Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table 30-1
Table 30-1
Uploaded by
Dragutin Petrić0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
Table 30–1_
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageTable 30-1
Table 30-1
Uploaded by
Dragutin PetrićCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Critical Care >Acute Kidney Injury and Failure
John M. Oropello, Stephen M. Pastores, Vladimir Kvetan+
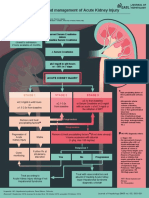
Table 30–1Comparison of AKI staging criteria versus RIFLE staging criteria.4
AKI Staging Urine Output (Common to Both) RIFLE
Serum Creatinine Class Serum Creatinine of GFR
Stage 1 Increase of more than or equal to 0.3
mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l) or increase to more than or Increase in serum creatinine × 1.5 or GFR
Less than 0.5 ml/kg/h for more than 6 hours Risk
equal to 150% to 200% (1.5- to 2-fold) from decrease >25%
baseline
Stage 2 Increased to more than 200% to 300%
Less than 0.5 ml/kg/h for more than 12 hours Injury Serum creatinine × 2 or GFR decreased >50%
(> 2- to 3-fold) from baseline
Stage 3 Increased to more than 300% (> 3-fold)
Serum creatinine × 3, or serum creatinine >4
from baseline, or more than or equal to 4.0 mg/dl Less than 0.3 ml/kg/h for 24 hours or anuria for
Failure mg/dl (> 354 μmol/l) with an acute rise >0.5
(≥ 354 μmol/l) with an acute increase of at least 12 hours
mg/dl (> 44 μmol/l) or GFR decreased >75%
0.5 mg/dl (44 μmol/l) or on RRT
Persistent acute renal failure=complete loss of
Loss
kidney function >4 weeks
End-stage kidney disease ESRD >3 months
Reproduced with permission from KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Section 2: AKI Definition, Kidney Int Suppl. 2012 Mar;2(1):19-36).
Date of download: 01/01/23 from AccessMedicine: accessmedicine.mhmedical.com, Copyright © McGraw Hill. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Psychopharmacology (Fourth Edition) (Jerry Meyer) (Z-Library)Document841 pagesPsychopharmacology (Fourth Edition) (Jerry Meyer) (Z-Library)Dragutin Petrić100% (1)
- Clinical Handbook of Psychotropic Drugs, 25e (May 8, 2023) - (0889376328) - (Hogrefe Publishing) (Etc.) (Z-Library)Document555 pagesClinical Handbook of Psychotropic Drugs, 25e (May 8, 2023) - (0889376328) - (Hogrefe Publishing) (Etc.) (Z-Library)Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- NBME 22 OfflineDocument200 pagesNBME 22 OfflineGautham Kanagala86% (14)
- Importance of Pathology in Nursing Unit 1Document8 pagesImportance of Pathology in Nursing Unit 1Kiran69% (26)
- BA Domain Day-1Document46 pagesBA Domain Day-1Nikhil Satav0% (1)
- ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AutoRecovered)Document21 pagesACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AutoRecovered)Axsa Alex100% (1)
- Laryngo Broncho EsophagologyDocument94 pagesLaryngo Broncho EsophagologyFrederick Mars UntalanNo ratings yet
- Table 54-9Document1 pageTable 54-9Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Table 54-10Document1 pageTable 54-10Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- 2.2gangguan Ginjal Akut Pada AnakDocument34 pages2.2gangguan Ginjal Akut Pada AnakMUNIFRIZALNo ratings yet
- 15-Acute Kidney InjuryDocument18 pages15-Acute Kidney Injuryمصطفى محمد جواد كاظمNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury: Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Is A Clinical Syndrome Generally Defined by AnDocument13 pagesAcute Kidney Injury: Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Is A Clinical Syndrome Generally Defined by AnARMANo ratings yet
- AKI Diagnosis and ClassificationDocument12 pagesAKI Diagnosis and ClassificationIndah Nur LathifahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28-1 - Approach To The Patient With Acute Kidney Injury - Case 1Document9 pagesChapter 28-1 - Approach To The Patient With Acute Kidney Injury - Case 1fabyuiNo ratings yet
- KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline For Acute Kidney Injury.Document18 pagesKDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline For Acute Kidney Injury.Madalina TalpauNo ratings yet
