 1)Document8 pagesStudy Guide - Tact Training (Miguel & Kobari-Wright) - BEHV 5618 Section 918 - ABA Foundations, Concepts and Principles 2 (Spring 2023 1)chynaNo ratings yet
- Matrix NTOT 6daysDocument4 pagesMatrix NTOT 6daysKemberly Semaña PentonNo ratings yet
- Study Planner and Test Planner - XI (TYM) - April To October 20-21 (Phase-1) - Min PDFDocument96 pagesStudy Planner and Test Planner - XI (TYM) - April To October 20-21 (Phase-1) - Min PDFUmar FarooqueNo ratings yet
- 8 OldDocument1 page8 OldNischal Reddy SareddyNo ratings yet
- Final Exam AG1-1Document20 pagesFinal Exam AG1-1Maria Belen VilcapumaNo ratings yet
- Design Thinking Online Assessment - FinalDocument28 pagesDesign Thinking Online Assessment - FinalVrinda Maheshwari-DM 20DM248No ratings yet
- Assessment 2 - Module 2 Quiz - CourseraDocument1 pageAssessment 2 - Module 2 Quiz - CourseraCarla MissionaNo ratings yet
- (FNDMATH) Activity Sheet 4 - Word Problems Fractional and Quadratic Equations (1191 - FNDMATH - EC) - FOUNDATION COURSE IN MATHEMDocument1 page(FNDMATH) Activity Sheet 4 - Word Problems Fractional and Quadratic Equations (1191 - FNDMATH - EC) - FOUNDATION COURSE IN MATHEMerwin cahanapNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Examplar ScienceDocument1 pageLesson Plan - Examplar Scienceemo mHAYNo ratings yet
- 6.2 Knowledge Check - ANOVA, Covariance, and Correlation - MAST6201-712-1227Document3 pages6.2 Knowledge Check - ANOVA, Covariance, and Correlation - MAST6201-712-1227Rachana SontakkeNo ratings yet
- Wind Resource Assessment - Coursera2Document1 pageWind Resource Assessment - Coursera2Franklin Josue Ticona Coaquira100% (1)
- NorthStar L4 Listening Speaking - Scope and SequenceDocument4 pagesNorthStar L4 Listening Speaking - Scope and SequenceJack ForeverNo ratings yet
- English2 CurmapDocument8 pagesEnglish2 Curmapruclito morataNo ratings yet
- ASQSE2 at A Glance - 2020Document1 pageASQSE2 at A Glance - 2020HOA TRƯƠNGNo ratings yet
- DLL Grade 7 Week 5 October23-27Document2 pagesDLL Grade 7 Week 5 October23-27S2 Princess M. NatividadNo ratings yet
- December 2-6 LGDocument2 pagesDecember 2-6 LGElla EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Editing Quiz Electrical EngineeringDocument4 pagesEditing Quiz Electrical Engineeringsudip modakNo ratings yet
- DLL Esp-6 Q1 W1Document4 pagesDLL Esp-6 Q1 W1Lloyd MontecalvoNo ratings yet
- Weekly CalendarDocument1 pageWeekly Calendarmonkey poddleNo ratings yet
- Assignment-3 Noc18 ch23 43Document4 pagesAssignment-3 Noc18 ch23 43Samarjeet Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- English Language For Competitive Exams - Unit 12 - Week 10Document4 pagesEnglish Language For Competitive Exams - Unit 12 - Week 10Niket BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Occidental Mindoro State College Marou P. Barreno April 25, 2022 08:30 - 09:30 AMDocument18 pagesOccidental Mindoro State College Marou P. Barreno April 25, 2022 08:30 - 09:30 AMmarsNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Quiz: Attempt HistoryDocument11 pagesUnit 11 Quiz: Attempt HistoryM. Alfin PrayogoNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Project InitiationDocument3 pagesWeek 4 Project InitiationFarooqNo ratings yet
- Thèse EverVigneDocument1 pageThèse EverVigneFarooqNo ratings yet
- B BJ HJGDocument3 pagesB BJ HJGFarooqNo ratings yet
- Project RoadmapDocument2 pagesProject RoadmapFarooqNo ratings yet
- Operations and Training PlanDocument2 pagesOperations and Training PlanFarooqNo ratings yet
- Budget Beast Burndown ChartDocument2 pagesBudget Beast Burndown ChartFarooqNo ratings yet
- Guide For Applicants Intake 7 1st CallDocument9 pagesGuide For Applicants Intake 7 1st CallFarooqNo ratings yet
- CookingDocument16 pagesCookingFarooqNo ratings yet
- Pared BacteriasDocument18 pagesPared BacteriasenadesNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiological Recording Techniques PDFDocument7 pagesElectrophysiological Recording Techniques PDFAndrei TatomirNo ratings yet
- Heredity UnitDocument60 pagesHeredity Unitapi-224842598No ratings yet
- Contemporary Chemical Approaches For Green and Sustainable Drugs 1St Edition Torok M Ed Full ChapterDocument51 pagesContemporary Chemical Approaches For Green and Sustainable Drugs 1St Edition Torok M Ed Full Chapterjohn.mclarty382100% (15)
- Sustained Release Drug FormulationDocument14 pagesSustained Release Drug Formulationapi-3750955100% (5)
- Determinants of HealthDocument29 pagesDeterminants of HealthMayom MabuongNo ratings yet
- Toxicogenic Insects by MIAN NASiR MEHMOODDocument15 pagesToxicogenic Insects by MIAN NASiR MEHMOODMIAN NASIR100% (2)
- Biodegradation of Phenol by Pseudomonas PDFDocument8 pagesBiodegradation of Phenol by Pseudomonas PDFKelly RamosNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 171022084035Document16 pagesPresentation1 171022084035Akkipero123No ratings yet
- Genetic AlgorithmDocument6 pagesGenetic AlgorithmFilip MajstorovićNo ratings yet
- BIORESTEC 2023 PosterDocument1 pageBIORESTEC 2023 PosterSebastian MariangelNo ratings yet
- SchedulesDocument193 pagesSchedulesSuresh ParamuNo ratings yet
- BioqmicaDocument7 pagesBioqmicaEdu VargasNo ratings yet
- The Primary Structure of The Saccharmoces Cerevisiae Gene For ADH1 - Bennetzen & Hall 1981 PDFDocument9 pagesThe Primary Structure of The Saccharmoces Cerevisiae Gene For ADH1 - Bennetzen & Hall 1981 PDFMeidayNo ratings yet
- Competency AddressedDocument46 pagesCompetency AddressedJaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Award of The Degree ofDocument47 pagesSubmitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Award of The Degree ofGaurav KNo ratings yet
- Flowchart GaDocument1 pageFlowchart GaSidney Bruce ShikiNo ratings yet
- mcb101 Syllabus S'14Document10 pagesmcb101 Syllabus S'14PreciousNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Metabolism: Dr. Md. Rageeb Md. Usman Associate Professor Department of PharmacognosyDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Metabolism: Dr. Md. Rageeb Md. Usman Associate Professor Department of PharmacognosyAnonymous TCbZigVqNo ratings yet
- Prospects and Challenges of Biochemistry - From The Perspective of BangladeshDocument7 pagesProspects and Challenges of Biochemistry - From The Perspective of BangladeshShimanta Easin100% (1)
- Chapter 01-Reproduction in Organisms STD XiiDocument27 pagesChapter 01-Reproduction in Organisms STD XiiAbcNo ratings yet
- W&L CatalogDocument184 pagesW&L CatalogjwwisnerNo ratings yet
- CumulativetestDocument14 pagesCumulativetestapi-254428474No ratings yet
- CIE Alevel Biology Mock Papers Paper 2 As Structured Questions Sample PagesDocument96 pagesCIE Alevel Biology Mock Papers Paper 2 As Structured Questions Sample PagesSalman Farsi TaharatNo ratings yet
- Helicobacter PyloriDocument42 pagesHelicobacter Pyloritummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles & ProcessesDocument3 pagesBiotechnology Principles & ProcessesKambaska Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- WAEC BIOLOGY SyllabusDocument78 pagesWAEC BIOLOGY SyllabusMaggieNo ratings yet
- Review SheetDocument2 pagesReview Sheetapi-289866381No ratings yet
- Short Notes Form 4 Biology (Chapter 1-4)Document6 pagesShort Notes Form 4 Biology (Chapter 1-4)Ema Fatimah75% (8)
- Responses To Exposed Variant Surface T-Cell-Independent and T-Cell-Dependent B-CellDocument7 pagesResponses To Exposed Variant Surface T-Cell-Independent and T-Cell-Dependent B-CellNicoli Arthur Balita BorromeoNo ratings yet