Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth and Life Science Quarter 1-Week3
Uploaded by
KISHACopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Earth and Life Science Quarter 1-Week3
Uploaded by
KISHACopyright:
Available Formats
EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCES
Week 3(1st Quarter)
MINERALS
Name: _________________________ Year & Section: _____________ Date: _________ Score: _____
Learning Objectives:
Identify the examples of minerals
Explain the different characteristics of minerals
Differentiate minerals based on their properties
Develop awareness on the importance of minerals around us
CONCEPT NOTES:
Minerals make up the rocks beneath your feet, the soil that support plants, and the deep rock of earth’s
mantle. Any thorough study of Earth must include an understanding in minerals. But it is not sufficient to
study minerals isolated from the rest of the planet. Rather we can learn more by observing the ways that
minerals interact with other earth systems.
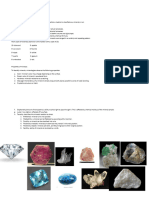
What are Minerals?
Minerals are the building blocks of rocks. Mineralogists use the criteria to determine whether a material is
classified or not. A mineral is a naturally occurring inorganic element or compound having an orderly
internal structure and characteristic chemical composition, crystal form, and physical properties
Characteristic of Minerals
1. naturally occurring- a product of Earth’s natural processes.
2. inorganic- it must be product of earth’s physical processes.
3. homogeneous solid- minerals should have definite volume and rigid shape
4. definite chemical composition- represented by a chemical formula
5. orderly crystalline structure atoms of minerals are arranged in an orderly and repeating
pattern.
Properties of Minerals
To identify minerals, mineralogists observe the following properties
a. Color- mineral’s color may change depending on the surface.
b. Streak- color of mineral in powdered form.
c. Hardness- minerals resistance to scratching.
Mohs Scale of Hardness (Diamond is the Hardest with a scale of 10)
10- Diamond
9- Corundum
8- Topaz
7- Quartz
6- Orthoclase
5- Apatite
4- Fluorite
3- Calcite
2- Gypsum
1- Talc
d. Cleavage- mineral’s resistance to being broken and fracture
e. Crystalline structure or habit
f. Diaphaneity/ amount of transparency- ability to allow light to pass through it. This is affected by
chemical makeup of the mineral sample.
g. Luster- how light is reflected off a surface
h. Tenacity- describes the minerals reaction to stress.
Brittleness- a mineral turns into powder
Malleability- a mineral can be flattened by pounding with a hammer.
Ductility- a mineral can be stretched into wire.
Flexible and inelastic- minerals are bent, and they bring back to their original position.
Sectility- ability of minerals to be sliced by a knife.
ACTIVITY 1
List some of the uses of minerals around us. Number 1 is done for you.
Minerals Uses
1. Halite Mineral found in table salt; as preservatives.
ACTIVITY 2.
Prepare a list of minerals based on the Mohs Scale of Hardness ad identify some products that make use
of these minerals.
Minerals Products that contain the mineral
1. Diamond
2. corundum
3. Topaz
4. Quartz
5. Orthoclase
Additional Question:
1. As a student, how can you help in conserving and preserving the natural sources of these
minerals? (10 pts.)
