Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Binder 1
Uploaded by
BharathiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Binder 1
Uploaded by
BharathiCopyright:
Available Formats
Important Question for Class 6
Mathematics
Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes
Very Short Answer Questions 1 Mark
1. 1 mm = ____ cm
Ans: 0.1
2. Instrument used to measure angle is called_____.
Ans: Protractor
3. Standard unit for measuring angle is called ______ and is denoted by
______.
Ans: degree,
4. 90.5 is called ____ angle.
Ans: Obtuse
5. 177 is called _____ angle.
Ans: Obtuse
6. The sum of angles of a quadrilateral is _______.
Ans: 360
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 1
7. The diagonals of an isosceles trapezium are ______.
Ans: Equal
8. A sphere has _____ vertex and 0 edge.
Ans: Zero
9. Cube and cuboid have equal number of faces, vertices and edges. Say True
or False.
Ans: True
10. A triangular pyramid is called a ______.
Ans: Tetrahedron
Short Answer Questions 2 Marks
1. How many degrees are there in
(a) four right angles
Ans: four right angles 4 90 360 .
1
(b) 2 right angles
2
Ans:
1 1
2 right angles 2 90
2 2
5
90 225
2
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 2
2. How many degrees are there in between the clock hands when it displays
70 clock?
Ans:
It is 30 between any two numbers on the clock.
So, there are 7 divisions between 12 and 7.
Thus, total degrees 7 30 210
3. What is the condition for two triangles to be congruent?
Ans: Two triangles are said to be congruent if the corresponding sides and angles
of both triangles are equal to each other.
4. What is the perimeter of a triangle?
Ans: The sum of all three sides of a triangle is called the perimeter of a triangle.
5. Find the value of x 0 .
Ans: Sum of angles of a triangle 180 (By angle sum property of a triangle)
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 3
8 35 x 180
43 x 180
x 180 43
x 137
6. Find angles of a triangle which are in ratio 4: 6: 8.
Ans: Let the angles be 4 x0 ,6 x0 ,8x0
4 x 6 x 8x 180 (Angle sum property of triangle)
18x 180
x 10
So, angles are 40 ,60 ,80
7. Name the solid objects for each of the 3D shape
(a) cone
Ans: Party hats, oil funnel, Ice cream cone
(b) cylinder
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 4
Ans: Coke can, gas cylinder, electric cells
(c) cube
Ans: Rubix, dice, sugar and ice cubes
Short Answer Questions 3 Marks
1. Explain the various types of triangles considering the length of their sides.
Ans: On the basis of length of sides, there are three types of triangles:
(a) Equilateral triangle: It is a triangle in which all sides and all angles equal to
each other.
(b) Isosceles triangle: It is the triangle with two sides and two angles opposite to
the two sides are equal to each other.
(c) Scalene triangle: It has none of the sides or angles equal to each other.
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 5
2. Explain the types of triangles considering the angles.
Ans: On the basis of angles, there are three types of triangles:
a. Acute angled triangle: Triangle in which all the three angles are acute (less than
90 ) X , Y , Z 90
b. Right angled triangle: Triangle in which one angle is 90 , B 90
c. Obtuse angled triangle: Triangle in which at least one angle is obtuse(greater
than 90 and less than 180 )
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 6
Long Answer Questions 4 Marks
1. Say True or False
(a) Equilateral triangle, each angle measures 600 .
Ans: True
(b) A scalene triangle has two sides equal.
Ans: False, In scalene triangle none of the sides are equal.
(c) The angle opposite to equal sides of an Isosceles triangle are equal.
Ans: True
(d) In a right angled triangle, the sum of two acute angles is 180 .
Ans: False, the sum of two acute angles is \(90) .
2. The measure of two angles of a triangle are 720 and 550 . Find the measure of
the third angle.
Ans: Let A, B, C are the angles of a triangle
Let the required missing triangle be x
A B C 180 (By angle sum property of triangle)
Thus,
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 7
72 55 x 180
127 x 180
x 180 127
x 53
3. In ABC if 3A 4B 5C . Calculate A, B, C
Ans: let 3A 4B 5C x
3A x , 4B x and 5C x
x x x
A , B and C
3 4 5
x x x
180 (by angle sum property of triangle)
3 4 5
1 1 1
x 180
3 4 5
20 15 12
x 1802
60
47
x 180
60
180 60
x 229.78
47
x x x
So, A 76.5 , B 57.4 , C 45.9
3 4 5
4. Explain the following:
(a) Convex quadrilateral
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 8
Ans: Quadrilateral which has each of the interior angles less than 180 is called a
convex quadrilateral.
(b) Concave quadrilateral
Ans: Quadrilateral which has each of the interior angles greater than 180 is called
a concave quadrilateral.
Long Answer Questions 5 Marks
1. Define the following:
(a) Acute angle
Ans: Acute angle: Angle which is less than 90 is called an acute angle
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 9
(b) Right angle
Ans: Right angle: Angle which is equal to 90 is called a right triangle.
(c) Obtuse angle
Ans: Obtuse angle: Angle greater than 90 and less than 180 is called an obtuse
angle.
(d) Straight angle
Ans: Straight angle: Angle equal to 180 is called a straight angle.
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 10
(e) Complete angle
Ans: Complete angle: Angle equal to 360 is called a complete angle.
(f) Zero angle
Ans: Zero angle: Angle equal to 0 is called a zero angle.
2. State the type of angle
(a)
Ans: Straight angle
(b)
Ans: Right angle
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 11
(c)
Ans: Obtuse angle
(d)
Ans: Zero angle
(e)
Ans: Acute angle
(f)
Ans: Reflex angle
3. Explain the difference between Square and Rectangle.
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 12
Ans: The differences are:
Square Rectangle
All sides are equal. Only opposite sides are equal.
4. Explain similarity between Rhombus and Parallelogram.
Ans: The similarity is:
Both Rhombus and Parallelogram have two pairs of parallel sides.
Both Rhombus and Parallelogram diagonal bisect each other.
Parallelogram Rhombus
5. Say True or False
(a) Parallelogram has both the diagonals equal.
Ans: True
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 13
(b) The diagonals of a rectangle are perpendicular to each other.
Ans: False
(c) A square is also a parallelogram.
Ans: True
(d) The diagonals of a rhombus are equal.
Ans: True
6. Write the number of faces, edges and vertices of
(a) Square based pyramid
Ans: Square based pyramid
Faces 5 ( 4 triangular, 1 square)
Edges 8
Vertices 1
(b) Triangular based prism
Triangular based prism
Faces 5
Edges 9
Vertices 6
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 14
Important Question for Class 6
Mathematics
Chapter 8 – Decimals
Very Short Answer Type Questions 1 Mark
2 5 5
1. Write in decimal form: 400 60 7
10 100 1000
Ans: Let’s use basic arithmetic operations:
2 5 5
400 60 7
10 100 1000
200 50 5
467
1000
467 0.255
467.255
2. Express the term 4 m in km using decimals.
Ans: The expression is:
1 km = 1000 m
4
4 m km 0.004 km
1000
9
3. , in decimal form can be written as:
1000
9
Ans: 0.009
1000
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 1
4. The correct expanded form of 3.07 is
(a) (3 10) 7
1
10
(b) (3 1) 7
1
10
(c) (3 1) 7
1
100
(d) None of these
Ans: (C)
Since,
3.07 3 0.07
1
(3 1) 7
100
5. Fill in the blanks, 2 0.7 ___
Ans:
2.0 0.7 1.3
Short Answer Type Questions 2 Marks
13
1. Express 17 as decimals
1000
Ans:
13
17
1000
17 1000 13
1000
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 2
17000 13
1000
17013
1000
17.013
2. Convert 6.3, 8.19, 0.276 and 74 into like decimals
Ans: So, we need to convert the given number 6.3, 8.19, 0.276, 74 into like
decimals. Since, we know that decimals that have same number of decimal places
are called like decimals.
Therefore, the like decimals will be:
6.300, 8.190, 0.276, 74.000
3. Compare 34.7 and 34.68
Ans: In the given question we need to compare two numbers. So for comparing
two numbers, we always need to compare each of the digits places.
Here, it can be seen that before the decimal places both have the same digits. So
now we will compare the digits after the decimals.
Therefore, on comparing it, we get:
34.7 34.68
4. Add and express in kilograms using decimals: 3 kg and 448 g .
Ans: 3 kg and 448 g
3 kg 448 g
1
1g =
1000 kg
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 3
448
3kg kg
1000
3 kg 0.448 kg
3.448 kg
5. Express 4 g in kilograms using decimals.
Ans:
1
1g =
1000 kg
4
4g kg 0.004 kg
1000
6. Express in kilometres using decimals 8 km 56 m .
Ans: 8 km 56 m
1
1m =
1000 km
8 km 56 m
56
8 km km
1000
8 km 0.056 km = 8.056 km
Short Answer Type Questions 3 Marks
1. Write the following in ascending order 3.83, 5.07, 0.8, 0.365 and 6.4
Ans: Converting into like terms
3.830, 5.070, 0.800, 0.365, 6.400
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 4
So, the ascending order is:
0.365, 0.800, 3.830, 5.070, 6.400
39
2. Convert into decimal fraction
4
Ans: By performing division:
9.75
4 ) 39
36
30
28
20
20
0
5
3. Convert into decimal fraction 4
8
Ans: By solving given fraction
5 (4 8) 5 37
4
8 8 8
By performing division:
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 5
4.625
8) 37
32
50
48
20
16
40
40
0
5
4. Convert into decimal fraction
26
Ans: By performing division:
0.192307692
4 50
26
240
234
60
52
80
78
200
182
180
156
240
234
60
52
8
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 6
5. Add: 37.8, 56, 165.08, 574.6.
Ans: By adding given numbers
37.8 56.00 165.08 574.60 833.48
Therefore, on adding 37.8, 56, 165.08, 574.6, we get 833.48 .
6. Subtract 27.56 from 52.1.
Ans: By subtracting 27.56 from 52.1
52.10 27.56 24.54
Therefore, we get 24.54 on subtracting 25.76 from 52.1
7. Simplify: 42.4 23.57 53.64 17.8
Ans: By adding 42.4 and 53.64
42.40
53.64
96.04
By adding
23.57 and 17.8
23.57
17.80
41.37
Now, by subtracting
41.37 from 96.04
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 7
96.04
41.37
54.67
Long Answer Type Questions 4 Marks
1. Arrange the digits 178.264 in the place value chart. Write the place value of
each digit. AIso, write 178.264 in expanded form.
Ans: Place value chart:
Hundred’s Ten’s One’s . 1
th
1
th
1
th
10 100 1000
1 7 8 2 6 4
Expanded from:
178.264 178 0.264
1 1 1
1100 7 10 8 1 2 6 4
10 100 1000
2 6 4
100 70 8
10 100 1000
2. Convert decimals into a fraction in its simplest form
(a) 0.08
Ans: Simplest form of given decimals can be written as
8 4 2
0.08
100 50 25
(b) 0.525
Ans: Simplest form of given decimals can be written as
525 105 21
0.525
1000 200 40
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 8
3. Convert decimals as mixed fraction
(a) 34.8
Ans: The conversion is:
34.8 34 0.8
8
34
10
4
34
5
4
34
5
(b) 4.284
Ans: The conversion is:
4.284 4 0.284
284
4
1000
142
4
500
71 71
4 4
250 250
4. Convert fractions into decimals
249
(a)
100
Ans: The conversion is:
249
2.49
100
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 9
3104
(b)
100
Ans: The conversion is:
3104
31.04
100
4002
(c)
1000
Ans: The conversion is:
4002
4.002
1000
Long Answer Type Questions 5 Marks
1. A student covers a journey of bus in 4 hours. He covers distance of
74 km224 m during first and second hour, 58 km56 m during third hour and
62 km8 m during fourth hour. What is the length of his journey?
Ans: In the question, it is given that,
The distance covered during first and second hour is 74 km224 m .
The distance covered during third hour is 58 km56 m .
Distance covered during fourth hour is 62 km8 m .
Total distance covered in 4 hours is 194 km 288 m .
74 km 224 m
58 km 56 m
62 km 8m
194km 288m
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 10
2. Ganesh purchased a book worth Rs.156.65 from a bookseller and he gave
him Rs.500 note. How much balance did he get back?
Ans: Cost of book Rs. 156.65
Total amount given by Ganesh Rs. 500
500.00
156.65
343.35
So, the balance given by shopkeeper Rs. 343.35
3. The total weight of a box containing 14 kg750 g of mangoes, 5 kg80 g of apples
is 22 kg 200 g . How much is the weight of the empty box?
Ans: Weight of mangoes 14 kg750 g
Weight of Apples 5 kg80 g
Total weight of box 22 kg200 g
14 kg 750g
5 kg 80g
19 kg 830 g
So, the weight of empty box = total box weight - total weight of fruits
22kg 200 g - 19 kg 830 g = 2 kg370 g .
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 11
Important Questions for Class 6
Mathematics
Chapter 10 - Mensuration
Very Short Answer Questions. 1 Mark
Q1. Length of boundary of a plane figure is called_____
Ans:
We need to fill the blank with appropriate identity.
Perimeter
Q2. Perimeter of rectangle ____?
Ans:
We know that Perimeter of rectangle 2(l b),
Here,
l length
b breadth
Q3. Perimeter of square = ___?
Ans:
We know that perimeter is the length of the boundaries of a figure.
Square has four sides.
Therefore, Perimeter of square 4 side
Q4. The ratio of circumference of a circle and it’s ______ is always constant.
Ans:
The ratio of circumference of a circle and it’s diameter is always constant.
We know that, circumference of a circle 2 r
Diameter of a circle d 2r
2 r
Ratio will be 2r
2
Hence, the ratio is constant.
Q5. Circumference of a circle, C ________?
Class 6: Mathematics www.vedantu.com 1
Ans:
We know that circumference is the total length of the boundary of a figure.
So, C 2 r
Q6. Value of :
(a) In fractions is ________
(b) In decimals is ________
Ans:
22
(a) Value of in fraction is .
7
(b) Value of in decimals is 3.14
Q7. Area of rectangle (a) _______ (b) ______square units.
Ans:
We know that area of rectangle length breadth
Therefore,
(a) Length
(b) Breadth
Q8. Area of square (a) _______ (b) ______square units.
Ans:
We know that area of a square is side side
Therefore,
(a) Side
(b) Side
Short Answer Questions. 2 Mark
Q1. Length and breadth of a rectangle are 12.3cm and 9.6 cm respectively. Find
its perimeter.
Ans:
Given: Length 12.3 cm
Breadth 9.6 cm
Class 6: Mathematics www.vedantu.com 2
We know perimeter 2(l b)
2(12.3 9.6)
31.5 cm
Q2. Find the cost of fencing a square field of 175 m at Rs. 60 per metre.
Ans:
Given: Perimeter of square field 175m
We need to find the cost of fencing the field.
Perimeter 175 m
Cost of fencing per metre Rs.60
So, total cost of fencing will be
175 60
Rs. 10,500
Q3. Find the perimeter of a square whose has sides measuring 6.4cm
Ans:
Given: Side of square 6.4cm
We need to find the perimeter of the square.
We know that the perimeter of the square 4 side
So, Perimeter of square will be
P 4 6.4
25.6cm
Q4. Find circumference of a circle of radius 13 cm.
Ans:
Given: Radius 13 cm
We need to find the circumference of the circle.
We know, Circumference 2 r
22
2 13
7
81.714cm
Q5. Find the diameter of a circle whose circumference is 88cm.
Ans:
Class 6: Mathematics www.vedantu.com 3
Given: Circumference of a circle 88cm
We need to find the diameter of the circle.
We know that circumference d
C
d
88
88
7
22
4 7
28cm
Short Answer Questions. 3 Mark
Q1. The length and breadth of a rectangle field are 340m and 160m. A
watchman walked 5 rounds around the field. Find the distance covered by
him.
Ans:
Given: length of rectangular field, l 340m
Breadth of rectangular field, b 160cm
We need to find the distance covered by the watchman.
We know that Perimeter, P 2(l b)
2(340 160)
2(500)
1000 cm
This is the length of one round but watchman walked 5 rounds.
So, distance covered by watchman will be
5 1000
5000 cm
Q2. The length and breadth of a rectangular box is in the ratio 4 : 5. If its
perimeter 4m 40cm. Find its dimensions.
Ans:
l 4
Given:
b 5
Perimeter 4 m 40 cm
Class 6: Mathematics www.vedantu.com 4
We need to find the length and breadth of the rectangular box.
Let length of the box 4x
Breadth of the box 5x
So, we know that
P 2(l b) 4m 40cm
2(4 x 5 x) 4m 40cm
2(9 x) 4.4m
18 x 4.4m
4.4
x
18
0.244m
Therefore, the dimensions of the rectangular box will be
l 4x
4 0.244
0.976 cm
97.6 m
b 5x
5 0.244
1.22 cm
122 m
Q3. How many square tiles each of side 0.25m will be required to pane the
floor of a room which is 4m broad and 3m long?
Ans:
Given: Length of room, l 4 m
Breadth of the room, b 3m
Area of the room will be
4 3square meters
12square meters
0.25 m
Side of square tile 1
m
4
Area of each square tile will be
Class 6: Mathematics www.vedantu.com 5
1 1
sq. meters
4 4
1
sq. meters
16
Therefore, number of tiles needed to pane the floor of the room will be
1
12
16
12 16
192 tiles
Q4. Calculate area( all units are in m)
Given:
We need to find the area of the figure.
We know that area of rectangle l b
So, area of rectangle, 1 A1 l b
3 1
3 sq. meters
Area of rectangle, 2 A2 l b
6 1
6 sq. meters
Area of rectangle, 3 A3 l b
Class 6: Mathematics www.vedantu.com 6
3 1
3 sq. meters
Therefore, area of the figure will be
A A1 A2 A3
363
12 sq. meters
Long Answer Questions. 4 Mark
Q1. Find the perimeter of a regular heptagon having each side equal to 5.5 cm
Ans:
Given: A regular heptagon with side 5.5 cm
We need to find the perimeter of the heptagon.
We know that perimeter is the length of outer sides of a figure.
Regular heptagon means a figure of 7 sides and all sides are equal.
Therefore, the perimeter of the heptagon will be
7 side
7 5.5
38.5 cm
Q2. Find the perimeter of the below figure and the figure is symmetrical
about its horizontal axis.
16cm 4cm
12cm
8cm
16cm 4cm 12cm
Ans:
Given: the figure which is symmetrical about its horizontal axis.
We need to find the perimeter of the given figure.
We know that the perimeter is the total length of all sides of the given figure.
Therefore, perimeter of the given figure will be
Class 6: Mathematics www.vedantu.com 7
8 16 4 12 12 4 16
8 20 21 20
70 cm
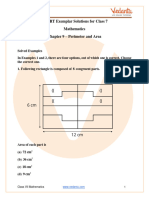
Q3. Find the area of the following figure with each square of area 1 cm2 .
Ans:
Given: the figure having each square of area 1 cm2
We need to find the area of the figure.
Total number of squares the figure have 16
Area of one square 1 cm2
Therefore, the area of the figure will be
16 1 cm 2
16 cm 2
Q4. Find area of rectangle whose length and breadth are 35 cm and 15 cm .
Find the perimeter of the rectangle.
Ans:
Given: length of rectangle, l 35 cm
Breadth of rectangle, b 15 cm
We need to find the area and perimeter of the rectangle.
We know that area of rectangle l b
Therefore, area will be
35 15
525 cm 2
Also, we know that perimeter of a rectangle 2(l b)
Therefore, perimeter will be
Class 6: Mathematics www.vedantu.com 8
2(35 15)
2 50
100 cm
Very Long Answer Questions. 5 Mark
Q1. The cost of cultivating a square field is Rs.130 per meter is Rs. 8, 450 . Find
the length of each side of the field.
Ans:
Given: Cost of cultivating a square field Rs.130 per meter
Total cost of cultivating the square field Rs. 8, 450
We need to find the length of the side of square field.
Total cost of cultivating
Area of square field
Per meter cost of cultivating
Therefore, area will be
8450
130
650 m2
Now, we know that area of a square side side
Therefore, the length of the each side of square field will be
650 side side
s 2 650
s 650
s 25.4 cm
Class 6: Mathematics www.vedantu.com 9
Important Questions for Class 6
Maths
Chapter 11- Algebra
Very Short Answer Questions 1 Marks
1. Express algebraically: 3 more than x .
Ans: The algebraic expression of the given statement is x 3 .
2. What is the exponential form of x x x x ....15 times ?
Ans: The given expression x x x x ...15 times .
Recall that, x x x 2 ,
x x x x3 ,
x x x x x 4 , etc.
Therefore, the number of times x is multiplied with itself equals x to the power
of that number.
Thus, x x x x ...15 times x15 .
3. What is the product form of x2 y 7 ?
Ans: The given algebraic expression is x 2 y 7 .
Recall that, the number of times x is multiplied with itself equals x to the power
of that number.
Therefore, x 2 x x .
Similarly, y7 y y y y y y y .
Thus, x 2 y7 x x y y y y y y y .
4. What is the coefficient of b in -8abc ?
Ans: The given algebraic expression is 8abc .
Recall that, the coefficient of any term in an algebraic expression is the
multiplication of other terms in that algebraic expression.
Therefore, the coefficient of the term b in the expression 8abc is 8ac .
5. What is the numerical coefficient of 4a2 ?
Ans: The given expression is 4a 2 .
It is known that, the numerical coefficient in an algebraic expression is the
number multiplied in that expression.
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 1
Therefore, the numerical coefficient of 4a 2 is 4 .
6. What is the constant term of 2a 2 9 ?
Ans: The constant term of the expression 2a 2 9 is 9 .
y
7. If 1 , then y ?
5
Ans: The given equation is
y
1.
5
Multiply 5 both sides of the equation.
y
5 1 5
5
y 5.
Short Answer Questions 2 Marks
1. Express algebraically the following statement:
8 times a number x is less than a number .
Ans: The required algebraic expression of the given statement is
8x z y .
2. What are the terms in the following algebraic expression?
4ab2 + 3c2 - 5ab + 9 .
Ans: The terms of in the given expression are
4ab2 ,3c2 , 5ab, and 9 .
3. Solve the following equation and evaluate x . Also, justify the result.
x 8 17 .
Ans: The given equation is
x 8 17
Add 8 both sides of the equation.
x 8 8 17 8
x 25
Justification:
LHS x 8
25 8
17
RHS
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 2
Thus, Left-hand-side Right-hand-side.
4. Solve the following equation and evaluate x . Also, justify the result.
4
x = 18 .
6
Ans: The given equation is
4
x 18
6
Multiply 6 both sides of the equation.
4
6 x 6 18
6
4x 18 6
Divid both sides of the equation by 4 .
4x 18 6
4 4
x 27 .
Justification:
4
LHS x
6
4
27
6
18
RHS
Hence, Left-hand-side Right-hand-side.
Long Answer Questions 3 Marks
1. Sanjit scored 70 marks in mathematics and "x" marks in English. Find
the total score in both the subjects?
Ans: He got marks in mathematics 70 .
He got marks in English x .
Therefore, the total marks in mathematics and English x 70 .
2. Let p 1, q 1, and r 3 . What is the value of p3 + q3 + r 3 - 3pqr ?
Ans: The given algebraic expression is
p3 q3 r 3 3pqr …… (i)
Substituting p 1,q 1, and r 3 into the equation (i) gives
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 3
p3 q 3 r 3 3pqr
1 1 3 3 1 1 3
3 3 3
1 1 27 9
27 9
36
3. Choose the similar terms from the following expressions.
xyz, xy 2z, xzy 2 , z 2xy, y 2xz, x2yz, zxy 2
Ans: The like terms are those which have exactly one square term involved.
Therefore, the similar terms are
xy2z, xzy2 , y2 xz, and zxy 2 .
4. Solve the equation 12x 30 6 .
Ans: The given equation is
12x 30 6
Add 30 both sides of the equation.
12x 30 30 6 30
12x 36
Divide 12 both sides of the equation.
12x 36
12 12
x 3.
Hence, the solution is x 3 .
5. Verify whether y 4 satisfy the equation 3y 5 7 .
Ans: The given equation is 3y 5 7 .
Then,
LHS 3 4 5
12 5
7
RHS
Thus, Left-hand-side Right-hand-side.
Hence, y 4 satisfy the given equation.
6. Solve the equation 6x 10 26 2x and evaluate x by using the method
of transposition. Then justify the answer.
Ans: The given equation is
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 4
6x 10 26 2x
6x 26 2x 10 , by the method of transposition.
6x 16 2x
6x 2x 16 , by the method of transposition.
8x 16
Divide 8 both sides of the equation.
8x 16
8 8
x 2.
Justification:
LHS 6x 10
6 2 10
12 10
22
Also,
RHS 26 2x
26 2 2
26 4
22
Thus, Left-hand-side Right-hand-side.
Hence, x 2 is the solution of the given equation.
Long Answer Questions 4 or 5 Marks
1. Find the algebraic expression of the statements given below.
(a) 6 less than the quotient of x and y .
Ans: The required algebraic expression is
x
6.
y
(b) The sum of the quotient of p , q and the product of p, q .
p
Ans: The quotient of p,q is .
q
The product of p,q is pq .
Therefore, the required algebraic expression is given by
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 5
p
pq .
q
(c) One fourth of the sum of x and y .
Ans: The sum of x and y is x y .
Therefore, the required algebraic expression is given by
1
x y.
4
(d) 8 removed from twice the term x .
Ans: Twice the term x is 2x .
Therefore, the required algebraic expression is 2x 8 .
2. Classify monomials, binomials, and trinomials from the following
algebraic expressions.
y 5, 6x3y, 8, 3pqr, a2 + b 2 + z 2
Ans: Recall that, sum of two terms is called binomials, sum of three terms is
called trinomials and single algebraic term is called monomials.
The following table shows the required classifications.
Monomials Binomials Trinomials
6x 3 y y5 a 2 b2 z 2
8
3pqr
3. Determine the solution of 3x 12 , by using the method of trial and errors.
Ans: The given equation is 3x 12 .
First substitute x 1 into the given equation.
3x 3 1 3 12 .
So, x 1 .
Then, substitute x 2 into the equation.
3x 3 2 6 12 .
So, x 2 .
Again, substitute x 3 into the given equation.
3x 3 3 9 12 .
Therefore, x 3 .
Now, substitute x 4 into the given equation.
Then 3x 3 4 12 .
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 6
Thus, x 4 is the solution of the given equation.
4. Solve the following equation and evaluate x by using the method of
isolation.
a
a7 5 .
2
Ans: The given equation is
a
a 7 5
2
Add 7 on both sides of the equation.
a
a 77 57
2
a
a 12
2
a
Add on both sides of the equation.
2
a a a
a 12
2 2 2
a a a
a 12
2 2 2
2a a
12
2
a
12
2
Multiply 2 on both sides of the equation.
a
2 12 2
2
a 24 .
Hence, the required solution is a 24 .
5. Solve the following equation and justify the result.
3 a + 3 + 3 a - 1 5 a + 5 .
Ans: The given equation is
3 a+3 +3 a-1 5 a+5
3a 9 3a 3 5a 25 , multiplying the terms.
6a 6 5a 25 , adding the like terms.
6a 5a 25 6 , by the method of transposition.
a 19 .
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 7
Justification:
LHS 3 a 3 3 a 1
3 19 3 3 19 1
3 22 3 18
66 54
120
Also,
RHS 5 a 5
5 19 5
5 24
120
Thus, Left-hand-side Right-hand-side.
Hence, the required solution of the given equation is a 19 .
6. Determine two numbers so that one is greater by 21 than another and sum
of them is 91 .
Ans: Let x be one number.
Then, another number is x 21.
By the given conditions,
x x 21 91
2x 21 91
Add 21 on both sides of the equation.
2x 21 21 91 21
2x 21 21 91 21
2x 70
Divide 2 on both sides of the equation.
2x 70
2 2
x 35
Hence, the required numbers are 35 and 35 21 , that is 35, 56 .
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 8
Important Questions for Class 6
Mathematics
Chapter 12 - Ratio and Proportion
1 Mark
1. In a ratio, first term is called ____ and second term is called ______.
Ans: Antecedent, Consequent
For example, in ratio13:15, 13 is Antecedent and 15 is Consequent.
2. Product of ______ = Product of extremes.
Ans: Means
In a proportion, the first and last terms are known as the extremes, while the
second and third terms are known as the means.
3. If a, b, c, d are in proportion, then
a) ac bd
b) ad bc
c) ab cd
d) None of these.
Ans. (b) ad bc
If the ratio of the first two quantities equals the ratio of the last two quantities, the
numbers a, b, c, and d are proportional.
4. A ratio has _____ units
Class 11 Mathematics www.vedantu.com 1
Ans: No
Because a ratio is made up of similar quantities, the units cancel each other out,
and thus there is no unit for a ratio.
2 Mark
1. Convert 80:50 into simplification.
Ans. Given ratio 80:50
Expressing as fractions
80 8 10 8
50 5 10 5
2. Find the ratio of 40 cm to 2.5 m
Ans. let’s first convert 2.5 m into cm
(2.5) m 2.5 100 250 cm
Now,
40 cm : 2.5 cm 40 cm : 250 cm
40 : 250
40
250
4
25
The required ratio is 4:25
3. The length and breadth of a field are 80 m and 30 m . what is the ratio of the
breadth and length of park?
Ans. Given,
Length of park = 80 m
Class 11 Mathematics www.vedantu.com 2
Breadth of park = 30 m
Bredth 30 m
Ratio of the breadth and length =
Length 80 m
3
8
Required ratio is 3:8
4. If 30 oranges cost Rs.120 . What is the cost of 50 oranges?
Ans.
Here we will use unitary method.
Cost of 30 oranges = Rs.120
120
Now, cost of one orange = Rs. 4
30
Cost of 50 oranges = cost of one orange x cost of fifty oranges
4 50
Rs. 200
3 Mark
1. Find the ratio of 45 minutes to an hour?
Ans. To find - 45 min :1 hour
We know that one hour 60 min
Therefore, 45 min :1 hour 45 min : 60 mnt
45
60
Dividing numerator and denominator by 3
Class 11 Mathematics www.vedantu.com 3
45 3 15
60 3 20
Dividing numerator and denominator by 5
15 5 3
20 5 4
2. Find the ratio 250 ml to 4 l .
Ans. To find: 250 ml : 4l
First let’s convert 4 l into ml
We know
1l 1000 ml
4 l 1000 4 ml
4 l 4000 ml
Now,
250 ml : 4 l 250 ml : 4000 ml
250 : 4000
250 10 25 5
4000 10 400 5
5 5
80 5
1
16
1:16
Required Ratio - 1:16
3. Find the equivalent ratio of 75 : 100
Class 11 Mathematics www.vedantu.com 4
Ans.
n 75 :100
75 5 15
n
100 5 20
15 5
n
20 5
3
n
4
The equivalent ratios for 75 : 100 are15: 20 and 3: 4
4. Are 20, 40, 60, 120 are in proportion?
Ans. First we will find 20:40 and 60:120
20 2 1
20 : 40
40 4 2
60 6 1
60 :120
120 12 2
The numbers in simplest form are equal. Yes. 20, 40, 60, 120 are in proportion.
5. 15 men can reap a field in 25 days. In how many days can 20 men reap the
same field?
Ans. 15 men can reap field in = 25days.
1 men can reap field in = (25 15 ) days
25 15
20 men can reap field in = days
20
Class 11 Mathematics www.vedantu.com 5
25 15
20
5 3
4
15
days
4
3
3 days
4
3
Therefore, 20 men can reap the same field in 3 days .
4
4 Mark
2 14 6
1. Fill up the blanks
3
Ans. Le,
2 14
3 x
2 x 14 3
14 3
x 7 3 21
2
Let’s substitute
2 14
3
Similarly,
Class 11 Mathematics www.vedantu.com 6
2 6
3
2x 3 6
3 6
x 3 3 9
2
2 6
3
2 14 6
Hence,
3 21 9
3. Two numbers are in the ratio 3:5 and their sum is 192. Find the numbers.
Ans. Let common ratio is x
Therefore, numbers are 3x and 5x
According to question,
3x 5x 192
8 x 192
192
x 24
8
Required numbers are,
3x 3 24 72
5 x 5 24 120
4. Compare the ratios 1 : 2 and 4 : 5
Ans. Given,
Class 11 Mathematics www.vedantu.com 7
1
1: 2
2
4
4:5
5
LCM of 5 and 2 is 10.
Therefore,
1 5 5
2 5 10
4 2 8
5 2 10
5 8
Here,
10 10
5 1 8 4
;
10 2 10 5
Therefore,
1 4
2 5
1: 2 4 : 5
5. If x:63::36:81
Ans. We can use formula
Product of means = Product of extremes
Class 11 Mathematics www.vedantu.com 8
63 36 81 x
81 x 63 36
63 36
x
81
7 36
9
74
x 28
5 Mark
1. Divide Rs. 2000/- between Asha and Kiran in the ratio 4:6.
Ans. Given amount = Rs. 2000/-
Given ratio = 4:6
Let common ratio is x
Then, Asha’s share = 4x
Similarly, Kiran’s share = 6x
According to Question,
4 x 6 x 2000
10 x 2000
2000
x 200
10
Now,
Asha’s share = 4 200 Rs. 800
Kiran’s share = 6 200 Rs.1200
2. Divide Rs. 500 among A,B,C in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3
Class 11 Mathematics www.vedantu.com 9
Ans. Given amount = Rs. 500
Given ratio = 1 : 2 : 3
Let common ratio = x
A’s Share = x
B’s Share = 2x
C’s Share =3x
According to question
x 2 x 3 x 500
6 x 500
500
x
6
x 83.33
Now,
A’s Share = Rs. 83.33
B’s share = Rs. (2 83.33) Rs.166.66
C’s Share = Rs. 3 83.33 Rs. 250
3. If 4:x::x:36. Find the value of x .
Ans. We will use formula
Product of means = Product of extremes
x x 4 36
x 2 144
x 144
x 12
Class 11 Mathematics www.vedantu.com 10
4. If 10, 15, x are in proportion. Find the value of x .
Ans. Given, 10, 15, x are in proportion.
10: 15:: 15: x
We will use formula
Product of means = Product of extremes
15 15 10 x
10 x 15 15
15 15
x
10
15 3
2
45
2
x 22.5
5. Find the ratio of price of coffee powder to that of milk powder when coffee
powder cost 24 / per 100g and milk powder cost 180 / per kg .
Ans. Given, cost of 100g coffee powder = Rs. 24
24
Cost of 1g coffee powder = Rs.
100
Cost of 1000 g coffee powder = Rs.
24
1000 Rs. 240
100
Cost of 1 kg of coffee powder = Rs. 240
Cost of 1 kg of milk powder = Rs.180
Cost of 1 kg of coffee: Cost of 1 kg of milk powder
Class 11 Mathematics www.vedantu.com 11
Rs. 240 : Rs.180
240
180
24 8
18 6
4
4:3
3
Required ratio is 4:3.
Class 11 Mathematics www.vedantu.com 12
You might also like
- Grade 7 Math Test GeometryDocument7 pagesGrade 7 Math Test Geometryruel pabloNo ratings yet
- Load CalculationDocument6 pagesLoad CalculationBharathi100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions - 1 Mark Each: Maths Assignment Chapter 1 To 7Document7 pagesMultiple Choice Questions - 1 Mark Each: Maths Assignment Chapter 1 To 7api-233604231No ratings yet
- Math MajorDocument59 pagesMath MajorEstepanie Gopet100% (1)
- Digital SAT Math Problem Set 12 Answers and ExplanationsDocument4 pagesDigital SAT Math Problem Set 12 Answers and ExplanationswwwmacyNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 15 Properties of Triangles PDFDocument55 pagesRD Sharma Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 15 Properties of Triangles PDFsamridh guptaNo ratings yet
- Digital SAT Math Problem Set 13 Answers and ExplanationsDocument6 pagesDigital SAT Math Problem Set 13 Answers and ExplanationswwwmacyNo ratings yet
- NNPC Past Questions and AnswersDocument64 pagesNNPC Past Questions and AnswersSkonto RigaNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET-understanding Quadrilaterals - Class 8Document12 pagesWORKSHEET-understanding Quadrilaterals - Class 8Manoj Pandey50% (2)
- Bergen County Academies Entrance Practice Tests: Five Full-Length Math and English Essay Tests with Detailed Answer ExplanationsFrom EverandBergen County Academies Entrance Practice Tests: Five Full-Length Math and English Essay Tests with Detailed Answer ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Master Fundamental Concepts of Math Olympiad: Maths, #1From EverandMaster Fundamental Concepts of Math Olympiad: Maths, #1No ratings yet
- Alleyn's School 11plus Maths 1Document11 pagesAlleyn's School 11plus Maths 1madhujayanNo ratings yet
- RasGas Onshore Expansion Project Instrument Cable InstallationDocument11 pagesRasGas Onshore Expansion Project Instrument Cable InstallationBharathiNo ratings yet
- Knox 2016 2U Trials & SolutionsDocument25 pagesKnox 2016 2U Trials & SolutionsSumNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Cable Splicing and Termination Test ReportDocument2 pagesFiber Optic Cable Splicing and Termination Test ReportBharathiNo ratings yet
- Mathematical LogicDocument47 pagesMathematical LogicSaddam SevenmatikaNo ratings yet
- Xxxii Brazilian Math Olympiad 2010: (Page 1)Document33 pagesXxxii Brazilian Math Olympiad 2010: (Page 1)sohrabNo ratings yet
- DOD-ITP - INS-008-ITP FOR Installation and Testing of Fiber Optic Cable - Rev.0Document2 pagesDOD-ITP - INS-008-ITP FOR Installation and Testing of Fiber Optic Cable - Rev.0Bharathi100% (1)
- DOD-MST-INS-002, MST For Installation of Field Instruments.-Rev-1Document15 pagesDOD-MST-INS-002, MST For Installation of Field Instruments.-Rev-1BharathiNo ratings yet
- General Notes 8A22-V09 D01 MD-502-8A22-EG-PR-PID-1011 8A22-V01 8A22-R03Document1 pageGeneral Notes 8A22-V09 D01 MD-502-8A22-EG-PR-PID-1011 8A22-V01 8A22-R03Bharathi100% (1)
- Math6 q1 Mod1 AddingSimpleFractionsandMixedNumbersWithoutandWithRegrouping VADocument35 pagesMath6 q1 Mod1 AddingSimpleFractionsandMixedNumbersWithoutandWithRegrouping VASherie Mae Divinagracia100% (1)
- CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes Important Questions 2022-23Document14 pagesCBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes Important Questions 2022-23BharathiNo ratings yet
- Class 7 WwsDocument22 pagesClass 7 Wwsgamer.zen.1092No ratings yet
- Question No 01. Choose The Correct OptionDocument3 pagesQuestion No 01. Choose The Correct Optionmuzammil khaliqNo ratings yet
- Math Homwork 7Document87 pagesMath Homwork 7abdul subhanNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Maths - Understanding Quadrilaterals PDFDocument32 pagesClass 8 - Maths - Understanding Quadrilaterals PDFAnand MekalaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 3Document14 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 3NidaNo ratings yet
- 1 Year: Q Nso: 1 Encircle The Correct Answer.Document1 page1 Year: Q Nso: 1 Encircle The Correct Answer.Rana Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- Mathes Class 5Document4 pagesMathes Class 5Narendra PatelNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Assessments 2021 Class 7thDocument7 pages1st Term Assessments 2021 Class 7thJotish JavidNo ratings yet
- PNUAT Numerical SkillsDocument10 pagesPNUAT Numerical SkillsRhonel Galutera100% (1)
- SHS Qa 2Document6 pagesSHS Qa 2YowNo ratings yet
- Time: 2 Hours Total Marks: 80: CBSE Board Class VII Mathematics Term II Sample Paper 2Document15 pagesTime: 2 Hours Total Marks: 80: CBSE Board Class VII Mathematics Term II Sample Paper 2aclNo ratings yet
- JAR 66 Module 1 Exam Practice Exam Mathematics: This Is Exam Number 1Document48 pagesJAR 66 Module 1 Exam Practice Exam Mathematics: This Is Exam Number 1Amila FernandoNo ratings yet
- True About Spherical Triangles?: Society of Young Engineers Towards Achieving ExcellenceDocument3 pagesTrue About Spherical Triangles?: Society of Young Engineers Towards Achieving ExcellenceAslagNo ratings yet
- JAR 66 Module 1 Exam Practice Exam Mathematics: This Is Exam Number 1Document55 pagesJAR 66 Module 1 Exam Practice Exam Mathematics: This Is Exam Number 1Ashwin GaneshNo ratings yet
- Cycle Test November RevisionDocument21 pagesCycle Test November Revisiontaminhthien2009No ratings yet
- GeometryDocument30 pagesGeometryPaulNo ratings yet
- Adamson University Physics Society Qualifying Exam Review: Mathematics (AlgebraDocument16 pagesAdamson University Physics Society Qualifying Exam Review: Mathematics (AlgebraKirstie Alley San JoseNo ratings yet
- Time: 2 Hours Total Marks: 80: CBSE Board Class VI MathematicsDocument13 pagesTime: 2 Hours Total Marks: 80: CBSE Board Class VI MathematicsRubab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Palawan Polytechnic College Inc. Refresher Course 1Document5 pagesPalawan Polytechnic College Inc. Refresher Course 1heheloveNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions For Chapter 6 - The Triangle and Its PropertiesDocument27 pagesClass 7 Maths NCERT Solutions For Chapter 6 - The Triangle and Its PropertiesJyoti BhagatNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - Quadrilateral and Heron's Formula MCQ'sDocument9 pagesClass 9 - Quadrilateral and Heron's Formula MCQ'sPradyot ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- 92class V AssingmentDocument67 pages92class V AssingmentkhalidpandithNo ratings yet
- Final Term Sample PaperDocument5 pagesFinal Term Sample PaperKirat KaurNo ratings yet
- BYJU'S Tuition CenterDocument11 pagesBYJU'S Tuition CenterJanice BulaoNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 9 Perimeter & AreaDocument124 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 9 Perimeter & Areaat2lk22No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledHazeel HashimNo ratings yet
- Conquering SAT Math Practice Test 1 AnswersDocument18 pagesConquering SAT Math Practice Test 1 AnswerssarahleeabcNo ratings yet
- Pre-Algebra Chapter 9 Real Numbers and Right Triangles Chapter TestDocument7 pagesPre-Algebra Chapter 9 Real Numbers and Right Triangles Chapter Testzoohyun91720No ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 MathsDocument47 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 9 Mathsfunson123No ratings yet
- NNPC Recruitment Past Questions GuideDocument64 pagesNNPC Recruitment Past Questions GuidenwabukingzNo ratings yet
- E3 PUBLIC SCHOOL Pre-Board Exam Class X MathsDocument5 pagesE3 PUBLIC SCHOOL Pre-Board Exam Class X MathsBGTM 1988No ratings yet
- Sample Paper - CBSE: Section ADocument5 pagesSample Paper - CBSE: Section ASachin YadavNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions Chapter 11: Class Vi Revision Questions Chapter 04/05: Class ViDocument1 pageRevision Questions Chapter 11: Class Vi Revision Questions Chapter 04/05: Class ViSanayaNo ratings yet
- Answer 1Document5 pagesAnswer 1raj mohanNo ratings yet
- The Triangle and Its Properties (Class 7)Document13 pagesThe Triangle and Its Properties (Class 7)RAJESH JAINAL100% (1)
- Maths 6 18th JanDocument11 pagesMaths 6 18th JanKalimNo ratings yet
- Final Cass 9th Maths - 2023 24Document2 pagesFinal Cass 9th Maths - 2023 24pandeyshobhit463No ratings yet
- Test Questions For GeometryDocument4 pagesTest Questions For GeometryLore NaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Regional Geometry Exam Final PDFDocument15 pages2016 Regional Geometry Exam Final PDFPartha SarathiNo ratings yet
- NNPC Past Test and Interview Questions - Dmainman PDFDocument96 pagesNNPC Past Test and Interview Questions - Dmainman PDFrasaq100% (1)
- ICSE Sample Papers For Class 6 Mathematics Paper 1 (2019-2020)Document16 pagesICSE Sample Papers For Class 6 Mathematics Paper 1 (2019-2020)Brijesh Kumar GiriNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment-I, 2016 Mathematics: Time: 3 Hrs. Class VI M.M.: 100Document3 pagesSummative Assessment-I, 2016 Mathematics: Time: 3 Hrs. Class VI M.M.: 100Pandimadevi GanesanNo ratings yet
- Post Test in Mathematics 7Document8 pagesPost Test in Mathematics 7zaldy mendozaNo ratings yet
- Its Don 99999999Document25 pagesIts Don 99999999Ishant Kumar PandaNo ratings yet
- Class 5 Final Exam 2023Document2 pagesClass 5 Final Exam 2023Abdi Nasir AdanNo ratings yet
- Ix Maths Weekly AssessmentDocument5 pagesIx Maths Weekly AssessmentSrinivasanNo ratings yet
- 10ma 23 Revision Exam v1Document16 pages10ma 23 Revision Exam v1jameschales369No ratings yet
- Dod-Rgx-F425 - Fibre Optic Cable Pre-Installation Test ReportDocument2 pagesDod-Rgx-F425 - Fibre Optic Cable Pre-Installation Test ReportBharathiNo ratings yet
- DOD-RGX-F049 Rev 0 - Over - Short - Damage ReportDocument1 pageDOD-RGX-F049 Rev 0 - Over - Short - Damage ReportBharathiNo ratings yet
- DOD-ITP - INS-008-ITP FOR Installation and Testing of Fiber Optic Cable - Rev.0Document1 pageDOD-ITP - INS-008-ITP FOR Installation and Testing of Fiber Optic Cable - Rev.0BharathiNo ratings yet
- Slides Flow Measurement SeminarDocument147 pagesSlides Flow Measurement SeminarmessallamNo ratings yet