- N Engl J Med 2022 386 964 - AppendixDocument5 pagesN Engl J Med 2022 386 964 - AppendixEvelynNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury in HospitaDocument7 pagesAcute Kidney Injury in HospitaRobertNo ratings yet
- Hidac (High Dose Cytarabine) For Aml: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesHidac (High Dose Cytarabine) For Aml: Page 1 of 2OttoNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and Management Sepsis - Aki: Fajar Yuwanto Rsud Abdul Moeloek Bandar LampungDocument21 pagesPathogenesis and Management Sepsis - Aki: Fajar Yuwanto Rsud Abdul Moeloek Bandar LampungNodi Rahma DiniNo ratings yet
- Arf - Aki - Dwi - FinalDocument38 pagesArf - Aki - Dwi - FinalNovitha DestaryNo ratings yet
- 11.0 Acute Kidney InjuryDocument26 pages11.0 Acute Kidney InjuryHeny KsNo ratings yet
- Digoxi N: Therapeutic Drug Monitoring ofDocument17 pagesDigoxi N: Therapeutic Drug Monitoring ofsky.blueNo ratings yet
- Infusions 1Document4 pagesInfusions 1Mohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Kadcyla Trastuzumab Emtansine HER-2 Positive Breast CancerDocument11 pagesKadcyla Trastuzumab Emtansine HER-2 Positive Breast CancersmokkerNo ratings yet
- AKI LectureDocument95 pagesAKI LectureDaryl Gay NanoNo ratings yet
- Git Case 3 Kunwor, BishalDocument15 pagesGit Case 3 Kunwor, BishalBishal JB KunworNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument26 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryUmmuhani AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0168827816306183Document2 pagesPi Is 0168827816306183sigmundmaharaja2368No ratings yet
- (R) Choep: IndicationDocument5 pages(R) Choep: IndicationAlina CrissNo ratings yet
- Perioperativeacute Kidneyinjury: Risk Factors and Predictive StrategiesDocument18 pagesPerioperativeacute Kidneyinjury: Risk Factors and Predictive StrategiesBillyNicolasNo ratings yet
- Carboplatin PaclitaxelgynaeDocument5 pagesCarboplatin PaclitaxelgynaefazarNo ratings yet
- Notes in Neonates محمد ابراهيم مستشفى قوص قنا.WhiteKnightLoveDocument77 pagesNotes in Neonates محمد ابراهيم مستشفى قوص قنا.WhiteKnightLoveMaRwa IbrahimNo ratings yet
- AKI MBCHB VDocument64 pagesAKI MBCHB VSsenyonga DominicNo ratings yet
- Leziunea Acuta de Rinichi (LAR) : Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Insuficienta Renala Acuta (IRA)Document49 pagesLeziunea Acuta de Rinichi (LAR) : Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Insuficienta Renala Acuta (IRA)mihai mayorNo ratings yet
- (April 2020) : Is The Indication Appropriate For A Doac?Document1 page(April 2020) : Is The Indication Appropriate For A Doac?SNo ratings yet
- Dose Modification GuidelinesDocument1 pageDose Modification GuidelinesAhmed Maged FadelNo ratings yet
- Annrheumdis 2019 June 78 6 736 Inline Supplementary Material 3Document12 pagesAnnrheumdis 2019 June 78 6 736 Inline Supplementary Material 3PPDS IKA KAHFIANo ratings yet
- Hira Ayub OD02163015: GlaucomaDocument5 pagesHira Ayub OD02163015: GlaucomaAsad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Capecitabine IrinotecanDocument7 pagesCapecitabine Irinotecantanasa adrianNo ratings yet
- Aetiopathogenesis & Management of Acute Renal FailureDocument37 pagesAetiopathogenesis & Management of Acute Renal Failuremeikha tari batjunNo ratings yet
- Docetaxel-Gemcitabinev1 2Document8 pagesDocetaxel-Gemcitabinev1 2Salman FaridziNo ratings yet
- GOOVCATX ProtocolDocument7 pagesGOOVCATX Protocolthanh ngôNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Antibiotic Dosing Card 2012Document2 pagesPediatric Antibiotic Dosing Card 2012yoshilimsiacoshigyoNo ratings yet
- Frequent Asking & QuestionDocument18 pagesFrequent Asking & QuestionLhynda Priarti LatifNo ratings yet
- NCP Kasus 5Document9 pagesNCP Kasus 5Inne PratidinaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Diseaseapi-668470097No ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematous: Aqmarina Thalia AzdhaniDocument14 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematous: Aqmarina Thalia AzdhaniReisky NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric PharmacologyDocument30 pagesPediatric PharmacologyHussamNo ratings yet