You might also like
- Little Rocks & Small Minerals! | Rocks And Mineral Books for Kids | Children's Rocks & Minerals BooksFrom EverandLittle Rocks & Small Minerals! | Rocks And Mineral Books for Kids | Children's Rocks & Minerals BooksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- LAS Week 2Document8 pagesLAS Week 2Arsyl Mae DenaloNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 3 - MineralsDocument48 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 3 - MineralsRachelle Toledo AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Q1 LAS 2 Earth and Life ScienceDocument5 pagesQ1 LAS 2 Earth and Life ScienceYueru RanNo ratings yet
- Minerals (Grade 11)Document1 pageMinerals (Grade 11)Kristhia Cyra Rivera100% (1)
- W 2 - EarthandLifeScience - q1 - CLAS2 - CommonRockFormingMineralsDocument15 pagesW 2 - EarthandLifeScience - q1 - CLAS2 - CommonRockFormingMineralsPeter Paul PaalanNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Quarter 1Document222 pagesEarth Science Quarter 1Mickaella TaborlupaNo ratings yet
- Science ProjectDocument10 pagesScience ProjectJovith Piel G. VeranaNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical PropertiesDocument35 pagesPhysical and Chemical PropertiesBien DielNo ratings yet
- El 3 4Document3 pagesEl 3 4jcriztineNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6-8 Chapter 4: Earth'S Materials: Rocks and Minerals: Midterm PeriodDocument74 pagesWEEK 6-8 Chapter 4: Earth'S Materials: Rocks and Minerals: Midterm PeriodRenNo ratings yet
- CORE 11 Earth Science q1 CLAS2 CommonRockFormingMineralsDocument13 pagesCORE 11 Earth Science q1 CLAS2 CommonRockFormingMineralskitkit.buddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 MidtermDocument18 pagesChapter 4 MidtermJoshua ManaliliNo ratings yet
- WK2 Earth Materials ProcessesDocument24 pagesWK2 Earth Materials ProcessesAifa EspinoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science MineralsDocument61 pagesEarth Science MineralsKen Juliana Fe IsaacNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals For Grade 11 Earth and Life SciencesDocument47 pagesRocks and Minerals For Grade 11 Earth and Life SciencesRegz CustodioNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Lesson 4Document62 pagesEarth Science Lesson 4charisse grace esquivelNo ratings yet
- SHS ELS Q1 M3 Minerals-and-RocksDocument23 pagesSHS ELS Q1 M3 Minerals-and-RocksTrisha DiohenNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 3Document11 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 3Austin Capal Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Earth Life Week 3Document8 pagesEarth Life Week 3ElleKaye MercadoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Mineral Resources Solved UnsolvedDocument32 pagesUnit 1 Mineral Resources Solved UnsolvedRovan HamdyNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals For Grade 11 Earth and Life SciencesDocument47 pagesRocks and Minerals For Grade 11 Earth and Life SciencesRegz CustodioNo ratings yet
- Earthy Materials and ProcessesDocument5 pagesEarthy Materials and ProcessesAngèll RòseNo ratings yet
- MINERALSDocument33 pagesMINERALSdeaththereaper47No ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document3 pagesLesson 3ritzel c. endeNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Earth and Life ScienceDocument41 pagesModule 2 Earth and Life Scienceprincess velascoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science AIR LM Module3Document21 pagesEarth Science AIR LM Module3Zarraiah HistoriaNo ratings yet
- ELS - Lesson 3 - MineralsDocument4 pagesELS - Lesson 3 - MineralsSaira YhukiNo ratings yet
- ELECT1-week 6-8 EARTH'S MATERIALS ROCKS AND MINERALSDocument16 pagesELECT1-week 6-8 EARTH'S MATERIALS ROCKS AND MINERALSRenNo ratings yet
- Applied Geology - 40 CharacterDocument30 pagesApplied Geology - 40 CharacterRamy HusseinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document30 pagesLesson 3delectormaria63No ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science Module 3Document6 pagesEarth & Life Science Module 3Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Module 5 (4th LECTURE) Minerals and RocksDocument7 pagesWeek 3 Module 5 (4th LECTURE) Minerals and RocksMarvin SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Q1 Week 2Document22 pagesEarth and Life Science Q1 Week 2Mary Kristine Silerio-Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- ROCKS FORMING MINERALSDocument13 pagesROCKS FORMING MINERALSSalve BernalNo ratings yet
- Minerals & RocksDocument28 pagesMinerals & RocksLejeb TCNo ratings yet
- ROCKDocument3 pagesROCKAna ArgonzaNo ratings yet
- Earth's Science (Minerals)Document6 pagesEarth's Science (Minerals)Prince Edrow Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE Q1 WK 1.c For Student 1Document15 pagesEARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE Q1 WK 1.c For Student 1VernonNo ratings yet
- PE SC2015 Practical 1-5Document16 pagesPE SC2015 Practical 1-5Radu ChibzuiNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument4 pagesRocks and Mineralsxiejie22590No ratings yet
- 2 Minerals and RocksDocument98 pages2 Minerals and RocksJohnerros RevillaNo ratings yet
- Block B1Document19 pagesBlock B1Gerald FernandezNo ratings yet
- Core (STEM) - EarthScience-SLMG11Q1W1-Identify Common Rock-Forming Minerals Using Their Physcial and Chemical PropertiesDocument18 pagesCore (STEM) - EarthScience-SLMG11Q1W1-Identify Common Rock-Forming Minerals Using Their Physcial and Chemical PropertiesRM L. JamandronNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals For Grade 11Document2 pagesRocks and Minerals For Grade 11len100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science Activity Sheet Quarter 1 - MELC 3 Week 1Document11 pagesEarth and Life Science Activity Sheet Quarter 1 - MELC 3 Week 1Darl TamayoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Week 2 What You Are Expected To Learn:: Chapter 2: Rocks and MineralsDocument11 pagesEarth Science Week 2 What You Are Expected To Learn:: Chapter 2: Rocks and MineralsHannah RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: First SemesterDocument17 pagesEarth Science: First SemesterAshley Kait MarceloNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science: First Quarter-Module 3: Minerals and RocksDocument25 pagesEarth & Life Science: First Quarter-Module 3: Minerals and RocksAyen xlisaNo ratings yet
- Minerals - RocksDocument67 pagesMinerals - RocksChandramala ANo ratings yet
- Minerals 2Document28 pagesMinerals 2Khana KhajanaNo ratings yet
- Rocks & Minerals WorksheetDocument14 pagesRocks & Minerals WorksheetRuth May-osNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Q1 Module 3 Classification and Properties of Rocks 1Document16 pagesGrade 11 Q1 Module 3 Classification and Properties of Rocks 1Gia AbongNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument8 pagesRocks and MineralsSuvashreePradhanNo ratings yet
- Minerals Around Us!: Learner's Activity Sheet in Earth and Life ScienceDocument12 pagesMinerals Around Us!: Learner's Activity Sheet in Earth and Life ScienceMiguel BabarinNo ratings yet
- LESSON-4-MINERALS-EDITEDDocument47 pagesLESSON-4-MINERALS-EDITEDmizpehman12No ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument46 pagesRocks and MineralsMark Angelo Beltran NadayaoNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Learning Materials For Senior High SchoolDocument12 pagesSupplementary Learning Materials For Senior High Schooljaylyn carasNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 11 - Q1 - MOD 3 - Physical and Chemical Properties of MineralsDocument12 pagesEarth Science 11 - Q1 - MOD 3 - Physical and Chemical Properties of MineralsNiña SalvatieraNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 1Document30 pagesFundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 1KISHANo ratings yet
- Earth Science Week 1 (2 Quarter) Name: - Year & Section: - Date: - Score: - Concept NotesDocument2 pagesEarth Science Week 1 (2 Quarter) Name: - Year & Section: - Date: - Score: - Concept NotesKISHANo ratings yet
- Earth Science q2-Wk2Document2 pagesEarth Science q2-Wk2KISHANo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics q2-Wk1Document1 pageBusiness Mathematics q2-Wk1KISHANo ratings yet
- Earth Science For STEM: Quarter 1 - Module 10: Activities That Affect The Quality and Availability of Water For Human UseDocument19 pagesEarth Science For STEM: Quarter 1 - Module 10: Activities That Affect The Quality and Availability of Water For Human UseHope Nyza Ayumi F. ReservaNo ratings yet
- Signed Off Inquires Investigations ImmersionG12 q1 Mod2 Brainstorming Your Research v3Document33 pagesSigned Off Inquires Investigations ImmersionG12 q1 Mod2 Brainstorming Your Research v3Unk NownNo ratings yet
- Fabm 1 Module 2 Principles and ConceptsDocument10 pagesFabm 1 Module 2 Principles and ConceptsKISHA100% (1)
- Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment MapDocument23 pagesClassroom Instruction Delivery Alignment MapKISHANo ratings yet
- Branches of Accounting: Module 2 - Fabm-1Document5 pagesBranches of Accounting: Module 2 - Fabm-1KISHANo ratings yet
- K to 12 ABM Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and ManagementDocument7 pagesK to 12 ABM Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and ManagementMica SaeronNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 - Module 4: Books of AccountsDocument12 pagesQuarter 3 - Module 4: Books of AccountsKISHANo ratings yet
- Forms of Business OrganizationsDocument13 pagesForms of Business OrganizationsKISHANo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of: The Learners Shall Be Able To: The Learners: The LearnersDocument4 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of: The Learners Shall Be Able To: The Learners: The LearnersKISHANo ratings yet
- FABM1 Module 4 Types of Major AccountsDocument26 pagesFABM1 Module 4 Types of Major AccountsKISHANo ratings yet
- Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan-General MathDocument2 pagesFlexible Instructional Delivery Plan-General MathHerra Luna Bautista93% (14)
- Physical Science Aligned Classroom Instruction Delivery PlanDocument4 pagesPhysical Science Aligned Classroom Instruction Delivery PlanKISHANo ratings yet
- Home Economics Appetizers & DessertsDocument2 pagesHome Economics Appetizers & DessertsKISHANo ratings yet
- FIDP for Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and ManagementDocument3 pagesFIDP for Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and ManagementByerus Tv100% (4)
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of: The Learners Shall Be Able To: The Learners: The LearnersDocument8 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of: The Learners Shall Be Able To: The Learners: The LearnersKISHANo ratings yet
- Dry-Heat Preparation Moist-Heat PreparationDocument1 pageDry-Heat Preparation Moist-Heat PreparationKISHANo ratings yet
- Ucsp CidamDocument11 pagesUcsp CidamRica Villanueva100% (2)
- Home Economics Sandwiches Storage GuidelinesDocument2 pagesHome Economics Sandwiches Storage GuidelinesKISHANo ratings yet
- q2 wk1 TleDocument2 pagesq2 wk1 TleKISHANo ratings yet
- q2 wk1 TleDocument2 pagesq2 wk1 TleKISHANo ratings yet
- Cook Meals According to RecipesDocument3 pagesCook Meals According to RecipesKISHANo ratings yet
- Home Economics Sandwiches Storage GuidelinesDocument2 pagesHome Economics Sandwiches Storage GuidelinesKISHANo ratings yet
- Week 2Document2 pagesWeek 2KISHANo ratings yet
- Home Economics Appetizers & DessertsDocument2 pagesHome Economics Appetizers & DessertsKISHANo ratings yet
- Dry-Heat Preparation Moist-Heat PreparationDocument1 pageDry-Heat Preparation Moist-Heat PreparationKISHANo ratings yet
- q2 wk1 TleDocument2 pagesq2 wk1 TleKISHANo ratings yet
- Mineral SheetsDocument35 pagesMineral SheetsJohn Israel R. CatedralNo ratings yet
- October 2017 (IAL) QP - Paper 3 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelDocument16 pagesOctober 2017 (IAL) QP - Paper 3 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelAbrar ZarifNo ratings yet
- Power Cables & Wires Technical ManualDocument163 pagesPower Cables & Wires Technical Manualbharatsehgal00@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- SSPC PCS Exam Preparation GuideDocument4 pagesSSPC PCS Exam Preparation Guidetaimoor faisal100% (1)
- Aquaculture Fish Fisheries - 2023 - McCuskerDocument22 pagesAquaculture Fish Fisheries - 2023 - McCuskerIbnu MustofaNo ratings yet
- UraniumDocument19 pagesUraniumEdgar Apaza HuallpaNo ratings yet
- Chen, 2022Document14 pagesChen, 2022MM afsahiNo ratings yet
- Carlos 2011Document14 pagesCarlos 2011alifNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet Material Science Final ExamDocument6 pagesAnswer Sheet Material Science Final ExamM Hoqqil FatwaNo ratings yet
- Plating Process For ElectrolessDocument5 pagesPlating Process For ElectrolessFrancisco BocanegraNo ratings yet
- ALevel Physical Chemistry Past PapersDocument24 pagesALevel Physical Chemistry Past PaperssabihagailaniNo ratings yet
- Biotik Abiotik KurvaDocument28 pagesBiotik Abiotik KurvaAlfira JunitaNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of Different Surface Treatments For Intraoral Repair of Veneered Zirconia FrameworksDocument8 pagesEfficacy of Different Surface Treatments For Intraoral Repair of Veneered Zirconia FrameworksJulio Torres OrtodonciaNo ratings yet
- Faraz Chem ProjectDocument13 pagesFaraz Chem ProjectFaraz AhmedNo ratings yet
- CK-MB Liquiuv: Liquid Nac Activated Uv Test Creatine Kinase (Ec 2.7.3.2)Document1 pageCK-MB Liquiuv: Liquid Nac Activated Uv Test Creatine Kinase (Ec 2.7.3.2)Maher100% (1)
- Chemistry MYP 3 Section 3Document15 pagesChemistry MYP 3 Section 3Hadeel IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Faculty description-5d95832c8fdf0JEEChemistryDocument1 pageFaculty description-5d95832c8fdf0JEEChemistrysarvesh goyalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Atomic StructureDocument7 pagesLesson 3 Atomic Structuremichael-education KNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 - Development of Thermochemical and Biochemical Technologies For BiorefineriesDocument32 pagesChapter 27 - Development of Thermochemical and Biochemical Technologies For Biorefineries1qwertyNo ratings yet
- Medicine List 19 AprDocument2 pagesMedicine List 19 AprVishal ChandanNo ratings yet
- 2002 Shi Steric StabilizationDocument45 pages2002 Shi Steric Stabilizationdaniel putra adinataNo ratings yet
- Aromaticity NewDocument4 pagesAromaticity NewJaysukh KanzariyaNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 26 Asal Chem CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 26 Asal Chem CBHaoyu XuNo ratings yet
- Repair Mortar Technical LeafletDocument2 pagesRepair Mortar Technical Leafletwey5316No ratings yet
- Separation Techniques Part 2Document45 pagesSeparation Techniques Part 2Maan Joy Revelo GallosNo ratings yet
- 4CH0 1CR Que 20140513Document36 pages4CH0 1CR Que 20140513Christopher LevinNo ratings yet
- Efficient Mineralization and Osteogenic Gene Overexpression of Mesenchymal Stem Cells On Decellularized Spinach Leaf ScaffoldDocument9 pagesEfficient Mineralization and Osteogenic Gene Overexpression of Mesenchymal Stem Cells On Decellularized Spinach Leaf ScaffoldMartin ContardeNo ratings yet
- Cosmetic Ingredients and Their Functions PDFDocument35 pagesCosmetic Ingredients and Their Functions PDFChris Jerick MenesesNo ratings yet
- Lead Drier Replacement in Solvent Based Alkyd Decorative PaintsDocument24 pagesLead Drier Replacement in Solvent Based Alkyd Decorative PaintsIwan TirtaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Qualitative Analysis-1Document8 pagesInorganic Qualitative Analysis-1Jeeva JohnNo ratings yet