- DOD-RGX-F051 Rev 2 - Material Receipt Cum Inspection ReportDocument1 pageDOD-RGX-F051 Rev 2 - Material Receipt Cum Inspection ReportBharathiNo ratings yet
- DOD-QCP-INS-002, Rev-0Document7 pagesDOD-QCP-INS-002, Rev-0BharathiNo ratings yet
- DOD-ITP-INS-008 - Cover Sheet - Rev.0Document2 pagesDOD-ITP-INS-008 - Cover Sheet - Rev.0BharathiNo ratings yet
- How To Convert Amps To Kilowatts & KW To AmpsDocument3 pagesHow To Convert Amps To Kilowatts & KW To AmpsBharathiNo ratings yet
- DOD-ITP-INS-002 - Installation of Field Instrument Rev.1Document3 pagesDOD-ITP-INS-002 - Installation of Field Instrument Rev.1BharathiNo ratings yet
- DOD-MST-INS-004, MST For Insta. of Tubes, Pipes & Pressure Testing.-Rev.0Document11 pagesDOD-MST-INS-004, MST For Insta. of Tubes, Pipes & Pressure Testing.-Rev.0BharathiNo ratings yet
- DOD-MST-INS-008 Installation and Testing of Fiber Optic Cable - Rev.0Document14 pagesDOD-MST-INS-008 Installation and Testing of Fiber Optic Cable - Rev.0BharathiNo ratings yet
- DOD-ITP-INS-003 - Rev-2Document4 pagesDOD-ITP-INS-003 - Rev-2BharathiNo ratings yet
- DOD ITP INS 006 Rev 1Document1 pageDOD ITP INS 006 Rev 1BharathiNo ratings yet
- DOD QCP INS 001.rev.1Document7 pagesDOD QCP INS 001.rev.1BharathiNo ratings yet
- Class 9 History PDFDocument191 pagesClass 9 History PDFankitaNo ratings yet
- DOD-ITP - INS-008-ITP FOR Installation and Testing of Fiber Optic Cable - Rev.0Document1 pageDOD-ITP - INS-008-ITP FOR Installation and Testing of Fiber Optic Cable - Rev.0BharathiNo ratings yet
- INSPECTION & TEST PLAN FOR IMPULSE, AIR TUBING AND TESTINGDocument1 pageINSPECTION & TEST PLAN FOR IMPULSE, AIR TUBING AND TESTINGBharathiNo ratings yet
- DOD MST INS 001 Rev.0Document8 pagesDOD MST INS 001 Rev.0BharathiNo ratings yet
- DOD ITP INS 001 Rev 1Document1 pageDOD ITP INS 001 Rev 1BharathiNo ratings yet
- Water TherapyDocument3 pagesWater TherapyBharathiNo ratings yet
- History MapsDocument2 pagesHistory MapsBharathiNo ratings yet
- Why Vacuum Flasks Keep Liquids Hot or Cold LongerDocument2 pagesWhy Vacuum Flasks Keep Liquids Hot or Cold LongerBharathiNo ratings yet
- JACOBS Template (Repaired)Document5 pagesJACOBS Template (Repaired)BharathiNo ratings yet
- Binder 1Document16 pagesBinder 1BharathiNo ratings yet
- pdf101 PDFDocument3 pagespdf101 PDFMohd RafiqNo ratings yet
- TEACHING PLANS FOR NUMBER SYSTEMS, POLYNOMIALS AND COORDINATE GEOMETRYDocument15 pagesTEACHING PLANS FOR NUMBER SYSTEMS, POLYNOMIALS AND COORDINATE GEOMETRYRadhika SinghNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W7Document7 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W7Arnel LopezNo ratings yet
- Plotting Johnson's S Distribution Using A New ParameterizationDocument7 pagesPlotting Johnson's S Distribution Using A New ParameterizationJoanne WongNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Model of Robots:: Robotics 2Document45 pagesDynamic Model of Robots:: Robotics 2toufik1986No ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document8 pagesLecture 4engrhamayun06No ratings yet
- Taguchi's Design of Experiments and Selection of Orthogonal ArrayDocument22 pagesTaguchi's Design of Experiments and Selection of Orthogonal ArrayBhavin DesaiNo ratings yet
- Loci in Two Dimensions Form 2 - ActivityDocument7 pagesLoci in Two Dimensions Form 2 - ActivityWan FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 ELL701Document21 pagesAssignment 1 ELL701Bet3aNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument23 pagesTerm PaperUday RajNo ratings yet
- A Review of Litterature Gender Differences in Mathematical Problem Solving PatternDocument17 pagesA Review of Litterature Gender Differences in Mathematical Problem Solving PatternZaidComunicationNo ratings yet
- How Many Angels Can Dance on a Needle's Point? Transcendental Theology Meets Modal MetaphysicsDocument29 pagesHow Many Angels Can Dance on a Needle's Point? Transcendental Theology Meets Modal MetaphysicsSantiago FrancoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of A Mathematical Problem-Solving Test On Speed and StudDocument15 pagesAnalysis of A Mathematical Problem-Solving Test On Speed and StudWiandi AfrizahNo ratings yet
- Dmoi TabletDocument345 pagesDmoi TabletRinesa RamaNo ratings yet
- Math 10 1ST Quarter Exam 2023-24Document10 pagesMath 10 1ST Quarter Exam 2023-24ronnie.sisonNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Derivation and Analysis of Fourth OrdDocument6 pagesA Simplified Derivation and Analysis of Fourth OrdKumaar RanjanNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis of Systems Using Routh-Hurwitz CriterionDocument32 pagesStability Analysis of Systems Using Routh-Hurwitz CriterionUmer AbbasNo ratings yet
- Dawson Reproving TheoremsDocument18 pagesDawson Reproving Theoremsalbak01No ratings yet
- 1 Statement and Notations 14 Jul 2020material I 14 Jul 2020 Day 1Document7 pages1 Statement and Notations 14 Jul 2020material I 14 Jul 2020 Day 1khushboo kanwar rajawatNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/12Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/12José Antonio Álvarez CuberoNo ratings yet
- Math 6Document3 pagesMath 6RubyCaliguiranMacasinagNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Steel Quantity For SlabDocument4 pagesHow To Calculate Steel Quantity For SlabAl Patrick Dela Calzada100% (1)
- Contestproblembook3 (1966-1972)Document196 pagesContestproblembook3 (1966-1972)Ahmed RazaNo ratings yet
- Some Remarks On Problem U23: Dorin Andrica and Mihai PiticariDocument8 pagesSome Remarks On Problem U23: Dorin Andrica and Mihai PiticariSergio Alberto De LeónNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Solves PDE ProblemsDocument11 pagesLaplace Transform Solves PDE ProblemsElliot KimNo ratings yet
- Aarohi Maths TestDocument4 pagesAarohi Maths TestKratgya GuptaNo ratings yet
- CMR College ECE Course File on Probability Theory and Random ProcessesDocument162 pagesCMR College ECE Course File on Probability Theory and Random Processesniharikarllameddy.kaNo ratings yet