- Lampiran OM & FaringitisDocument6 pagesLampiran OM & FaringitisAdhinyDistiHelmiNo ratings yet
- Thromboprophylaxis in Sepsis Case BasedDocument32 pagesThromboprophylaxis in Sepsis Case BasedVasantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Revision 1Document21 pagesRevision 1NaifmxNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure UPDATES 2020Document2 pagesChronic Renal Failure UPDATES 2020AHMED TANJIMUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Classification of InfectiousDocument3 pagesClassification of InfectiousabubakarNo ratings yet
- CRRT Cu CitratDocument35 pagesCRRT Cu CitratAndreea MitranNo ratings yet
- NH Protocol For Covid Management FinalDocument7 pagesNH Protocol For Covid Management FinalhoneyworksNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Haerani Rasyid FK Unhas 2016Document46 pagesAcute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Haerani Rasyid FK Unhas 2016Ana Yusriana AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Class Indications Available Dosage Form in The Hospital DosageDocument1 pageClass Indications Available Dosage Form in The Hospital DosageȘtefana StefiNo ratings yet
- If Yes To Any Question, Go To STEP 2: Table 2Document2 pagesIf Yes To Any Question, Go To STEP 2: Table 2Chelo Jan GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Gem Carbo NHSDocument2 pagesGem Carbo NHSSyed Touseef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Kidney Emergency: M. Syamsul BakhriDocument30 pagesKidney Emergency: M. Syamsul BakhrierahadeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Aki Presentation EportfolioDocument32 pagesClinical Case Aki Presentation Eportfolioapi-463444835No ratings yet
- Paediatricshouseofficerguidehospitalkulim 151026150042 Lva1 App6891Document14 pagesPaediatricshouseofficerguidehospitalkulim 151026150042 Lva1 App6891Nadia SalwaniNo ratings yet
- Lyrica Epar Product Information - enDocument96 pagesLyrica Epar Product Information - enshr3d3rNo ratings yet
- Critical ValuesDocument4 pagesCritical ValuesYousef AlshawafahNo ratings yet
- PsihijatrijaDocument223 pagesPsihijatrijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Psychiatry - A Case-Based Textbook, 2e (Mar 30, 2024)_(3031478010)_(Springer) (Ana Hategan, James a. Bourgeois Etc.) (Z-Library)Document939 pagesGeriatric Psychiatry - A Case-Based Textbook, 2e (Mar 30, 2024)_(3031478010)_(Springer) (Ana Hategan, James a. Bourgeois Etc.) (Z-Library)Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- EtikaDocument218 pagesEtikaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Emocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDocument153 pagesEmocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Emocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDocument153 pagesEmocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- ŠizofrenijaDocument216 pagesŠizofrenijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- ŠizofrenijaDocument3 pagesŠizofrenijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- 8Document1 page8Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Etika (Benedikt de Spinoza) (Z-Library)Document238 pagesEtika (Benedikt de Spinoza) (Z-Library)Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Selected Root Causes of Moral DistressDocument1 pageSelected Root Causes of Moral DistressDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Gender PsychiatryDocument12 pagesGender PsychiatryDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Kurs Pozitivne Filozofije Auguste ConteDocument152 pagesKurs Pozitivne Filozofije Auguste ConteDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Agitacija Verbalna DeeskalacijaDocument2 pagesAgitacija Verbalna DeeskalacijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- ŠizofrenijaDocument1 pageŠizofrenijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Liječenje Depresije Naknadni PosjetiDocument3 pagesLiječenje Depresije Naknadni PosjetiDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Textbook of PsychiatryDocument3 pagesTextbook of PsychiatryDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy For Patients With Bipolar DisordersDocument1 pageDrug Therapy For Patients With Bipolar DisordersDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Stablo Odlučivanja StepDocument3 pagesStablo Odlučivanja StepDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Faze Liječenja Velikog Depresivnog PoremećajaDocument2 pagesFaze Liječenja Velikog Depresivnog PoremećajaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- FDADocument2 pagesFDADragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- 7Document24 pages7Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Stablo Odlučivanja Kako Odrediti Je Li Osoba Prikladna Za Liječenje Usmjereno Na PonašanjeDocument2 pagesStablo Odlučivanja Kako Odrediti Je Li Osoba Prikladna Za Liječenje Usmjereno Na PonašanjeDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- 6Document34 pages6Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- C C C 3 3 J JDocument30 pagesC C C 3 3 J JmrchilliciousNo ratings yet
- Medicine: Congenital Chloride Losing DiarrheaDocument9 pagesMedicine: Congenital Chloride Losing DiarrheaGabriela PopescuNo ratings yet
- Nursing Board Exam Test Taking StrategiesDocument39 pagesNursing Board Exam Test Taking StrategiesHenry ApolNo ratings yet
- List of Anesthetic, Analgesic and Tranquilizer Drugs Veterinary)Document25 pagesList of Anesthetic, Analgesic and Tranquilizer Drugs Veterinary)drbadman77100% (2)
- What The Doctor Should Have Ordered?Document2 pagesWhat The Doctor Should Have Ordered?AutismeyeNo ratings yet
- AcetylcysteineDocument2 pagesAcetylcysteineGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Skisofrenia: DR Dickson Legoh, SPKJDocument45 pagesSkisofrenia: DR Dickson Legoh, SPKJVeraNo ratings yet
- Blood Product CompatibilityDocument6 pagesBlood Product CompatibilityTina MooreNo ratings yet
- E 2184 - 02 - Rtixodq - PDFDocument10 pagesE 2184 - 02 - Rtixodq - PDFumur kaçamaklıNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting of PregnancyDocument1 pageNausea and Vomiting of Pregnancypuskesmas ciapusNo ratings yet
- Family Case Study.Document4 pagesFamily Case Study.sleep what100% (1)
- Consultant Archetypes: A Junior Doctors Survival GuideDocument2 pagesConsultant Archetypes: A Junior Doctors Survival GuideShaf IslamNo ratings yet
- Pituitary AdenomasDocument48 pagesPituitary AdenomasRegina Lestari0% (1)
- Croatian Journal For Public HealthDocument4 pagesCroatian Journal For Public HealthanlaucNo ratings yet
- AshwashilaDocument3 pagesAshwashilaDr. Avnish UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Pulse PressureDocument3 pagesPulse PressureYovie Anggara SaputraNo ratings yet
- Difficulties in Diagnosis of Psittacosis or Ornithosis: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesDifficulties in Diagnosis of Psittacosis or Ornithosis: A Case ReportYusrinabillaNo ratings yet
- African Horse Sickness GuidelinesDocument6 pagesAfrican Horse Sickness GuidelinesFajarAriefSumarnoNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung-Disease Case StudyDocument20 pagesHirschsprung-Disease Case StudyFaith TorralbaNo ratings yet
- MSDC 5555Document11 pagesMSDC 5555John M. Hemsworth100% (1)
- Myasthenia GravisDocument10 pagesMyasthenia GravisLuis LazaroNo ratings yet
- Adderall Risks - Much More Than You Wanted To Know - Slate Star CodexDocument21 pagesAdderall Risks - Much More Than You Wanted To Know - Slate Star CodexPatrick LumambaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Clinical Nursing Skills 8 e 8th Edition 013511473xDocument4 pagesSolution Manual For Clinical Nursing Skills 8 e 8th Edition 013511473xGregoryRussellajwd100% (46)
- Clinical Signs of Retroperitoneal Abscess From.74Document6 pagesClinical Signs of Retroperitoneal Abscess From.74Ali Sibra MulluziNo ratings yet
- MCQ SyllabusDocument4 pagesMCQ SyllabusSauharda DhakalNo ratings yet
- Meta AnalysisDocument22 pagesMeta AnalysisNuryasni Nuryasni100% (1)