Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Minerals (Grade 11)
Uploaded by
Kristhia Cyra RiveraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Minerals (Grade 11)
Uploaded by
Kristhia Cyra RiveraCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic #3: MINERALS
Minerals are the building blocks of rocks. Mineralogists use the criteria to determine whether a
material is classified as a mineral or not.
Characteristics of Minerals
1. Naturally Occurring – a product of Earth’s natural processes
2. Inorganic – it must be product of Earth’s physical processes.
3. Homogeneous Solid – minerals should have definite volume and rigid shape
4. Definite Chemical Composition — represented by a chemical formula
5. Orderly Crystalline Structure – atoms of minerals are arranged in an orderly and repeating
pattern
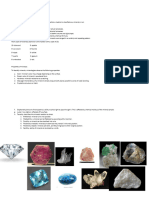
Properties of Minerals
To identify minerals, mineralogists observe the following properties:
a. Color - mineral’s color may change depending on the surface.
b. Streak - color of mineral in powdered form.
c. Hardness - minerals resistance to scratching
• Mohs Scale of Hardness (Diamond is the Hardest with a scale of 10)
10 - Diamond
9 - Corundum
8 - Topaz
7 - Quartz
6 - Orthoclase
5 - Apatite
4 - Fluorite
3 - Calcite
2 - Gypsum
1 – Talc
d. Cleavage - mineral’s resistance to being broken and fracture Crystalline structure or habit
e. Diaphaneity/amount of transparency - ability to allow light to pass through it. This is affected by
chemical makeup of the mineral sample.
f. Luster - how light is reflected off a surface
g. Tenacity - describes the minerals reaction to stress.
h. Brittleness - a mineral turns into powder
i. Malleability - a mineral can be flattened by pounding with a hammer.
j. Ductility- A mineral can be stretched into wire.
k. Flexible but Inelastic - Minerals are bent but they remain in the new position.
l. Flexible and Elastic - Minerals are bent, and they bring back to their original position.
m. Sectility - ability of minerals to be sliced by a knife.
You might also like
- Science ProjectDocument10 pagesScience ProjectJovith Piel G. VeranaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 3 - MineralsDocument48 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 3 - MineralsRachelle Toledo AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - MineralsDocument33 pagesLesson 2 - MineralsKirito HatakuNo ratings yet
- Minerals Module 3Document30 pagesMinerals Module 3cristalNo ratings yet
- LAS Week 2Document8 pagesLAS Week 2Arsyl Mae DenaloNo ratings yet
- Q1 LAS 2 Earth and Life ScienceDocument5 pagesQ1 LAS 2 Earth and Life ScienceYueru RanNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Quarter 1-Week3Document2 pagesEarth and Life Science Quarter 1-Week3KISHANo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document3 pagesLesson 3ritzel c. endeNo ratings yet
- ELS - Lesson 3 - MineralsDocument4 pagesELS - Lesson 3 - MineralsSaira YhukiNo ratings yet
- Minerals Around Us!: Learner's Activity Sheet in Earth and Life ScienceDocument12 pagesMinerals Around Us!: Learner's Activity Sheet in Earth and Life ScienceMiguel BabarinNo ratings yet
- Geo RWDocument2 pagesGeo RWSHYR SOPHIA LA CORDANo ratings yet
- Earth Science Lesson 3Document3 pagesEarth Science Lesson 3deljesalva102406No ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument46 pagesRocks and MineralsMark Angelo Beltran NadayaoNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals For Grade 11 Earth and Life SciencesDocument47 pagesRocks and Minerals For Grade 11 Earth and Life SciencesRegz CustodioNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A MineralDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of A Mineraljanice alquizarNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Week 3Document8 pagesEarth Life Week 3ElleKaye MercadoNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals For Grade 11 Earth and Life SciencesDocument47 pagesRocks and Minerals For Grade 11 Earth and Life SciencesRegz CustodioNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument29 pagesMineralsSevilla RonabelleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 MineralsDocument3 pagesLesson 3 Mineralsvedina3823No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Earth ProcessesDocument15 pagesLesson 4 Earth Processescourse heroNo ratings yet
- El 3 4Document3 pagesEl 3 4jcriztineNo ratings yet
- Nicolas Steno: The Law of Constancy of Interfacial AnglesDocument4 pagesNicolas Steno: The Law of Constancy of Interfacial AnglesMarc Eric GuerreroNo ratings yet
- ELSDocument14 pagesELSAshley Faith AgunosNo ratings yet
- MINERALSDocument17 pagesMINERALSClaudene GellaNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument30 pagesMineralsCarl LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Earthy Materials and ProcessesDocument5 pagesEarthy Materials and ProcessesAngèll RòseNo ratings yet
- Earth Science MineralsDocument61 pagesEarth Science MineralsKen Juliana Fe IsaacNo ratings yet
- 2 Minerals and RocksDocument98 pages2 Minerals and RocksJohnerros RevillaNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument16 pagesMineralsJustin Mhel VaquilarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document17 pagesUnit 2Godson GodsonNo ratings yet
