Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modal Verbs
Uploaded by
annie aneeschCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modal Verbs
Uploaded by
annie aneeschCopyright:
Available Formats
Modal Verbs
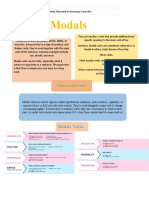
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs (also known as "helping verbs"). Normally modal
verbs cannot work alone and must work with a main verb. The so-called "semi-
modals" work partly like modals and partly like main verbs.
Modals:
can, could, will, would, shall, should, may, might
must, ought (to)
can, could, be able to
can and could are modal auxiliary verbs. Be able to is not an auxiliary verb (it uses
the verb be as a main verb). We include be able to here for convenience.
have to, must
must is a modal auxiliary verb. Have to is not an auxiliary verb (it uses the
verb have as a main verb). We include have to here for convenience.
shall versus will
People sometimes say that there is no difference between shall and will, or even
that today nobody uses shall (except in offers such as Shall I call a taxi?). They
say the same thing about should, but it's not really true.
would
We use the modal auxiliary verb would mainly to talk about the past, talk about the
future in the past and express the conditional mood.
should
We use the modal auxiliary verb should mainly to give advice or make
recommendations, talk about obligation or talk about probability and expectation.
You might also like
- Modal Verbs (Modal Auxiliaries) : Can, Could, Be Able To QuizDocument1 pageModal Verbs (Modal Auxiliaries) : Can, Could, Be Able To QuizRuth Änne DungoNo ratings yet
- What Is Modal Verbs and ExamplesDocument14 pagesWhat Is Modal Verbs and ExamplesJanice Fuchay SawiNo ratings yet
- What Are Modal VerbsDocument34 pagesWhat Are Modal VerbsMunazza AnsareNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs and Auxiliary Verbs Work - 125151Document7 pagesModal Verbs and Auxiliary Verbs Work - 125151Rodrigues Lcn SlarNo ratings yet
- Uniav August 12 TH 2023Document6 pagesUniav August 12 TH 2023Arturo MontielNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs - Definition & Usage ExamplesDocument12 pagesModal Verbs - Definition & Usage ExamplesCherenet TomaNo ratings yet
- What Are Modal VerbsDocument3 pagesWhat Are Modal VerbsDaniela BlagojevicNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Verbs-Definitio and ExamplesDocument24 pagesAuxiliary Verbs-Definitio and ExamplesMoises ChongoNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs - Definition & Usage ExamplesDocument7 pagesModal Verbs - Definition & Usage Examplesনীল সমুদ্রNo ratings yet
- Semi-Modal Auxiliary VerbsDocument6 pagesSemi-Modal Auxiliary VerbssheshirNo ratings yet
- Say What You Mean!: Move up the Social and Business Ladder--One Perfect Word After Another.From EverandSay What You Mean!: Move up the Social and Business Ladder--One Perfect Word After Another.No ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: My Keys Must Be in The Car. It Might Rain Tomorrow. That Can't Be Eshan's Car. It's Too SmallDocument6 pagesModal Verbs: My Keys Must Be in The Car. It Might Rain Tomorrow. That Can't Be Eshan's Car. It's Too SmallSanu100% (1)
- 03 - Unidad 3Document21 pages03 - Unidad 3Anonymous 3D8vtRNo ratings yet
- Ben Mtoto Eng VerbsDocument13 pagesBen Mtoto Eng VerbsSalha MfumiaNo ratings yet
- The 9 English Parts of Speech: 1. VerbsDocument8 pagesThe 9 English Parts of Speech: 1. VerbsAna Karem Kashmir DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Ud3 Comunicacion Prof InglesDocument21 pagesUd3 Comunicacion Prof InglesJose Miguel Ortega AndresNo ratings yet
- Effective Writing Skills Unit 1-3Document20 pagesEffective Writing Skills Unit 1-3Phalla OudomNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs (For Talking About The Present)Document28 pagesModal Verbs (For Talking About The Present)Mariana BlancoNo ratings yet
- ModalsDocument12 pagesModalskhushiali301No ratings yet
- Modal Verbs NotesDocument10 pagesModal Verbs NotesPem TshomoNo ratings yet
- Verbos Modales. Muy Completo.Document18 pagesVerbos Modales. Muy Completo.sexmeltNo ratings yet
- VerbDocument17 pagesVerbZulkifli Paldana Akbar100% (1)
- Structure of Should: Modal Verb Should Should Is An Auxiliary Verb, A Modal Auxiliary Verb. We Use Should Mainly ToDocument2 pagesStructure of Should: Modal Verb Should Should Is An Auxiliary Verb, A Modal Auxiliary Verb. We Use Should Mainly ToAnonymous OQmcDMgNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument46 pagesModal VerbsRobert Masso100% (3)
- ExerciseDocument2 pagesExercise2970864No ratings yet
- Verbs: Universitatea Valahia Facultatea de Stiinte Economice Sectia ManagementDocument6 pagesVerbs: Universitatea Valahia Facultatea de Stiinte Economice Sectia ManagementLungu NicolaeNo ratings yet
- Examples of Modal Auxiliary VerbsDocument6 pagesExamples of Modal Auxiliary VerbsEdna ConejosNo ratings yet
- Helping VerbsDocument3 pagesHelping Verbskrishnachivukula100% (1)
- Auxilary VerbsDocument13 pagesAuxilary Verbsakmal sajaNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs in EnglishDocument2 pagesModal Verbs in EnglishgotmyvampNo ratings yet
- Gerunds, Infinitives Modal VerbsDocument19 pagesGerunds, Infinitives Modal Verbslizarraga.13117251No ratings yet
- Taller de InglesDocument7 pagesTaller de InglesDaisy UsugaNo ratings yet
- CSG Grammar Modal Verbs Todos N Ejercicios A EstudiantesDocument77 pagesCSG Grammar Modal Verbs Todos N Ejercicios A EstudiantesCarolina SepúlvedaNo ratings yet
- Materi 4 Modal AuxllaryDocument29 pagesMateri 4 Modal AuxllaryRhicky Novrizal ChandraNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary VerbsDocument5 pagesAuxiliary VerbsSan WaniNo ratings yet
- Structure Class Words Structure-Class Words, Sometimes Called Function Words, Are Words That Signal How The FormDocument14 pagesStructure Class Words Structure-Class Words, Sometimes Called Function Words, Are Words That Signal How The FormFatima. JNo ratings yet
- The Strange Behaviour of Modal Verbs: 94 CommentsDocument4 pagesThe Strange Behaviour of Modal Verbs: 94 CommentsSabir HussainNo ratings yet
- Explanation About Should and Shouldn'tDocument6 pagesExplanation About Should and Shouldn'tMiguel RiveraNo ratings yet
- Syntax I MAV ModalityDocument10 pagesSyntax I MAV ModalityVictoria del Rosario MaidanaNo ratings yet
- Helping VerbsDocument2 pagesHelping VerbsArjun LyngdohNo ratings yet
- B LoveDocument8 pagesB LoveRibeiro Eugenio SardenhaNo ratings yet
- Special VerbsDocument3 pagesSpecial VerbsProfessora Mariana PereiraNo ratings yet
- How To Use Modal Verbs in The Passive Voice - inDocument23 pagesHow To Use Modal Verbs in The Passive Voice - inFaria MaryamNo ratings yet
- Modal+Verbs+ (May Might) + (Will Would) + (Shall Should) + (Can Could)Document4 pagesModal+Verbs+ (May Might) + (Will Would) + (Shall Should) + (Can Could)luis marioNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs ReviewDocument2 pagesModal Verbs ReviewAlex OrdazNo ratings yet
- MODALSDocument2 pagesMODALSRanto JoNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs 1 Material#1Document3 pagesModal Verbs 1 Material#1Sai TadikondaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Modal Verb?Document5 pagesWhat Is A Modal Verb?nugraha_schevner409No ratings yet
- Should: Nama: Ekuivalen Sutridani Tolampi NPM: PK 115 018 026 Prodi: Keperawatan Semester 2Document5 pagesShould: Nama: Ekuivalen Sutridani Tolampi NPM: PK 115 018 026 Prodi: Keperawatan Semester 2Imam RifkiNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice With ModalsDocument5 pagesPassive Voice With ModalsKhalid Mehmood AzaadNo ratings yet
- Modals Verbs: Samy Yoshay Zuleta Díaz Jason David Rivera NavarroDocument11 pagesModals Verbs: Samy Yoshay Zuleta Díaz Jason David Rivera Navarroelbo radorNo ratings yet
- ModalsDocument1 pageModalsArely SamNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Verbs: Simple. Generally We Only Use It in Question and NegativeDocument14 pagesAuxiliary Verbs: Simple. Generally We Only Use It in Question and NegativeMaxi ygn100% (1)
- Writing Informative or Explanatory Texts English Presentation in Colorful Pastel Doodle StyleDocument5 pagesWriting Informative or Explanatory Texts English Presentation in Colorful Pastel Doodle StylectgarroteNo ratings yet
- Auxilary VerbsDocument29 pagesAuxilary Verbsvargas199511No ratings yet
- Fundamental Structure, MODAL VERBS, INTRODUCTIONDocument11 pagesFundamental Structure, MODAL VERBS, INTRODUCTIONNadifah ZahraNo ratings yet
- Model Verbs Helping MaterialDocument6 pagesModel Verbs Helping Materialf230575No ratings yet
- Modal Verbs HomeworkDocument7 pagesModal Verbs Homeworkh4aa4bv8100% (1)
- Modal Verbs and Their FeaturesDocument21 pagesModal Verbs and Their FeaturesHirko BelayNo ratings yet
- Speaking Doc2a MOEDocument1 pageSpeaking Doc2a MOEannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Speaking Doc1 MOEDocument1 pageSpeaking Doc1 MOEannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Depression Complementary and Alternative TreatmentsDocument2 pagesDepression Complementary and Alternative Treatmentsannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Ask Students To Say What They Can See in The PhotoDocument1 pageAsk Students To Say What They Can See in The Photoannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Essay 200 WordsDocument1 pageGlobal Warming Essay 200 Wordsannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Depression Brain StimulationDocument1 pageDepression Brain Stimulationannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- 1E Social Studies Assessment Lesson 1 and 2Document1 page1E Social Studies Assessment Lesson 1 and 2annie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Women Empowerment Essay 200 WordsDocument1 pageWomen Empowerment Essay 200 Wordsannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Health Is Wealth Essay in EnglishDocument1 pageHealth Is Wealth Essay in Englishannie aneesch0% (1)
- Independence Day Essay in EnglishDocument1 pageIndependence Day Essay in Englishannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- My School Essay 200 WordsDocument1 pageMy School Essay 200 Wordsannie aneesch100% (2)
- At The End of Unit 1 Students Will Be Able To RecognizeDocument3 pagesAt The End of Unit 1 Students Will Be Able To Recognizeannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Show Your Work My SummaryDocument7 pagesShow Your Work My Summaryannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Through The Course BookDocument1 pageThrough The Course Bookannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument6 pagesPast Simpleannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Why Study in The USADocument4 pagesWhy Study in The USAannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- AdjectiveDocument1 pageAdjectiveannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- My Mother Essay 200 WordsDocument1 pageMy Mother Essay 200 Wordsannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument6 pagesPresent Continuousannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- My Family Essay 200 WordsDocument1 pageMy Family Essay 200 Wordsannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- An AdjectiveDocument1 pageAn Adjectiveannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- My Favourite Game EssayDocument1 pageMy Favourite Game Essayannie aneesch100% (1)
- Book Club 2Document1 pageBook Club 2annie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Present Continous TenseDocument1 pagePresent Continous Tenseannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Adverbs FormationDocument1 pageAdverbs Formationannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- You Start Books and Never Finish ThemDocument10 pagesYou Start Books and Never Finish Themannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect Tense Is A Rather Important Tense in EnglishDocument3 pagesThe Present Perfect Tense Is A Rather Important Tense in Englishannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Present Continous TenseDocument1 pagePresent Continous Tenseannie aneeschNo ratings yet
- Yusar's Academic Writing Class 2021Document1 pageYusar's Academic Writing Class 2021annie aneeschNo ratings yet
- What To Do Before The Book ClubDocument1 pageWhat To Do Before The Book Clubannie aneeschNo ratings yet