- Finalminerologyppt 150223221945 Conversion Gate01Document22 pagesFinalminerologyppt 150223221945 Conversion Gate01Sagar DadhichNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Minerals - 103013Document10 pagesLesson 3 Minerals - 103013Marian Evangelista MoralesNo ratings yet
- q1 Lesson 3 Rock Forming MineralsDocument59 pagesq1 Lesson 3 Rock Forming MineralsJohn Ray LomedaNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical PropertiesDocument35 pagesPhysical and Chemical PropertiesBien DielNo ratings yet
- Science 11 Rock Forming MineralsDocument7 pagesScience 11 Rock Forming MineralsKimmy Grace TañoNo ratings yet
- Rock-Forming MineralsDocument2 pagesRock-Forming MineralsShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- MineralDocument2 pagesMineralJeany Lyn BiñasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document30 pagesLesson 3delectormaria63No ratings yet
- Minerals: Lesson 3 Earth and Life ScienceDocument23 pagesMinerals: Lesson 3 Earth and Life ScienceRegine LiscanoNo ratings yet
- MINERALOGYDocument38 pagesMINERALOGYMark BalinsayoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 MineralsDocument16 pagesModule 3 MineralsWiljay Duyan BandoNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument4 pagesRocks and Mineralsxiejie22590No ratings yet
- Minerals Forming RocksDocument22 pagesMinerals Forming RocksCio CioNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument32 pagesUntitledMa’am Diana V.No ratings yet
- MINERALSDocument33 pagesMINERALSdeaththereaper47No ratings yet
- Rock Forming MineralsDocument21 pagesRock Forming MineralsDAKSINo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals For Grade 11Document2 pagesRocks and Minerals For Grade 11len100% (1)
- Document 11Document4 pagesDocument 11louisandreiabadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 MidtermDocument18 pagesChapter 4 MidtermJoshua ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument22 pagesRocks and MineralsKenneth ShayNo ratings yet
- ELECT1-week 6-8 EARTH'S MATERIALS ROCKS AND MINERALSDocument16 pagesELECT1-week 6-8 EARTH'S MATERIALS ROCKS AND MINERALSRenNo ratings yet
- Minerals and Rocks-1Document2 pagesMinerals and Rocks-1Arish VinluanNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6-8 Chapter 4: Earth'S Materials: Rocks and Minerals: Midterm PeriodDocument74 pagesWEEK 6-8 Chapter 4: Earth'S Materials: Rocks and Minerals: Midterm PeriodRenNo ratings yet
- W 2 - EarthandLifeScience - q1 - CLAS2 - CommonRockFormingMineralsDocument15 pagesW 2 - EarthandLifeScience - q1 - CLAS2 - CommonRockFormingMineralsPeter Paul PaalanNo ratings yet
- Discussion 4 (Rocks and Minerals)Document3 pagesDiscussion 4 (Rocks and Minerals)Jerica CagadasNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Quarter 1Document222 pagesEarth Science Quarter 1Mickaella TaborlupaNo ratings yet
- MineralogyDocument35 pagesMineralogyHak DogNo ratings yet
- Rocs Forming MineralsDocument13 pagesRocs Forming MineralsSalve BernalNo ratings yet
- Little Rocks & Small Minerals! | Rocks And Mineral Books for Kids | Children's Rocks & Minerals BooksFrom EverandLittle Rocks & Small Minerals! | Rocks And Mineral Books for Kids | Children's Rocks & Minerals BooksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- RESEARCH PAPER IN ENGLISH - SampleDocument18 pagesRESEARCH PAPER IN ENGLISH - SampleKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- Stem 12 Idr Group 12 Full PaperDocument17 pagesStem 12 Idr Group 12 Full PaperKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- Exogenic Processes (Grade 11)Document1 pageExogenic Processes (Grade 11)Kristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- ELS Worksheet (Grade 11)Document4 pagesELS Worksheet (Grade 11)Kristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- Rocks (Grade 11)Document2 pagesRocks (Grade 11)Kristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- Balance-Stability Grade 10Document4 pagesBalance-Stability Grade 10Kristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument1 pagePlant CellKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- Organ SystemsDocument13 pagesOrgan SystemsKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument22 pagesEvolutionKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- Depths of EvolutionDocument39 pagesDepths of EvolutionKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of A StarDocument20 pagesLife Cycle of A StarKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- My Philosophy of TeachingDocument2 pagesMy Philosophy of TeachingKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument56 pagesEvolutionKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- My Classroo M Managem Ent Plan: Philosophical StatementDocument4 pagesMy Classroo M Managem Ent Plan: Philosophical StatementKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- Matrix For Action ResearchDocument2 pagesMatrix For Action ResearchKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- LessonPlan ElectromagneticDocument10 pagesLessonPlan ElectromagneticKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Ramos, Mhica Angelica Recto, Anthony Ricalde, Rhazen Kate Rivera, Kristhia CyraDocument27 pagesHeat Transfer: Ramos, Mhica Angelica Recto, Anthony Ricalde, Rhazen Kate Rivera, Kristhia CyraKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet